Django框架学习-day4补充
ORM操作
select * from tb where id >1
Django中:models.tb.objects.filter(id__gt=1)
select * from tb where id =1
Django中:models.tb.objects.filter(id=1)
select * from tb where id <1
Django中:models.tb.objects.filter(id__lt=1)

############################# 2、 视图函数 ################################################# 1 request.GET request.POST request.FILES 2 #checkbox 等多选内容 POST取值 多选框 req.POST.getlist("favor") 3 #上传文件 form 表单要设置 enctype="multipart/form-data" obj=request.FILES.get("fafafa") obj.name f=open(obj.name ,"wb") for item in obj,chunks(): f.write(item) f.close() 4 FBV&CBV function base view //// class base view url.py index -> 函数名 view.py def 函数(req): ... =====> /index/ -> function /index/ -> 类方法 url.py url(r'^home/',views.Home.as_view()), view.py from django.views import View class Home(View): def get(self,req): return render(req,"home.html") def post(self,req): pass ############################# 1、 路由系统 ################################################# 1、Django请求的生命周期 -> URL对应关系(匹配) -> 视图函数 -> 返回用户字符串 -> URL对应关系(匹配) -> 视图函数 -> 打开一个HTML文件,读取内容 2、创建django project django-admin startproject mysite(项目名称) mysite .... .. cd mysite python manage.py startapp blog(程序名称) blog ..... 3、配置 模板路径 静态文件路径 #CSRF 4、编写程序 a. url.py /index/ -> func b. views.py def func(request): #包含请求数据 ... return HttpResponse("字符串") return render(request,"index.html",{""}) return redirect("URL") c. 模板语言 return render(request,"index.html",{""}) {% for item in dic1 %} <h1>{{item}}</h1> {% endfor %} 索引取值>>>>>>>>>>>>> 万能的点 <h2> {{ item.1 }} </h2>
路由
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path,re_path
from blog import views
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
re_path('^index/',views.index),
#re_path('^detail/', views.detail),
re_path('^detail-(\d+).html', views.detail),#动态路由
]

from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse # Create your views here. # dic={ # "k1": "root1", # "k2": "root2", # "k3": "root3", # "k4": "root4", # # } USER_DICT={ "1":{'name':'root1','email':'root1@163.com'}, "2": {'name': 'root2', 'email': 'root2@163.com'}, "3": {'name': 'root3', 'email': 'root3@163.com'}, "4": {'name': 'root4', 'email': 'root4@163.com'}, "5": {'name': 'root5', 'email': 'root5@163.com'}, } def index(req): return render(req,"index.html",{"user_dict":USER_DICT}) # def detail(req): # nid=req.GET.get("nid") # detail_info=USER_DICT[nid] # return render(req,"detail.html",{"detail_info":detail_info}) def detail(req,nid): return HttpResponse(nid) # nid=req.GET.get("nid") # detail_info=USER_DICT[nid] # return render(req,"detail.html",{"detail_info":detail_info})

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <ul> {% for k,row in user_dict.items %} <li><a target="_blank" href="/detail-{{k}}.html">{{row.name}}</a></li> {% endfor %} </ul> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>详细信息</h1> <h4>用户名: {{detail_info.name}}</h4> <h4>邮箱:{{detail_info.email}}</h4> </body> </html>
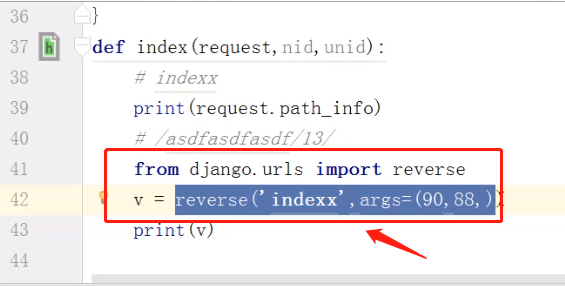

def orm(request): #创建数据1 # models.UserInfo.objects.create( # username='root', # password='123', # ) #创建数据2 # obj=models.UserInfo( # username='admin', # password='123', # ) # obj.save() # 创建数据3 # dic={"username":"李逵","password":"333"} # models.UserInfo.objects.create( **dic ) #查数据 #result=models.UserInfo.objects.all()#查所有 # result=models.UserInfo.objects.filter(id__gt=3,password=123)#条件查询 filter相当于while # # print(result) # for i in result: # print(i.id,i.username,i.password) #删数据 # models.UserInfo.objects.all().delete() # models.UserInfo.objects.filter(id=4).delete() #更新 # models.UserInfo.objects.all().update(password=666) models.UserInfo.objects.filter(id=3).update(password=222) return HttpResponse("orm")

"""mysite URL Configuration The `urlpatterns` list routes URLs to views. For more information please see: https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/topics/http/urls/ Examples: Function views 1. Add an import: from my_app import views 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('', views.home, name='home') Class-based views 1. Add an import: from other_app.views import Home 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('', Home.as_view(), name='home') Including another URLconf 1. Import the include() function: from django.urls import include, path 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('blog/', include('blog.urls')) """ from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path,include urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('cmdb/', include('blog.urls')) ]

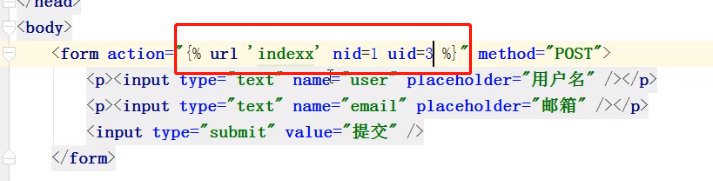
from django.urls import path,re_path from blog import views urlpatterns = [ re_path('^login/',views.login), re_path('^orm/', views.orm), re_path('^index/',views.index), re_path('^user_info',views.user_info), re_path('^user_group', views.user_group), re_path('^user_detail-(?P<nid>\d+)',views.user_detail), re_path('^user_del-(?P<nid>\d+)', views.user_del), re_path('^user_edit-(?P<nid>\d+)', views.user_edit), ]

from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse,redirect # Create your views here. def login(request): if request.method=="GET": return render(request,"login.html") if request.method=="POST": u=request.POST.get('user') p=request.POST.get('pwd') obj=models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=u,password=p).first() print(obj) if obj: return render(request,"index.html") else: return render(request,"login.html") else: return HttpResponse("不是get /post") from blog import models def orm(request): #创建数据1 # models.UserInfo.objects.create( # username='root', # password='123', # ) #创建数据2 # obj=models.UserInfo( # username='admin', # password='123', # ) # obj.save() # 创建数据3 # dic={"username":"李逵","password":"333"} # models.UserInfo.objects.create( **dic ) #查数据 #result=models.UserInfo.objects.all()#查所有 # result=models.UserInfo.objects.filter(id__gt=3,password=123)#条件查询 filter相当于while # # print(result) # for i in result: # print(i.id,i.username,i.password) #删数据 # models.UserInfo.objects.all().delete() # models.UserInfo.objects.filter(id=4).delete() #更新 # models.UserInfo.objects.all().update(password=666) models.UserInfo.objects.filter(id=3).update(password=222) return HttpResponse("orm") def index(request): return render(request,"index.html") def user_group(request): pass def user_info(request): if request.method=="GET": user_list=models.UserInfo.objects.all() # print(user_list.query) return render(request,"user_info.html",{"user_list":user_list}) elif request.method=="POST": u=request.POST.get("user") p=request.POST.get("pwd") models.UserInfo.objects.create(username=u,password=p) return redirect("/cmdb/user_info/") def user_detail(requset,nid): obj=models.UserInfo.objects.filter(id=nid).first() #models.UserInfo.objects.get(id=nid)取单条数据 如果不存在 报错 return render(requset,"user_detail.html",{"obj":obj}) def user_del(request,nid): models.UserInfo.objects.filter(id=nid).delete() return redirect("/cmdb/user_info/") def user_edit(request,nid): if request.method=="GET": obj=models.UserInfo.objects.filter(id=nid).first() return render(request,"user_edit.html",{"obj":obj}) elif request.method=="POST": nid=request.POST.get("id") u=request.POST.get("username") p=request.POST.get("pwd") models.UserInfo.objects.filter(id=nid).update(username=u,password=p) return redirect("/cmdb/user_info/")

AutoField(Field) - int自增列,必须填入参数 primary_key=True BigAutoField(AutoField) - bigint自增列,必须填入参数 primary_key=True 注:当model中如果没有自增列,则自动会创建一个列名为id的列 from django.db import models class UserInfo(models.Model): # 自动创建一个列名为id的且为自增的整数列 username = models.CharField(max_length=32) class Group(models.Model): # 自定义自增列 nid = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) name = models.CharField(max_length=32) SmallIntegerField(IntegerField): - 小整数 -32768 ~ 32767 PositiveSmallIntegerField(PositiveIntegerRelDbTypeMixin, IntegerField) - 正小整数 0 ~ 32767 IntegerField(Field) - 整数列(有符号的) -2147483648 ~ 2147483647 PositiveIntegerField(PositiveIntegerRelDbTypeMixin, IntegerField) - 正整数 0 ~ 2147483647 BigIntegerField(IntegerField): - 长整型(有符号的) -9223372036854775808 ~ 9223372036854775807 自定义无符号整数字段 class UnsignedIntegerField(models.IntegerField): def db_type(self, connection): return 'integer UNSIGNED' PS: 返回值为字段在数据库中的属性,Django字段默认的值为: 'AutoField': 'integer AUTO_INCREMENT', 'BigAutoField': 'bigint AUTO_INCREMENT', 'BinaryField': 'longblob', 'BooleanField': 'bool', 'CharField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)', 'CommaSeparatedIntegerField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)', 'DateField': 'date', 'DateTimeField': 'datetime', 'DecimalField': 'numeric(%(max_digits)s, %(decimal_places)s)', 'DurationField': 'bigint', 'FileField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)', 'FilePathField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)', 'FloatField': 'double precision', 'IntegerField': 'integer', 'BigIntegerField': 'bigint', 'IPAddressField': 'char(15)', 'GenericIPAddressField': 'char(39)', 'NullBooleanField': 'bool', 'OneToOneField': 'integer', 'PositiveIntegerField': 'integer UNSIGNED', 'PositiveSmallIntegerField': 'smallint UNSIGNED', 'SlugField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)', 'SmallIntegerField': 'smallint', 'TextField': 'longtext', 'TimeField': 'time', 'UUIDField': 'char(32)', BooleanField(Field) - 布尔值类型 NullBooleanField(Field): - 可以为空的布尔值 CharField(Field) - 字符类型 - 必须提供max_length参数, max_length表示字符长度 TextField(Field) - 文本类型 EmailField(CharField): - 字符串类型,Django Admin以及ModelForm中提供验证机制 IPAddressField(Field) - 字符串类型,Django Admin以及ModelForm中提供验证 IPV4 机制 GenericIPAddressField(Field) - 字符串类型,Django Admin以及ModelForm中提供验证 Ipv4和Ipv6 - 参数: protocol,用于指定Ipv4或Ipv6, 'both',"ipv4","ipv6" unpack_ipv4, 如果指定为True,则输入::ffff:192.0.2.1时候,可解析为192.0.2.1,开启刺功能,需要protocol="both" URLField(CharField) - 字符串类型,Django Admin以及ModelForm中提供验证 URL SlugField(CharField) - 字符串类型,Django Admin以及ModelForm中提供验证支持 字母、数字、下划线、连接符(减号) CommaSeparatedIntegerField(CharField) - 字符串类型,格式必须为逗号分割的数字 UUIDField(Field) - 字符串类型,Django Admin以及ModelForm中提供对UUID格式的验证 FilePathField(Field) - 字符串,Django Admin以及ModelForm中提供读取文件夹下文件的功能 - 参数: path, 文件夹路径 match=None, 正则匹配 recursive=False, 递归下面的文件夹 allow_files=True, 允许文件 allow_folders=False, 允许文件夹 FileField(Field) - 字符串,路径保存在数据库,文件上传到指定目录 - 参数: upload_to = "" 上传文件的保存路径 storage = None 存储组件,默认django.core.files.storage.FileSystemStorage ImageField(FileField) - 字符串,路径保存在数据库,文件上传到指定目录 - 参数: upload_to = "" 上传文件的保存路径 storage = None 存储组件,默认django.core.files.storage.FileSystemStorage width_field=None, 上传图片的高度保存的数据库字段名(字符串) height_field=None 上传图片的宽度保存的数据库字段名(字符串) DateTimeField(DateField) - 日期+时间格式 YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM[:ss[.uuuuuu]][TZ] DateField(DateTimeCheckMixin, Field) - 日期格式 YYYY-MM-DD TimeField(DateTimeCheckMixin, Field) - 时间格式 HH:MM[:ss[.uuuuuu]] DurationField(Field) - 长整数,时间间隔,数据库中按照bigint存储,ORM中获取的值为datetime.timedelta类型 FloatField(Field) - 浮点型 DecimalField(Field) - 10进制小数 - 参数: max_digits,小数总长度 decimal_places,小数位长度 BinaryField(Field) - 二进制类型

null 数据库中字段是否可以为空 db_column 数据库中字段的列名 db_tablespace default 数据库中字段的默认值 primary_key 数据库中字段是否为主键 db_index 数据库中字段是否可以建立索引 unique 数据库中字段是否可以建立唯一索引 unique_for_date 数据库中字段【日期】部分是否可以建立唯一索引 unique_for_month 数据库中字段【月】部分是否可以建立唯一索引 unique_for_year 数据库中字段【年】部分是否可以建立唯一索引 verbose_name Admin中显示的字段名称 blank Admin中是否允许用户输入为空 editable Admin中是否可以编辑 help_text Admin中该字段的提示信息 choices Admin中显示选择框的内容,用不变动的数据放在内存中从而避免跨表操作 如:gf = models.IntegerField(choices=[(0, '何穗'),(1, '大表姐'),],default=1) error_messages 自定义错误信息(字典类型),从而定制想要显示的错误信息; 字典健:null, blank, invalid, invalid_choice, unique, and unique_for_date 如:{'null': "不能为空.", 'invalid': '格式错误'} validators 自定义错误验证(列表类型),从而定制想要的验证规则 from django.core.validators import RegexValidator from django.core.validators import EmailValidator,URLValidator,DecimalValidator,\ MaxLengthValidator,MinLengthValidator,MaxValueValidator,MinValueValidator 如: test = models.CharField( max_length=32, error_messages={ 'c1': '优先错信息1', 'c2': '优先错信息2', 'c3': '优先错信息3', }, validators=[ RegexValidator(regex='root_\d+', message='错误了', code='c1'), RegexValidator(regex='root_112233\d+', message='又错误了', code='c2'), EmailValidator(message='又错误了', code='c3'), ] )

class UserInfo(models.Model): nid = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) username = models.CharField(max_length=32) class Meta: # 数据库中生成的表名称 默认 app名称 + 下划线 + 类名 db_table = "table_name" # 联合索引 index_together = [ ("pub_date", "deadline"), ] # 联合唯一索引 unique_together = (("driver", "restaurant"),) # admin中显示的表名称 verbose_name # verbose_name加s verbose_name_plural 更多:https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.10/ref/models/options/

1.触发Model中的验证和错误提示有两种方式: a. Django Admin中的错误信息会优先根据Admiin内部的ModelForm错误信息提示,如果都成功,才来检查Model的字段并显示指定错误信息 b. 调用Model对象的 clean_fields 方法,如: # models.py class UserInfo(models.Model): nid = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) username = models.CharField(max_length=32) email = models.EmailField(error_messages={'invalid': '格式错了.'}) # views.py def index(request): obj = models.UserInfo(username='11234', email='uu') try: print(obj.clean_fields()) except Exception as e: print(e) return HttpResponse('ok') # Model的clean方法是一个钩子,可用于定制操作,如:上述的异常处理。 2.Admin中修改错误提示 # admin.py from django.contrib import admin from model_club import models from django import forms class UserInfoForm(forms.ModelForm): username = forms.CharField(error_messages={'required': '用户名不能为空.'}) email = forms.EmailField(error_messages={'invalid': '邮箱格式错误.'}) age = forms.IntegerField(initial=1, error_messages={'required': '请输入数值.', 'invalid': '年龄必须为数值.'}) class Meta: model = models.UserInfo # fields = ('username',) fields = "__all__" class UserInfoAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin): form = UserInfoForm admin.site.register(models.UserInfo, UserInfoAdmin)
325 457
auto_now -> 创建时,自动生成时间
auto_now_add -> 更新时,自动更新为当前时间
#obj=UerGroup.object.filter(id=1).update(caption="CEO")
#这种方式是不会更新的。
obj=UerGroup.object.filter(id=1).first()
pbj.caption="CEO"
#这种方式才会更新时间
obj.save()
#获取用户提交的数据 request.POST.get() request.GET.get() request.FILES.get() #checkbox request.POST.getlist() request.path_info
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
from app01 import models
# Create your views here.
def business(request):
v1 = models.Bussiness.objects.all().values
v2=models.Bussiness.objects.all().values("id","caption")
#QuerySet
#[{},{},...] 字典
v3 = models.Bussiness.objects.all().values_list("id", "caption")
#[(),(),....]内部元素是元组
return render(request,"business.html",{"v1":v1,"v2":v2,"v3":v3})
def host(request):
v1=models.Host.objects.filter(nid__gt=0)
for row in v1:
print(row.nid,row.hostname,row.ip,row.prot,row.b.caption)
# return render(request,"host.html",{"v1":v1})
v2 = models.Host.objects.filter(nid__gt=0).values('nid','hostname','b_id','b__caption')
print(v2)#跨表取值 用双下划线
v3 = models.Host.objects.filter(nid__gt=0).values_list('nid', 'hostname', 'b_id', 'b__caption')
print(v3) # 跨表取值 用双下划线
return HttpResponse("ok")

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>业务线列表-对象</h1> <ul> {% for row in v1 %} <li>{{ row.id }}-{{ row.caption }}--{{ row.code }}</li> {% endfor %} </ul> <h1>业务线列表-字典</h1> <ul> {% for row in v2 %} <li>{{ row.id }}-{{ row.caption }}</li> {% endfor %} </ul> <h1>业务线列表-元组</h1> <ul> {% for row in v3 %} <li>{{ row.0 }}-{{ row.1}}</li> {% endfor %} </ul> </body> </html>
10.16
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<style>
.hide{display: none}
.shade{
position: fixed;
top:0;
right: 0;
bottom:0;
left: 0;
background-color: black;
opacity: 0.6;
z-index: 100;
}
.add-modal{
position: fixed;
height: 300px;
width: 400px;
top: 100px;
left: 50%;
margin-left: -200px;
z-index: 101;
border: 1px solid red;
background-color: white;
}
</style>
<body>
<h1>主机列表-对象</h1>
<input id="add_host" type="button" value="添加">
<table border="1" cellspacing="0">
<tr>
<th>序号</th>
<th>主机名</th>
<th>IP</th>
<th>端口</th>
<th>业务线名称</th>
</tr>
{% for row in v1 %}
<tr>
<td>{{ forloop.counter }}</td>
<td>{{ row.hostname }}</td>
<td>{{ row.ip }}</td>
<td>{{ row.prot }}</td>
<td>{{ row.b.caption }}</td></tr>
{% endfor %}
</table>
<div class="shade hide"></div>
<div class="add-modal hide">
<div style="padding: 20px ">
<form method="post" action="/host/">
<p><input id="host" type="text" placeholder="主机名" name="hostname"/></p>
<p><input id="ip" type="text" placeholder="IP" name="ip"/></p>
<p><input id="prot" type="text" placeholder="端口" name="prot"/></p>
<p>
<select id="sel" name="b_id">
{% for row in b_list %}
<option value="{{ row.id }}">{{ row.caption }}</option>
{% endfor %}
</select>
</p>
<p><input type="submit" value="提交"/><a id="ajax_submit">悄悄发送消息</a>
</p>
<p><input id="cancel" type="button" value="取消"></p>
</form>
</div>
</div>
<script src="/static/jquery-3.3.1.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(function () {
$("#add_host").click(function () {
$('.shade,.add-modal').removeClass("hide");
})
$("#cancel").click(function () {
$('.shade,.add-modal').addClass("hide");
})
$("#ajax_submit").click(function () {
$.ajax({
url:"/test_ajax/",
type:"POST",
data:{"user":$("#host").val(),"ip":$("#ip").val(),"prot":$("#prot").val(),"b_id":$("#sel").val()},
success:function (data) {
if(data=="ok"){
location.reload()
}
else{
alert(data)
}
}
})
})
})
</script>
</body>
</html>

"""mysitedemo URL Configuration
The `urlpatterns` list routes URLs to views. For more information please see:
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/topics/http/urls/
Examples:
Function views
1. Add an import: from my_app import views
2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('', views.home, name='home')
Class-based views
1. Add an import: from other_app.views import Home
2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('', Home.as_view(), name='home')
Including another URLconf
1. Import the include() function: from django.urls import include, path
2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('blog/', include('blog.urls'))
"""
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from app01 import views
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('business/',views.business),
path('host/',views.host),
path('test_ajax/',views.test_ajax)
]

from django.db import models
# Create your models here.
class Bussiness(models.Model):
caption=models.CharField(max_length=32)
code=models.CharField(max_length=32)
class Host(models.Model):
nid=models.AutoField(primary_key=True)
hostname=models.CharField(max_length=32,db_index=True)
ip=models.GenericIPAddressField(protocol="ipv4",db_index=True)
prot=models.IntegerField()
b=models.ForeignKey("Bussiness",to_field="id",on_delete=models.CASCADE)

"""
Django settings for mysitedemo project.
Generated by 'django-admin startproject' using Django 2.1.1.
For more information on this file, see
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/topics/settings/
For the full list of settings and their values, see
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/ref/settings/
"""
import os
# Build paths inside the project like this: os.path.join(BASE_DIR, ...)
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
# Quick-start development settings - unsuitable for production
# See https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/howto/deployment/checklist/
# SECURITY WARNING: keep the secret key used in production secret!
SECRET_KEY = 'df-*=bi#_19x^v7cn7-c31*bs270wi#o*)cm)4+qbh%v=(w23#'
# SECURITY WARNING: don't run with debug turned on in production!
DEBUG = True
ALLOWED_HOSTS = []
# Application definition
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'app01.apps.App01Config',
]
MIDDLEWARE = [
'django.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware',
'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware',
'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
#'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware',
'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware',
'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware',
]
ROOT_URLCONF = 'mysitedemo.urls'
TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')]
,
'APP_DIRS': True,
'OPTIONS': {
'context_processors': [
'django.template.context_processors.debug',
'django.template.context_processors.request',
'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
],
},
},
]
WSGI_APPLICATION = 'mysitedemo.wsgi.application'
# Database
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/ref/settings/#databases
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.sqlite3',
'NAME': os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'db.sqlite3'),
}
}
# Password validation
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/ref/settings/#auth-password-validators
AUTH_PASSWORD_VALIDATORS = [
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.UserAttributeSimilarityValidator',
},
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.MinimumLengthValidator',
},
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.CommonPasswordValidator',
},
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.NumericPasswordValidator',
},
]
# Internationalization
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/topics/i18n/
LANGUAGE_CODE = 'en-us'
TIME_ZONE = 'UTC'
USE_I18N = True
USE_L10N = True
USE_TZ = True
# Static files (CSS, JavaScript, Images)
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/howto/static-files/
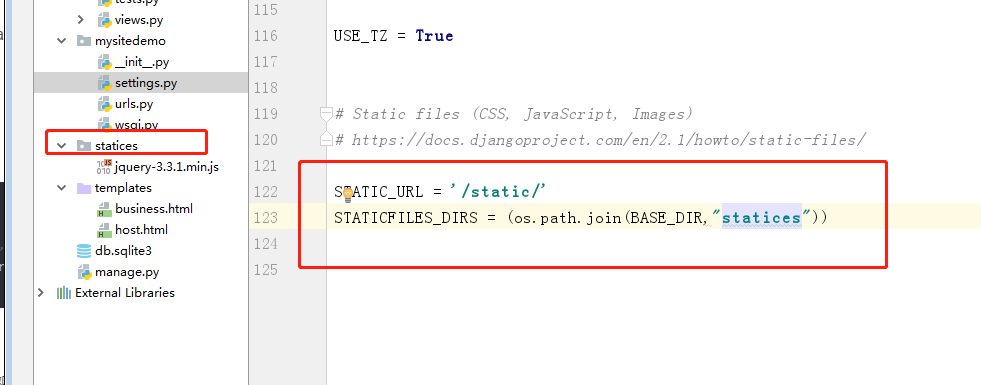
STATIC_URL = '/static/'
STATICFILES_DIRS = (
os.path.join(BASE_DIR,"statices"),
)

from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse,redirect
from app01 import models
# Create your views here.
def business(request):
v1 = models.Bussiness.objects.all().values
v2=models.Bussiness.objects.all().values("id","caption")
#QuerySet
#[{},{},...] 字典
v3 = models.Bussiness.objects.all().values_list("id", "caption")
#[(),(),....]内部元素是元组
return render(request,"business.html",{"v1":v1,"v2":v2,"v3":v3})
# def host(request):
# v1=models.Host.objects.filter(nid__gt=0)
# for row in v1:
# print(row.nid,row.hostname,row.ip,row.prot,row.b.caption)
# # return render(request,"host.html",{"v1":v1})
# v2 = models.Host.objects.filter(nid__gt=0).values('nid','hostname','b_id','b__caption')
# print(v2)#跨表取值 用双下划线
# v3 = models.Host.objects.filter(nid__gt=0).values_list('nid', 'hostname', 'b_id', 'b__caption')
# print(v3) # 跨表取值 用双下划线
# return render(request,"host.html",{"v1":v1})
def host(request):
if request.method=="GET":
b_list=models.Bussiness.objects.all()
v1=models.Host.objects.filter(nid__gt=0)
return render(request,"host.html",{"v1":v1,"b_list":b_list})
elif request.method=="POST":
h=request.POST.get("hostname")
i=request.POST.get("ip")
p=request.POST.get("prot")
b=request.POST.get("b_id")
models.Host.objects.create(hostname=h,ip=i,prot=p,b_id=b)
return redirect("/host")
def test_ajax(request):
print(request.method,request.POST,sep="\t")
h = request.POST.get("user")
i = request.POST.get("ip")
p = request.POST.get("prot")
b = request.POST.get("b_id")
if h and len(h)>5:
models.Host.objects.create(hostname=h, ip=i, prot=p, b_id=b)
return HttpResponse("ok")
else:
return HttpResponse("太短了")

li={"1":2,"3":4} {1: 2, 3: 4} li {1: 2, 3: 4} s=JSON.parse(li) VM158:1 Uncaught SyntaxError: Unexpected token o in JSON at position 1 at JSON.parse (<anonymous>) at <anonymous>:1:8 (anonymous) @ VM157:1 s=JSON.stringify(li) "{"1":2,"3":4}" JSON.parse(s) {1: 2, 3: 4}
$("#ajax_submit").click(function () {
$.ajax({
url:"/test_ajax/",
type:"POST",
//data:{"user":$("#host").val(),"ip":$("#ip").val(),"prot":$("#prot").val(),"b_id":$("#sel").val()},
data:$("#add_form").serialize(),
success:function (data) {
var obj=JSON.parse(data);
if (obj.status){
location.reload()
}
else{
$("#error-msg").text(obj.errors);
}
}
})
})
def test_ajax(request):
import json
ret={'status':True,'errors':None,'data':None}
try:
print(request.method,request.POST,sep="\t",end="\n")
# h = request.POST.get("user")
# i = request.POST.get("ip")
# p = request.POST.get("prot")
# b = request.POST.get("b_id")
#
data_dic={}
for row in request.POST:
data_dic[row]=request.POST[row]
print(data_dic)
if data_dic["hostname"] and len(data_dic["hostname"])>5:
models.Host.objects.create(**data_dic)
# return HttpResponse(data_dic["hostname"])
else:
ret['status']=False
ret['errors']="太短了"
except Exception as e:
ret['status']=False
ret['errors']='请求错误'
return HttpResponse(json.dumps(ret))
340 从入门到逼疯
https://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/5246483.html




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号