Lecture 01 Relation model
Relational Model:
A relation is unordered set that contain the relationship of attributes that represent entities.
A relational database consists of a collection of tables, each of which is assigned a
unique name.
An example is the table below:
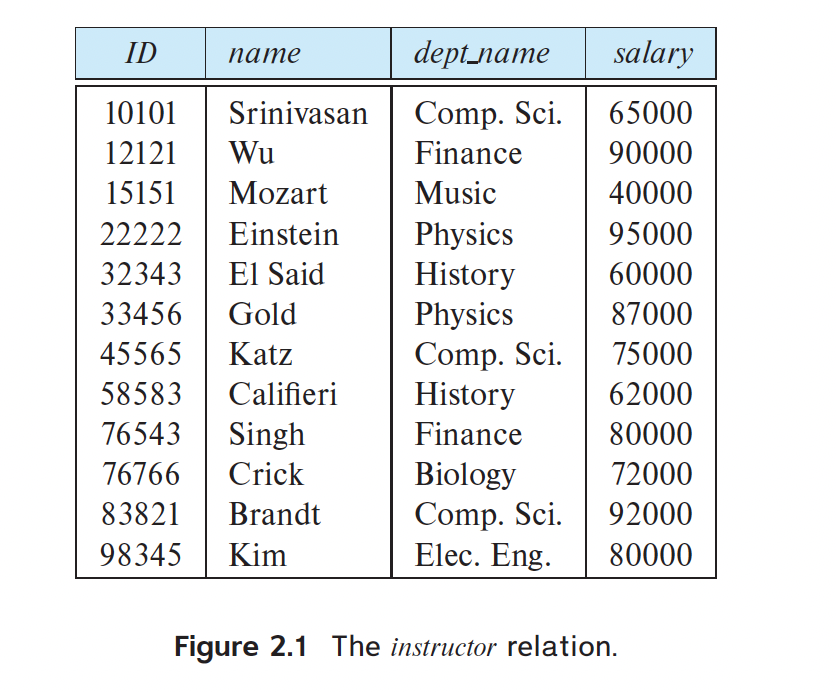
When we consider this table, a row in the table can be thought of as representing the relationship
course id title dept name credits.
In the relational model the term relation is used to refer to a table, while the
term tuple is used to refer to a row. Similarly, the term attribute refers to a column of a
table.
We use the term relation instance to refer to a specific instance of a relation, that
is, containing a specific set of rows. The instance of instructor shown in Figure 2.1 has
12 tuples, corresponding to 12 instructors.
For each attribute of a relation, there is a set of permitted values, called the domain
of that attribute.
Keys:
A superkey is a set of one or more attributes that, taken collectively, allow us to
identify uniquely a tuple in the relation.
We are often interested in superkeys for which no proper subset is a
superkey. Such minimal superkeys are called candidate keys.
We shall use the term primary key to denote a candidate key that is chosen by the
database designer as the principal means of identifying tuples within a relation.
Entity:
A definable thing—such as a person, object, concept or event—that can have data stored about it. Think of entities as nouns. Examples: a customer, student, car or product. Typically shown as a rectangle.

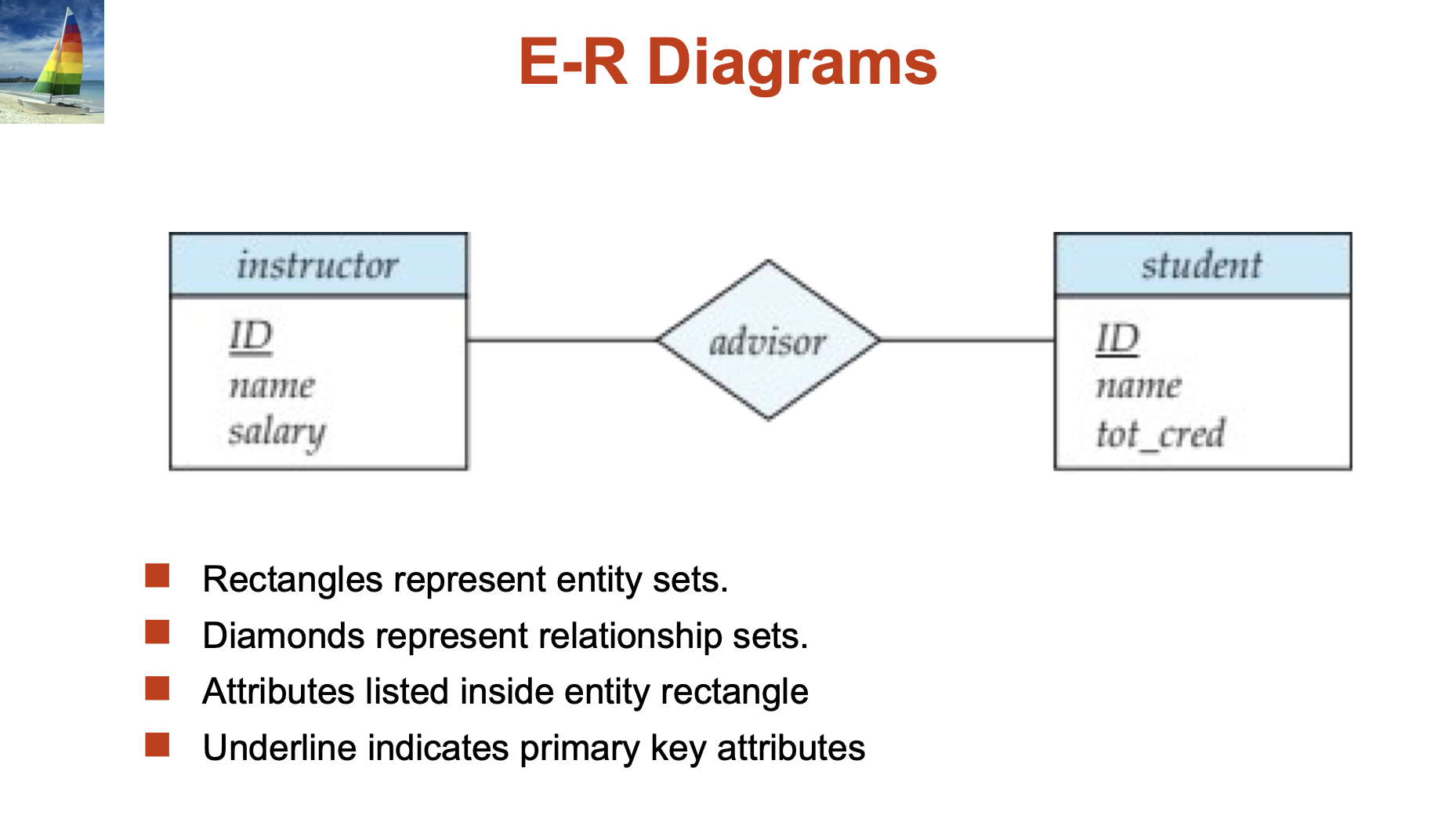
Relationship Sets:
A relationship is an association among several entities
A relationship set is a mathematical relation among n >= 2 entities, each taken from entity sets
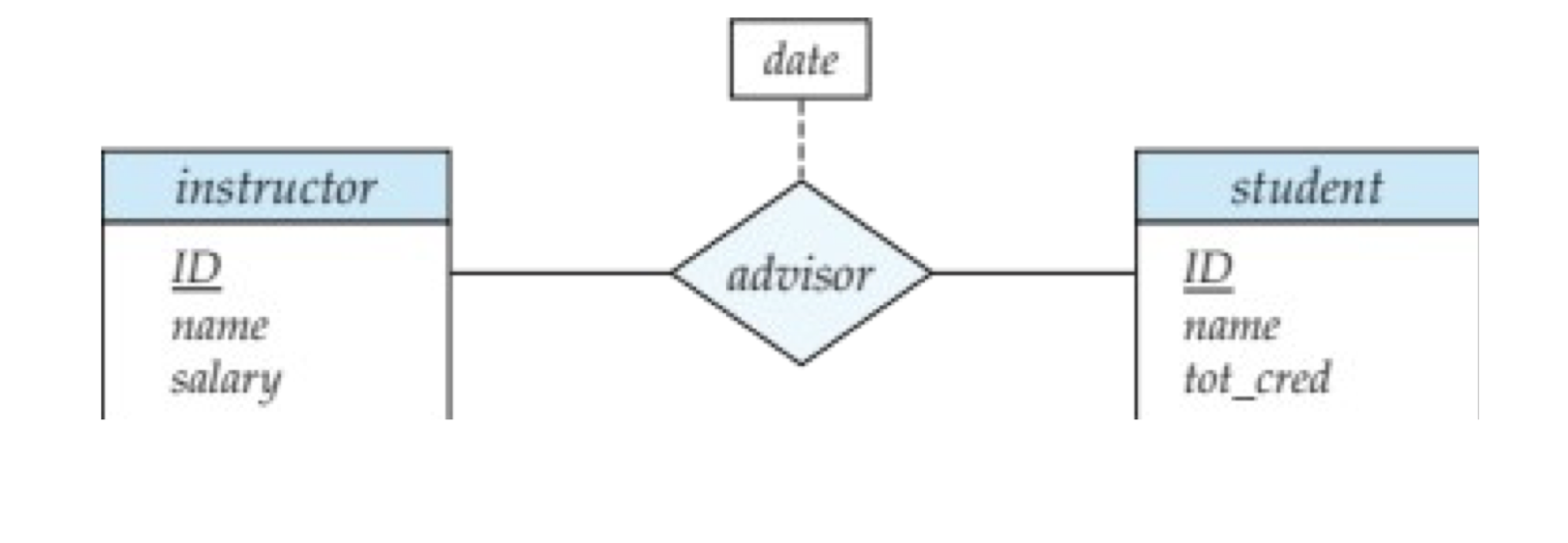
An attribute can also be associated with a relationship set.
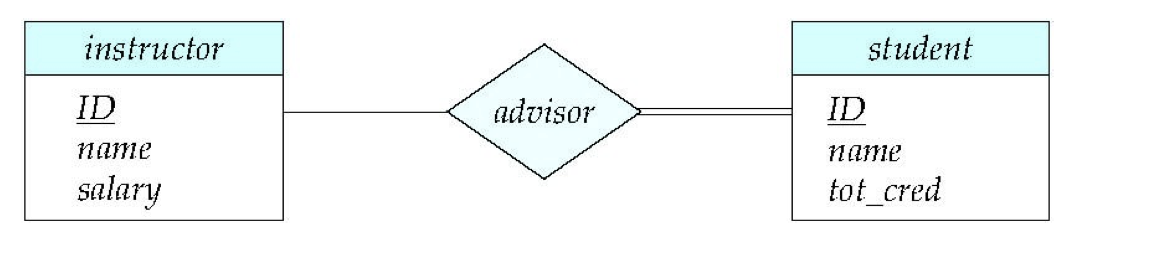
For instance, the advisor relationship set between entity sets instructor and student may have the attribute date which tracks when the student started being associated with the advisor.
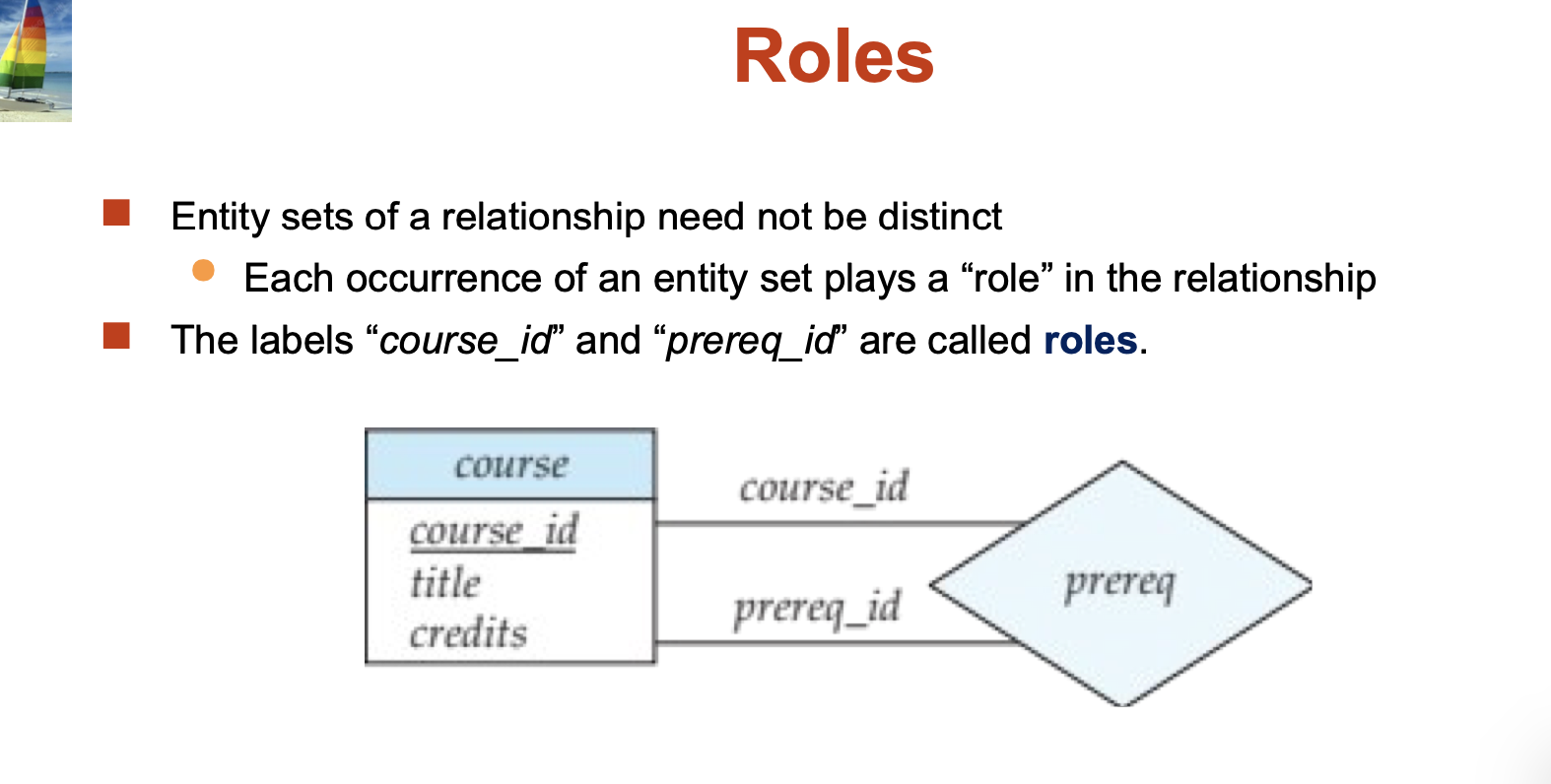
Degree of a Relationship Set:
binary relationship
involve two entity sets (or degree two).
most relationship sets in a database system are binary.
Relationships between more than two entity sets are rare. Most relationships are binary. (More on this later.)
Example: students work on research projects under the guidance of an instructor.
relationship proj_guide is a ternary relationship between instructor, student, and project
Attributes:
An entity is represented by a set of attributes, that is descriptive properties possessed by all members of an entity set.
Example:
instructor = (ID, name, street, city, salary )
course= (course_id, title, credits)
Domain – the set of permitted values for each attribute
Attribute types:
Simple and composite attributes.
Single-valued and multivalued attributes
Example: multivalued attribute: phone_numbers
Derived attributes:Can be computed from other attributes
Example: age, given date_of_birth
Cardinality Constraints:
We express cardinality constraints by drawing either a directed line (->), signifying “one,” or an undirected line (—), signifying “many,” between the relationship set and the entity set.
Total participation (indicated by double line): every entity in the entity set participates in at least one relationship in the relationship set.
Weak Entity Sets:
An entity set that does not have a primary key is referred to as a weak entity set.
The existence of a weak entity set depends on the existence of a
identifying entity set
It must relate to the identifying entity set via a total, one-to-many relationship set from the identifying to the weak entity set
Identifying relationship depicted using a double diamond
The discriminator (or partial key) of a weak entity set is the set of attributes that distinguishes among all the entities of a weak entity set.
The primary key of a weak entity set is formed by the primary key of the strong entity set on which the weak entity set is existence dependent, plus the weak entity set’s discriminator.
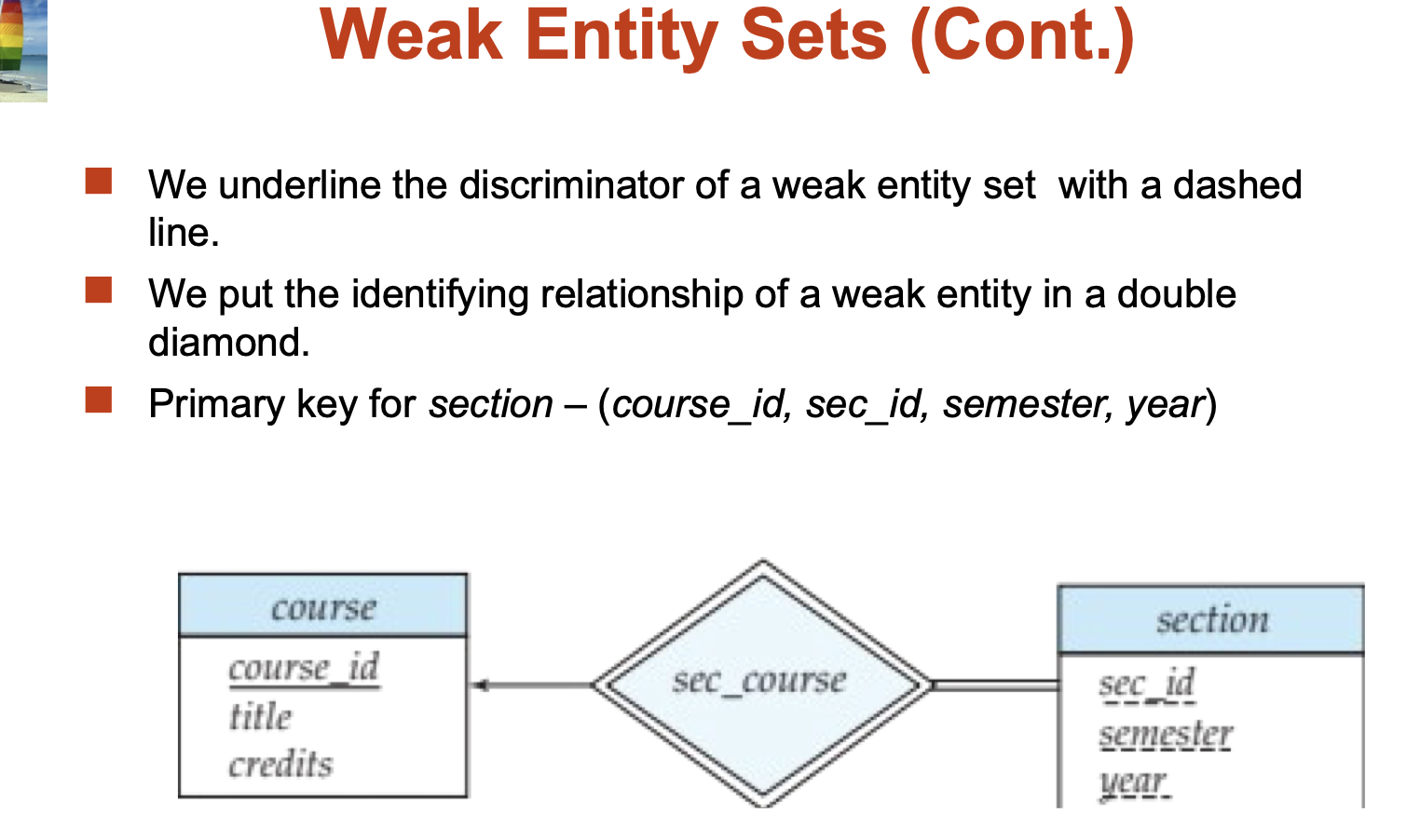
We underline the discriminator of a weak entity set with a dashed line.
We put the identifying relationship of a weak entity in a double diamond.
Primary key for section – (course_id, sec_id, semester, year)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号