Vue3
Vue3介绍
一、 Vue3的变化
1.性能的提升
打包大小减少41%
初次渲染快55%, 更新渲染快133%
内存减少54%
2.源码的升级
使用Proxy代替defineProperty实现响应式
重写虚拟DOM的实现和Tree-Shaking(摇树--清除死代码进行优化)
3.拥抱TypeScript
Vue3可以更好的支持TypeScript
4.新的特性
Composition API(组合API)
setup配置
ref与reactive
watch与watchEffect
provide与inject
新的内置组件
Fragment
Teleport
Suspense
其他改变
新的生命周期钩子
data 选项应始终被声明为一个函数
组合式API和配置项api
组合式api:都写到一个函数中,定义变量和定义方法,定义计算属性都是放在一起,不是拆到不同地方了
vue3兼容vue2 ---》vue2 的内容,vue3完全适用
vue3 不建议这么用来,建议使用组合式api,不建议使用配置项api
配置项api:之前vue2中的写法
new Vue({
data:{
name:'lqz'
},
methods:{
# 使用变量
}
})
组合式api
setup{
var name=ss
console.log(name)
}
二、创建vue3
1. 使用vue-cli创建
官方文档:https://cli.vuejs.org/zh/guide/creating-a-project.html#vue-create
## 查看@vue/cli版本,确保@vue/cli版本在4.5.0以上 vue --version ## 安装或者升级你的@vue/cli npm install -g @vue/cli ## 创建 vue create vue_test ## 启动 cd vue_test npm run serve
2. 使用vite 创建
官方文档:https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/guide/installation.html#vite
vite官网:https://vitejs.cn
介绍:https://cn.vitejs.dev/guide/why.html#the-problems
1. 什么是vite?
vite是新一代前端构建工具
2. vite的优点:
- 开发环境中,无需打包操作,可快速的冷启动
- 轻量快速的热重载(HMR)
- 真正的按需编译,不在等待整个应用编译完成
## 创建工程 npm init vite-app <project-name> ## 进入工程目录 cd <project-name> ## 安装依赖 npm install ## 运行 npm run dev
补充:
编程语言的链式调用:
对象.changeName('lqz').printName().showAge()
python是如何实现链式调用的
class Person:
def changeName(self,name):
self.name=name
return self
def printName(self):
print(self.name)
return self
三、setup函数
1. setup为Vue3.0中一个新的配置项,值为一个函数2. setup是所有Composition API(组合API)编写的位置
3. 组件中所用到的:数据、方法等等,均要配置在setup中
4.setup函数的返回值:返回一个对象,对象中的属性、方法, 在模板中均可以直接使用
5. 注意:
尽量不要与Vue2.x配置混用
- Vue2.x配置(data、methos、computed...)中可以访问到setup中的属性、方法。
- 但在setup中不能访问到Vue2.x配置(data、methos、computed...)。
- 如果有重名, setup优先
基本使用:
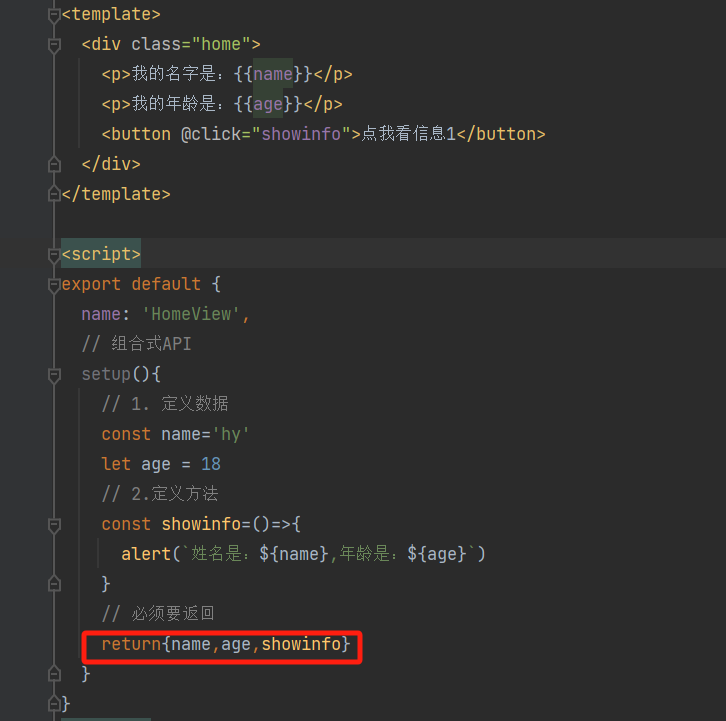
结果:
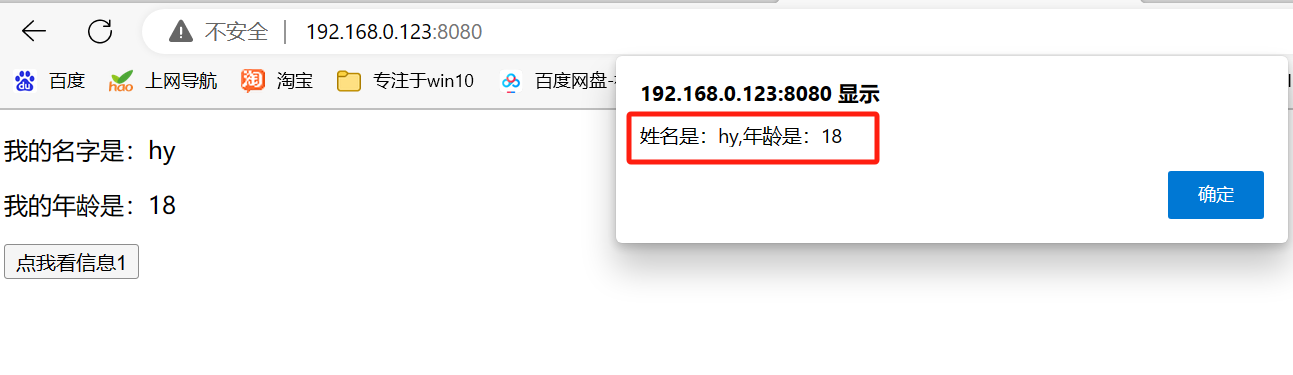
setup的两个注意点:
1. setup执行的时机
在beforeCreate之前执行一次,所以this是undefined
2. setup的参数
props:值为对象,包含:组件外部传递过来,且组件内部声明接收了的属性
context:上下文对象
attrs:值为对象,包含:组件外部传递过来的,但没有在props配置中声明的属性,相当于this.$attrs
slots:收到的插槽内容,相当于this.$slots
emit:分发自定义事件的函数,相当于this.$emit
总结:
1. setup执行时在beforeCreate,没有this对象,以后不要用this了
2. 如果写setup函数,想接收父组件自定义属性传入的值,需要:
export default {
setup(props) {
console.log(props.msg)
},
props: ['msg']
}
3. 如果是vue3的最新写法,想接收父组件自定义属性传入的值,需要:
<script setup>
defineProps(['msg'])
</script>
四、ref函数
作用: 定义一个响应式的数据
语法:const xxx = ref(initValue)
- 创建一个包含响应式数据的引用对象(reference对象,简称ref对象)
- js中操作数据:xxx.value
- 模版中读取数据:不需要.value,直接:<div>{{xxx}}</div>
接收的数据可以是:基本类型(值类型)、也可以是对象(引用类型)类型。
值类型:数字,字符串,布尔,用ref做响应式
// 变量要具备响应式---》页面内容变化,变量和变,变量变化,页面也变
// 普通变量,通过ref绑定响应式
// 引用类型变量:通过reactive 绑定响应式
<template> <div class="home"> <p>我的名字是:{{ name }}</p> <p>我的年龄是:{{ age }}</p> <button @click="handleAdd">点我年龄+1</button> <button @click="handleChangeName">点我秒变彭于晏</button> </div> </template> <script> import {ref} from 'vue' export default { setup() { // 1 定义数据 let name = ref('lqz') let age = ref(19) // 2 定义方法 const handleAdd = () => { age.value += 1 console.log(typeof age) } const handleChangeName = () => { name.value = '彭于晏' } return {name, age, handleAdd,handleChangeName} }, } </script>
五、reactive函数
作用:定义一个对象类型的响应式数据
语法:const 代理对象 = reactive(源对象)接收一个对象(或数组),返回一个代理对象(Proxy的实例对象,简称proxy对象)
reactive定义的响应式数据是‘深层次的’,无论套多少层,都具备响应式
<template> <div class="home"> <p>我的名字是:{{ data.name }}</p> <p>我的年龄是:{{ data.age }}</p> <p>我的爱好是:{{ hobby }}</p> <button @click="addAge">点我年龄+1</button> <br> {{ obj.hobby }} <br> <button @click="changeHobby">点我把保龄球换成足球</button> <hr> <HelloWorld msg="asdfasdfasdfasdf"></HelloWorld> </div> </template> <script> // 变量要具备响应式---》页面内容变化,变量和变,变量变化,页面也变 // 普通变量值类型,通过ref绑定响应式 数字,字符串 // 引用类型变量:通过reactive 绑定响应式 对象,数组 import {reactive, ref} from 'vue' import HelloWorld from "@/components/HelloWorld.vue"; export default { name: 'HomeView', setup(props) { let hobby = ref('篮球') let obj = ref({ age: 99, hobby: '保龄球' }) const changeHobby = () => { console.log(obj) obj.value.hobby = '足球' } let data = reactive({ name: '彭于晏', age: 19 }) const addAge = () => { //data.age++ console.log(typeof data) console.log(data) // 是一个代理对象,无法拿出原来对象,但是操作起来跟操作源对象一样 data.age++ } return {hobby, data, addAge, obj, changeHobby} }, components: { HelloWorld } }
</script>
总结:
如果用基本数据类型:数字,字符串,布尔,用ref 做响应式
如果是对象类型,用ref 和 reactive 都可以,但是建议使用reactive
如果使用ref 包裹对象类型,多了一层value
六、计算属性与监听
1. computed函数
与Vue2中computed配置功能一样
写法:
<template> <p>姓:<input type="text" v-model="person.firstName"></p> <p>名:<input type="text" v-model="person.lastName"></p> <p>全名:{{ person.fullName }}</p> <p>全名修改:<input type="text" v-model="person.fullName"></p> </template> <script> import {ref, reactive} from 'vue' import {computed} from 'vue' export default { name: 'App', setup() { const person = reactive({ firstName: '刘', lastName: '清政' }) // let fullName = computed(() => { // return person.firstName + '-' + person.lastName // }) // 或者,传入箭头函数 // person.fullName=computed(() => { // return person.firstName + '-' + person.lastName // }) // 修改,传入配置项目 person.fullName = computed({ get() { return person.firstName + '-' + person.lastName }, set(value) { const nameArr = value.split('-') person.firstName = nameArr[0] person.lastName = nameArr[1] } }) return {person} }, } </script>
2. watch函数
与Vue2中watch配置功能一致
两个注意点:
- 1. 监听reactive定义的响应式数据时:oldValue无法正确获取,强制开启了深度监视(deep配置失效)
- 2. 监听reactive定义的响应式数据中某个属性时:deep配置有效
<template> <h2>年龄是:{{ age }}</h2> <button @click="age++">点我年龄增加</button> <hr> <h2>姓名是:{{ person.name }}</h2> <button @click="person.name+='?'">点我姓名变化</button> <hr> <h2>sum是:{{ sum }},msg是:{{ msg }}</h2> <button @click="sum++">点我sum变化</button> | <button @click="msg+='?'">点我msg变化</button> </template> <script> import {ref, reactive} from 'vue' import {watch} from 'vue' export default { name: 'App', setup() { const age = ref(19) const person = reactive({ name: 'lqz', age: 20 }) //1 监听普通 watch(age, (newValue, oldValue) => { console.log('sum变化了', newValue, oldValue) }) // 2 监听对象 watch(() => person.name, (newValue, oldValue) => { console.log('person.name变化了', newValue, oldValue) }) // 3 监听多个 const sum = ref(100) const msg = ref('很好') watch([sum, msg], (newValue, oldValue) => { console.log('sum或msg变化了', newValue, oldValue) }) return {person, age, sum, msg} }, } </script>
3. watchEffect函数
watch的套路是:既要指明监听的属性,也要指明监听的回调
watchEffect的套路是:不用指明监听哪个属性,监听的回调中用到哪个属性,那就监听哪个属性
watchEffect有点像computed:
- 但computed注重的是计算出来的值(回调函数的返回值),所以必须要写返回值
- 而watchEffect更注重的是过程(回调函数的函数体),所以不用写返回值
//watchEffect所指定的回调中用到的数据只要发生变化,则直接重新执行回调。
watchEffect(() => {
const x1 = sum.value
const x2 = person.age
console.log('watchEffect配置的回调执行了')
})
七、生命周期
Vue3 中可以继续使用Vue2中的生命周期钩子,但是有两个被更名:
- beforeDestroy改名为 beforeUnmount
- destroyed 改名为 unmounted
在Vue3中把生命周期写下setup函数中,把生命周期写在配置项中
Vue3也提供了Composition API 形式的生命周期钩子 ,与Vue2中钩子对应关系如下:
beforeCreate ----> setup()
created -----------> setup()
beforeMount -----> onBeforeMount
mounted ----------> onMounted
beforeUpdate ----> onBeforeUpdate
updated -----------> onUpdated
beforeUnmount --> onBeforeUnmount
unmounted --------> onUnmounted
<template> <div class="home"> <h1>首页</h1> </div> </template> <script> import axios from "axios"; import { computed, watch, reactive, ref, watchEffect, onBeforeMount, onMounted, onBeforeUpdate, onUpdated, onBeforeUnmount, onUnmounted } from 'vue' export default { name: 'HomeView', setup() { // 第一个beforeCrete console.log('我是beforeCrete') // 第二个Creted let name = ref('lqz') console.log('Creted') // axios.get().then(res => { // name.value = res.data.name // }) // 直接启动定时器 let t = setInterval(() => { console.log('lqz') }, 3000 ) // 第三个:onBeforeMount onBeforeMount(() => { console.log('挂载了') }) onBeforeUnmount(() => { clearInterval(t) t = null }) return {} }, } </script>
八、toRef
作用:创建一个ref对象,其value值指向另一个对象中的某个属性
语法:const name = toRef(person, 'name')
应用:要将响应式对象中的某个属性单独提供给外部使用
扩展:toRefs 与 toRef功能一致,但可以批量创建多个ref 对象,语法:toRefs(person)
<template> <div> <h2>姓名:{{ name }}</h2> <h2>年龄:{{ age }}</h2> <button @click="age++">改年龄</button>| <button @click="name+='~'">改姓名</button> </div> </template> <script> import {ref, reactive,toRefs} from 'vue' export default { name: 'App', setup() { const person = reactive({ name: 'lqz', age: 19 }) return { ...toRefs(person) } }, } </script> //对象展开语法 let obj1 = {foo: 'bar', x: 42}; let obj2 = {foo: 'baz', y: 13}; let mergedObj = {...obj1, ...obj2}; console.log(mergedObj)
九、
1. 以后vue3推荐,把setup函数的代码,直接写在script中
<script setup>
定义变量
写函数
不用return,在html中直接使用
</script>
2. 使用组件,直接导入,不需要配置,直接用即可
import HelloWorld from "../components/HelloWorld.vue";
在html中直接用:<HelloWorld msg="NB"></HelloWorld>
3. 自定义属性,在子组件中接收
<script setup>
defineProps({
msg: {
type: String,
required: true
}
})
</script>



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号