HDLBits(12)2.22
3 电路
3.1 组合逻辑
3.1.2 数据选择器/多路复用器(Multiplexers)(MUX)
- Mux2to1(2-to-1 multiplexers)
创建位宽为 1 的 2 对 1 数据选择器。当 sel=0 时,选择 a。当 sel=1 时,选择 b
module top_module(
input a, b, sel,
output out );
assign out = sel?b:a;
endmodule
- Mux2to1v(2-to-1 bus multiplexers)
创建位宽为 100 的 2 对 1 数据选择器。当 sel=0 时,选择 a。当 sel=1 时,选择 b
module top_module(
input [99:0] a, b,
input sel,
output [99:0] out );
assign out = sel ? b : a;
endmodule
- Mux9to1(9-to-1 multiplexers)
创建位宽为 16 的 9 对 1 数据选择器。当 sel=0 时,选择 a。当 sel=1 时,选择 b,以此类推,对于未使用的情况(sel = 9 to 15)输出位为1
module top_module(
input [15:0] a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i,
input [3:0] sel,
output [15:0] out );
always @(*)
begin
case(sel)
0: out = a ;
1: out = b ;
2: out = c ;
3: out = d ;
4: out = e ;
5: out = f ;
6: out = g ;
7: out = h ;
8: out = i ;
default out = {16{1'b1}}; //复制操作符
endcase
end
endmodule
- Mux256to1(256-to-1 multiplexers)
创建位宽为 1 的 256 对 1 的数据选择器,将 256 个输入全部打包成一个 256 位的输入向量。sel=0 应该选择in[0], sel=1 选择[1]中的位, sel=2 选择[2]中的位,以此类推
module top_module(
input [255:0] in,
input [7:0] sel,
output out );
assign out = in[sel];
endmodule
- Mux256to1v(256-to-1 4-bit multiplexers)
创建位宽为 4 的 256 对 1 的数据选择器,将 256 个 4 位输入全部打包成一个 1024 位的输入向量。sel=0 应该选择 [3:0] 中的位, sel=1 选择 [7:4] 中的位, sel=2 选择 [11:8] 中的位,以此类推
module top_module(
input [1023:0] in,
input [7:0] sel,
output [3:0] out );
assign out = {in[sel*4+3],in[sel*4+2],in[sel*4+1],in[sel*4]};
endmodule
3.1.3 运算电路(Arithmetic Circuits)
- Hadd(Half adder)
创建一个半加法器。半加器将两位相加(没有进位)得到加和和进位
module top_module(
input a, b,
output cout, sum );
assign sum = a ^ b ;
assign cout = a & b ;
endmodule
- Fadd(Full adder)
创建一个全加器,全加器将三位相加(包括进位)并产生加和和进位
module top_module(
input a, b, cin,
output cout, sum );
assign sum = a^b^cin;
assign cout = a&b | a&cin | b&cin;
endmodule
- Adder3(3-bit binary adder)
创建 3 个实例来创建一个 3 位二进制波纹进位加法器。加法器将两个 3 位数字和一个进位相加产生一个 3 位加和和进位。为了鼓励实例化全加器,还要输出纹波进位加法器中每个全加器的进位。cout[2] 是最后一个全加器的最终进位,也是通常看到的进位。
module top_module(
input [2:0] a, b,
input cin,
output [2:0] cout,
output [2:0] sum );
add1 u1 (.a(a[0]),.b(b[0]),.cin(cin),.sum(sum[0]),.cout(cout[0])); //按名称连接端口以实例化模块
add1 u1 (.a(a[1]),.b(b[1]),.cin(cout[0]),.sum(sum[1]),.cout(cout[1]));
add1 u1 (.a(a[2]),.b(b[2]),.cin(cout[1]),.sum(sum[2]),.cout(cout[2]));
endmodule
module add1 (input a, input b, input cin, output sum, output cout);
assign sum = a^b^cin;
assign cout = a&b | a&cin | b&cin;
endmodule//用generate实现,直接定义逻辑,未例化模块,适用于逻辑不复杂的多模块电路
module top_module(
input [2:0] a, b,
input cin,
output [2:0] cout,
output [2:0] sum );
genvar i;
generate
for(i=0;i<3;i=i+1) begin:adder
if(i==0)
begin
assign sum[i] = a[i]^b[i]^cin;
assign cout[i] = a[i]&b[i] | a[i]&cin | b[i]&cin;
end
else
begin
assign sum[i]=a[i]^b[i]^cout[i-1];
assign cout[i]=a[i]&b[i] | a[i]&cout[i-1] | b[i]&cout[i-1];
end
end
endgenerate
endmodule
- Adder
实现下图电路,其中FA为加法器
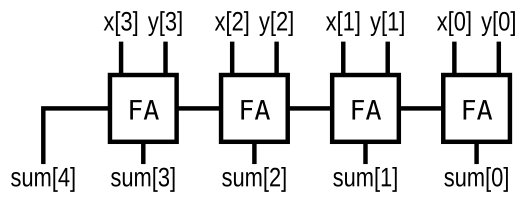
module top_module(
input [3:0] x,
input [3:0] y,
output [4:0] sum);
wire [3:0] cout; //未声明进位,故此处以线性信号声明进位(cout)作为中间变量
genvar i;
generate //用generate实现多模块重复例化
for(i=0;i<4;i=i+1) begin:adder
if(i==0)
FA u1 (.a(x[0]),.b(y[0]),.sum(sum[0]),.cout(cout[0]));
else
FA u1 (.a(x[i]),.b(y[i]),.cin(cout[i-1]).sum(sum[i]),.cout(cout[i]));
end
assign sum[4] = cout[3];
endgenerate
endmodule
module FA (input a, input b, input cin, output sum, output cout);
assign sum = a^b^cin;
assign out = a&b | a&cin | b&cin;
endmodule//这种写法也是成立且正常工作的,但不确定是否有什么缺陷
module top_module (
input [3:0] x,
input [3:0] y,
output [4:0] sum
);
assign sum = x+y;
endmodule- signed addition overflow
假设有两个 8 位的补码,a[7:0] 和 b[7:0]。这些数字相加产生 s[7:0]。还要计算是否发生了(有符号的)溢出。
* 当两个正数相加产生负结果或两个负数相加产生正结果时,会发生有符号溢出。有几种检测溢出的方法:可以通过比较输入和输出数的符号来计算,或者从位 n 和 n-1 的进位推导出。
module top_module (
input [7:0] a,
input [7:0] b,
output [7:0] s,
output overflow
);
assign s = a+b;
assign overflow = (a[7]&b[7]&~s[7])|(~a[7]&~b[7]&s[7]);
endmodule- 100-bit binary adder
创建一个100 位二进制加法器。加法器将两个 100 位数字和一个进位相加,产生一个 100 位加和和进位。
module top_module(
input [99:0] a, b,
input cin,
output cout,
output [99:0] sum );
assign {cout,sum} = a+b+cin;
endmodule- 4-digit BCD adder
实例化四个 bcd_fadd 副本以创建一个4位BCD(binary-coded decimal 二进制编码的十进制)波纹进位加法器。加法器应将两个4位BCD数字(打包成16位向量)和一个进位相加,以产生一个4位加和和进位
module top_module (
input [15:0] a, b,
input cin,
output cout,
output [15:0] sum );
wire cout1, cout2, cout3;
bcd_fadd u0(
.a(a[3:0]),
.b(b[3:0]),
.cin(cin),
.cout(cout1),
.sum(sum[3:0]));
bcd_fadd u1(
.a(a[7:4]),
.b(b[7:4]),
.cin(cout1),
.cout(cout2),
.sum(sum[7:4]));
bcd_fadd u2(
.a(a[11:8]),
.b(b[11:8]),
.cin(cout2),
.cout(cout3),
.sum(sum[11:8]));
bcd_fadd u3(
.a(a[15:12]),
.b(b[15:12]),
.cin(cout3),
.cout(cout),
.sum(sum[15:12]));
endmodule*会产生Warning:
Warning (10230): Verilog HDL assignment warning at tb_modules.sv(8):
truncated value with size 32 to match size of target (4)
File: /home/h/work/hdlbits.9423193/tb_modules.sv Line: 8Truncating values occur when the right side of an assignment is wider than the left side and the upper bits are cut off. This can indicate a bug if there is a truncation you didn't expect, so check these carefully. The most common case where this isn't a bug is when you're using literals without a width (32 bits is implied), e.g., using assign a[1:0] = 1; instead of assign a[1:0] = 2'd1;
暂不知原因


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号