AtCoder Beginner Contest 361
AtCoder Beginner Contest 361 (2/6)
昨晚比赛状态确实不好
A - Insert
Problem Statement
You are given an integer sequence \(A\) of length \(N\) and integers \(K\) and \(X\).
Print the integer sequence \(B\) obtained by inserting the integer \(X\) immediately after the \(K\)-th element of the sequence \(A\).
Constraints
- All input values are integers.
- \(1 \le K \le N \le 100\)
- \(1 \le A_i, X \le 100\)
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
\(N\) \(K\) \(X\)
\(A_1\) \(A_2\) \(\dots\) \(A_N\)
Output
Print the integer sequence \(B\) obtained by inserting the integer \(X\) immediately after the \(K\)-th element of the sequence \(A\), in the following format:
\(B_1\) \(B_2\) \(\dots\) \(B_{N+1}\)
Sample Input 1
4 3 7
2 3 5 11
Sample Output 1
2 3 5 7 11
For \(K=3\), \(X=7\), and \(A=(2,3,5,11)\), we get \(B=(2,3,5,7,11)\).
Solution
这题的题意就是让你在数组A的第K个位置插入元素X
就让第K个位置为X,之后的元素次序依次加一就好了,数据范围很小,可以直接开两个数组做
Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int n, k, x;
int a[N], b[N];
void solve()
{
cin >> n >> k >> x;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i ++ ) b[i] = a[i];
b[k + 1] = x;
for (int i = k + 1; i <= n; i ++ ) b[i + 1] = a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i ++ ) cout << b[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
solve();
return 0;
}
B - Intersection of Cuboids 思维题
Problem Statement
You are trying to implement collision detection in a 3D game.
In a \(3\)-dimensional space, let \(C(a,b,c,d,e,f)\) denote the cuboid with a diagonal connecting \((a,b,c)\) and \((d,e,f)\), and with all faces parallel to the \(xy\)-plane, \(yz\)-plane, or \(zx\)-plane.
(This definition uniquely determines \(C(a,b,c,d,e,f)\).)
Given two cuboids \(C(a,b,c,d,e,f)\) and \(C(g,h,i,j,k,l)\), determine whether their intersection has a positive volume.
问题陈述
你正试图在 3D 游戏中实现碰撞检测。
在 \(3\) /维空间中,让 \(C(a,b,c,d,e,f)\) 表示一个对角线连接 \((a,b,c)\) 和 \((d,e,f)\) 的长方体,并且所有面都平行于 \(xy\) /平面、 \(yz\) /平面或 \(zx\) /平面。
(这个定义唯一地决定了 \(C(a,b,c,d,e,f)\) )。
给定两个长方体 \(C(a,b,c,d,e,f)\) 和 \(C(g,h,i,j,k,l)\) ,判断它们的交点是否有正体积。
Constraints
- \(0 \leq a \lt d \leq 1000\)
- \(0 \leq b \lt e \leq 1000\)
- \(0 \leq c \lt f \leq 1000\)
- \(0 \leq g \lt j \leq 1000\)
- \(0 \leq h \lt k \leq 1000\)
- \(0 \leq i \lt l \leq 1000\)
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
\(a\) \(b\) \(c\) \(d\) \(e\) \(f\)
\(g\) \(h\) \(i\) \(j\) \(k\) \(l\)
Output
Print Yes if the intersection of the two cuboids has a positive volume, and No otherwise.
Sample Input 1
0 0 0 4 5 6
2 3 4 5 6 7
Sample Output 1
Yes
The positional relationship of the two cuboids is shown in the figure below, and their intersection has a volume of \(8\).

Sample Input 2(就是这个样例模拟错了 导致没做出来)
0 0 0 2 2 2
0 0 2 2 2 4
Sample Output 2
No
The two cuboids touch at a face, where the volume of the intersection is \(0\).
Solution
最近两次比赛B题都没有做出来,确实够抽象的,不过B题确实比C题难多了。比赛的时候读题都都不明白,没明白为什么如果一个立方体将另一个立方体包含在内也算有交集。
才发现我是个若只,第二个样例都模拟错了,模拟成有交集的情况了,怪不得比赛的时候对我的数学产生了深深的怀疑,实际上题目很简单,就是读题读错了。
其实就可以拆分来看,这题有x y z三个平面,那我们就单独对每个面分析就可以了,当每个面都存在交集,那两个立方体必然存在交集体积。举个例子
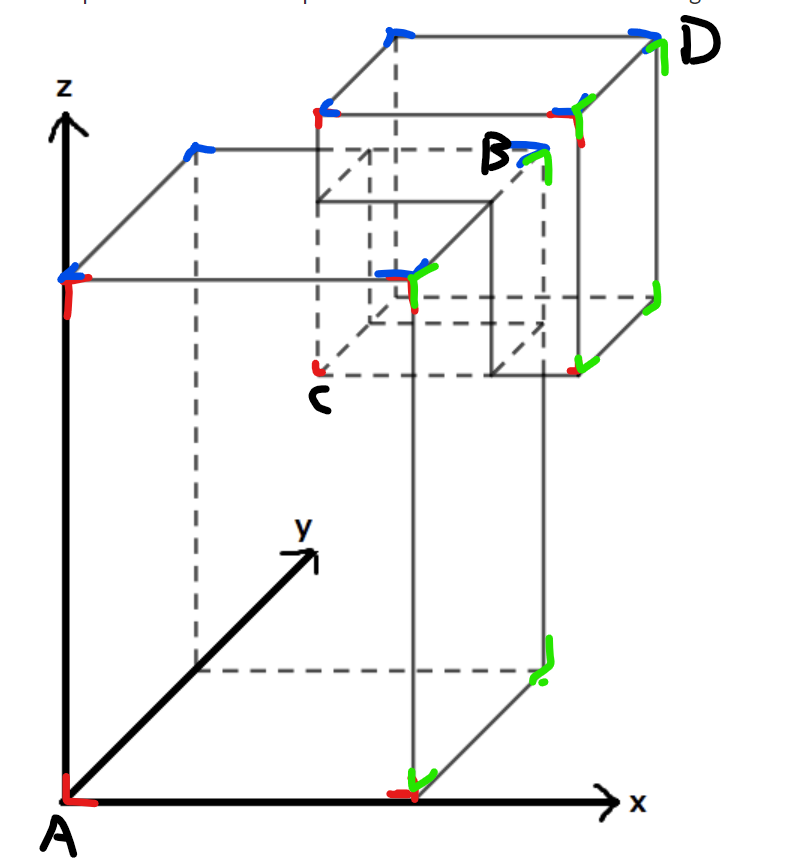
题目给我们了A B C D 四个点的坐标,我们可以唯一确定这两个立方体。
我们先来看xoz面也就是红色区域,看图显然存在交集,那该怎么判断呢,如果A点高于C点同时C点又低于B点,那么就可以说这个面存在交集,注意若小立方体的xoz面包含于大立方体中,也算交集,交集就是小面的面积,和集合里的韦恩图判断是一样的。
那么我们就可以发现当xoz xoy yoz 三个面都存在交集的时候,就会产生由交点构成的立方体,符合题目要求。
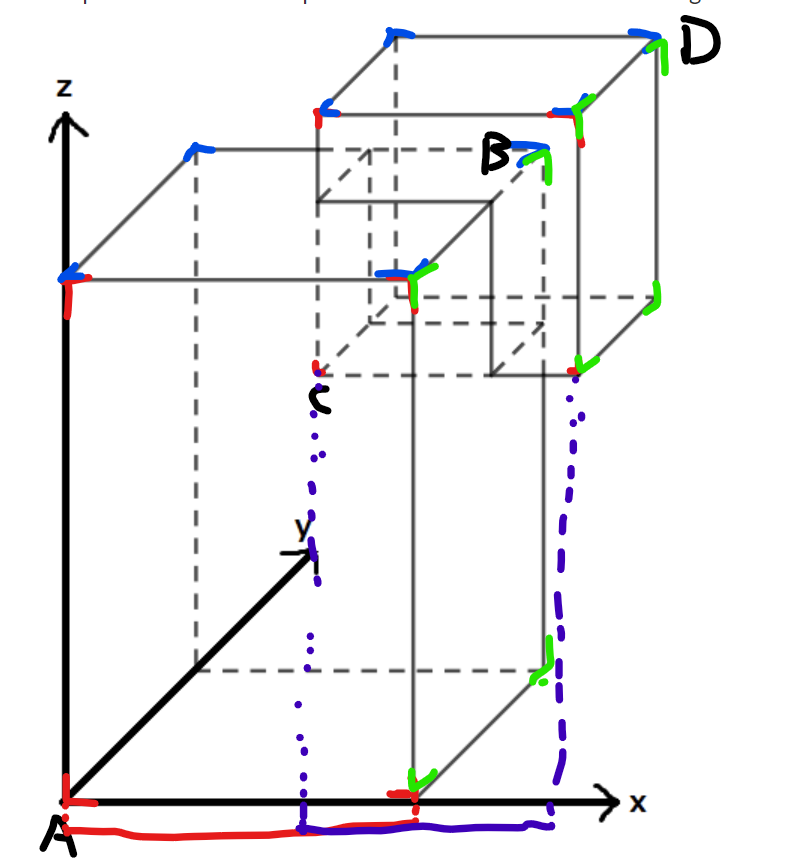
但这时候我们每次判断一个面都要用点的对应两个坐标来判断,实际上可以简化成判断x y z方向有无交集,若都有交集 则会构成立方体。 下图模拟了样例 x方向的判断情况,存在交集。那么我们只需要判断是不是三个方向都有交集来判断交集是否能构成立方体。
Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int a, b, c, d, e, f;
int g, h, i, j, k, l;
//判断是否有交集的函数
bool Intersect(int x, int y, int z, int w) //输入为某一方向两个立方体端点的坐标
{
//根据线段起点的前后进行翻转,让起点小的在前
if (x > z)
{
swap(x, z);
swap(y, w);
}
return z < y; //当第二个线段的起点在第一个线段的终点前,证明有交点
}
void solve()
{
cin >> a >> b >> c >> d >> e >> f;
cin >> g >> h >> i >> j >> k >> l;
//在x y z三个方向上进行判断,若均满足输出Yes
if (Intersect(a, d, g, j) && Intersect(b, e, h, k) && Intersect(c, f, i, l))
cout << "Yes" << endl;
else
cout << "No" << endl;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
solve();
return 0;
}
C - Make Them Narrow 思维题 贪心思想
Problem Statement
You are given a sequence \(A\) of length \(N\).
Freely choose exactly \(K\) elements from \(A\) and remove them, then concatenate the remaining elements in their original order to form a new sequence \(B\).
Find the minimum possible value of this: the maximum value of \(B\) minus the minimum value of \(B\).
问题陈述
给你一个长度为 \(N\) 的序列 \(A\) 。
请从 \(A\) 中任意选择 \(K\) 个元素并将其删除,然后按原来的顺序将剩余的元素连接起来,形成一个新的序列 \(B\) 。
求其最小值: \(B\) 的最大值减去 \(B\) 的最小值。
Constraints
- All inputs are integers.
- \(1 \le K \lt N \le 2 \times 10^5\)
- \(1 \le A_i \le 10^9\)
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
\(N\) \(K\)
\(A_1\) \(A_2\) \(\dots\) \(A_N\)
Output
Print the answer as an integer.
Sample Input 1
5 2
3 1 5 4 9
Sample Output 1
2
Consider removing exactly two elements from \(A=(3,1,5,4,9)\).
- For example, if you remove the 2nd element \(1\) and the 5th element \(9\), the resulting sequence is \(B=(3,5,4)\).
- In this case, the maximum value of \(B\) is \(5\) and the minimum value is \(3\), so (maximum value of \(B\)) \(-\) (minimum value of \(B\)) \(=2\), which is the minimum possible value.
Solution
这题题意就是从数组里任意删除K个元素,找出删除后数组内 最大元素减去最小元素 的最小值。
很容易想到先对数组排个序,由于此时数组每个元素之间的差值不确定,所以并不知道是从前面删还是从后面删,但可以证明,一定是从前面和后面删,不能从中间删,因为你要让Max-min最小,肯定是删当前数组的Max或者min,那相当于剩下的n-k个元素在原数组内肯定是连续的,以大小为n-k的窗口开始滑动,遍历数组找出窗口内首尾差值的最小值就好了。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n, k;
int res = 1e10;
int a[N];
void solve()
{
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a, a + n);
for (int i = 0; (i + (n - k) - 1) < n && i < n; i ++ )
{
res = min(res, a[i + (n - k) - 1] - a[i]);
}
cout << res << endl;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
solve();
return 0;
}
D - Go Stone Puzzle BFS
Problem Statement
There are \(N+2\) cells arranged in a row. Let cell \(i\) denote the \(i\)-th cell from the left.
There is one stone placed in each of the cells from cell \(1\) to cell \(N\).
For each \(1 \leq i \leq N\), the stone in cell \(i\) is white if \(S_i\) is W, and black if \(S_i\) is B.
Cells \(N+1\) and \(N+2\) are empty.
You can perform the following operation any number of times (possibly zero):
- Choose a pair of adjacent cells that both contain stones, and move these two stones to the empty two cells while preserving their order.
More precisely, choose an integer \(x\) such that \(1 \leq x \leq N+1\) and both cells \(x\) and \(x+1\) contain stones. Let \(k\) and \(k+1\) be the empty two cells. Move the stones from cells \(x\) and \(x+1\) to cells \(k\) and \(k+1\), respectively.
Determine if it is possible to achieve the following state, and if so, find the minimum number of operations required:
- Each of the cells from cell \(1\) to cell \(N\) contains one stone, and for each \(1 \leq i \leq N\), the stone in cell \(i\) is white if \(T_i\) is
W, and black if \(T_i\) isB.
问题陈述
有 \(N+2\) 个单元格排成一行。让 \(i\) 单元格表示从左边开始的第 \(i\) 个单元格。
从 \(1\) 单元格到 \(N\) 单元格,每个单元格中都有一块石头。
对于每一个 \(1 \leq i \leq N\) ,如果 \(S_i\) 是 "W",那么 \(i\) 单元格中的棋子就是白色的;如果 \(S_i\) 是 "B",那么 \(i\) 单元格中的棋子就是黑色的。
\(N+1\) 和 \(N+2\) 单元格为空。
您可以执行以下操作任意多次(可能为零):
- 选择一对都包含棋子的相邻单元格,并将这两个棋子移动到空的两个单元格中,同时保持它们的顺序。
更确切地说,选择一个整数 \(x\) ,使得 \(1 \leq x \leq N+1\) 和 \(x\) 以及 \(x+1\) 两个单元格都包含棋子。假设 \(k\) 和 \(k+1\) 是空的两个单元格。将 \(x\) 和 \(x+1\) 两个单元格中的棋子分别移动到 \(k\) 和 \(k+1\) 两个单元格中。
判断是否可以达到下面的状态,如果可以,求所需的最小操作次数:
- 从单元格 \(1\) 到单元格 \(N\) 的每个单元格中都有一颗棋子,对于每个单元格 \(1 \leq i \leq N\) ,如果 \(T_i\) 为 "W",则单元格 \(i\) 中的棋子为白色;如果 \(T_i\) 为 "B",则单元格 \(i\) 中的棋子为黑色。
Constraints
- \(2 \leq N \leq 14\)
- \(N\) is an integer.
- Each of \(S\) and \(T\) is a string of length \(N\) consisting of
BandW.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
\(N\)
\(S\)
\(T\)
Output
If it is possible to achieve the desired state, print the minimum number of operations required. If it is impossible, print -1.
Sample Input 1
6
BWBWBW
WWWBBB
Sample Output 1
4
Using . to represent an empty cell, the desired state can be achieved in four operations as follows, which is the minimum:
BWBWBW..BW..BWBWBWWBB..W..WBBBWWWWWBBB..
Solution
dubug半天,实际上是字符串在使用的时候发生了改变,但我并没有发现,导致了错误。
刚开始用DFS来做导致了超时,从这里引出一个疑问,什么时候用DFS什么时候用BFS呢,我目前总结的经验是让你求最短路径 最少操作数这种要直接找出最优情况的问题使用BFS,其余用DFS,DFS适用范围更广,但求最优时可能会超时,因为它是深搜并不会先求到最优情况,求到最优也不会直接返回,这就导致可能超时。
本题是让S字符串经过移动操作后变为T,由于数据范围非常小,我们考虑DP或搜索,本题显然是搜索,由于求最少操作数,所以采用BFS,用一个队列来模拟,注意对每一个字符串,我们都要走所有的一步路,也就是将所有一次操作的情况全部入队,跟走迷宫类似,这里就是把相邻两块石头移入空穴,原本位置就变为了空穴。
可以加一个小优化,只有当S中B和W石头数等于T中B石头数时,才可能移动后变成T。
Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<string, int> PII;
int n;
string s, tt;
void solve()
{
cin >> n >> s >> tt;
//优化 特判
int cnt1 = 0, cnt2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
if (s[i] == 'W') cnt1 ++ ;
if (tt[i] == 'W') cnt2 ++ ;
}
if (cnt1 != cnt2)
{
cout << "-1" << endl;
return;
}
if (s == tt)
{
cout << 0 << endl;
return;
}
//给s和t都加上空穴 方便后面字符串判断
s += "00";
tt += "00";
queue<PII> q;
map<string, int> mp; //用来记录每种移动后字符串的第一个空穴位置
mp[s] = s.size() - 2; //s字符串的第一个空穴位置
//bfs板子
q.push({s, 0});
while (q.size())
{
auto t = q.front();
//cout << t.first << endl;
q.pop();
//bfs的优点 会先搜到最优情况,然后直接退出,从而避免超时的问题
if (t.first == tt)
{
cout << t.second << endl;
return;
}
auto str = t.first;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size() - 1; i ++ )
{
if (str[i] != '0' && str[i + 1] != '0')
{
string str1 = str; //这里就是debug很久才发现的问题出现的地方 一定要单独设一个str1来存我们移动后的字符串 不要改变原本字符串的值 会影响for循环字符串的移动
swap(str1[i], str1[mp[str]]);
swap(str1[i + 1], str1[mp[str] + 1]);
//cout << str << endl;
if (mp[str1]) continue; //当移动后的字符串我们已经搜过了就不用放进队列了 直接continue 关键一步 避免重复操作
mp[str1] = i; //记录当前移动后的字符串的空穴
q.push({str1, t.second + 1});
}
}
}
cout << "-1" << endl; //没搜到返回-1
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
solve();
return 0;
}
E - Tree and Hamilton Path 2
Problem Statement
In the nation of AtCoder, there are \(N\) cities numbered \(1\) to \(N\) and \(N-1\) roads numbered \(1\) to \(N-1\).
Road \(i\) connects cities \(A_i\) and \(B_i\) bidirectionally, and its length is \(C_i\). Any pair of cities can be reached from each other by traveling through some roads.
Find the minimum travel distance required to start from a city and visit all cities at least once using the roads.
问题陈述
在 AtCoder 国家中,有 \(N\) 座城市,编号为 \(1\) 至 \(N\) ;有 \(N-1\) 条道路,编号为 \(1\) 至 \(N-1\) 。
道路 \(i\) 双向连接城市 \(A_i\) 和 \(B_i\) ,其长度为 \(C_i\) 。任何一对城市都可以通过一些道路相互到达。
求从一个城市出发,通过这些道路至少到达所有城市一次所需的最小路程。
Constraints
- \(2 \leq N \leq 2\times 10^5\)
- \(1 \leq A_i, B_i \leq N\)
- \(1 \leq C_i \leq 10^9\)
- All input values are integers.
- Any pair of cities can be reached from each other by traveling through some roads.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
\(N\)
\(A_1\) \(B_1\) \(C_1\)
\(\vdots\)
\(A_{N-1}\) \(B_{N-1}\) \(C_{N-1}\)
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
4
1 2 2
1 3 3
1 4 4
Sample Output 1
11
If you travel as \(4 \to 1 \to 2 \to 1 \to 3\), the total travel distance is \(11\), which is the minimum.
Note that you do not need to return to the starting city.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号