合并两个有序链表
21. 合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:

输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0] 输出:[0]
提示:
- 两个链表的节点数目范围是
[0, 50] -100 <= Node.val <= 100l1和l2均按 非递减顺序 排列
解法1最笨的解法:
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * struct ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode *next; 6 * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} 7 * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} 8 * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} 9 * }; 10 */ 11 class Solution { 12 public: 13 void insertNodeAtTail(ListNode *&head, int val) { 14 ListNode *newNode = new ListNode(val); 15 ListNode *currentNode = head; 16 if (head == nullptr) { 17 head = newNode; 18 return; 19 } 20 while (currentNode->next != nullptr) { 21 currentNode = currentNode->next; 22 } 23 currentNode->next = newNode; 24 return; 25 } 26 27 ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) { 28 if (list1 == nullptr && list2 == nullptr) { 29 return nullptr; 30 } 31 vector<int> vec; 32 while (list1 != nullptr) { 33 vec.push_back(list1->val); 34 list1 = list1->next; 35 } 36 while (list2 != nullptr) { 37 vec.push_back(list2->val); 38 list2 = list2->next; 39 } 40 sort(vec.begin(), vec.end()); 41 ListNode *newHead = nullptr; 42 for (const auto &v : vec) { 43 insertNodeAtTail(newHead, v); 44 } 45 return newHead; 46 } 47 };
解法二(两个链表按照先拼接较小的):
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class ListNode { 7 public: 8 ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} 9 ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} 10 ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} 11 12 public: 13 int val; 14 ListNode *next; 15 }; 16 17 class Solution { 18 public: 19 ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) { // 合并两个有序链表 20 ListNode *dummyNode = new ListNode(0); 21 ListNode *currentNode = dummyNode; 22 ListNode *newHead = nullptr; 23 while (list1 != nullptr && list2 != nullptr) { 24 if (list1->val <= list2->val) { 25 currentNode->next = list1; 26 list1 = list1->next; 27 } else { 28 currentNode->next = list2; 29 list2 = list2->next; 30 } 31 currentNode = currentNode->next; 32 } 33 if (list1 != nullptr) { 34 currentNode->next = list1; 35 } else { 36 currentNode->next = list2; 37 } 38 newHead = dummyNode->next; 39 delete dummyNode; 40 return newHead; 41 } 42 // 尾插法插入链表元素 43 void insertNodeAtTail(ListNode *&head, int val) { 44 ListNode *newNode = new ListNode(val); 45 ListNode *currentNode = head; 46 if (head == nullptr) { 47 head = newNode; 48 return; 49 } 50 while (currentNode->next != nullptr) { 51 currentNode = currentNode->next; 52 } 53 currentNode->next = newNode; 54 return; 55 } 56 // 打印链表元素 57 void printfListNode(ListNode *head) { 58 while (head != nullptr) { 59 std::cout << head->val << "->"; 60 head = head->next; 61 } 62 std::cout << "NULL" << endl; 63 return; 64 } 65 }; 66 int main() 67 { 68 Solution *test = new Solution(); 69 vector<int> vec1 = {1, 2, 4 }; 70 ListNode *list1 = nullptr; 71 // 插入节点 72 for (const auto &v : vec1) { 73 test->insertNodeAtTail(list1, v); 74 } 75 test->printfListNode(list1); // 1->2->4->NULL 76 77 vector<int> vec2 = {1, 3, 4 }; 78 ListNode *list2 = nullptr; 79 // 插入节点 80 for (const auto &v : vec2) { 81 test->insertNodeAtTail(list2, v); 82 } 83 test->printfListNode(list2); // 1->3->4->NULL 84 85 ListNode *mergedNewHead = test->mergeTwoLists(list1, list2); 86 test->printfListNode(mergedNewHead); // 1->1->2->3->4->4->NULL 87 88 delete test; 89 system("pause"); 90 return 0; 91 }
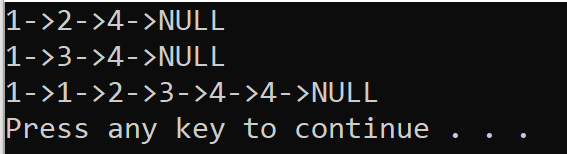
运行结果:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号