Lecture 06 Intermediate SQL
Join Expressions:
Natural Join:
Natural join matches tuples with the same values for all common attributes, and retains only one copy of each common column
select *
from instructor natural join teaches;
select name, title
from (instructor natural join teaches) join course using(course_id);
is equal to
select name, title
from instructor natural join teaches, course where teaches.course_id= course.course_id;
Joined Relations:
Join operations take two relations and return as a result another relation.
A join operation is a Cartesian product which requires that tuples in the two relations match (under some condition). It also specifies the attributes that are present in the result of the join.
Outer Join:
An extension of the join operation that avoids loss of information.
Computes the join and then adds tuples form one relation that does not match tuples in the other relation to the result of the join.

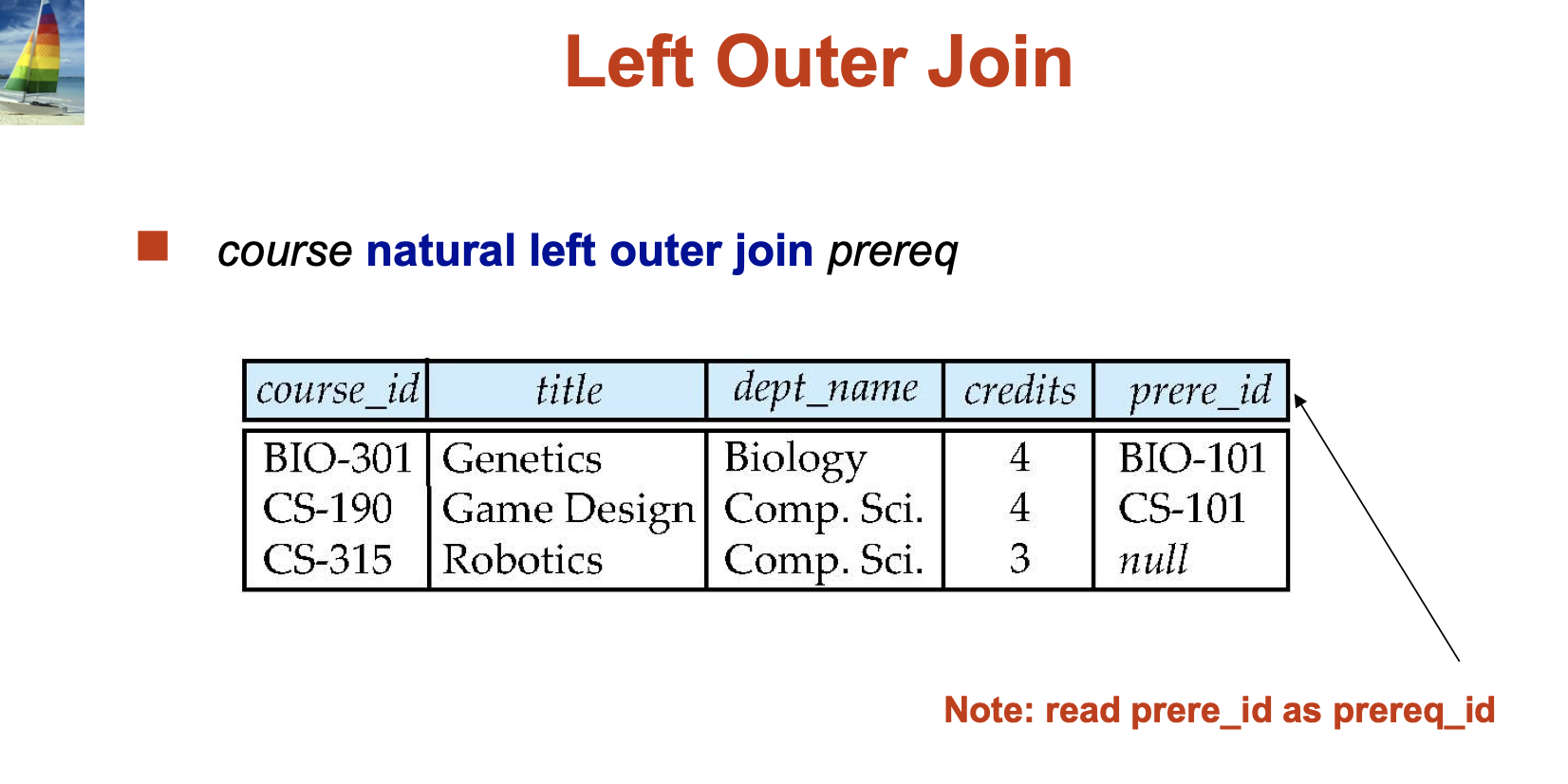
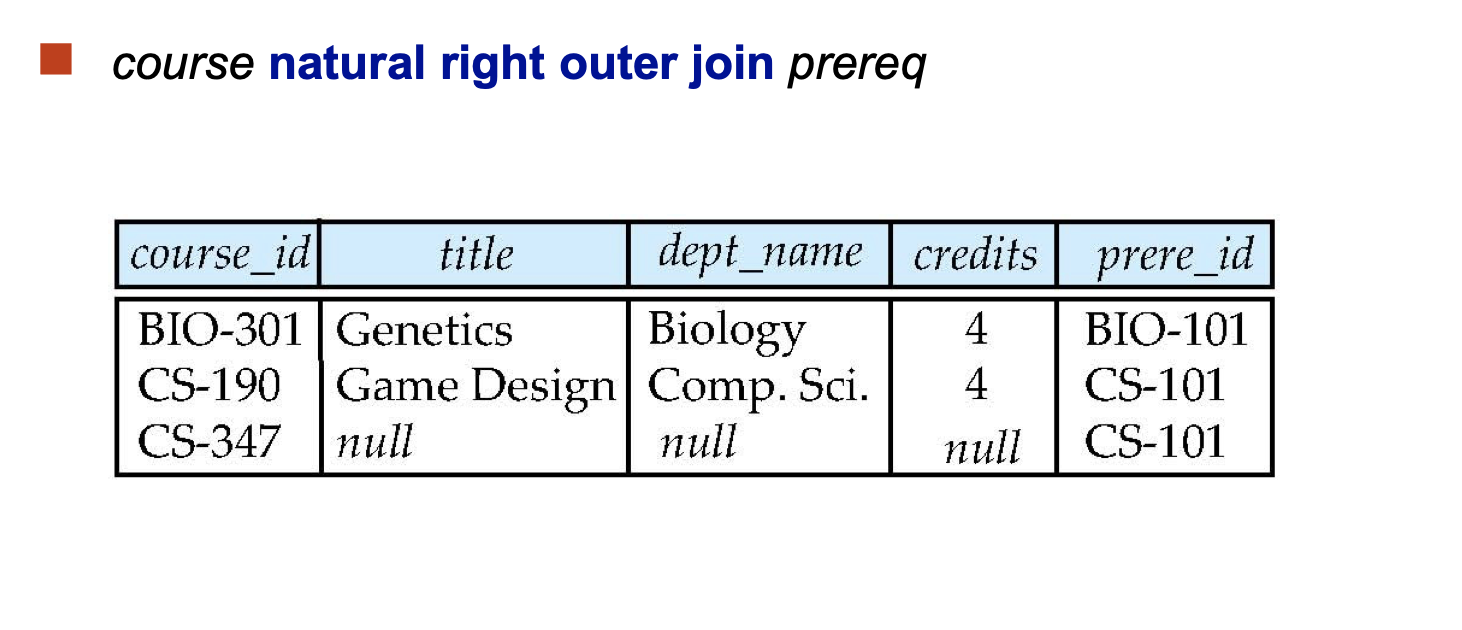
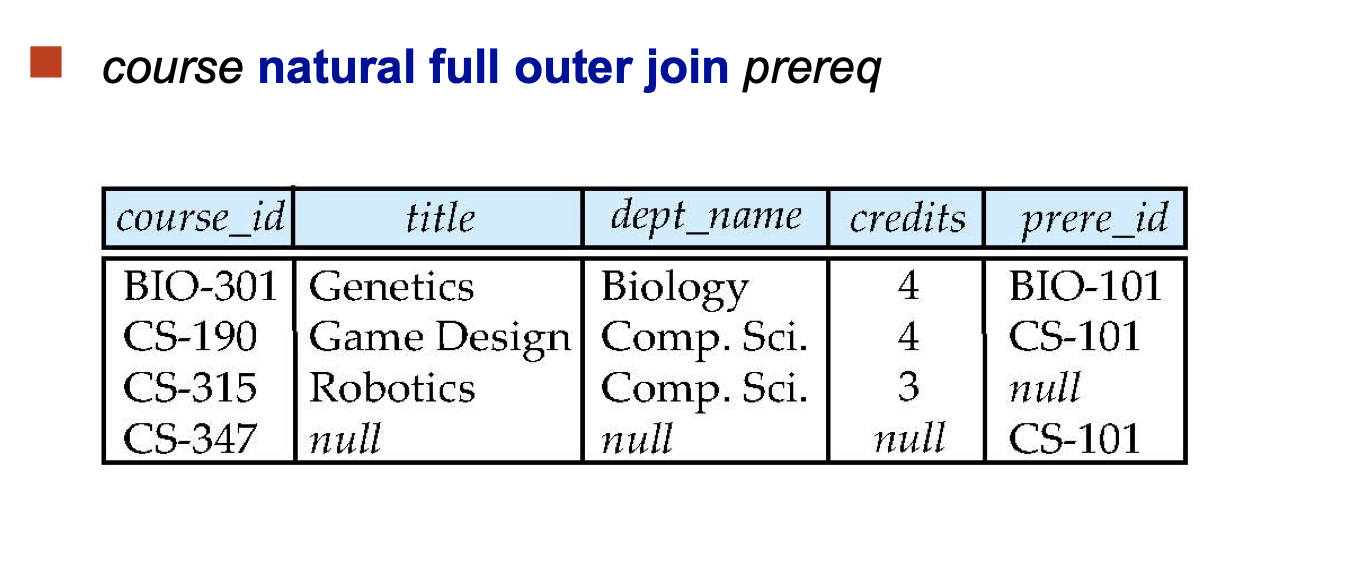
Joined Relations:
Join operations take two relations and return as a result another relation.
These additional operations are typically used as subquery expressions in the from clause
Join condition – defines which tuples in the two relations match, and what attributes are present in the result of the join.
Join type – defines how tuples in each relation that do not match any tuple in the other relation (based on the join condition) are treated.
Views:
In some cases, it is not desirable for all users to see the entire logical model (that is, all the actual relations stored in the database.)
A view provides a mechanism to hide certain data from the view of certain users.
View Definition:
A view is defined using the create view statement which has the form
create view v as < query expression >
where <query expression> is any legal SQL expression. The view
name is represented by v.

Update of a View:
Add a new tuple to faculty view which we defined earlier insert into faculty values (’30765’, ’Green’, ’Music’);
This insertion must be represented by the insertion of the tuple (’30765’, ’Green’, ’Music’, null)
into the instructor relation.
But usually we don't update views since it may cause issues.
Authorization:
Forms of authorization on parts of the database:
Forms of authorization to modify the database schema
Read - allows reading, but not modification of data.
Insert - allows insertion of new data, but not modification of existing data.Update - allows modification, but not deletion of data.
Delete - allows deletion of data.
Index - allows creation and deletion of indices.
Resources - allows creation of new relations.
Alteration - allows addition or deletion of attributes in a relation. Drop - allows deletion of relations.
Authorization Specification in SQL:
The grant statement is used to confer authorization grant <privilege list>
on <relation name or view name> to <user list>
Granting a privilege on a view does not imply granting any privileges on the underlying relations.
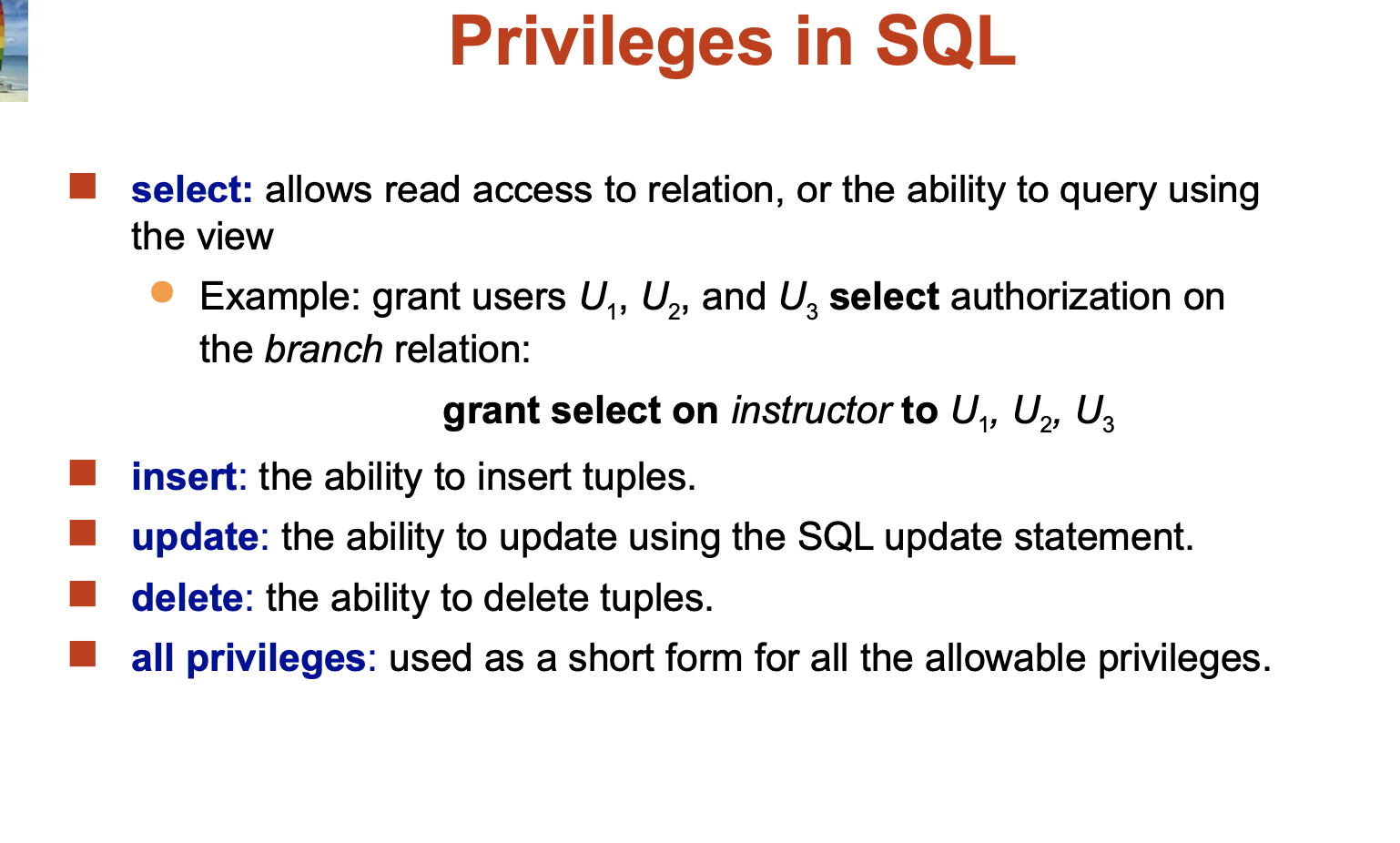
The revoke statement is used to revoke authorization. revoke <privilege list>
on <relation name or view name> from <user list>
Roles:
create role instructor;
grant instructor to Amit;
Privileges can be granted to roles:
grant select on takes to instructor;
Roles can be granted to users, as well as to other roles
create role teaching_assistant
grant teaching_assistant to instructor;
Instructor inherits all privileges of teaching_assistant
Chain of roles:
create role dean;
grant instructor to dean;
grant dean to Satoshi;


Referential Integrity:
Ensures that a value that appears in one relation for a given set of attributes also appears for a certain set of attributes in another relation
Let A be a set of attributes. Let R and S be two relations that contain attributes A and where A is the primary key of S. A is said to be a foreign key of R if for any values of A appearing in R these values also appear in S.
Cascading Actions in Referential Integrity:

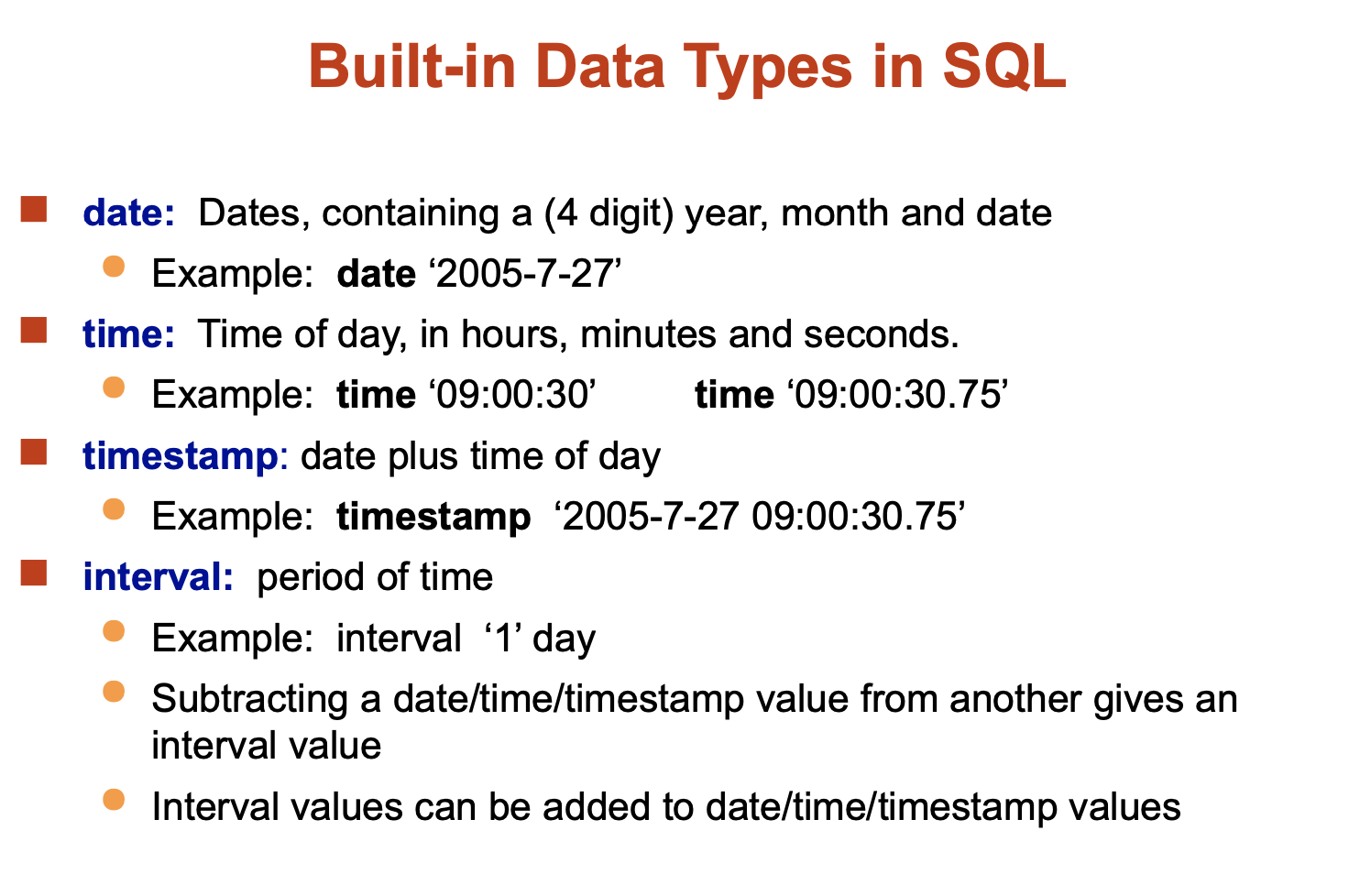 Built-in Data-types in SQL:
Built-in Data-types in SQL:


Date/Time Operations:

Index Creation:
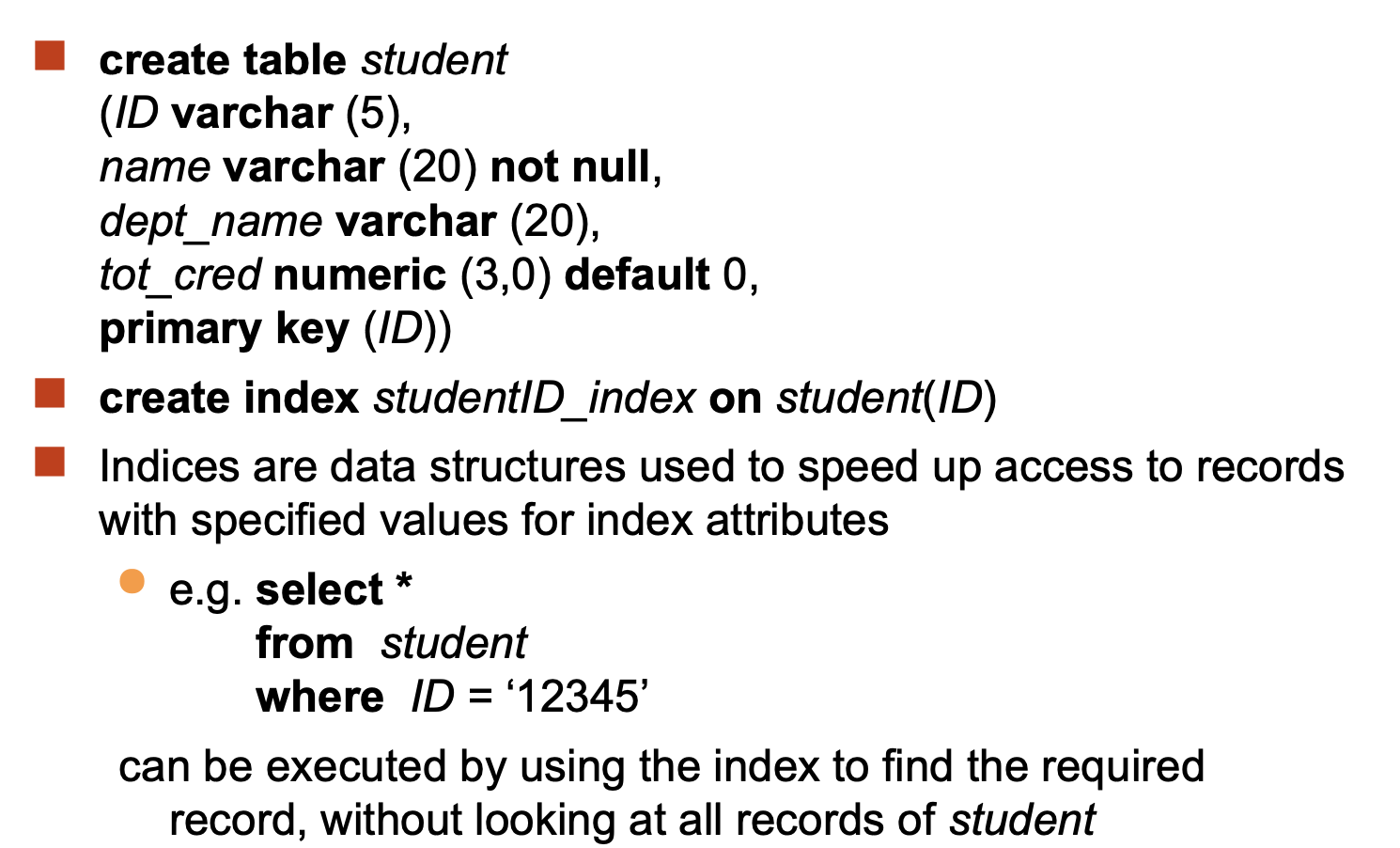
User-Defined Types:
create type construct in SQL creates user-defined type
create type Dollars as numeric (12,2) final
create table department (
dept_name varchar (20),
building varchar (15),
budget Dollars);


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号