Android APP启动流程
预备知识
ServiceManager
通过init进程解析init.rc脚本构建,ServiceManager是Binder机制中的DNS服务器,负责将某Binder服务在ServiceManager注册时提供的ID到底层Binder驱动分配值的解析
是一个Linux程序,所属class为core。core组意味着这些进程会被同时启动或停止。有Zygote、media、surfaceflinger等
Zygote
通过init进程解析init.rc脚本构建,负责大部分应用进程和系统进程的创建。是Android系统的首个Java进程。
Zygote进程在App层中孵化出的第一个进程是Launcher进程,即手机的桌面APP。Zygote还会孵化出Browser、Email、Phone等APP进程,每个APP至少运行在一个进程上。所有APP进程都由Zygote进程fork生成。
nativeZygoteInit主导的本地系统服务启动
applicationInit负责的Java层系统服务启动(SystemServer)
SystemServer
提供系统服务,这些服务可以分为三类:BootStrap Services、Core Services、Other Services。
BootStrap Services:引导程序,代表系统服务中最核心的部分。这些Services依赖性强,需要统一启动。Android建议如果你的系统服务也有较强的依赖,可以添加到该服务中。启动的顺序大概是:Installer、AMS、电源管理、显示管理、包管理。
Core Services:优先级略低,包含LED和背光管理器,电池电量管理器,应用程序使用情况管理器等
Other Services:优先级最低,包含WMS等。
Android的C/S模式
在Android Framework中,四大组件的创建生命周期等是通过CS模式通信的
Server:指SystemServer,提供很多服务,如AMS、WMS、PMS
Client:指各个独立的APP进程。在开发过程中,我们可以通过包名和Activity类名来打开一个APP。然而startActivity背后的逻辑是这样的:先通过一系列调用发送请求给SystemServer的AMS,AMS接收到请求后,通知Zygote fork一个进程。APP中的Activity生命周期,都有AMS统一调度。这个过程涉及到3个进程:APP进程、SystemServer进程、Zygote进程。
APP进程与SystemServer进程通过Binder机制,进行跨进程通信。
SystemServer进程与Zygote进程通过Socket,进行跨进程通信。
Android Binder机制
在Android系统中,一个进程的空间,分为用户空间和内核空间两部分。进程内的用户空间和内核空间可以进行数据交互。进程间的用户空间是隔离开来的,只有内核空间能进行数据交互。
APP进程与SystemServer进程的交互,就是通过Binder机制进行跨进程通信(IPC),实现进程间的内核数据交互过程。Android专门设计了2个Binder接口,用作交互使用。
Looper
概括成一句话就是,Looper不断从MessageQueue中获取Message,然后交给Handler处理。
Looper对象的构造方法中,创建了消息队列对象,保存了当前线程信息。
Looper.prepare()为线程创建Looper。Looper.loop()开启消息循环,调用队列的阻塞方法next获取消息,为空则退出循环。
Handler
Handler 的sendMsg过程仅仅是向消息队列中插入了一条消息,MessageQueue 的 next 方法就会返回这条消息给 Looper,Looper 收到消息后就开始处理了,最终消息由Looper 交由Handler 处理,即 Handler 的 dispatchMessage 方法会被调用,这时Handler 就进入了处理消息的阶段。
ThreadLocal
线程内部存储类,通过它可以在指定线程中存储数据。日常开发中用到TL的很少,但是在Android源码中广泛使用。比如对于Handler,他需要获取当前线程Looper,这个时候通过TL就能轻松实现Looper在线程中的存取。
在不同线程中访问的同一个ThreadLocal对象,但是它们通过ThreadLocal获取到的值却是不一样的,这就是ThreadLocal的奇妙之处。
ThreadLocal之所以有这么奇妙的效果,是因为不同线程访问同一个ThreadLocal的get方法,ThreadLocal内部会从各自的线程中取出一个数组,然后再从数组中根据当前ThreadLocal的索引去查找出对应的value值。
Thread、Handler、Queue、Message的对应关系
一个Thread对应一个Looper。
一个Looper对应一个Queue。
一个Queue对应多个Handler。
一个Handler对应一个Queue。
场景一:在线程中使用Looper,没有创建handler,调用了Toast.makeText().show()。根据一个Handler对应一个Queue,查看Toast源码后可以发现,Toast使用了getLooper方法获取了当前线程了Looper,然后new Handler(looper),创建了Handler。之后sendMessage时,就会发送到该looper对应的Queue去。
场景二:在线程中使用Looper,创建了handler。那么根据一个Handler对应一个Queue,sendMessage时,就会发送到该looper对应的Queue去。
场景三:在主线程中使用了Toast.makeText().show()。根据一个Handler对应一个Queue,主线程在初始化时已经有了Looper。
ActivityStackSupervisor
活动栈的大管家,负责创建stack,创建task,移动task到stack,移动stack,启动activity等。
保存了各种状态的Activity的List。
UI层级
一个display包含多个stack
一个stack包含多个task
一个task包含多个activity
一个activity在wms中代表一个AppWindowToken,每个AppwindowToken上可能包含多个子Window,用WindowToken表示。
APP冷启动分析
1、启动APP进程: 当我们点击桌面程序的APP图标时,Launcher程序会调用Activity.startActivity()函数,通过Binder跨进程通信,发送消息给system_server进程。在system_server进程中,由AMS通过socket通信告知Zygote进程fork出一个子进程(APP进程)。
Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar =
mInstrumentation.execStartActivity(
this, mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, this,
intent, requestCode, options);private final void startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app, String hostingType,
String hostingNameStr, String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs) {
···
if (entryPoint == null) entryPoint = "android.app.ActivityThread";
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "Start proc: " +
app.processName);
checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: asking zygote to start proc");
ProcessStartResult startResult;
if (hostingType.equals("webview_service")) {
···
} else {
startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, invokeWith, entryPointArgs);
}
···
}2、开启APP主线程: APP进程启动后,会实例化一个ActivityThread,并执行其main函数,同时会创建ApplicationThread、Looper、Handler对象,开启主线程消息循环Looper.loop()。
3、创建并初始化Application和Activity: ActivityThread的main函数通过调用attach方法进行 Binder 通信,通知system_server进程执行AMS的attachApplication方法。在attachApplication方法中,AMS分别通过bindApplication、scheduleLaunchActivity方法,通知APP进程的主线程Handler,对APP进程的Application和Activity进行初始化,并执行Application、Activity的生命周期。
初始化Application
ActivityThread.attach()->IActivityManager.attachApplication(thread)->AMS.attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid)->IApplicationThread.bindApplication()->ActivityThread.sendMessage()->handleMessage()->ActivityThread.handleBindApplication()
->Application app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
->app = mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.newApplication( cl, appClass, appContext);//创建Application对象
mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app)//执行Application生命周期
初始化Activity
ActivityThread.attach()->IActivityManager.attachApplication(thread)->AMS.attachApplicationLocked(mAppThread)->mStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked()->realStartActivityLocked->IApplicationThread.scheduleLaunchActivity()->ActivityThread.sendMessage()->ActivityThread.handleMessage()->ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity()->ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity()
->activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity( cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);//创建Activity对象
activity.attach();
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState);执行Activity生命周期
//ActivityThread.java
public static void main(String[] args) {
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
// CloseGuard defaults to true and can be quite spammy. We
// disable it here, but selectively enable it later (via
// StrictMode) on debug builds, but using DropBox, not logs.
CloseGuard.setEnabled(false);
Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>");
Looper.prepareMainLooper();//创建Looper
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = new Handler();
}
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);//与AMS进行Binder通信,把线程信息发给AMS。
AsyncTask.init();
if (false) {
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
}
Looper.loop();//Looper循环
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}//ActivityThread.java
private void attach(boolean system) {
···
if (!system) {
···
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManager.getService();
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
···
} else {
···
}
···
}//ActivityManagerService.java
@Override
public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread) {
synchronized (this) {
···
attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid);
···
}
}
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,
int pid) {
···
try {
···
if (app.instr != null) {
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers,
app.instr.mClass,
profilerInfo, app.instr.mArguments,
app.instr.mWatcher,
app.instr.mUiAutomationConnection, testMode,
mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent,
new Configuration(getGlobalConfiguration()), app.compat,
getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked(),
buildSerial);
} else {
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers, null, profilerInfo,
null, null, null, testMode,
mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent,
new Configuration(getGlobalConfiguration()), app.compat,
getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked(),
buildSerial);
}
···
} catch (Exception e) {
···
}
···
// See if the top visible activity is waiting to run in this process...
if (normalMode) {
try {
if (mStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked(app)) {
didSomething = true;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
···
}
}
···
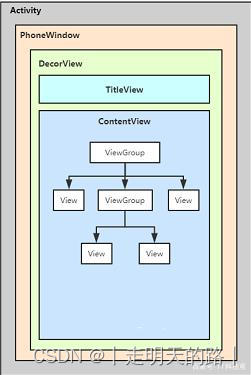
}4、UI布局和绘制: 主线程Handler初始化Activity时,会执行创建PhoneWindow、初始化DecorView的操作,并且添加布局到DecorView的ContentView中。ContentView,对应着Activity的setContentView中设置的layout.xml布局文件所在的最外层父布局。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号