1015 德才论(C++)
这道题同样理清楚给的条件和思路就行。
这道题总的就两个步骤:
- 分类
- 排序
我这里使用了tuple
分类
按照题干,分为:
1.才德全尽 2.德胜才 3.才德兼亡,但尚有“德胜才” 4.达标
排序
利用sort排序(如果使用冒泡排序会出现,在大量数据进行测试时,运行超时的情况),具体的排序标准为:
首先通过类别排序,排序为1,2,3,4 >>>> 再通过总分排序(降序) >>>> 然后通过德分排序(降序) >>>> 最后通过学号排序(升序)
注意:
- 需要使用sort排序,否则测试点2,3,4超时。
- 需要使用printf和scanf代替cout和cin,否则超时。
代码:
#include <iostream> #include <tuple> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> //#pragma warning(disable:4996) using namespace std; bool func1(tuple<int, int, int, int>& val1, tuple<int, int, int, int>& val2) {//排序 if (get<3>(val1) != get<3>(val2))//类别排序 return get<3>(val1) < get<3>(val2); else if (get<1>(val1) + get<2>(val1) !=//总分排序 get<1>(val2) + get<2>(val2)) return get<1>(val1) + get<2>(val1) > get<1>(val2) + get<2>(val2); else if (get<1>(val1) != get<1>(val2))//德分排序 return get<1>(val1) > get<1>(val2); else return get<0>(val1) < get<0>(val2);//学号排序 } int main() { vector<tuple<int, int, int, int> > vec, cvec; int a, b, c = 0, n, L, H, k = 0, str; cin >> n >> L >> H; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { scanf("%d%d%d", &str, &a, &b); vec.push_back({ str, a, b, c}); } for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {//分类 if (get<1>(vec[i]) >= L && get<2>(vec[i]) >= L) {//剔除不符合最低标准学生 if (get<1>(vec[i]) >= H && get<2>(vec[i]) >= H) { get<3>(vec[i]) = 1;//才德全尽 } else if (get<1>(vec[i]) >= H && get<2>(vec[i]) < H) { get<3>(vec[i]) = 2;//德胜才 } else if (get<1>(vec[i]) < H && get<2>(vec[i]) < H && get<1>(vec[i]) >= get<2>(vec[i])) { get<3>(vec[i]) = 3;//才德兼亡,但尚有“德胜才” } else{ get<3>(vec[i]) = 4;//达标 } ++k; cvec.push_back(vec[i]); } } cout << k << endl; sort(cvec.begin(), cvec.end(), func1); for (auto& i : cvec) { printf("%d %d %d\n", get<0>(i), get<1>(i), get<2>(i)); } return 0; }
简单用这两段代码测试了一下:
cout:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { // ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); for(int i = 0; i < 1e6; ++i) cout << i; return 0; }
![]()
printf:
#include <stdio.h> int main(void) { for(int i = 0; i < 1e6; ++i) printf("%d", i); return 0; }
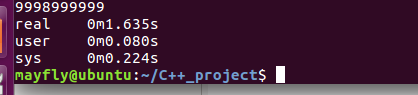
我们将cout注释部分去掉之后,运行:
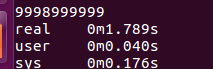
为什么scanf比cin更快?
在高层次上,它们都是read()系统调用的包装器,只是语法糖。唯一可见的区别是scanf()必须显式声明输入类型,而cin使用模板重载重定向操作。这似乎不足以让性能达到5倍。
事实证明,iostream使用了stdio的缓冲系统。因此,cin浪费时间与底层C库的stdio缓冲区同步,因此对scanf()和cin的调用都可以交错。
但是,libstdc ++提供了一个选项,可以使用相应的标准C流关闭所有iostream标准流的同步--ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号