Future
1. cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning)和isCancelled()
1 package Five_cancel_and_isCancelled; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.Callable; 4 5 public class MyCallable implements Callable<String> { 6 7 @Override 8 public String call() throws Exception { 9 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 10 System.out.println("begin : " + System.currentTimeMillis()); 11 Thread.sleep(2000); 12 System.out.println("end : " + System.currentTimeMillis()); 13 return "我的年龄是2000"; 14 } 15 16 }
1 package Five_cancel_and_isCancelled; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; 4 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 5 import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque; 6 import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; 7 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 8 import java.util.concurrent.Future; 9 10 public class Test { 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { 13 14 MyCallable mc = new MyCallable(); 15 16 ExecutorService executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(50, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS, 17 new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>()); 18 19 Future<String> f = executor.submit(mc); 20 System.out.println(f.get()); 21 System.out.println(f.cancel(true) + "----------" + f.isCancelled()); 22 } 23 }
运行结果:
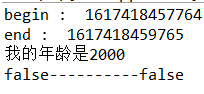
分析:
线程已经运行完毕,线程对象已经销毁,所以方法cancel(true)的返回值是false,代表发送中断线程的命令没有成功。因为这个命令中的参数的作用是:如果线程正在运行,则发送中断线程的命令。而线程已经运行结束了,所以没有满足这个命令执行的条件,所以命令没有执行成功。
修改:将这行代码注释掉
//System.out.println(f.get());
运行结果:
true----------true
成功中断正在执行中的线程。
分析:
将这行注释掉,意味着没有取线程的返回值,那么线程就一直在call()方法中运行,直到接到了取返回值的命令,才会走到return,这时也意味着线程执行结束。
2. Future的缺点
Future接口调用get()方法取得处理结果时是阻塞性的,就是说如果你调用了这个方法,它没有取到值,那么就会一直等在这儿,直到取到值为止,然后下面的程序才能接着运行。
这样带来的问题就是:如果当前分支线程执行的任务很多,那么在主线程使用get()方法调用这个分支线程的返回值的程序会一直阻塞在这里,直到分支线程运行完毕并返回值,而在这个过程中,主线程get()方法后面的程序将无法运行,就一直在这里排队等待,这样会大大影响运行的效率,也就是说主线程不能保证首先获得的是最先完成任务的返回值。
1 package Five_Future_Shortcoming; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.Callable; 4 5 public class MyCallable implements Callable<String> { 6 7 private String username; 8 private long sleepValue; 9 10 public MyCallable(String username, long sleepValue) { 11 super(); 12 this.username = username; 13 this.sleepValue = sleepValue; 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public String call() throws Exception { 18 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 19 System.out.println(username); 20 Thread.sleep(sleepValue); 21 return "return " + username; 22 } 23 24 }
1 package Five_Future_Shortcoming; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque; 4 import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; 5 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 6 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; 7 import java.util.concurrent.Future; 8 9 public class Test { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { 12 13 MyCallable mc1 = new MyCallable("uer-1", 5000); 14 MyCallable mc2 = new MyCallable("uer-2", 4000); 15 MyCallable mc3 = new MyCallable("uer-3", 3000); 16 MyCallable mc4 = new MyCallable("uer-4", 2000); 17 MyCallable mc5 = new MyCallable("uer-5", 1000); 18 19 ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS, 20 new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>()); 21 22 Future<String> f1 = executor.submit(mc1); 23 Future<String> f2 = executor.submit(mc2); 24 Future<String> f3 = executor.submit(mc3); 25 Future<String> f4 = executor.submit(mc4); 26 Future<String> f5 = executor.submit(mc5); 27 28 System.out.println("Run first time : " + System.currentTimeMillis()); 29 30 System.out.println(f1.get() + "----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 31 System.out.println(f2.get() + "----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 32 System.out.println(f3.get() + "----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 33 System.out.println(f4.get() + "----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 34 System.out.println(f5.get() + "----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 35 36 37 38 } 39 40 }
运行结果:
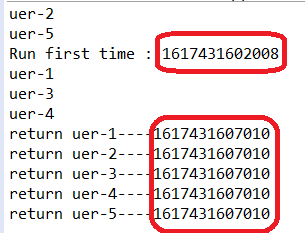
分析:
线程uer-1,睡眠的时间最长,为5秒钟,而在主线程中,第一个调用的就是uer-1的返回值,所以在主线程中,其他get()方法一直在等待uer-1的值get到之后才能运行,而uer-1的get()在等待uer-1线程执行完毕再返回值,所以就造成主线程里其它线程get的阻塞。
如果将get的顺序换过来,先get睡眠时间最短的
1 package Five_Future_Shortcoming; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque; 4 import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; 5 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 6 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; 7 import java.util.concurrent.Future; 8 9 public class Test { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { 12 13 MyCallable mc1 = new MyCallable("uer-1", 5000); 14 MyCallable mc2 = new MyCallable("uer-2", 4000); 15 MyCallable mc3 = new MyCallable("uer-3", 3000); 16 MyCallable mc4 = new MyCallable("uer-4", 2000); 17 MyCallable mc5 = new MyCallable("uer-5", 1000); 18 19 ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS, 20 new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>()); 21 22 Future<String> f1 = executor.submit(mc1); 23 Future<String> f2 = executor.submit(mc2); 24 Future<String> f3 = executor.submit(mc3); 25 Future<String> f4 = executor.submit(mc4); 26 Future<String> f5 = executor.submit(mc5); 27 28 System.out.println("Run first time : " + System.currentTimeMillis()); 29 30 31 32 System.out.println(f5.get() + "----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 33 System.out.println(f4.get() + "----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 34 System.out.println(f3.get() + "----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 35 System.out.println(f2.get() + "----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 36 System.out.println(f1.get() + "----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 37 38 } 39 40 }
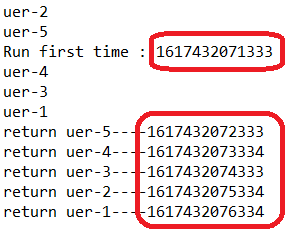
注:使用CompletionService接口可以解决这个问题
1 package Five_Future_Shortcoming; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque; 4 import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; 5 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 6 import java.util.concurrent.CompletionService; 7 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; 8 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorCompletionService; 9 10 public class Test1 { 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { 13 14 MyCallable mc1 = new MyCallable("uer-1", 5000); 15 MyCallable mc2 = new MyCallable("uer-2", 4000); 16 MyCallable mc3 = new MyCallable("uer-3", 3000); 17 MyCallable mc4 = new MyCallable("uer-4", 2000); 18 MyCallable mc5 = new MyCallable("uer-5", 1000); 19 20 ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS, 21 new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>()); 22 23 CompletionService csRef = new ExecutorCompletionService(executor); 24 25 csRef.submit(mc1); 26 csRef.submit(mc2); 27 csRef.submit(mc3); 28 csRef.submit(mc4); 29 csRef.submit(mc5); 30 31 System.out.println("Run first time : " + System.currentTimeMillis()); 32 33 System.out.println(csRef.take().get() + "----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 34 System.out.println(csRef.take().get() + "----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 35 System.out.println(csRef.take().get() + "----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 36 System.out.println(csRef.take().get() + "----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 37 System.out.println(csRef.take().get() + "----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 38 39 } 40 41 }
运行结果:
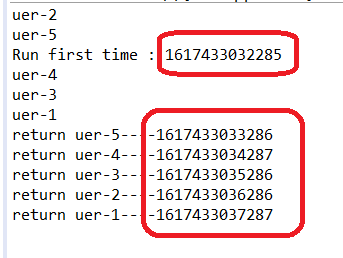
可以看到,哪个线程先执行完,哪个任务的返回值就先打印。解决了Future阻塞的特性。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号