Git操作说明
本篇文章主要综合了https://fa20.datastructur.es/materials/guides/using-git.html#b-local-repositories-narrative-introduction(UCB CS61B) 以及廖雪峰的博客https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/896043488029600/896827951938304 的相关内容。 如有细节问题可以在这两者中继续查找。
首先...什么是Git?
Git 是一个分布式版本控制系统(Version control systems are tools)。要理解这个东西,我们就要知道什么是版本控制系统。 在课程CS61B中,它的定义是“Version control allows you to view or revert back to previous iterations of files.”。简单来说,它就是能记录并保存每一次文件的改动。这么多历史版本组合在一起就是版本库(repository). “We call the entire history of an entire project a “repository”.实际上,Word里自带的“撤回(Undo)”功能就是一种版本控制系统。那么,什么又是“分布式”呢?”分布式“的反义词就是”集中式“。一个集中式版本管理系统就是指在这个系统中,每个电脑都将版本存储到一个中央服务器中。当电脑需要干活时,需要先从服务器中下载最新的版本,修改完成后再上传至中央服务器。而分布式就不一样了,每个人的电脑都是一个版本库。如果有人需要修改,则只需要将改动推送给其他人就好啦。一般来说,“集中式”管理系统是需要联网才能协作,而“分布式“则无需联网。当然,后者的优点还有很多很多。
Git操作之创建版本库
要创建一个版本库,你首先得在合适的地方创建一个空目录。比如在 MacOS中,采用
奋斗·
$ mkdir learngit $ cd learngit
(新建并进入新创建的文件夹中)
然后在终端中输入
$ git init就把当前目录变成一个仓库啦!当前目录下多了一个.git的目录,这个目录是Git来跟踪管理版本库的,没事千万不要手动修改这个目录里面的文件,不然改乱了,就把Git仓库给破坏了。
如果你要往一个仓库中间添加东西的话,首先你得保证它在目录里面(子目录也行),不然Git是肯定找不到这个文件的!
先用这个命令
$ git add readme.txt
告诉Git把文件加入仓库。但是很有趣的是这个命令并不能直接将文件加入仓库,下面是解释👇:
Now here’s where git is going to start seeming weird. Even after calling the add command, we still haven’t stored our recipe in the repository (i.e. in the safe).
Instead, what we’ve done is added kung_pao_tofu.txt to the list of files to track (i.e. to be added to the safe later). The idea is that you might not want to necessarily track every single file in the /users/sandra/recipes folder, so the add command tells git which ones it should be tracking. We can see the effect of this command by using the git status command.
In which case, you’d see the following in response:
On branch master
Initial commit
Changes to be committed:
(use "git rm --cached <file>..." to unstage)
new file: tofu/kung_pao_tofu.txt
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
seitan/
tofu/basil_ginger_tofu.txt
The “changes to be committed” portion of the output lists all files that are currently being tracked and whose changes are ready be committed (i.e. that are ready to be put in the safe). We also see that there are some untracked files, namely the seitan folder, and the tofu/basil_ginger_tofu.txt file. These are untracked because we have not added them using git add.
#当然,你要结合cs61b中的实例来理解#
接下来再用这个命令:
$ git commit -m "wrote a readme file"
把文件给提交到仓库。
简单解释一下git commit命令,-m后面输入的是本次提交的说明,可以输入任意内容,当然最好是有意义的,这样你就能从历史记录里方便地找到改动记录。
放张图来有助于理解👇
Rule of Thumb: If you commit, you can always revert your code or change it. However, if you don’t commit, you won’t be able to get old versions back. So commit often!
Git操作之时光机穿梭
在刚刚的解释中,我们用到了git status这个命令。这个命令可以让我们时刻掌握仓库当前的状态。
如果想看到具体发生了哪些改动,可以采用git diff命令。顾名思义嘛,就是找difference.
如果想直观地看到你做出的改动,可以使用 git log命令。他会显示修改的时间和用户。
下面这张图片能直观地显示Git 是如何追踪不同历史版本的
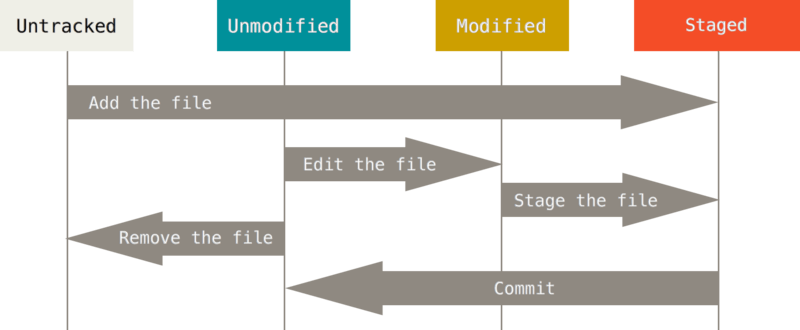
如果你要还原某个版本,怎们办呢?
The Git reference has a great section on undoing things. Please note that while Git revolves around the concept of history, it is possible to lose your work if you revert with some of these undo commands. Thus, be careful and read about the effects of your changes before undoing your work.
-
Unstage a file that you haven’t yet committed:
$ git reset HEAD [file]This will take the file’s status back to modified, leaving changes intact. Don’t worry about this command undoing any work. This command is the equivalent of deleting one of the temporary images that you’re going to combine into a panorama.
Why might we need to use this command? Let’s say you accidentally started tracking a file that you didn’t want to track. (an embarrassing video of yourself, for instance.) Or you were made some changes to a file that you thought you would commit but no longer want to commit quite yet.
- Amend latest commit (changing commit message or add forgotten files):
$ git add [forgotten-file] $ git commit --amendPlease note that this new amended commit will replace the previous commit.
-
Revert a file to its state at the time of the most recent commit:
$ git checkout -- [file]This next command is useful if you would like to actually undo your work. Let’s say that you have modified a certain
filesince committing previously, but you would like your file back to how it was before your modifications.Note: This command is potentially quite dangerous because any changes you made to the file since your last commit will be removed. Use this with caution!
-
Arrange a file to a specific edition:
本地库和远端库
添加一个远端的库:
$ git remote add [short-name] [remote-url]
The remote URL will look something like https://github.com/berkeley-cs61b/skeleton.git if you are using HTTP or git@github.com:berkeley-cs61b/skeleton.git if you are using SSH.
Renaming, Deleting, & Listing Remotes
-
You can rename your remote by using this command:
$ git remote rename [old-name] [new-name] -
You can also remove a remote if you are no longer using it:
$ git remote rm [remote-name]
Manipulating the romote repositories
·git clone [remote-repo-URL]: Makes a copy of the specified repository, but on your local computer. Also creates a working directory that has files arranged exactly like the most recent snapshot in the download repository. Also records the URL of the remote repository for subsequent network data transfers, and gives it the special remote-repo-name “origin”.·git remote add [remote-repo-name] [remote-repo-URL]: Records a new location for network data transfers.·git remote -v: Lists all locations for network data transfers.·git pull [remote-repo-name] master: Get the most recent copy of the files as seen in remote-repo-name·git push [remote-repo-name] master: Pushes the most recent copy of your files to the remote-repo-name.
For further information of branching and other features of git, view the webpage: https://fa20.datastructur.es/materials/guides/using-git.html#e-git-branching-advanced-git-optional



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号