invokeAny与执行快的任务异常
1 package Seven_invokeAny_Fast_Demo1; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.Callable; 4 5 public class MyCallableA implements Callable<String> { 6 7 @Override 8 public String call() throws Exception { 9 System.out.println("MyCallableA" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " begin " + System.currentTimeMillis()); 10 for (int i = 0; i < 123; i++) { 11 String newString = new String(); 12 Math.random(); 13 Math.random(); 14 Math.random(); 15 Math.random(); 16 Math.random(); 17 System.out.println("MyCallableA 在运行中= " + (i + 1)); 18 } 19 20 if (1 == 1) { 21 System.out.println("xxxxxxxxxxx=中断了"); 22 throw new NullPointerException(); 23 } 24 25 System.out.println("MyCallableA" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " end " + System.currentTimeMillis()); 26 27 return "return---A"; 28 } 29 30 }
1 package Seven_invokeAny_Fast_Demo1; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.Callable; 4 5 public class MyCallableB implements Callable<String> { 6 7 @Override 8 public String call() throws Exception { 9 System.out.println("MyCallableB" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " begin " + System.currentTimeMillis()); 10 for (int i = 0; i < 223; i++) { 11 String newString = new String(); 12 Math.random(); 13 Math.random(); 14 Math.random(); 15 Math.random(); 16 Math.random(); 17 System.out.println("MyCallableB 在运行中= " + (i + 1)); 18 } 19 20 System.out.println("MyCallableB" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " end " + System.currentTimeMillis()); 21 22 return "return---B"; 23 } 24 25 }
1 package Seven_invokeAny_Fast_Demo1; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.List; 5 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; 6 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 7 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 8 9 public class Run { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 try { 13 14 List list = new ArrayList(); 15 16 list.add(new MyCallableB()); 17 list.add(new MyCallableA()); 18 19 ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); 20 21 String getString; 22 23 getString = (String) service.invokeAny(list); 24 System.out.println("main取得返回值=" + getString); 25 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 26 System.out.println("main Interrupted_Exception"); 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } catch (ExecutionException e) { 29 System.out.println("main Execution_Exception"); 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } 32 33 } 34 35 }
运行结果:
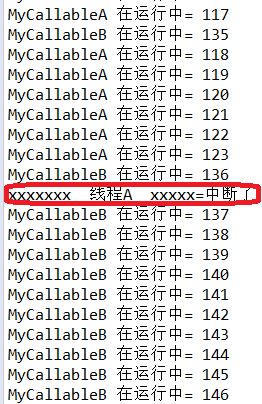
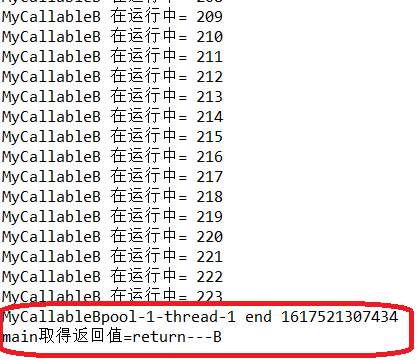
分析:
线程A是执行快的线程,线程B是执行慢的线程。线程A中断了,所以主线程中没有获取到A的返回值,线程A先执行完毕后,线程池将B设置为中断interrupte,但是线程B中没有对这个中断进行处理,所以线程B继续执行,不受影响。最终的结果是,线程B正常执行完毕,主线程中获取到线程B中return的值。
(2)倘若在执行快的线程A中,使用try_catch的方式对中断异常进行捕获
1 package Seven_invokeAny_Fast_Demo1; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.Callable; 4 5 public class MyCallableA implements Callable<String> { 6 7 @Override 8 public String call() throws Exception { 9 System.out.println("MyCallableA" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " begin " + System.currentTimeMillis()); 10 11 try{ 12 for (int i = 0; i < 123; i++) { 13 String newString = new String(); 14 Math.random(); 15 Math.random(); 16 Math.random(); 17 Math.random(); 18 Math.random(); 19 System.out.println("MyCallableA 在运行中= " + (i + 1)); 20 } 21 22 if (1 == 1) { 23 System.out.println("xxxxxxxxxxx=中断了"); 24 throw new NullPointerException(); 25 } 26 27 System.out.println("MyCallableA" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " end " + System.currentTimeMillis()); 28 }catch(Exception e){ 29 System.out.println(e.getMessage()+" : 左边信息就是捕获的异常信息"); 30 } 31 32 return "return---A"; 33 } 34 35 }
运行结果:
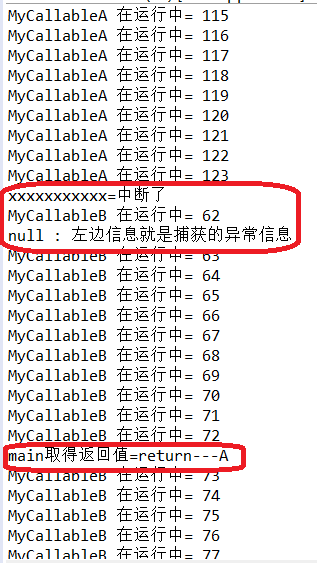
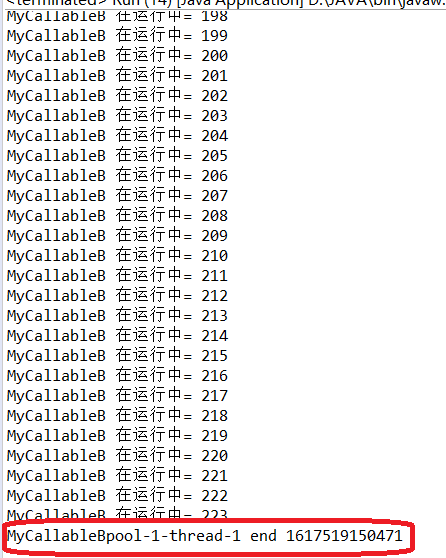
分析:
在A中进行了try_catch捕获中断异常,但是没有进行重新抛出异常。所带来的结果就是,主线程main获取到的不是没有异常的B线程的返回值,而是有中断异常的A线程的返回值。
这是因为,A线程虽然有中断异常,但是用try_cathch捕获后却没有重新抛出异常。导致主线程main误认为线程A是正确的,所以主线程main正常获取A的返回值,至于线程B,因为没有 对invokeAny()获取到第一个值(线程A的返回值)后调用的interrupt()方法发出的中断进行处理,所以线程B正常运行,只是最终主线程不获取线程B的返回值而已(因为之前主线程已经获取了线程A的返回值)。
(3)在线程A中,使用try_catch捕获中断异常后又重新抛出
1 package Seven_invokeAny_Fast_Demo1; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.Callable; 4 5 public class MyCallableA implements Callable<String> { 6 7 @Override 8 public String call() throws Exception { 9 System.out.println("MyCallableA" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " begin " + System.currentTimeMillis()); 10 11 try{ 12 for (int i = 0; i < 123; i++) { 13 String newString = new String(); 14 Math.random(); 15 Math.random(); 16 Math.random(); 17 Math.random(); 18 Math.random(); 19 System.out.println("MyCallableA 在运行中= " + (i + 1)); 20 } 21 22 if (1 == 1) { 23 System.out.println("xxxxxxxxxxx=中断了"); 24 throw new NullPointerException(); 25 } 26 27 System.out.println("MyCallableA" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " end " + System.currentTimeMillis()); 28 }catch(Exception e){ 29 System.out.println(e.getMessage()+" : 左边信息就是捕获的异常信息"); 30 31 throw e;//重新抛出异常 32 } 33 34 return "return---A"; 35 } 36 37 }
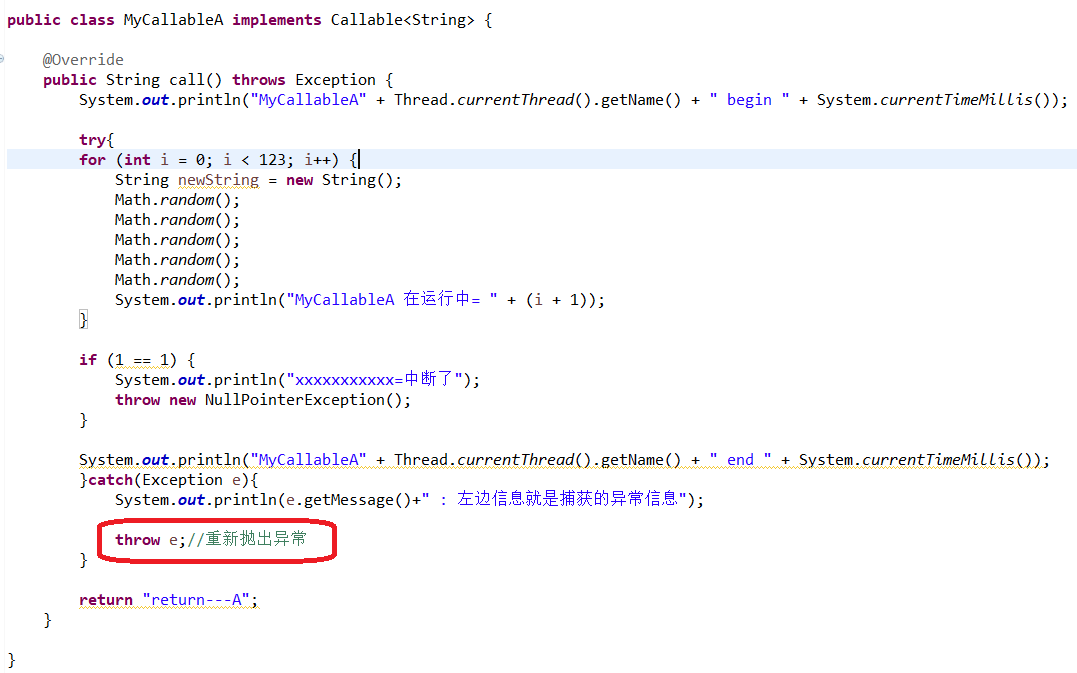
运行结果:
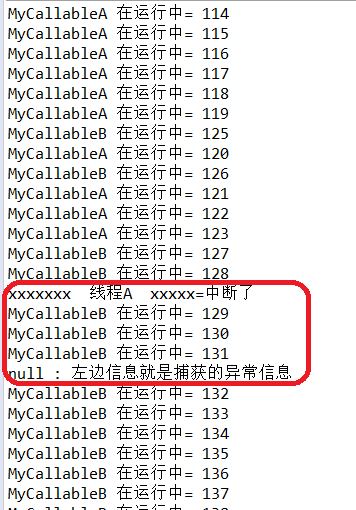

分析:
可以看到线程A通过try_catch捕获到中断异常,有采用 throw e将这个异常抛出,主线程main中就不会获得A的返回值,而是获得B的返回值



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号