drf-排序、过滤、分页、异常处理
一、排序
只有5个接口中的查询所有,才涉及到排序,所以继承GenericViewSet,
使用步骤:
1. 必须写在继承:GenericAPIView 类的视图中才行
2. 配置类属性:
filter_backends = [OrderingFilter]
ordering_fields=['id','user_type'] # 可以排序的字段
3. 使用:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/user/?ordering=user_type #按用户类型升序排
http://127.0.0.1:8000/user/?ordering=-user_type #按用户类型降序排
http://127.0.0.1:8000/user/?ordering=user_type,-id#先按用户类型升序排,如果用户类型一样,再按id降序排
二、过滤
1. 过滤:只针对查询所有接口,必须写在继承GenericAPIView类的视图类中
2.使用方法:
方式一:内置的
查询方式:http://127.0.0.1:8000/books/?search=1 模糊匹配:查询名字中有29或价格中有1都会搜出来
from .models import Book from .serializer import BookSerializer ## 方式一:使用内置的过滤类 from rest_framework.filters import SearchFilter, OrderingFilterclass BookView(ViewSetMixin, ListAPIView): queryset = Book.objects.all() serializer_class = BookSerializer # 方式一:内置的 # 查询方式http://127.0.0.1:8000/books/?search=1 #模糊匹配: 只要名字中有29或价格中有29都能搜出来 filter_backends = [SearchFilter] # filter_backends = [SearchFilter, OrderingFilter] #先过滤然后再排序 search_fields = ['name', 'price'] # 按名字或价格排序
postman:
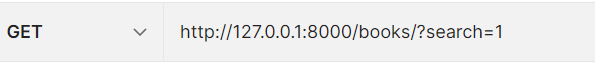
过滤结果:
![]()
方式二:第三方的:
需要安装一个第三方模块,django版本也要跟着换:
pip install django == 3.2.12
pip install django-filter
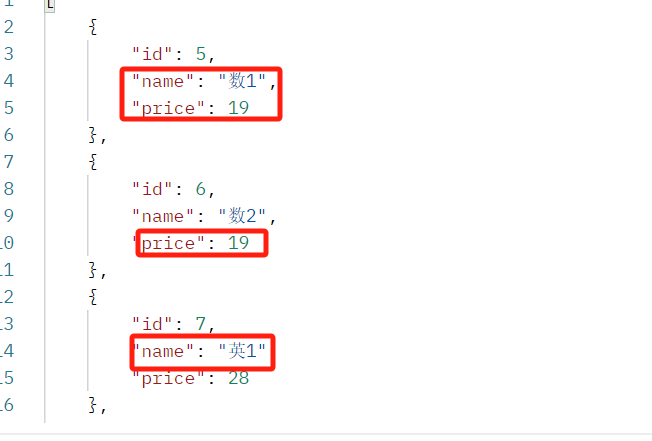
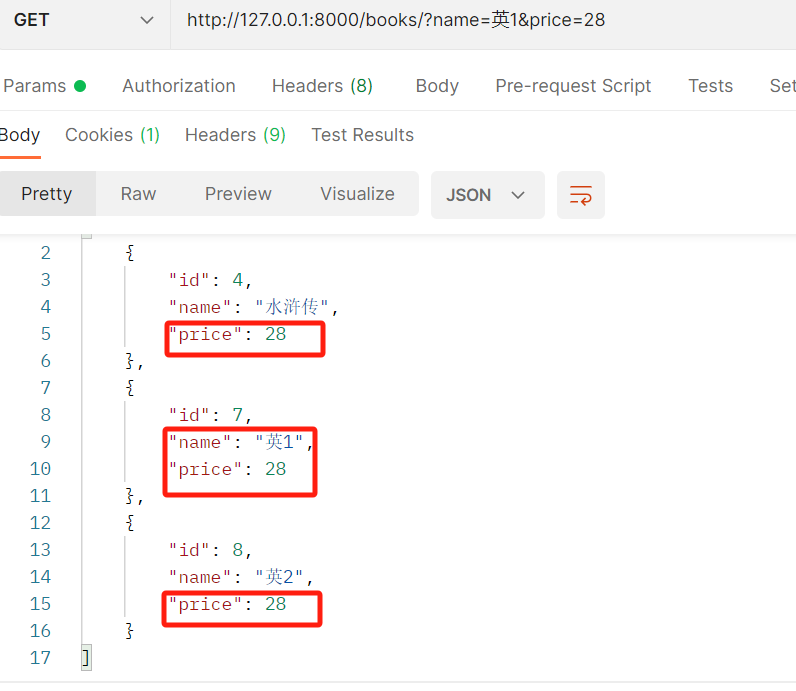
查询方式:http://127.0.0.1:8000/books/?name=红楼梦 ---》书名是西游记的书
http://127.0.0.1:8000/books/?price=19&name=西游记 ---》 精准匹配,价格为19并且书名是西游记的书
from .models import Book from .serializer import BookSerializer from django_filters.rest_framework import DjangoFilterBackend class BookView(ViewSetMixin, ListAPIView): queryset = Book.objects.all() serializer_class = BookSerializer # 方式二:精准匹配--》django-filter # http://127.0.0.1:8000/books/?name=红楼梦 # http://127.0.0.1:8000/books/?price=19&name=西游记 filter_backends = [DjangoFilterBackend] filterset_fields=['name','price']
postman结果:
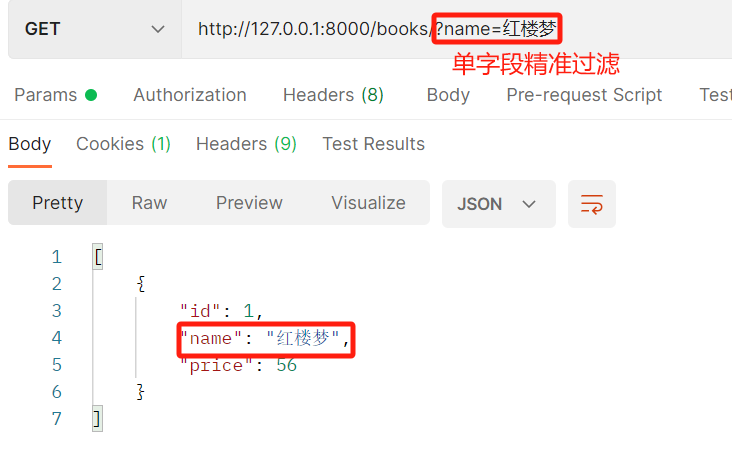
两个字段过滤:

方式三:自定义--完全自己控制
1. 自己写一个过滤类,继承BaseFilterBackend类
2. 重写filter_queryset方法
代码如下所示:
from rest_framework.filters import BaseFilterBackend from django.db.models import Q class MyFilter(BaseFilterBackend): def filter_queryset(self, request, queryset, view): # queryset:是待过滤的对象 # 前端查询的形式: name = request.query_params.get('name') price = request.query_params.get('price') if name and price: # queryset=queryset.filter(name=name,price=price) # 既要满足名字也要满足价格 queryset = queryset.filter(Q(name=name)|Q(price=price)) # 或者关系 return queryset
结果:
and关系:
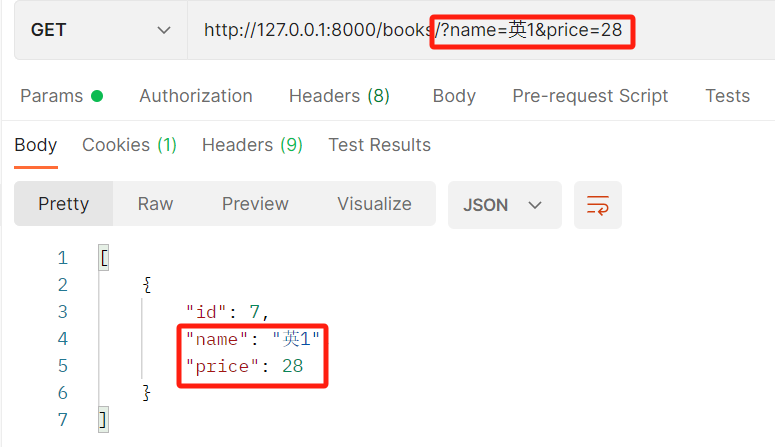
or关系:
1.2 继承APIView写过滤和排序
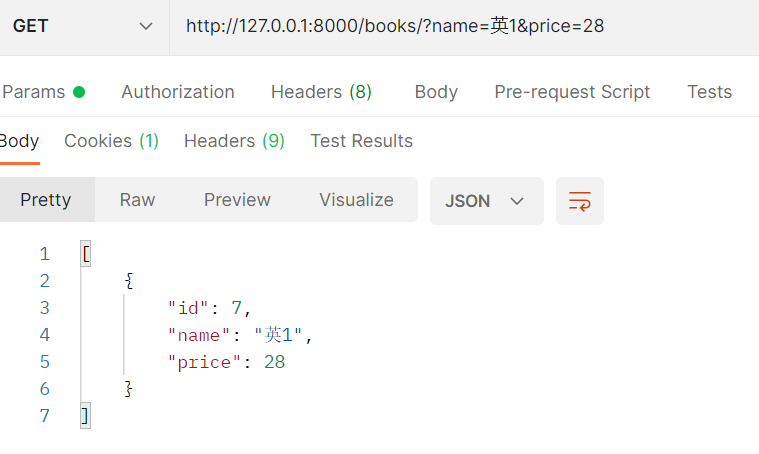
# 基于APIView类 from rest_framework.views import APIView from rest_framework.response import Response class BookView(ViewSetMixin,APIView): def list(self,request,*args,**kwargs): # 从前端获取要过滤的字段 name = request.query_params.get('name') price = request.query_params.get('price') book_list = Book.objects.filter(name=name,price=price) ser = BookSerializer(instance=book_list,many=True) return Response(ser.data)
结果:
1.3 继承GenericAPIView写过滤类,可以写多个
1. 写多个,他们是从左往右,依次执行的
2. 大原则,配置多个过滤类的时候,第一个放尽量多个过滤掉数据的过滤类
3. 配置多个的执行原理
- 先执行第一个过滤类的:filter_queryset返回qs对象
- 再执行第二个过滤类的filter_queryset,传入上一个返回的qs对象,在进行过滤,返回过滤完的qs对象
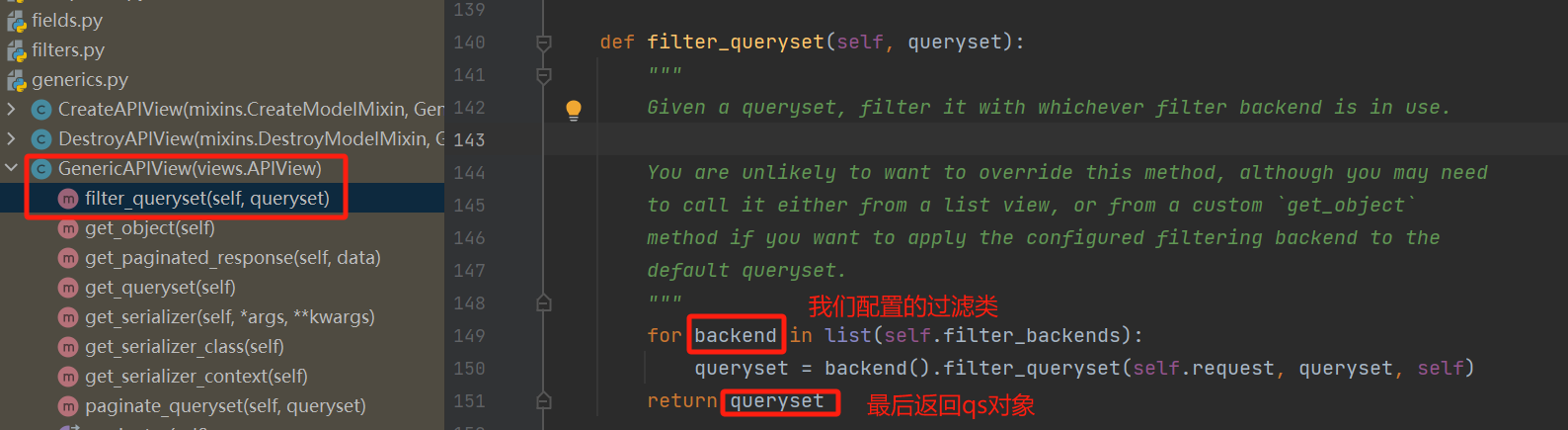
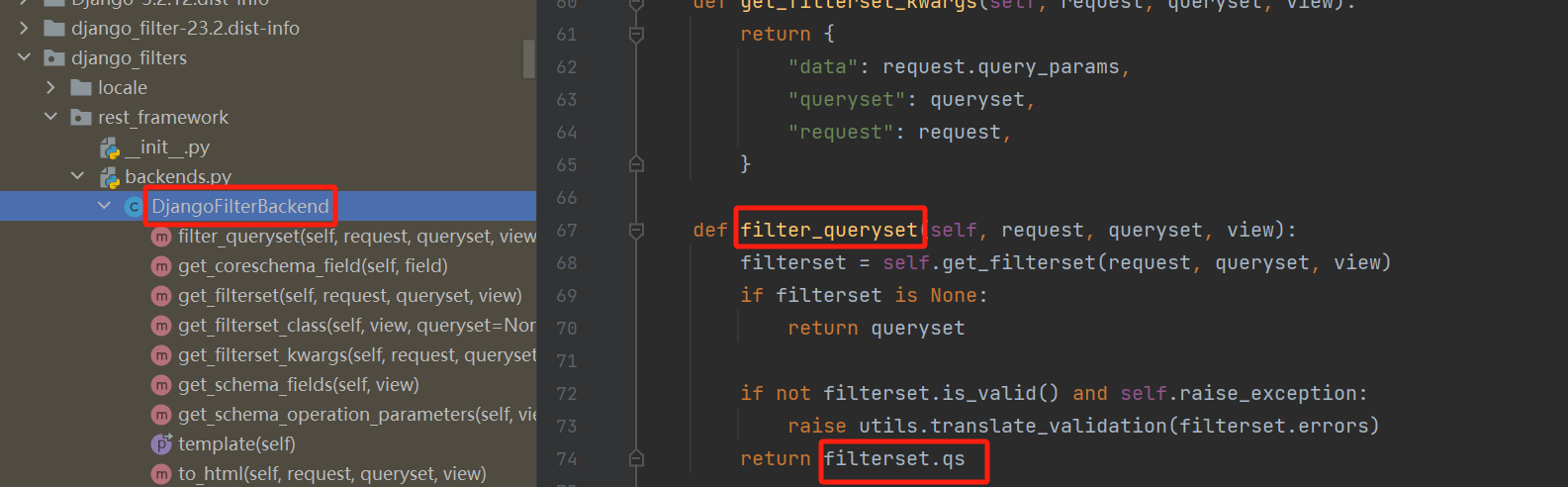
补充:为什么我们在视图类中配置了过滤类,就能执行对应的过滤类
filter_backends = [SearchFilter]:用的是GenericAPIView的filter_backends属性
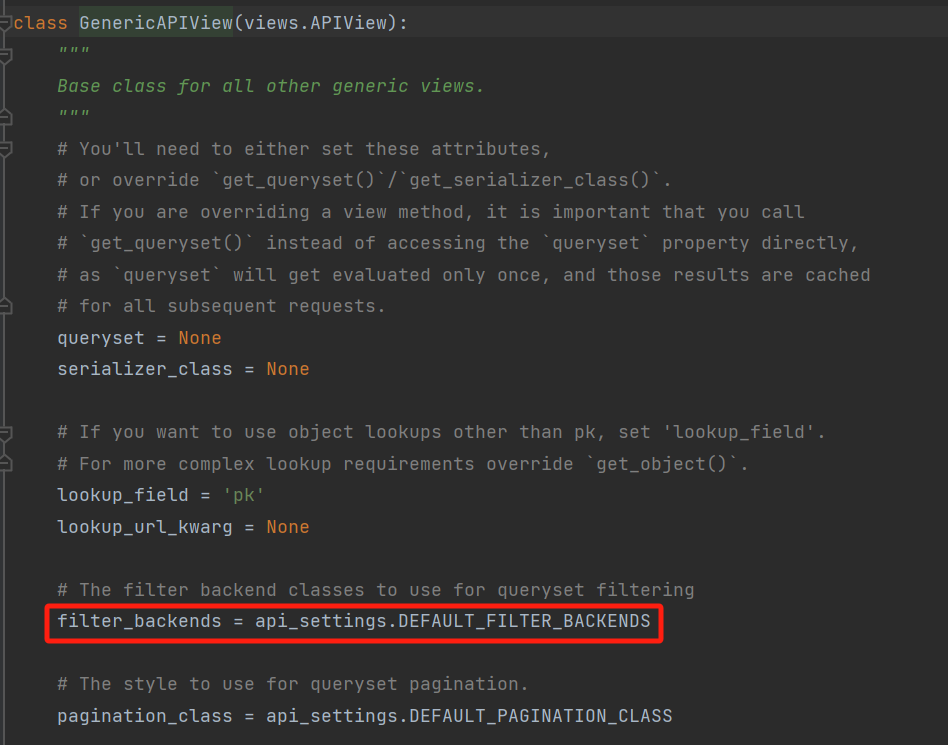
当发送get请求时,会执行对应的list方法,但是我们自己写的视图类中没有这个方法,因为继承的ListAPIView继承了LIstModelMixin类,就会执行LIstModelMixin类中的list方法
在list方法中,在对所有数据做过滤。但是发现其中并没有filter_queryset这个方法,最终我们在GenericAPIView类中找到了filter_queryset
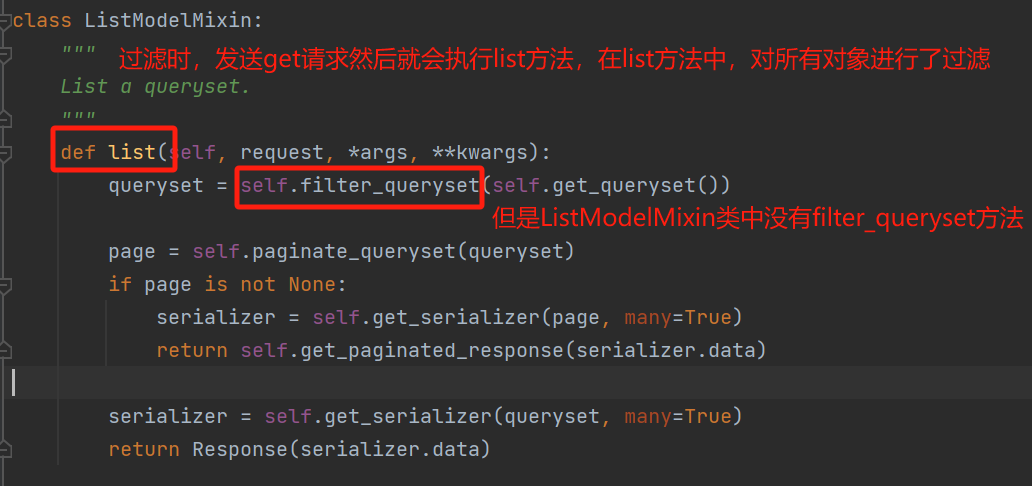
实际上,执行了GenericAPIView类中的filter_queryset方法,这里面执行了我们配置的过滤类,对他进行实例化,然后得到的过滤类对象去用filter_queryset方法。最后返回过滤完的queryset对象
六、分页
1. 分页:只针对查询所有的接口
- 分页展示形式:
web : 下一页,下一页
![]()
小程序,app:上拉加载更多
必须继承:GenericAPIView
使用方式:三种分页方式 ——》drf提供的
from rest_framework.pagination import PageNumberPagination, LimitOffsetPagination, CursorPagination #方式一: class CommonPageNumberPagination(PageNumberPagination): # web 用这个多 # http://api.example.org/accounts/?page=4 # http://api.example.org/accounts/?page=4&page_size=100 # 重写几个类属性 page_size = 3 # 每页显示多少条 page_query_param = 'page' # 指定第几页的key 值 page=4 page_size_query_param = 'size' # 可以指定每页显示多少条 size=300000 max_page_size = 5 # 每页最多显示5条 #方式二: class CommonLimitOffsetPagination(LimitOffsetPagination): # http://api.example.org/accounts/?limit=4 # 从开始取4条 # http://api.example.org/accounts/?offset=4&limit=5 从第4条开始,取5条 default_limit = 2 # 默认每页显示2条 limit_query_param = 'limit' # 每页显示多少条的查询条件 offset_query_param = 'offset' # 从第几条开始取数据 max_limit = 5 # limit最多取5条 # 方式三: class CommonCursorPagination(CursorPagination): # app上用这个多 # 只能上一页和下一页,不能指定跳转到中间的某页---》效率高,大数据量用它、 cursor_query_param = 'cursor' # 查询条件,用不到,需要有 page_size = 2 # 每页显示两条 ordering = 'id' # 按id排序 这个必须是表中字段
views文件中:
from .page import CommonPageNumberPagination,CommonLimitOffsetPagination,CommonCursorPagination class BookView(ViewSetMixin, ListAPIView): authentication_classes=[] queryset = Book.objects.all() serializer_class = BookSerializer pagination_class =CommonCursorPagination # 分页方式只有一种,配置一个类即可
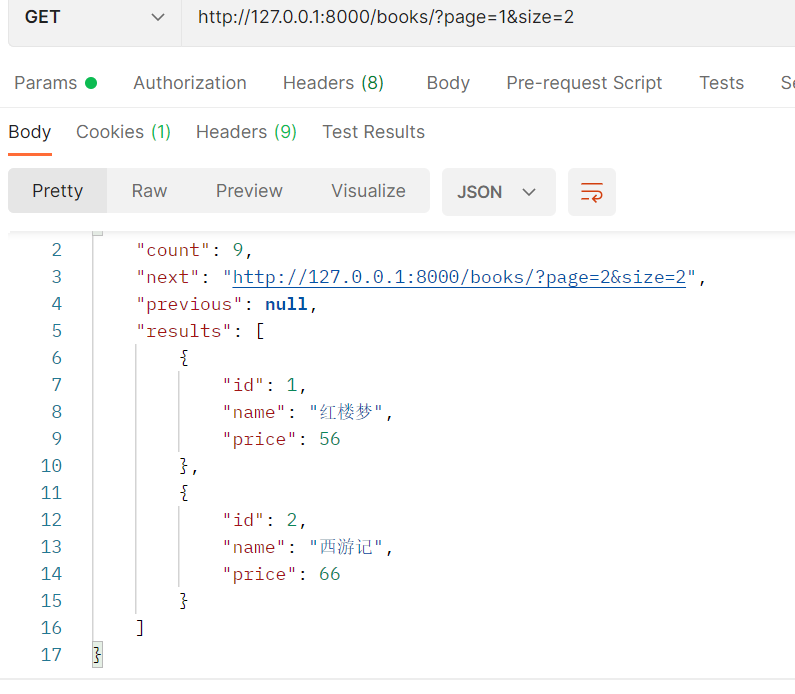
1. pagination_class = CommonPageNumberPagination
page=1&size=2:在第一页显示两条数据:
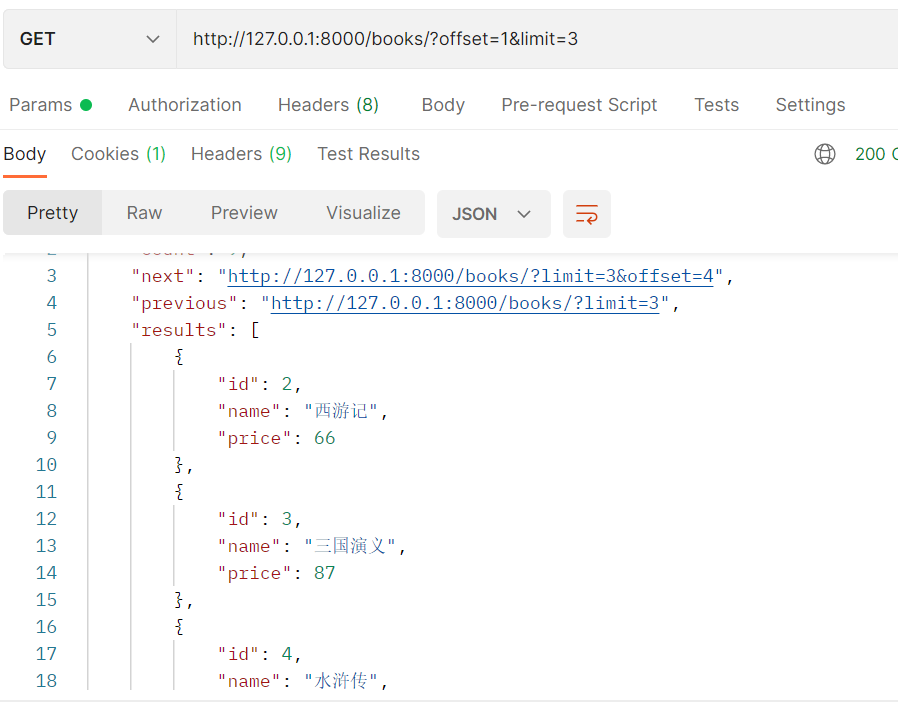
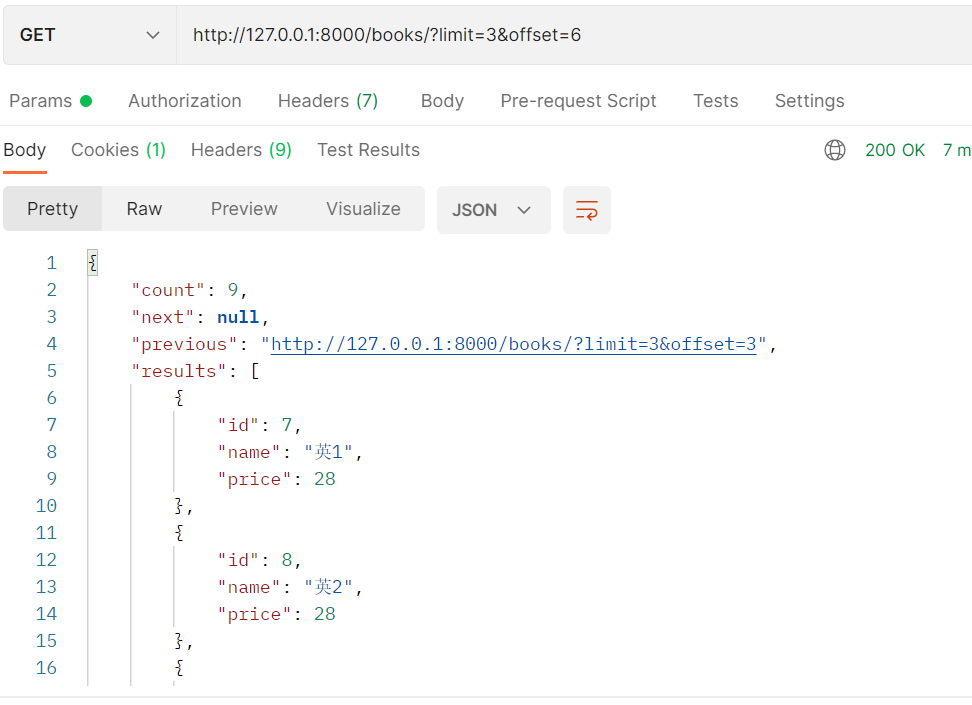
2.pagination_class =CommonLimitOffsetPaginatio
offset=1&limit=3:从第一条之后开始找,最多找三条数据
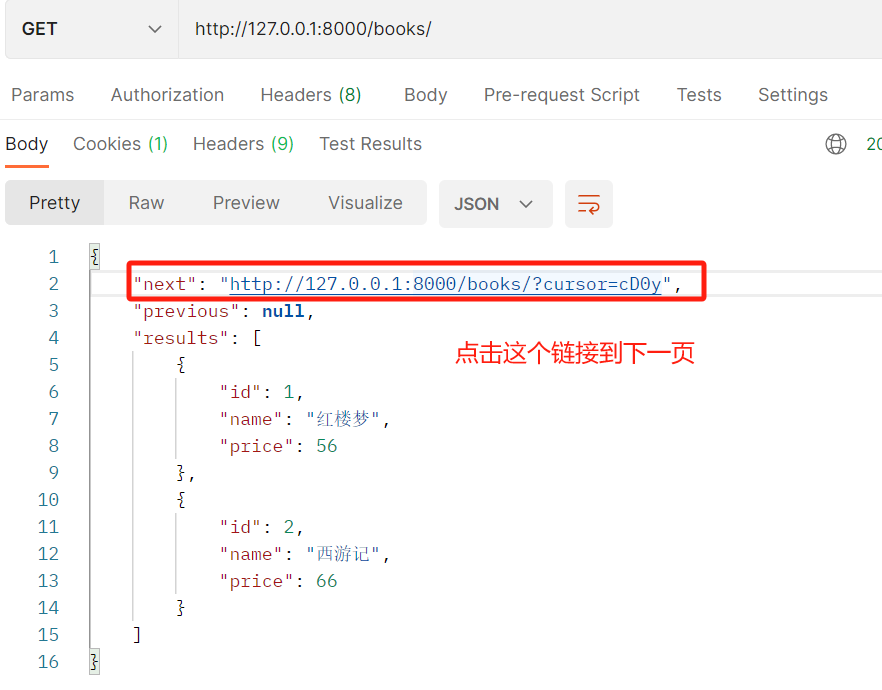
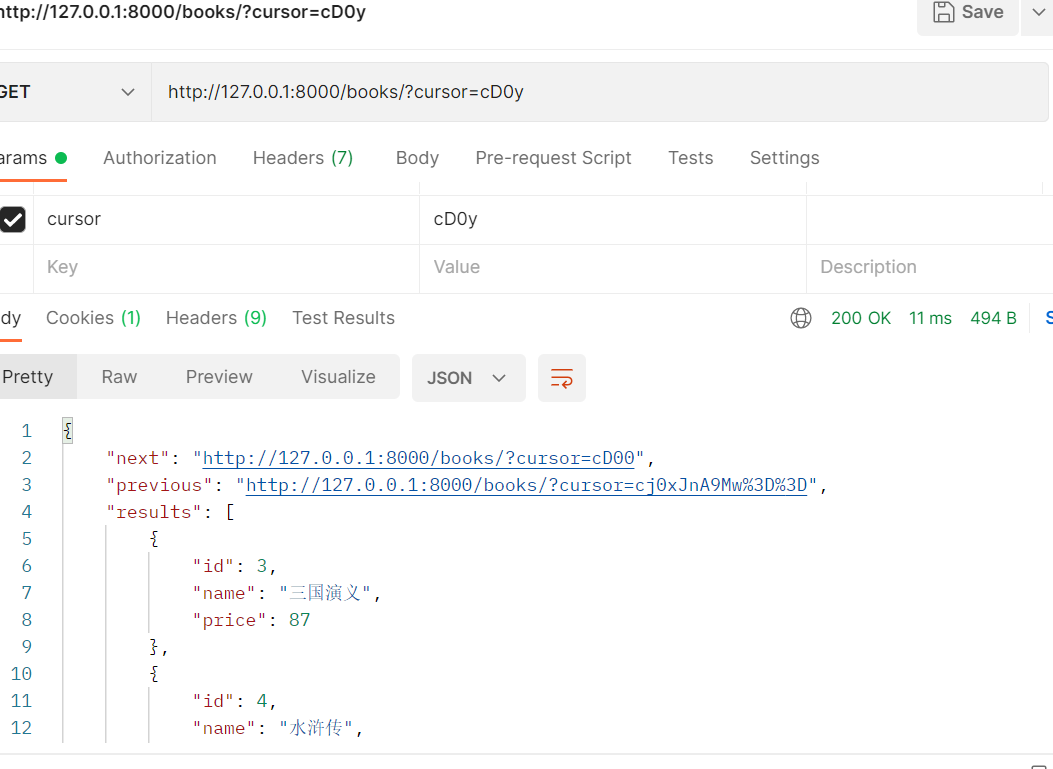
3. pagination_class =CommonCursorPagination
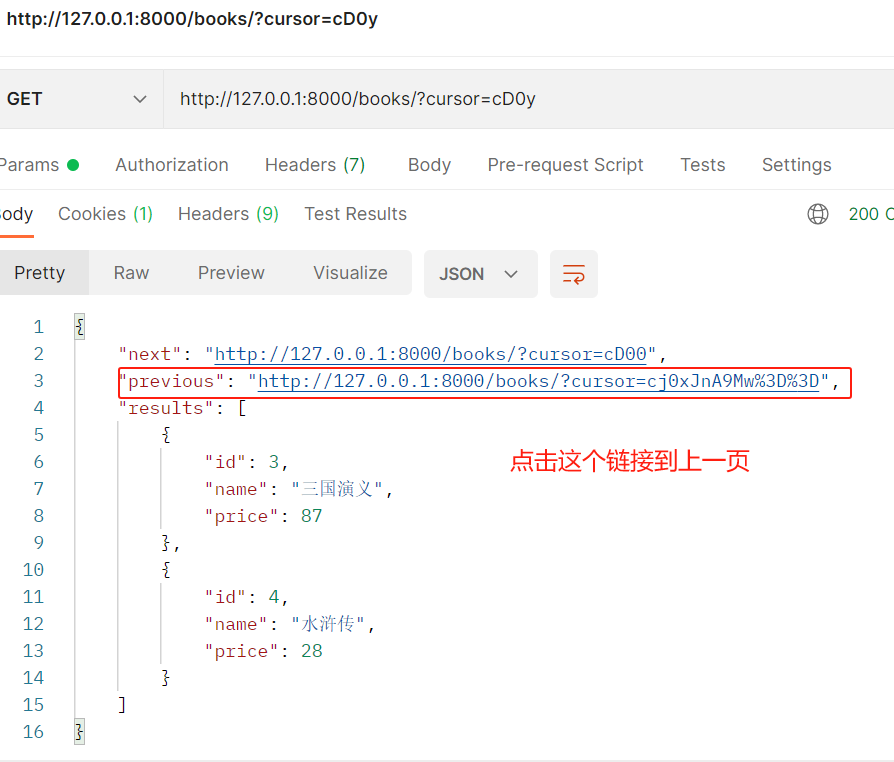
继承APIView实现三种分页
# 继承APIView类的分页 from rest_framework.views import APIView from .page import CommonPageNumberPagination,CommonLimiOffsetPagination,CommonCCursorPagination class BookView(ViewSetMixin,APIView): # def list(self,requset,*args,**kwargs): # book_list = Book.objects.all() # # pagination = CommonPageNumberPagination() # 实例化所写的过滤类得到对象 # # pagination=CommonCCursorPagination() # pagination =CommonLimiOffsetPagination() # page=pagination.paginate_queryset(book_list,requset) # ser = BookSerializer(instance=page,many=True) # return Response(ser.data) # 上面的第一种方法不能返回下一页的链接,所以我们查看源码有一个get_paginated_response这个方法可以实现我们想要的效果 def list(self,requset,*args,**kwargs): queryset =Book.objects.all() # pagination = CommonPageNumberPagination() # web常用的 # pagination = CommonLimiOffsetPagination() pagination =CommonCCursorPagination() # app常用的 page = pagination.paginate_queryset(queryset,requset) # 使用所有数据分页 if page is not None: ser = BookSerializer(instance=page, many=True) # 序列化分页后的数据 return pagination.get_paginated_response(ser.data)
结果:
pagination = CommonLimiOffsetPagination():
pagination =CommonCCursorPagination():
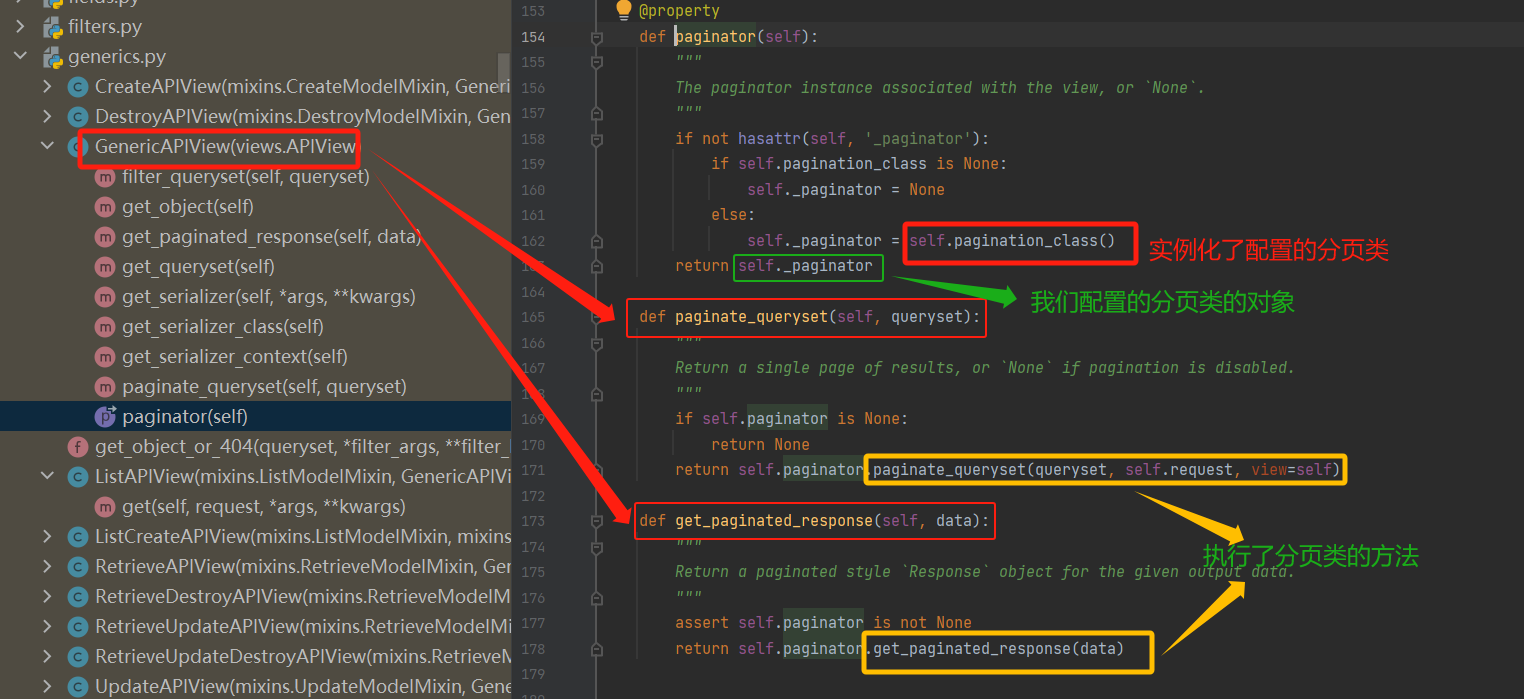
补充:为什么我们配置了分页类,就会执行?
- pagination_class = CommonCursorPagination # GenericAPIView类属性
在list 方法中,在对所有的数据进行了分页处理
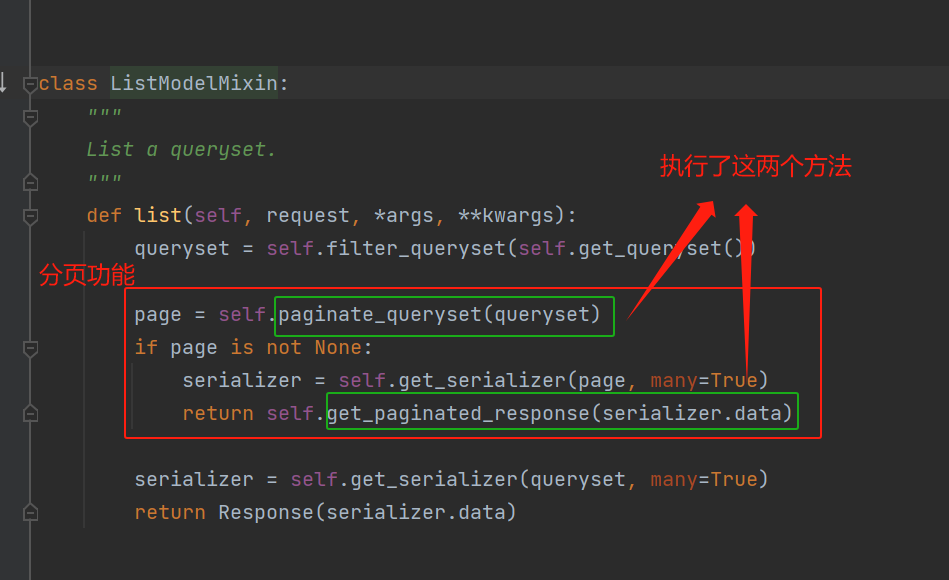
在GenericAPIView中,找到了这两个方法,然后调用了分页类对象的paginate_queryset完成了真正的分页。
三、异常处理
三大认证,视图类的方法中执行出错,都会被全局异常捕获
-认证类,认证不通过,就抛异常,前端不会报错,只是返回了提示信息 ----》处理了drf的异常
drf全局异常处理,会把drf的异常处理掉,统一返回格式,但是django原生的和python的都不会处理
我们要做的,无论返回什么异常,都返回固定格式
步骤:
1. 写一个函数
# 'EXCEPTION_HANDLER': 'rest_framework.views.exception_handler', from rest_framework.views import exception_handler from rest_framework.response import Response def common_exception(exc, context): # 执行一下原来的exception_handler---》它能处理drf的异常,我就不用处理了 res = exception_handler(exc, context) if not res: # 有值,说明是drf异常,它处理完了,没有值,是其他异常,我们自己处理 return Response({'code': 999, 'msg': '非drf错误,错误信息是:%s' % str(exc)}) else: return Response({'code': 888, 'msg': 'drf错误,错误信息是:' + res.data.get('detail')})
2 配置文件配置
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'EXCEPTION_HANDLER': 'app01.exceptions.common_exception', # 以后只要出了异常,都会走这个函数
}
为什么在配置文件中配置了自己写的全局异常处理函数,只要出了异常,它就会走
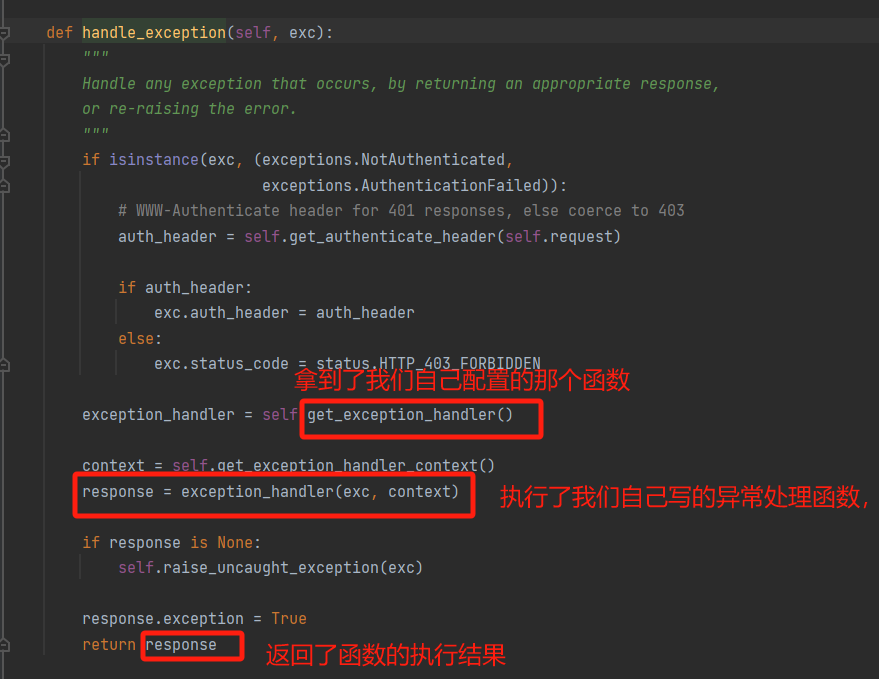
异常捕捉处理是在APIView中的dispatch方法中执行的
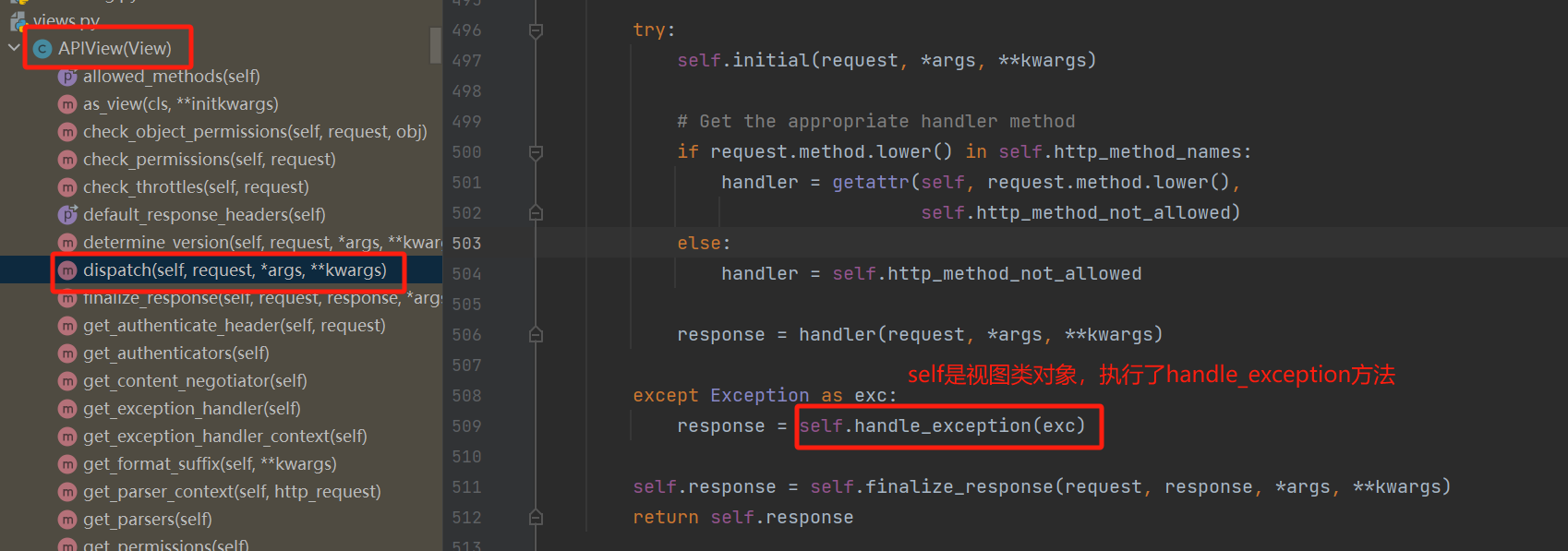
-APIView的handle_exception(exc):
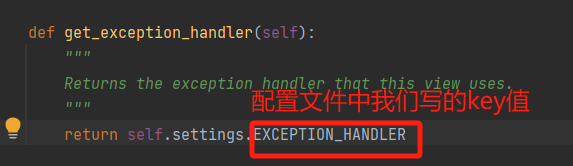
配置文件:
handle_exception(exc)源码:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号