Java if选择结构
Java if选择结构
if 单选择结构
- 我们很多时候需要去判断一个东西是否可行,然后我们才去执行,这样一个过程在程序中用if语句来表示
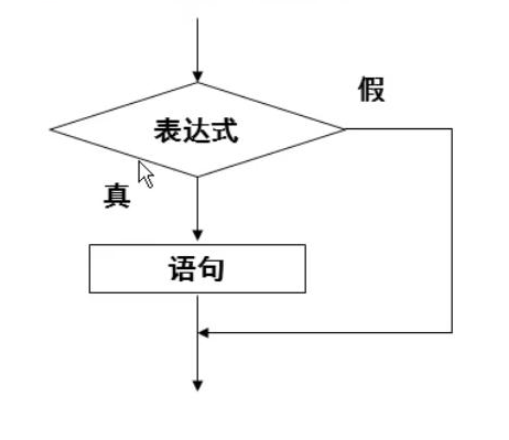
- 语法:
if(布尔表达式){
//如果布尔表达式为true将执行这里的语句
}
示例:
package com.shun.struct;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class IfDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//if单选择结构
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入内容:");
String s = scanner.nextLine();
//equals():判断字符串是否与括号中的相等
if (s.equals("Hello")){
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("and");
scanner.close();
}
}
if 双选择结构
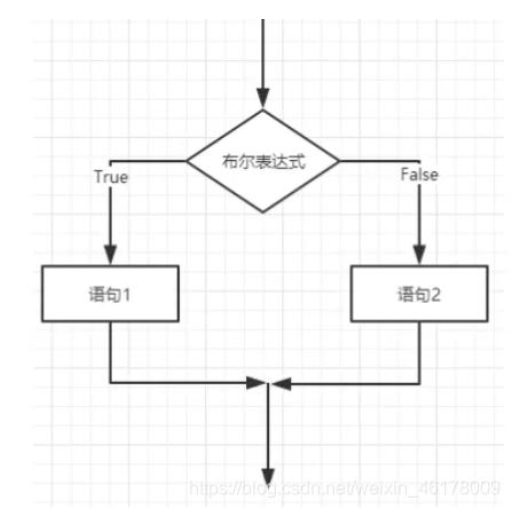
- 语法:
if(布尔表达式){
//如果布尔表达式为true将执行这里的语句
}else{
//如果布尔表达式为false将执行这里的语句
}
示例:
package com.shun.struct;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class IfDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//if双选择结构
//示例:考试分数大于60就是及格,小于60就是不及格
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入成绩:");
int score = scanner.nextInt();
if (score>=60){
System.out.println("及格");
}else{
System.out.println("不及格");
}
scanner.close();
}
}
if 多选择结构
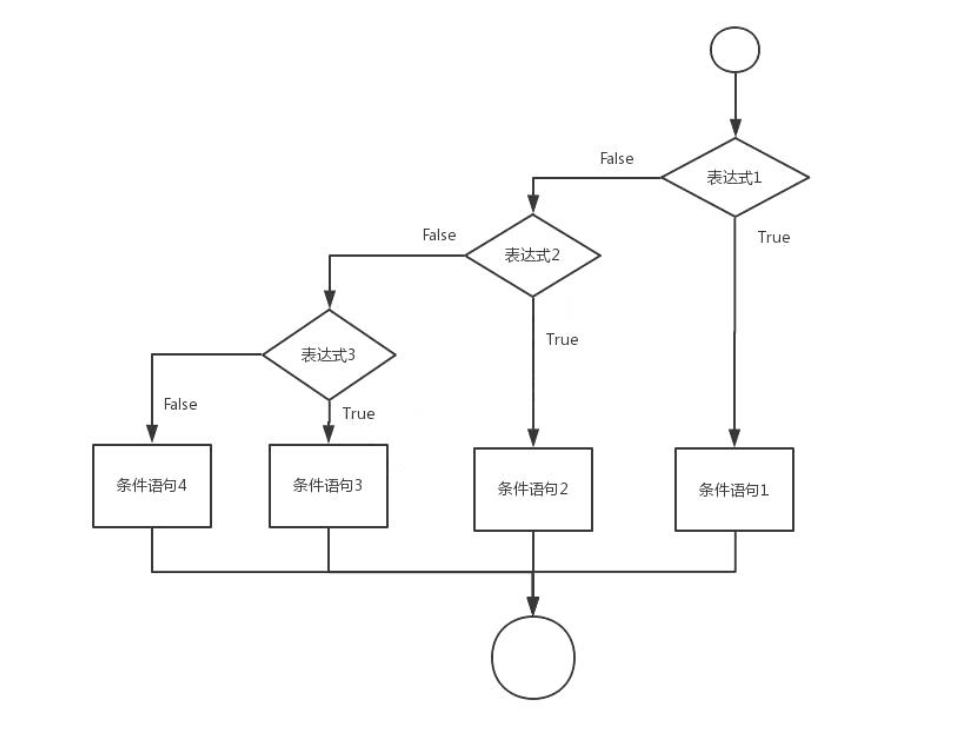
- 语法:
if(布尔表达式1){
//如果布尔表达式1为true将执行这里的语句
}else if(布尔表达式2){
//如果布尔表达式2为true将执行这里的语句
}else if(布尔表达式3){
//如果布尔表达式3为true将执行这里的语句
}else{
//如果以上布尔表达式都不为true将执行这里的语句
}
示例:
package com.shun.struct;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class IfDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//if多选择结构
/*
if语句至多有1个else语句,else语句在所有的else if 语句之前
if语句可以有若干个else if 语句,它们必须在else 语句之前
一旦其中一个else if 语句检测为true,其他的else if 以及 else语句都将跳过执行。
*/
//示例:考试分数大于60就是及格且分为ABCD,小于60就是不及格
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入成绩:");
int score = scanner.nextInt();
if (score==100){
System.out.println("恭喜获得满分");
}else if (score>=90 && score<100){
System.out.println("A");
}else if (score>=80 && score<90){
System.out.println("B");
}else if (score>=70 && score<80){
System.out.println("C");
}else if (score>=60 && score<70){
System.out.println("D");
}else if (score>=0 && score<6100){
System.out.println("不及格");
}else{
System.out.println("成绩不合法");
}
scanner.close();
}
}
嵌套的 if 结构
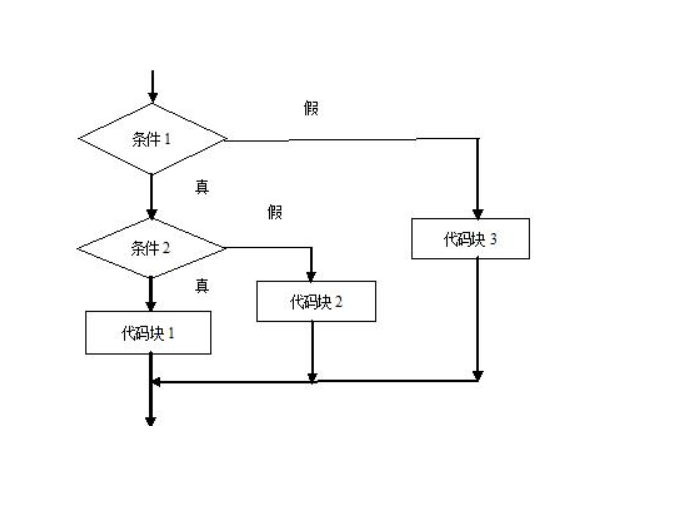
- 语法:
if(布尔表达式1){
//如果布尔表达式1为true将执行这里的语句
if(布尔表达式2){
//如果布尔表达式2为true将执行这里的语句
}else{
//如果布尔表达式2为false将执行这里的语句
}
}else{
//如果布尔表达式1为false将执行这里的语句
}
示例:
package com.shun.struct;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class IfDemo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//嵌套的if结构
//示例:输入考试成绩并判断是否是优秀成绩(>=80)
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入考试成绩:");
int score = scanner.nextInt();
if (score>=60 && score<=100){
if (score>=80){
System.out.println("恭喜及格,而且是优秀成绩");
}else{
System.out.println("恭喜及格");
}
}else if(score<60 && score>=0){
System.out.println("成绩不及格");
}else{
System.out.println("成绩不合法");
}
scanner.close();
}
}







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号