利用预测不确定性提高安卓恶意软件检测模型性能
文献简介
文献标题:MalCertain Enhancing Deep Neural Network Based Android Malware Detection by Tackling Prediction Uncertainty
引用:Yang, Limin et al. "BODMAS: An Open Dataset for Learning based Temporal Analysis of PE Malware", IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (2021): 78-84.
代码:https://github.com/Dirtyboy1029/MALCERTAIN/
一、引言及重要信息
1.基于的思想
预测不确定性可以区分被正确分类和非正确分类的样本。
原文:Therefore, a simple way to enhance DNN-based Android malware detection is to draw on the idea that prediction uncertainty can distinguish different samples (correctly classified samples and incorrectly classified samples)
2.文献创新点
(1)已有文献的不足:只局限于单个或很少的不确定性评估指标。因此,这些不确定性估计是否会受训练数据的影响,以及如何将他们应用于提高模型准确率上也是不清楚的。
原文:However, these existing works are mostly limited to a single or few uncertainty assessment metrics. Thus, it is not clear if the uncertainty estimations are potentially subject to the bias of their training data, and what are the optimal way to integrate these estimations to improve the model accuracy.
(2)本文的贡献:
① 首次尝试利用基于dnn的Android恶意软件检测模型的预测不确定性特征来提高其模型准确性。【这些模型的正确和不正确预测之间的预测不确定性差异可以使用一些指标(例如,熵,KL散度)来检测。】
② 提出了一个新的框架MalCertain,以精确定位可能被基于dnn的Android恶意软件检测模型错误分类的样本,并纠正错误分类的预测以提高模型性能。
③ 通过对26,748个应用程序进行了广泛的实验,以评估MalCertain的有效性。【将MalCertain应用于两个最先进的基于dnn的Android恶意软件检测模型,当这些模型用于检测OOD样本时,MalCertain能够提高模型性能(准确性提高约21%,F1分数提高49%)。同时,MalCertain还可以提高这些模型识别对抗性样本的能力。】
二、研究方法
- 首先进行了一项特征研究(a characteristic study),旨在衡量哪种不确定性估计方法和指标可以区分基于dnn的Android恶意软件检测模型的正确和不正确预测。
原文:To this end, we first conduct a characteristic study that aims to measure which uncertainty estimation method and metrics can distinguish correct and incorrect predictions of DNN-based Android malware detection models (see § 3).
characteristic study具体步骤
(1)首先,训练一个基于dnn的Android恶意软件检测模型(DeepDrebin),并将该模型应用于包含OOD应用程序样本(即具有不确定性的数据)的测试数据集,以获得正确和不正确的预测。
==> 实验结论:
① 漏报率大于误报率。
② 模型性能表现不佳说明存在概念漂移。
(2)然后,使用现有的不确定性估计方法训练一组模型集合,将这些模型集合应用于测试数据集以获得它们的预测,并根据这些预测结果计算不确定性估计度量。【结果表明,所有这些指标都能有效区分正确和错误的预测。特别是,使用变分贝叶斯推理方法计算的Kullback-Leibler (KL)散度度量是识别错误预测的最佳方法之一。】
==> 详细步骤
① 为了估计这些预测的不确定性,我们选择了五种常用的方法来构建模型集合:(i) Epoch Ensemble, (ii)变分贝叶斯推断Variational
Bayesian Inference,(iii) Monte Carlo Dropout, (iv) Deep Ensemble和(v) Weighted Deep Ensemble。(使用相同的训练集训练5个不确定性估计模型集合)
② 为了定量评估预测的不确定性,我们选择了三个常用的指标:熵Entropy、KL散度(Kullback-Leibler divergence)和标准差(standard
deviation),它们都可以用来量化一组数据的分散程度。通常,度量值越大,表明集成中模型之间的分歧越大,因此不确定性越高。
==> 实验结果分析
① 根据样本是否被Base Model误分类,将样本分为两类。之后,我们计算了每个类别中每个样本的不确定度度量。
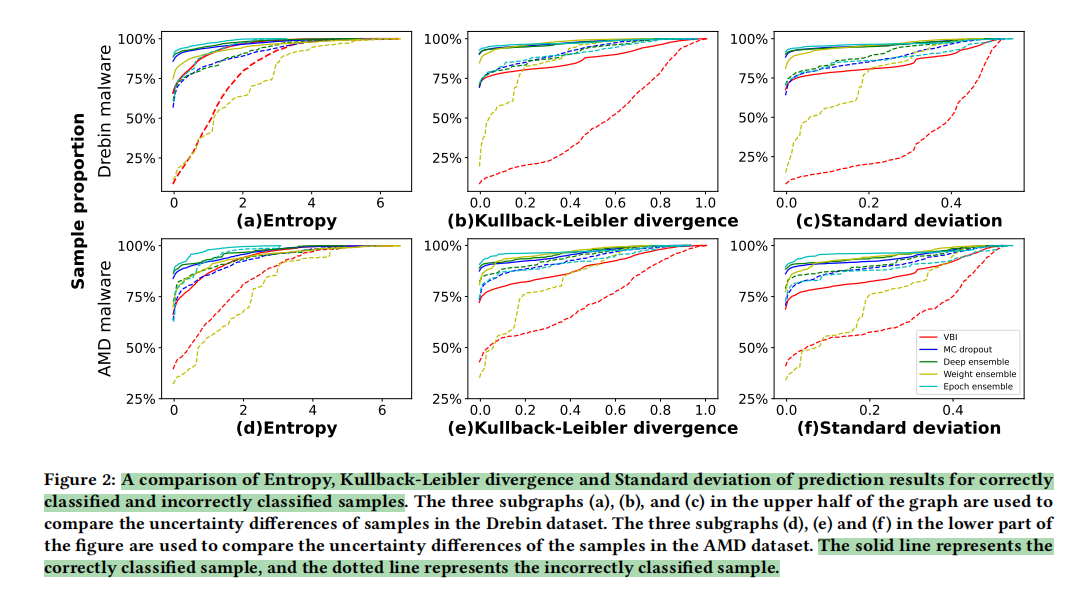
② 图2显示了正确分类样本(实线)和错误分类样本(虚线)的三个不确定性度量的CDF分布,每种颜色标记一种类型的模型集合。我们可以看到,所有的不确定性指标(熵、KL散度和标准差)在两种类型的样本中显示出显著不同的分布。错误分类样本的不确定度值一般大于正确分类样本的不确定度值。【这种差异对于VBI方法尤其明显,大约75%的正确预测的不确定性度量为0,而大约10%的不正确预测的不确定性度量为0。】
③ 因此,这些基于不同不确定性估计方法计算的不确定性度量可以作为区分可靠和不可靠预测的指标。这促使我们设计一种自动化的方法来标记不可靠的预测并纠正这些预测结果。
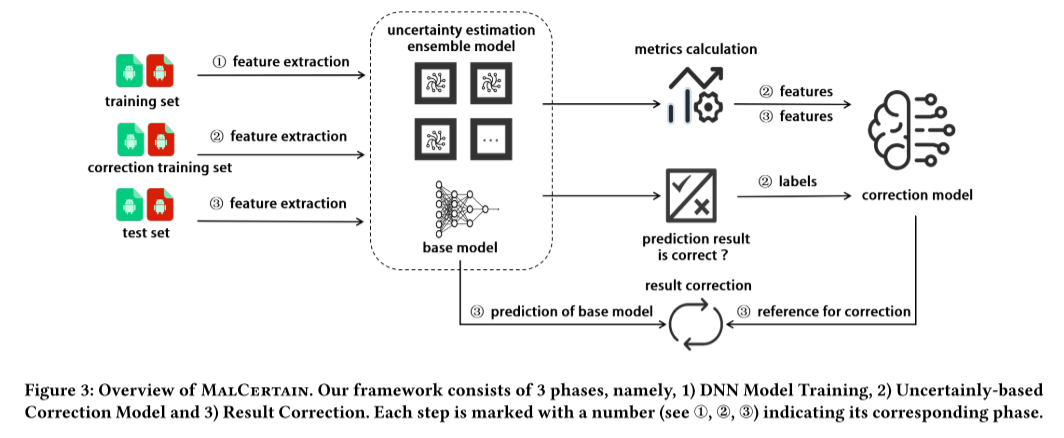
- 基于以上研究,提出了一个通用框架MalCertain,它找到了一种使用预测不确定性来提高基于dnn的Android恶意软件检测模型性能的最佳方法。
原文:Motivated by this study, we propose a general framework, MalCertain, which finds an optimal way of using prediction uncertainty to improve the performance of DNN-based Android malware detection models (see § 4)
MalCertain框架包含的实验步骤
(1)DNN Model Training:给定一个基于dnn的Android恶意软件检测模型(称为Base model), MalCertain首先在Base model上训练多个模型集合,并将Base model和这些模型集合应用到一个校正训练数据集上,以获得它们的预测结果。
==> 如何训练模型集合
微调模型参数,观察预测结果和微调前的预测结果是否存在很大不同。
原文:Given a classification model 𝑀 and a test sample 𝑆,
imagine that after we modify one parameter of 𝑀 and get a new
model 𝑀′, the prediction made by 𝑀′ for 𝑆 varies a lot compared
to 𝑀, then the uncertainty of the prediction made by 𝑀 for 𝑆 is
considered high (i.e., the prediction is likely to be unreliable).
(2)Uncertainty-based Correction Model training:MalCertain然后根据模型集合的预测结果计算不确定性估计度量,将Base model的预测结果分为正确预测和错误预测两类,并训练一个机器学习模型(称为Correction model),该模型可以区分样本是被底层DNN模型正确预测还是错误预测。【校正模型(Correction Model)在应用Base Model获得新的预测结果时,可以判断预测结果是否可靠,并对不可靠的预测结果进行校正,以提高Base Model的精度。】
原文:We use a set of features (i.e., uncertainty metrics) to train a model to classify whether a prediction result (of the Base Model) is correct.
==> 详细步骤
① 不确定性估计方法的输出是每个样本的一组预测概率。这些预测概率的差异可以被认为是潜在模型预测不确定性的表现。如果一个样本的预测概率变化很大,则底层模型对该样本的预测具有很高的不确定性,这意味着该预测可能是不可靠的。作者基于许多度量来度量这些样本的基础模型的不确定性,这将作为训练校正模型的特征。
原文:The outputs of the uncertainty estimation methods in § 4.1.2 are a set of predicted probabilities for each sample. The differences in these predicted probabilities can be considered as a manifestation of the underlying model's prediction uncertainty.
② 训练修正模型。我们为每个预测样本计算上述不确定性度量。然后将样本分成两组,即可靠或不可靠的预测。随后,将这些指标作为特征来训练机器学习模型,该模型旨在对可靠和不可靠的预测进行分类。这个模型被认为是“修正模型”,因为我们可以修改那些被模型分类为不可靠预测的样本的初始预测结果。具体来说,我们为校正模型选择了四种具有代表性的ML算法,分别是支持向量机(SVM)、k近邻(KNN)、决策树(DT)和随机森林(RF)。
原文:We calculate the aforementioned uncertainty metrics for each predicted sample. The samples are then grouped into two sets, i.e., reliable or unreliable predictions. Subsequently, the metrics are taken as features to train a machine learning model which is designed to classify reliable and unreliable predictions. This model is considered the “Correction Model”, as we can modify the initial prediction results for those samples that are classified as unreliable predictions by the model. Specifically, we select four representative ML algorithms for the Correction Model, which are Support Vector Machine (SVM), K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN), Decision Tree (DT), and Random Forest (RF).
(3)Result correction:给定一组测试样本,我们首先通过Base Model获得它们的预测标签。同时,我们可以通过修正模型(Correction model)来判断底层模型(即Base model)的预测是否可靠。此外,我们寻求基于校正模型的分类来校正基本模型的预测标签。
==> 结果校正的两个策略
① Correcting Unreliable Results:校正所有错误标签。
② Correcting Unreliable FNs:只校正漏报。
原文:Given a set of test samples, we first get their prediction labels by the Base Model. In parallel, we can determine whether the prediction of the underlying model (i.e., Base Model) is reliable through the Correction Model. Further, we seek to correct the predicted labels of the Base Model based on the classification of the Correction Model.
三、重要实验设置
1. 基于DNN模型,构造了三个模型
为了衡量MalCertain在改进基于DNN的Android恶意软件检测模型方面的有效性,给定一个DNN模型,我们构建了3个模型(Base model、Correction model和Large Base model)。具体如下:
•Base model: 使用一个数据集(训练集)对Base model进行训练,得到一些不确定性估计模型集合。
•校正模型: 使用另一个数据集(校正训练集)和基础模型的预测来训练基于4个ML算法(SVM, KNN, DT, RF)的校正模型。
•Large Base Model: 我们也合并训练集和校正训练集来训练Large Base Model。
==> 为什么有Large Base Model
虽然我们可以通过比较修正模型的结果与基本模型的结果来衡量改进,但这种比较并不完全公平,因为修正模型使用更多的数据进行训练。因此,参考有文献旨在通过增量训练和再训练来解决DNN模型的概念漂移问题,作者使用合并的数据集进一步训练Large Base Model。我们使用Base模型和Large Base模型作为基准模型,并比较了它们的性能。简单地说,如果修正模型处理的检测结果优于两个基线模型,那么可以说我们的框架MalCertain有效地提高了用于Android恶意软件检测的dnn模型的性能。
原文:given a DNN model, we construct 3 models (a Base Model, a Correction Model, and a Large Base Model) as follows:
• Base Model: we use a dataset (training set) to train a Base Model and obtain some uncertainty estimation model ensembles.
• Correction Model: we use another dataset (correction training set) and the predictions of the Base Models to train Correction Models based on 4 ML algorithms (SVM, KNN, DT, RF).
• Large Base Model: we also merge the training set and the correction training set to train a Large Base Model.
2. 数据集:我们将收集到的应用程序分为三种类型的数据集。
① 训练集:该数据集用于训练每个DNN模型的基础模型,并获得许多模型集合,这些模型集合用于估计底层基础模型预测的不确定性。据我们所知,MalGenome[78]和MalRadar[63]是我们社区中最可靠的恶意软件数据集,因为它们是通过仔细检查来自已建立的反病毒co Base Model的android相关安全报告和博客内容创建的。因此,我们使用它们来训练基本模型。具体来说,MalGenome包含1,260个样本,MalRadar包含4,534个样本,总共有来自196个独特家族的5,794个恶意软件样本。
② 校正训练集:该数据集用于训练校正模型。这些样本被输入到基本模型中,以便将它们分为两组,即正确分类和错误分类。它们也被输入到每个模型集合中,以便为每个样本计算不确定性度量(作为特征)。具体来说,恶意软件样本来自Drebin,其中包含来自179个不同恶意软件家族的5,560个应用程序。
③ 测试集:该数据集用于检查检测器在修改预测结果之前和之后的性能,从而可以评估校正模型的有效性。恶意软件样本来自AMD,其中包含来自71个不同恶意软件家族的24,650个应用程序。我们随机选择了2000个与Drebin数据集不一致的恶意软件样本。
原文:
Training Set: This dataset is used to train the Base Models of each DNN model and obtain a number of model ensembles (specified by different uncertainty estimation methods), which are used to estimate the uncertainty of the predictions of the underlying Base Model. To the best of our knowledge, MalGenome [78]and MalRadar [63] are the most reliable malware datasets in our community as they were created by carefully examining Android-related security reports and blog contents from established antivirus companies and active experts. We therefore use them to train the Base Model. Specifically, MalGenome contains 1,260 samples and MalRadar contains 4,534 samples, resulting in a total of 5,794 malware samples from 196 unique families.
• Correction Training Set: This dataset is used to train a Correction Model. These samples are fed into the Base Models so that they are grouped into two sets, i.e., correctly and incorrectly classified. They are also fed into each model ensemble so that the uncertainty metrics are computed for each sample (as features). Specifically, the malware samples come from Drebin [3] which contains 5,560 apps from 179 different malware families.
• Test Set: This dataset is used to check the performance of the detector before and after revising the prediction results, which allows for evaluating the efficacy of the Correction Model. The malware samples come from AMD [64], which contains 24,650 apps from 71 different malware families. We randomly select 2,000 malware samples that do not coincide with the Drebin dataset.
3. 模型
作者选择了两种不同的基于dnn的恶意软件检测器作为基本模型。
① 第一个基本模型是DeepDrebin。
② 第二个基本模型是MultimodelDNN。
4. 评估指标
① 准确性
② F1
由于我们观察到大多数错误分类是恶意应用被错误分类为良性应用的情况,因此增加了纠正预测结果的过程中只修改假阴性(FNs)时的性能:
③ Acc@FN
④ F1@FN
四、实验结果
- MalCertain应用于两个不同的恶意软件检测器,并实现了两者的性能改进(平均提高21.0%)。这些结果表明,MalCertain可以通过根据不确定性调整现有基于dnn的恶意软件检测器的预测结果来提高其性能。
MalCertain is applied on two different malware detectors and achieves performance improvements for both of them (by 21.0% on average). These results indicate that MalCertain can enhance the performance of the existing DNN-based malware detectors by adjusting their prediction results based on the uncertainty.
- 我们使用2种对抗性样本进行检测,Base Model(准确率为0到39.75%)和Large Base Model(准确率为0.13%到63.88%)的表现都很差。MalCertain可以显著提高对两种对抗样本的检测效率(AT-RFGSM的检测效率提高了85.5% ~ 158.8%,Basic DNN的检测效率提高了2.13% ~ 94.38%)。
Answer to RQ2: We use 2 kinds of adversarial samples for detection, and both the Base Model (accuracy being 0 to 39.75%) and the Large Base Model (accuracy being 0.13% to 63.88%) perform poorly. MalCertain can significantly improve their detection effectiveness for both kinds of adversarial samples (achieve over 85.5% to 158.8% improvements for AT-RFGSM and over 2.13% to 94.38% improvements for Basic DNN).
- 校正训练集的规模和样本的平衡对校正模型的性能没有显著影响。因此,MalCertain可以针对小尺寸的数据集进行定制(例如,只有数百个校正训练样本)。
Answer to RQ3: The scale of the correction training set and the balance of the samples have no significant impacts on the performance of the Correction Model. Thus, MalCertain can be tailored to datasets of small sizes (e.g., with only hundreds of correction training samples).



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号