lab10 mmap
lab10 mmap
实验结果

实验
编程前的思考以及解决方法
思考1
mmap返回了一个虚拟地址,但是看hints不分配实际的物理地址,但虚拟地址就确定了PTE,是否需要在PTE中做标记,否则usertrap怎么知道你这个page fault是啥原因?
lazy allocation is a win: the kernel doesn’t have to do any work at all for pages that the application never uses。真的不需要做任何工作?
操作系统怎么为lazy page分配一段连续的page ?
看到下一个hints,在proc的结构体中存储一个结构体数组,对应着这个进程锁分配的mmpages。usertrap时获取一下本进程可以分配。
所以在proc结构体中存储一个结构体数组来保存要mmap的地址,在结构体数组的元素的地址范围内有STAVAL的地址,说明是mmap产生的page fault。
思考2
2:mmap最后一个参数offset一定要page alined吗?感觉不page alined也可以读,为啥linux要限制它为page alined?xv6有限制吗?有也或者好像没有。
which takes an offset argument at which to read in the file (but you will have to lock/unlock the inode passed to readi)
readi是从文件中读取信息的,假设是inode文件,从either_copyout读。看二者的处理程序,either_copyout对于kernel和process的offsset,是没有page algned的限制的,所以我们也不要。
device文件提供的接口是没有offset的,这种page fault要怎么处理?pipe也没有?
ip->type == pipe,则应该返回错误,因为pipe文件弄完就消失,munmap,然后shared那怎么写回,应该是不行的。
取巧了,优点面向测试编程,mmaptest中测试的文件好像没有device文件,所以先考虑是device文件也返回错误。
思考3
长度+offset要是超过文件的末尾了怎么办?我要提供对这种情况的处理程序吗?还是有编程规范,肯定不会出现这种情况。
length是要读的长度,可以不page alinged。
无论mmaptest有没有意识到这种情况,就算编写者遵循这种情况,但是编写程序时也可能不小心写出了这种情况。
用filestat获取文件大小,如果长度+offset大于文件大小,则返回错误。
思考4
怎么找到一段足够长,而且没有使用过的虚拟地址用于mmap的使用。
一个process 一共有512512512个page,如果循环读写,判断每个page的valid位和下一个page的valid位,那么会浪费很多时间,且也不一定足够长。
参考linux内核中mmap的布局,从上一节得知一个inode所对应的文件长度最大应该为268kb,简单认为有512KB,512*16=8M。
因为有sbrk,即可以拓展。所以这一段区域布置在TRAPFRAME下两个page(no valid作为guard page)到8M的地方,(在两个page作为guard page)。。。。。面向测试编程
思考5
unmmap的add参数是否要page aligned呢?linux是要的,xv6要不要。
linux是一定要page aligned的,看xv6的测试,也是page aligned的,所以选择page aligned,否则有点难。
思考6
port为没有写权限,测试写了,那么这种异常情况我要怎么办?杀死进程??
看了测试代码,发现没有这种极端情况。
代码
下面是问题相关的重要代码,可能是头文件嵌套原因,所以一些头文件得用#ifndef xxxx #define xxx #ednif。一些地方也得补上这些头文件,但是这些我不展示了。
我主要思路还是跟cow有点像,每一mmap在有读写时,就把这一个page mmap,然后把文件内容读到这一页。
mmap结构体定义,记录mmap,unmmap的一些重要信息。
比如这个结构体有没有用过,记录port,flag,初始开始地址,初始长度,现在的长度和地址,偏移。
要用初始开始的地址和长度来确定每一page要从文件的哪里开始读,读多少,所以用两个变量来记录它们。
在kernel/proc.h中定义
struct __MmapStruct
{
int Port;
int Flag;
uint32 IsMaped;//0代表这个结构体没有map,1代表有。
uint64 StartVaAdd; //0xffffffffffffffff和下面length为0代表没有map,需要page aligned。
uint64 InitAdd;//unmmap可能会导致start改变,每页根file的offset是根据start弄的
uint64 InitLen;//与上面initAdd类似
uint64 Length;//实际mmap区域还剩下的长度
uint64 Offset;
struct file* MapMpedFile;//为0代表没有
};
// Per-process state
struct proc {
struct spinlock lock;
// p->lock must be held when using these:
enum procstate state; // Process state
void *chan; // If non-zero, sleeping on chan
int killed; // If non-zero, have been killed
int xstate; // Exit status to be returned to parent's wait
int pid; // Process ID
// wait_lock must be held when using this:
struct proc *parent; // Parent process
// these are private to the process, so p->lock need not be held.
struct __MmapStruct MapS[PROCESS_MMAPNUM];//16
uint64 kstack; // Virtual address of kernel stack
uint64 sz; // Size of process memory (bytes)
pagetable_t pagetable; // User page table
struct trapframe *trapframe; // data page for trampoline.S
struct context context; // swtch() here to run process
struct file *ofile[NOFILE]; // Open files
struct inode *cwd; // Current directory
char name[16]; // Process name (debugging)
};
mmap系统调用的具体实现。
在进程进程结构体中找到没有使用过的mmap结构体,根据参数来设置mmap结构体的值,增加mmap文件中inode的引用次数。
/**
*@brief
*/
uint64 sys_mmap(void)
{
struct proc* CurrentProc ;
struct file* UseFile;
struct stat UseFileSt;
uint64 Len;
int Port;
int Flag;
int Fd;
uint64 Offset;
int i;
Len = argraw(1);//修改这个,不static了。
argint(2, &Port);
argint(3, &Flag);
argint(4, &Fd);
Offset = argraw(5);
CurrentProc = myproc();
if ((Fd < 0) || (Fd >= NOFILE))
{
return 0xffffffffffffffff;
}
UseFile = CurrentProc->ofile[Fd];
if((UseFile->ip == 0))//device pipe, none不行
{
return 0xffffffffffffffff;
}
if (UseFile->readable == 0)
{
return 0xffffffffffffffff;
}
if (Flag == MAP_SHARED)
{
if ((UseFile->writable == 0) && ((Port & PROT_WRITE) != 0))
{
return 0xffffffffffffffff;
}
}
// filestat是用于进程,这里是kernel
ilock(UseFile->ip);
stati(UseFile->ip, &UseFileSt);
iunlock(UseFile->ip);
if ((Len + Offset) < UseFileSt.size)//偏移加要映射的长度小于文件大小,交给上一层处理
{
return 0xffffffffffffffff;
}
for(i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
if (CurrentProc->MapS[i].IsMaped == 0)
{
CurrentProc->MapS[i].IsMaped = 1;
CurrentProc->MapS[i].Flag = Flag;
CurrentProc->MapS[i].Length = Len;
CurrentProc->MapS[i].MapMpedFile = UseFile;
CurrentProc->MapS[i].Port = Port;
CurrentProc->MapS[i].StartVaAdd = MMAPSTART + (PGSIZE * 128 *i);
CurrentProc->MapS[i].InitAdd = CurrentProc->MapS[i].StartVaAdd;
CurrentProc->MapS[i].InitLen = CurrentProc->MapS[i].Length;
CurrentProc->MapS[i].Offset = Offset;
filedup( CurrentProc->MapS[i].MapMpedFile);
break;
}
}
if (i == 16)//16个mmap不够用了
{
return 0xffffffffffffffff;
}
return CurrentProc->MapS[i].StartVaAdd;
}
trap函数的具体实现。
在usertrap函数里,判断如果中断来自load pagefault或者store pagefault,就调用MmapHandler函数。如果失败,杀死该进程。
MmapHandler首先判断是进程哪个mmap结构体的mmap引起的pagefault,然后根port和flag设置权限,并将文件对应的数据读到该page对应的地方。
usertrap函数里。
if(r_scause() == 8){
// system call
if(p->killed)
exit(-1);
// sepc points to the ecall instruction,
// but we want to return to the next instruction.
p->trapframe->epc += 4;
// an interrupt will change sstatus &c registers,
// so don't enable until done with those registers.
intr_on();
syscall();
}
else if ((r_scause() == 13) || (r_scause() == 15))
{
uint64 Scause = r_scause();
uint64 Staval = r_stval();
if (MmapHandler(Scause, Staval) < 0)
{
p->killed = 1;//杀死该进程。
}
}
else if((which_dev = devintr()) != 0){
// ok
/**
* @brief
*/
int MmapHandler(uint64 Scause, uint64 Stval)
{
uint64 ThePage;
int i = 0;
struct proc *p = myproc();
uint32 PageStartOffset = 0;
int PageRemainLen = 0;
uint64* pa;
int flag;
ThePage = PGROUNDDOWN(Stval); //那一页的头
for(i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
if (p->MapS[i].IsMaped != 0)
{
if ((p->MapS[i].StartVaAdd <= ThePage) && ((p->MapS[i].StartVaAdd + p->MapS[i].Length) >= ThePage))
{
break;
}
}
}
if (16 == i)
{
return -1;//不是mmap的地方引起的page fault,个人决定引起这样的page fault,要杀掉。
}
pa = kalloc();
if (0 == pa)
{
return -1;
}
flag = 0;
if ((p->MapS[i].Port & PROT_READ) != 0)
{
flag |= PTE_R;
}
if ((p->MapS[i].Port & PROT_WRITE) != 0)
{
flag |= PTE_W;
}
flag |= PTE_U;
if (mappages(p->pagetable, ThePage, PGSIZE, (uint64)pa, flag ) < 0)
{
return -1;
}
//文件读到这一页上面。
PageStartOffset = ThePage - p->MapS[i].InitAdd;
PageRemainLen = p->MapS[i].InitLen - PageStartOffset;
PageStartOffset = PageStartOffset + p->MapS[i].Offset;
if (PageRemainLen > PGSIZE)
{
PageRemainLen = PGSIZE;
}
begin_op();
ilock(p->MapS[i].MapMpedFile->ip);
if (readi(p->MapS[i].MapMpedFile->ip, 1, ThePage, PageStartOffset, PageRemainLen) < 0)
{
iunlock(p->MapS[i].MapMpedFile->ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
iunlock(p->MapS[i].MapMpedFile->ip);
end_op();
return 0;
}
munmap系统调用的具体实现。
判断输入参数add和len是否对(比如add要page aligned,unmmap的区域要mmap过等),然后判断是否要shared,是的话写回文件,然后对页表释放映射,释放内存。
/**
*@brief
*/
uint64 sys_munmap(void)
{
uint64 UmmapAdd;
uint64 Length;
int i;
struct proc* CurrentProc;
uint64 TempAdd;
pte_t* TempAddp;
uint32 PageStartOffset = 0;
int PageRemainLen = 0;
argaddr(0, &UmmapAdd);
Length = argraw(1);
CurrentProc = myproc();
for(i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
if(CurrentProc->MapS[i].IsMaped != 0)
{
if((UmmapAdd >= CurrentProc->MapS[i].StartVaAdd) && (UmmapAdd <= (CurrentProc->MapS[i].StartVaAdd + CurrentProc->MapS[i].Length)))
{
//满足这个条件代表ummap的是这个结构体
if (((CurrentProc->MapS[i].StartVaAdd) != UmmapAdd) && \
((UmmapAdd + Length) < (CurrentProc->MapS[i].StartVaAdd + CurrentProc->MapS[i].Length)))
{
return -1;//不能挖中断这段
}
if ((UmmapAdd + Length) > (CurrentProc->MapS[i].StartVaAdd + CurrentProc->MapS[i].Length))
{
return -1;//挖的不止这个区域。
}
break;
}
}
}
if (16 == i)//没有找到
{
return -1;
}
if ((UmmapAdd % PGSIZE) != 0)
{
return -1;//必须要page aligned.
}
//哪怕len+add没满那个page,只要涉及了,也回写到file,就释放掉
for (TempAdd = UmmapAdd; TempAdd < (UmmapAdd + Length); TempAdd = TempAdd + PGSIZE)
{
TempAddp = walk(CurrentProc->pagetable, TempAdd, 1);
if (TempAddp == 0)
{
continue;
}
if (((*TempAddp) & PTE_V) == 0)
{
continue;;//要unmmap的区域PTE居然不是有效的。没有读写,直接调用了
}
if ((CurrentProc->MapS[i].Flag == MAP_SHARED) && ((CurrentProc->MapS[i].Port & PROT_WRITE) != 0) )//把MMAP写的东西回写到文件
{
PageStartOffset = TempAdd - CurrentProc->MapS[i].InitAdd;
PageRemainLen = CurrentProc->MapS[i].InitLen - PageStartOffset;
PageStartOffset = PageStartOffset + CurrentProc->MapS[i].Offset;
if (PageRemainLen > PGSIZE)
{
PageRemainLen = PGSIZE;
}
begin_op();
ilock(CurrentProc->MapS[i].MapMpedFile->ip);
writei(CurrentProc->MapS[i].MapMpedFile->ip, 1, TempAdd, PageStartOffset, PageRemainLen);
iunlock(CurrentProc->MapS[i].MapMpedFile->ip);
end_op();
}
uvmunmap(CurrentProc->pagetable, TempAdd, 1, 1);
}
//更新现在映射的地址和长度
if ((UmmapAdd == CurrentProc->MapS[i].StartVaAdd) && (CurrentProc->MapS[i].Length == Length))//这一块全部unmmap完了
{
fileclose(CurrentProc->MapS[i].MapMpedFile);
CurrentProc->MapS[i].IsMaped = 0;
CurrentProc->MapS[i].Flag = 0;
CurrentProc->MapS[i].InitAdd = 0;
CurrentProc->MapS[i].Length = 0;
CurrentProc->MapS[i].MapMpedFile = 0;
CurrentProc->MapS[i].Port = 0;
CurrentProc->MapS[i].StartVaAdd = 0;
}
else if ((UmmapAdd == CurrentProc->MapS[i].StartVaAdd) && (Length < CurrentProc->MapS[i].Length))//覆盖前半段
{
TempAdd = PGROUNDUP((UmmapAdd + Length));
CurrentProc->MapS[i].Length = CurrentProc->MapS[i].Length - (TempAdd - CurrentProc->MapS[i].StartVaAdd);
CurrentProc->MapS[i].StartVaAdd = TempAdd;
}
else if ((UmmapAdd > CurrentProc->MapS[i].StartVaAdd) && ((UmmapAdd + Length) == (CurrentProc->MapS[i].StartVaAdd + CurrentProc->MapS[i].Length)))//后半段,除了这3种,没有别的可能了
{
CurrentProc->MapS[i].Length = CurrentProc->MapS[i].Length - (CurrentProc->MapS[i].StartVaAdd + CurrentProc->MapS[i].Length - UmmapAdd);
}
return 0;
}
allocproc的相关实现。
增加对mmap结构体的初始化
found:
p->pid = allocpid();
p->state = USED;
// Allocate a trapframe page.
if((p->trapframe = (struct trapframe *)kalloc()) == 0){
freeproc(p);
release(&p->lock);
return 0;
}
// An empty user page table.
p->pagetable = proc_pagetable(p);
if(p->pagetable == 0){
freeproc(p);
release(&p->lock);
return 0;
}
// Set up new context to start executing at forkret,
// which returns to user space.
memset(&p->context, 0, sizeof(p->context));
p->context.ra = (uint64)forkret;
p->context.sp = p->kstack + PGSIZE;
//初始化mmap的所有结构体
for(int i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
p->MapS[i].Flag = 0;
p->MapS[i].InitAdd = 0;
p->MapS[i].InitLen = 0;
p->MapS[i].IsMaped = 0;
p->MapS[i].Length = 0;
p->MapS[i].MapMpedFile = 0;
p->MapS[i].Offset = 0;
p->MapS[i].Port = 0;
p->MapS[i].StartVaAdd = 0;
}
return p;
}
fork系统调用的具体实现。
把proc上mmap结构体的值复制到子进程的mmap结构体上。如果有mmap的区域,需要增加对应文件inode的引用次数,映射子进程需要的mmap page,并且把父进程的内容复制到上面。
// Create a new process, copying the parent.
// Sets up child kernel stack to return as if from fork() system call.
int
fork(void)
{
int i, pid;
struct proc *np;
struct proc *p = myproc();
// Allocate process.
if((np = allocproc()) == 0){
return -1;
}
// Copy user memory from parent to child.
if(uvmcopy(p->pagetable, np->pagetable, p->sz) < 0){
freeproc(np);
release(&np->lock);
return -1;
}
np->sz = p->sz;
// copy saved user registers.
*(np->trapframe) = *(p->trapframe);
// Cause fork to return 0 in the child.
np->trapframe->a0 = 0;
// increment reference counts on open file descriptors.
for(i = 0; i < NOFILE; i++)
if(p->ofile[i])
np->ofile[i] = filedup(p->ofile[i]);
np->cwd = idup(p->cwd);
safestrcpy(np->name, p->name, sizeof(p->name));
pid = np->pid;
release(&np->lock);
acquire(&wait_lock);
np->parent = p;
release(&wait_lock);
acquire(&np->lock);
np->state = RUNNABLE;
release(&np->lock);
//复制结构体,分配页面并复制
uint64 TempAdd;
uint64* PaP;
pte_t *pte;
uint64 OldPa, NewPa;
int TheFlag;
for(int i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
np->MapS[i].Flag = p->MapS[i].Flag;
np->MapS[i].Port = p->MapS[i].Port;
np->MapS[i].IsMaped = p->MapS[i].IsMaped;
np->MapS[i].StartVaAdd = p->MapS[i].StartVaAdd;
np->MapS[i].InitAdd = p->MapS[i].InitAdd;
np->MapS[i].InitLen = p->MapS[i].InitLen;
np->MapS[i].Length = p->MapS[i].Length;
np->MapS[i].Offset = p->MapS[i].Offset;
np->MapS[i].MapMpedFile = p->MapS[i].MapMpedFile;
if (np->MapS[i].IsMaped != 0)
{
filedup(np->MapS[i].MapMpedFile);
TempAdd = PGROUNDDOWN(np->MapS[i].StartVaAdd);
for(; TempAdd < PGROUNDUP(np->MapS[i].StartVaAdd + np->MapS[i].Length);TempAdd += PGSIZE)
{
pte = walk(p->pagetable, TempAdd, 1);
OldPa = PTE2PA(*pte);
if (0 == OldPa)//mmap以后,没有读写该page就fork了。
{
continue;
}
PaP = kalloc();
if (PaP == 0)
{
return -1;
}
TheFlag = 0;
if ((p->MapS[i].Port & PROT_READ) != 0)
{
TheFlag |= PTE_R;
}
if ((p->MapS[i].Port & PROT_WRITE) != 0)
{
TheFlag |= PTE_W;
}
TheFlag |= PTE_U;
if (mappages(np->pagetable, TempAdd, PGSIZE, (uint64)(PaP), TheFlag) < 0)
{
return -1;
}
pte = walk(np->pagetable, TempAdd, 1);
NewPa = PTE2PA(*pte);
pte = walk(p->pagetable, TempAdd, 1);
OldPa = PTE2PA(*pte);
memmove((char*)NewPa, (char*)OldPa, PGSIZE);
}
}
}
return pid;
}
exit系统调用的具体实现。
与munmap类似,把所有未unmap得unmap掉,有满足回写条件的要回写。
// Exit the current process. Does not return.
// An exited process remains in the zombie state
// until its parent calls wait().
void
exit(int status)
{
struct proc *p = myproc();
if(p == initproc)
panic("init exiting");
// Close all open files.
for(int fd = 0; fd < NOFILE; fd++){
if(p->ofile[fd]){
struct file *f = p->ofile[fd];
fileclose(f);
p->ofile[fd] = 0;
}
}
//释放掉unmmap
uint64 TempAdd;
uint32 PageStartOffset = 0;
int PageRemainLen = 0;
pte_t *pte;
uint64 ThePa;
for(int i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
if (p->MapS[i].IsMaped != 0)//没有释放掉
{
TempAdd = PGROUNDDOWN(p->MapS[i].StartVaAdd);
for(; TempAdd <= (p->MapS[i].StartVaAdd + p->MapS[i].Length); TempAdd = TempAdd + PGSIZE)
{
pte = walk(p->pagetable, TempAdd, 1);
ThePa = PTE2PA(*pte);
if (ThePa == 0)
{
continue;//这一页没有读写,实际都没分配过。
}
if ((p->MapS[i].Flag == MAP_SHARED) && ((p->MapS[i].Port & PROT_WRITE) != 0))//要写回文件
{
PageStartOffset = TempAdd - p->MapS[i].InitAdd;
PageRemainLen = p->MapS[i].InitLen - PageStartOffset;
PageStartOffset = PageStartOffset + p->MapS[i].Offset;
if (PageRemainLen > PGSIZE)
{
PageRemainLen = PGSIZE;
}
begin_op();
ilock(p->MapS[i].MapMpedFile->ip);
writei(p->MapS[i].MapMpedFile->ip, 1, TempAdd, PageStartOffset, PageRemainLen);
iunlock(p->MapS[i].MapMpedFile->ip);
end_op();
}
uvmunmap(p->pagetable, TempAdd, 1, 1);
}
fileclose(p->MapS[i].MapMpedFile);
p->MapS[i].Flag = 0;
p->MapS[i].InitAdd = 0;
p->MapS[i].InitLen = 0;
p->MapS[i].IsMaped = 0;
p->MapS[i].Length = 0;
p->MapS[i].MapMpedFile = 0;
p->MapS[i].Offset = 0;
p->MapS[i].Port = 0;
p->MapS[i].StartVaAdd = 0;
}
}
begin_op();
iput(p->cwd);
end_op();
p->cwd = 0;
acquire(&wait_lock);
// Give any children to init.
reparent(p);
// Parent might be sleeping in wait().
wakeup(p->parent);
acquire(&p->lock);
p->xstate = status;
p->state = ZOMBIE;
release(&wait_lock);
// Jump into the scheduler, never to return.
sched();
panic("zombie exit");
}
问题
问题2
test mmap f不通过
原因:在sys_mmap中调用了filestat获取文件的信息,非法调用。观察下面的3个函数,你会发现filestat中,传入的st地址应是为当前进程中的虚拟地址,我却用在了kernel中。
uint64
sys_fstat(void)
{
struct file *f;
uint64 st; // user pointer to struct stat
if(argfd(0, 0, &f) < 0 || argaddr(1, &st) < 0)
return -1;
return filestat(f, st);
}
int
filestat(struct file *f, uint64 addr)
{
struct proc *p = myproc();
struct stat st;
if(f->type == FD_INODE || f->type == FD_DEVICE){
ilock(f->ip);
stati(f->ip, &st);
iunlock(f->ip);
if(copyout(p->pagetable, addr, (char *)&st, sizeof(st)) < 0)
return -1;
return 0;
}
return -1;
}
int
copyout(pagetable_t pagetable, uint64 dstva, char *src, uint64 len)
{
uint64 n, va0, pa0;
while(len > 0){
va0 = PGROUNDDOWN(dstva);
pa0 = walkaddr(pagetable, va0);
if(pa0 == 0)
return -1;
n = PGSIZE - (dstva - va0);
if(n > len)
n = len;
memmove((void *)(pa0 + (dstva - va0)), src, n);
len -= n;
src += n;
dstva = va0 + PGSIZE;
}
return 0;
}
问题3
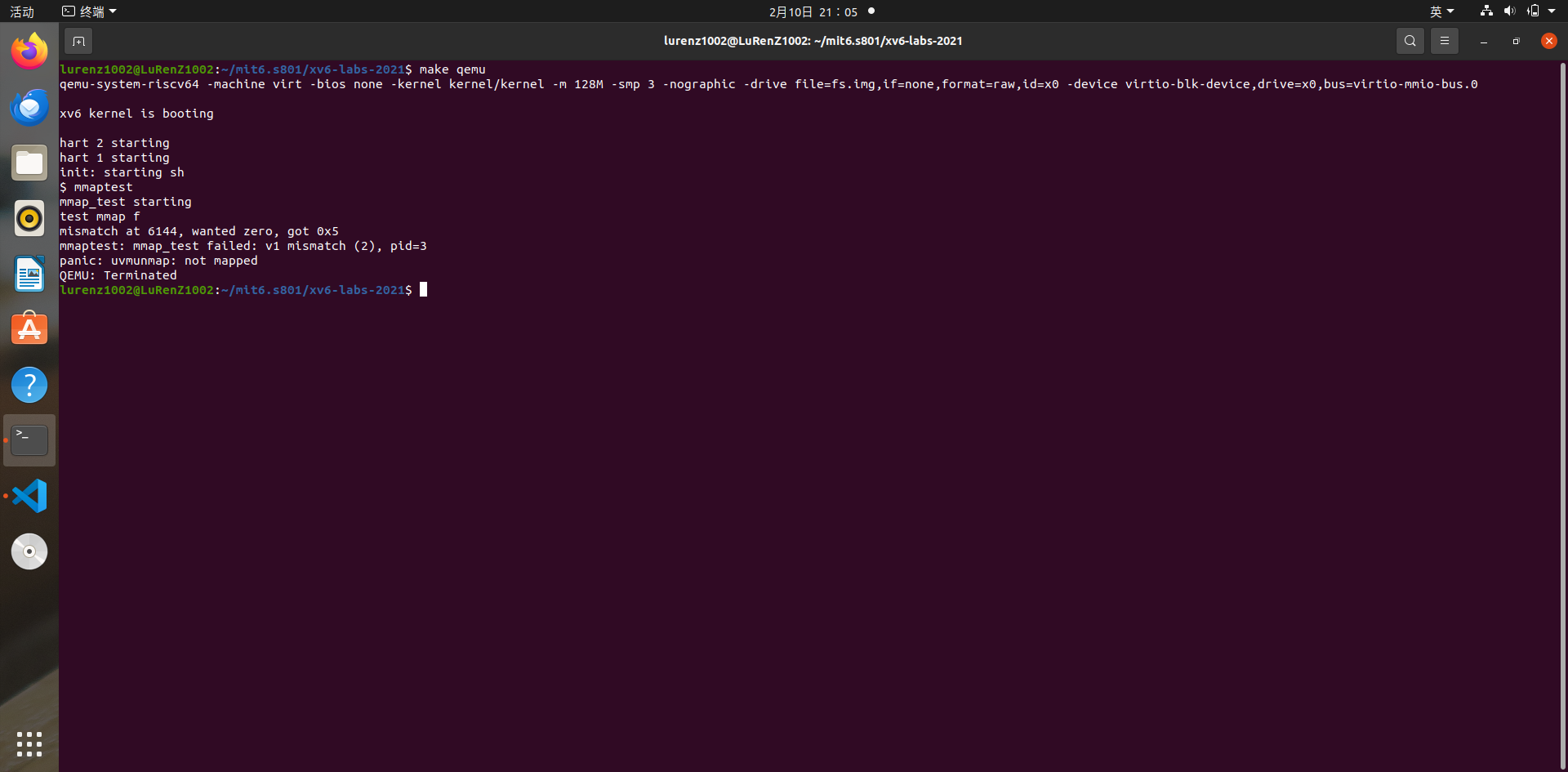
want zero,but got 5
首先觉得是file没有读到mmap的区域,于是重点整理了一下trap的逻辑,感觉没有问题。
然后想起kalloc分配后,置那个page的就是0x05。难道我没把file 0的部分写到mmap区域吗?
那个页肯定有写的,否则1.5page的A就错误了,那么redi长度有问题吗?理了一下逻辑,也没发现问题。
看了一下测试代码,发现它没写0,直接就默认后面open 文件后半页的就是0,其实后半页还是0x05;
//
// create a file to be mapped, containing
// 1.5 pages of 'A' and half a page of zeros.
//
void
makefile(const char *f)
{
int i;
int n = PGSIZE/BSIZE;
unlink(f);
int fd = open(f, O_WRONLY | O_CREATE);
if (fd == -1)
err("open");
memset(buf, 'A', BSIZE);
// write 1.5 page
for (i = 0; i < n + n/2; i++) {
if (write(fd, buf, BSIZE) != BSIZE)
err("write 0 makefile");
}
if (close(fd) == -1)
err("close");
}
更改一下kalloc的置5,改成了置7
于是就出现了wanted zero, got 0x7。
个人觉得是测试的写法不对,要么补充测试写法,要么kalloc改成置0
测试通过
问题4
mmap call should have failed, pid=3
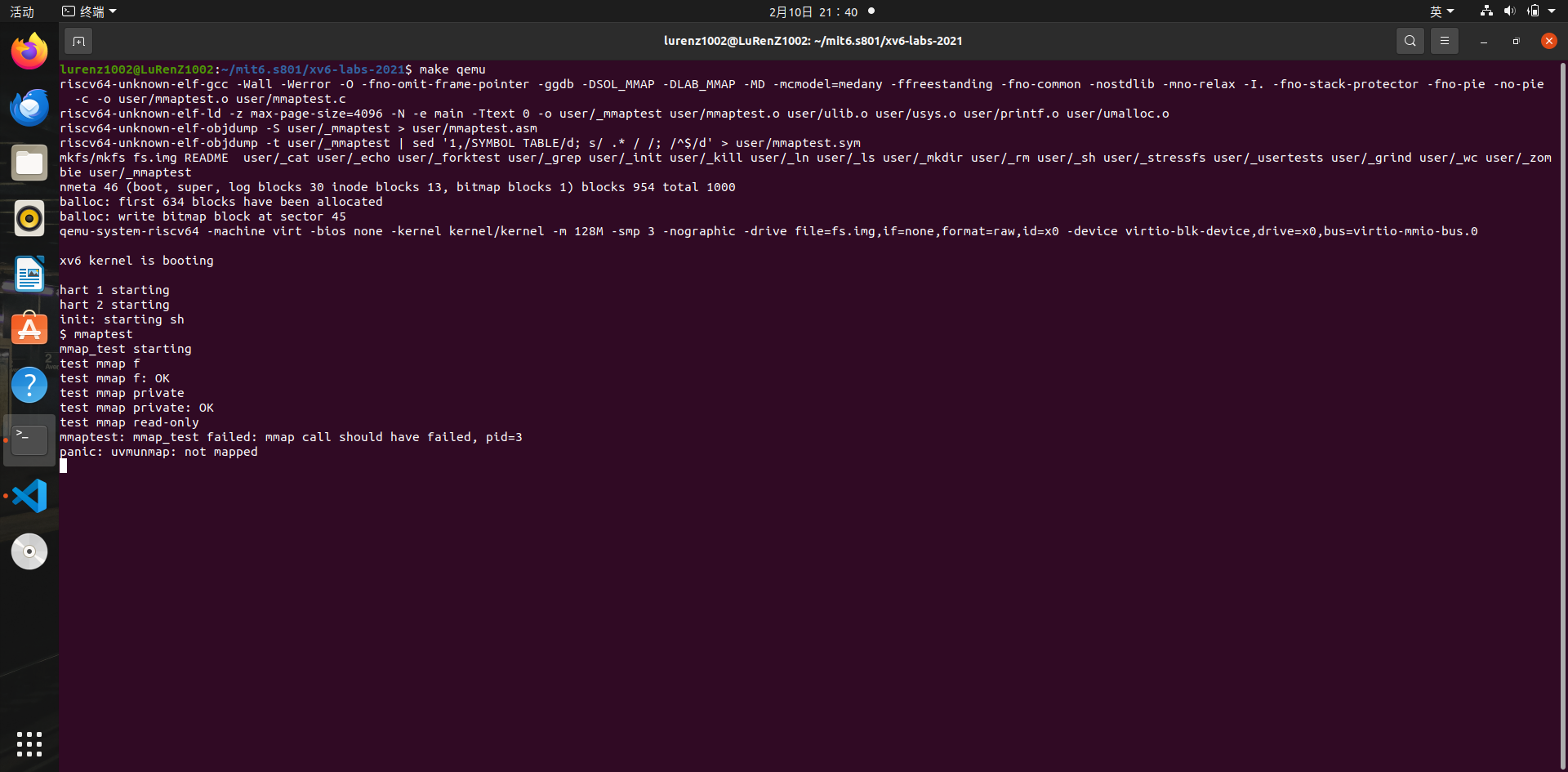
// check that mmap does allow read/write mapping of a
// file opened read/write.
if ((fd = open(f, O_RDONLY)) == -1)
err("open");
p = mmap(0, PGSIZE*3, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
if (p != MAP_FAILED)
err("mmap call should have failed");
if (close(fd) == -1)
err("close");
通过上面的代码可以看出,是mmap返回(void*)-1导致的,但是为啥前面通过了,这边没有通过。
是这个参数设置特殊吗?并没有,那么就是前面的积累导致的,应该是unmmap的问题。但unmmap也才3个,就算没unmmap掉也没问题。
仔细发现测试是要等于(void*)(-1)才通过?
没考虑到file属性与port属性不一致情况。
file 不可读,返回(void*)-1;
flag private,file可不可写与port可读可写无所谓,都可以mmap出来。但port没有可读却读了,要杀死进程?port没可写却写了要杀死进程,这个的情况不知道要怎么处理,杀死呢?还是panic?trap也没处理?
flag shared,file 不可写,那么port也不可写。
问题5
fork引起kernel trap.
pte = walk(np->pagetable, TempAdd, 1);
NewPa = PTE2PA(*pte);
pte = walk(p->pagetable, TempAdd, 1);
OldPa = PTE2PA(*pte);
printf("old %p new %p\n", OldPa, NewPa);
memmove((char*)NewPa, (char*)OldPa, PGSIZE);
打印OldPa,发现值是0,代表旧进程的页表没有映射实际物理地址,是0?
发现忘考虑了,mmap后,没有读写那个区域立即fork后的可能。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号