数据结构题单
P2021:逆向思维
思路1:标号:(建立值与编号对应)跑队列,最后将标号对应到原序列
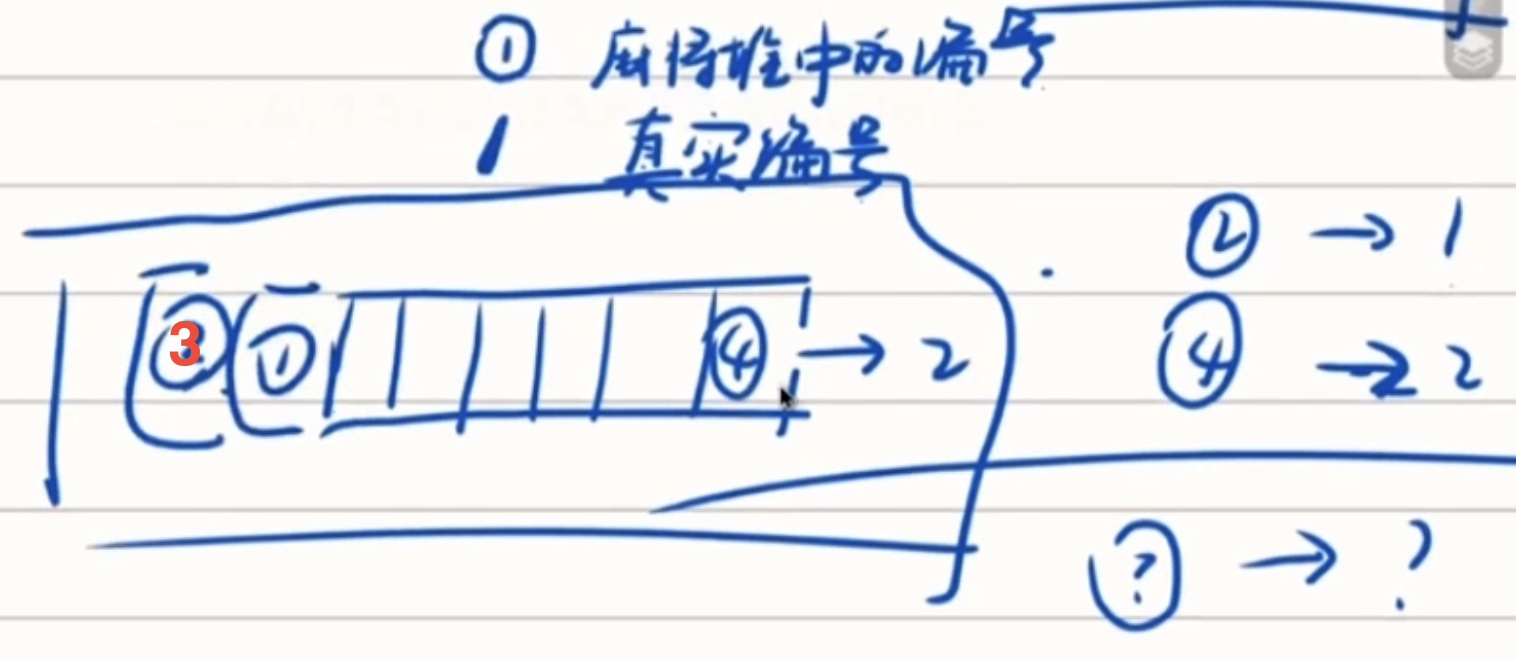
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int n, a[N];
queue<int> Q;
int main() {
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) Q.push(i);
int j = 1, k = 0;
while(!Q.empty()) {
if(j == 2) {
j = 1;
a[Q.front()] = ++ k;
Q.pop();
}
Q.push(Q.front());
Q.pop();
++ j;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
cout << a[i] << ' ';
}
return 0;
}
思路2:对于正向过程,思路取反即其逆过程
题意:每次把最上方的扑克牌放在牌堆底,然后把下一张扑克牌拿出来输出
理解为:(序列中)每次把当前队首位放入队尾,然后拿出下一张输出,1~n
- 逆向:n~1,每次加入,然后将队尾元素放入队首
重要的点是要考虑顺序,顺序取反
P3405:map数组 +处理冲突
思路1:26字母(转换为int冲突>26即可处理),维护,每次加上它对应值能找到它的次数,然后将新映射数量增加(题目自己到自己为不合法)
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, ans = 0, base = 100;//26字母冲突,base>26即可处理冲突
string s,t;
map<int, int> m[100005];//map数组
int main(){
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i){
cin >> s >> t;
int S = s[0] * base + s[1], T = t[0] * base + t[1];//将两个字符转化成数字
if(S!=T){//特判,如果省市开头相同,不符合条件
ans += m[T][S];//所以T到S路径即对应
m[S][T] ++; //记录S到T路径
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
城市<=>州为一组互相对应,那么我,记录州到城市,每次查询城市是否能到州
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
map<string, int> m;
vector<string> s[200005];
int cnt, n;
int main() {
cin >> n;
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
string x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
string key = x.substr(0, 2);
if(m.count(key) && y != key) {
int x = m[key];
for(int i = 0; i < s[x].size(); ++ i) {
if(s[x][i] == y) ++ ans;
}
}
if(!m.count(y)) m[y] = ++ cnt;
s[m[y]].push_back(key);
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
P8889:二分,map/unordered_map,双指针
思路:
- hash:
点击查看代码
- 二分:排序b数组,对a中每个元素二分b中是否存在(求得l,当q[l]!=x即无x)
对于log(1e5) = 16,1e6的操作次数
- 双指针
点击查看代码
map了一个元素下标,然后clear[b],最后wa了...
B3691:简单版P8889:桶即可
记录一下切割好的写法
点击查看代码
int last = 0, ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
if(vis[a[i]]) {
if(i > last + 1) {//当切割点左边存在值才会切割
++ ans;
}
last = i;
}
}
if(last != n) ++ ans;//判一下截止点右边是否是答案
P7935:抽屉原理,拓扑序
思路:对于长度相等的全等序列 (A为1~n无重复序列),BC重复数字
- lenA = lenB = len,那么BC缺少数字(一定不是出现在解中) 压入队列,维护BC缺少的数字队列,每次删除对应列
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, ans;
int a[N], b[N], c[N], af[N], bf[N], cf[N], vis[N];
queue<int> Q;
int main() {
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
cin >> a[i], af[a[i]] = i;//存元素i的位置
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) cin >> b[i], bf[b[i]] ++;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) cin >> c[i], cf[c[i]] ++;
//维护1~n中bc序列未出现数
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
if(bf[i] == 0 || cf[i] == 0) {//未出现数字
Q.push(i);
while(!Q.empty()) {
auto x = Q.front();
Q.pop();
if(vis[af[x]]) continue;//标记位置已删除过,防止bc两个序列重复访问位置
vis[af[x]] = 1;
bf[b[af[x]]] --;//x是位置,b[x]才是值
cf[c[af[x]]] --;
if(bf[b[af[x]]] == 0) Q.push(b[af[x]]);//为0则不出现在最终序列,将其对应下标删除
if(cf[c[af[x]]] == 0) Q.push(c[af[x]]);
++ ans;
}
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
P5250:map + 查询大于/小于x的第一个数
对于map二分:
- 虚拟结点
mp[x] = 1;//置入虚拟结点,查询左右然后删除虚拟结点
- lower_bound(x)
auto it = lower_bound(x);//使用迭代器lower_bound(x)
点击查看代码
mp[x] = 1;//虚拟
auto it = mp.find(x);
auto it2 = it;
it ++;
// 几种特判
if (it2 == mp.begin()) {//最短
cout << it -> first << endl;
mp.erase(it);
}
else if (it == mp.end()) {//最长
cout << (-- it2) -> first << endl;
mp.erase(it2);
}
// 长度比较
else if (x - (-- it2) -> first > it -> first - x) {
cout << it -> first << endl;
mp.erase(it);
}
else {//左右长度相等,则删除一边
cout << it2 -> first << endl;
mp.erase(it2);
}
mp.erase(x);//删虚拟
P1090:Huffman树(小根堆)
思路:对于当前合并出来的可能并不是最小的两堆,因此要动态维护最小两堆果子去进行合并
huffman树,优先队列
P6704
思路:n个单调栈,因为置0所以单增栈永远不为空
P1160:链表(需要复习)





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号