排序算法
1.冒泡排序
1 package PaiXu; 2 /* 3 * 每一趟比较,把最大的数沉下去 4 */ 5 public class MaoPaoDemo2 { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args){ 8 int a[]={1,3,5,7,8,6,2,0,11,13,20,18,16}; 9 int temp; 10 for(int i=0;i<a.length-1;i++){ 11 for(int j=0;j<a.length-1-i;j++){ 12 if(a[j]>a[j+1]){ 13 temp=a[j+1]; 14 a[j+1]=a[j]; 15 a[j]=temp; 16 } 17 } 18 19 } 20 21 for(int data:a){ 22 System.out.print(data+" "); 23 } 24 } 25 26 }
运行结果:
0 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 11 13 16 18 20
1.2冒泡算法优化
若发现某趟排序中,没有发生数据交换,则证明顺序已经排好,不用进行后面的比较排序工作
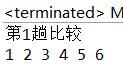
1 package PaiXu; 2 /* 3 * 每一趟比较,把最大的数沉下去 4 * 算法优化:当某一天趟未出现数据交换时,说明顺寻已经排好,不用再进行后面的排序工作 5 */ 6 public class MaoPaoDemo3 { 7 public static void main(String[] args){ 8 //int a[]={1,3,5,7,8,6,2,0,11,13,20,18,16}; 9 int a[]={1,2,3,4,5,6}; 10 int temp; 11 boolean flag=true; 12 for(int i=0;i<a.length-1;i++){ 13 System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"趟比较"); 14 for(int j=0;j<a.length-1-i;j++){ 15 if(a[j]>a[j+1]){ 16 temp=a[j+1]; 17 a[j+1]=a[j]; 18 a[j]=temp; 19 flag=false; 20 } 21 } 22 if(flag){ 23 break; 24 } 25 26 } 27 28 for(int data:a){ 29 System.out.print(data+" "); 30 } 31 } 32 }
运行结果:
1.3 算法复杂度
O(n^2)
2.选择排序算法
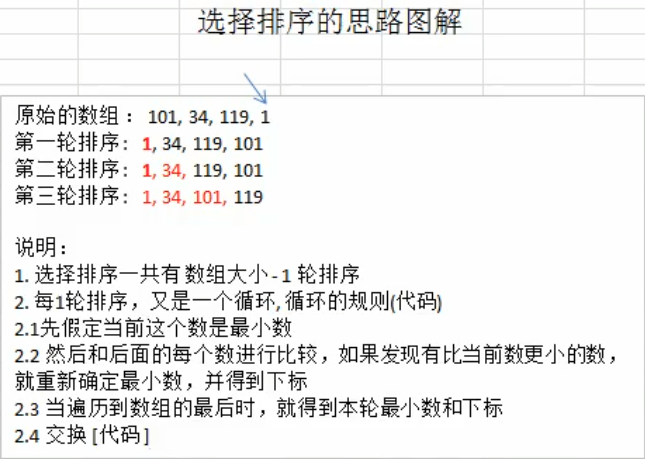
2.1选择排序算法思想

2.2 选择排序算法思路
2.3 代码实现
1 package PaiXu; 2 3 public class XuanZeDemo { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args){ 6 int a[]={1,3,5,7,8,6,2,0,11,13,20,18,16}; 7 int temp; 8 for(int i=0;i<a.length-1;i++){ 9 for(int j=(i+1);j<a.length;j++){ 10 if(a[i]>a[j]||a[i]==a[j]){ 11 temp=a[j]; 12 a[j]=a[i]; 13 a[i]=temp; 14 } 15 16 } 17 } 18 for(int num:a){ 19 System.out.print(num+" "); 20 } 21 } 22 }
运行结果:
0 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 11 13 16 18 20
2.4 算法复杂度
O(n^2)
3.插入排序算法
1 package PaiXu; 2 /* 3 * 插入排序算法 4 */ 5 public class ChaRuDemo { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args){ 8 int a[]={1,3,5,7,8,6,2,0,11,13,20,18,16}; 9 int index; 10 int value; 11 12 for(int i=1;i<a.length;i++){ 13 value=a[i]; 14 index=i-1; 15 16 while(index>-1&&value<a[index]){ 17 a[index+1]=a[index]; 18 index--; 19 } 20 21 a[index+1]=value; 22 } 23 24 25 for(int data:a){ 26 System.out.print(data+" "); 27 } 28 } 29 30 }
运行结果:
0 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 11 13 16 18 20
3.1 算法复杂度
4.希尔排序算法
希尔排序是希尔(Donald Shell)于1959年提出的一种排序算法。希尔排序也是一种插入排序,它是简单插入排序经过改进之后的一个更高效的版本,也称为缩小增量排序,同时该算法是冲破O(n2)的第一批算法之一。
简单插入排序很循规蹈矩,不管数组分布是怎么样的,依然一步一步的对元素进行比较,移动,插入,比如[5,4,3,2,1,0]这种倒序序列,数组末端的0要回到首位置很是费劲,比较和移动元素均需n-1次。而希尔排序在数组中采用跳跃式分组的策略,通过某个增量(gap)将数组元素划分为若干组,然后分组进行插入排序,随后逐步缩小增量,继续按组进行插入排序操作,直至增量为1。希尔排序通过这种策略使得整个数组在初始阶段达到从宏观上看基本有序,小的基本在前,大的基本在后。然后缩小增量,到增量为1时,其实多数情况下只需微调即可,不会涉及过多的数据移动。
我们来看下希尔排序的基本步骤,在此我们选择增量gap=length/2,缩小增量继续以gap = gap/2的方式,这种增量选择我们可以用一个序列来表示,{n/2,(n/2)/2...1},称为增量序列。希尔排序的增量序列的选择与证明是个数学难题,我们选择的这个增量序列是比较常用的,也是希尔建议的增量,称为希尔增量,但其实这个增量序列不是最优的。此处我们做示例使用希尔增量。
5.快速排序算法
快速排序实现的重点在于数组的拆分,通常将数组的第一个元素定义为比较元素,然后将数组中小于比较元素的数放到左边,将大于比较元素的放到右边,
这样就将数组拆分成了左右两部分:小于比较元素的数组;大于比较元素的数组。再对这两个数组进行同样的拆分,直到拆分到不能再拆分,数组就自然而然地以升序排列了。
1 package PaiXu; 2 3 public class KuaiSuDemo { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 int[] a={23,45,17,11,13,89,72,26,3,17,11,13}; 6 QuickSort(a,0,a.length-1); 7 for(int data:a){ 8 System.out.print(data+" "); 9 } 10 11 } 12 13 /* 14 * 对传过来的数组进行处理,将数组的首位元素设定为参考元素, 15 * 然后从两边遍历数组,将大于参考元素的数放到其右边,小于的放到左边 16 * 从右边先开始 17 * 最终返回参考元素的位置 18 */ 19 public static int PaiXu(int[] a,int left,int right){ 20 int temp=a[left];//暂存当前数组的首个元素 21 22 while(left<right){ 23 //从数组右边开始往左看,直到遇到的数小于temp 24 while(left<right&&a[right]>=temp){ 25 right--; 26 } 27 a[left]=a[right];//将小于temp的值赋给temp左边,left指向的位置。 28 29 while(left<right&&a[left]<=temp){ 30 left++; 31 } 32 a[right]=a[left]; 33 34 } 35 36 a[left]=temp;//将之前保存的数组首位元素放入此时left指针指向的位置 37 return left;//将当前left指针所在位置返回,及返回当前已处理好的数组的分界位置 38 39 40 } 41 42 // 43 public static void QuickSort(int[] a,int left,int right){ 44 45 int index=0; 46 if(left<right){//当left=right时,说明当前数组中只有一个元素,无序再进行排序 47 index=PaiXu(a,left,right); 48 QuickSort(a,left,index-1); 49 QuickSort(a,index+1,right); 50 } 51 } 52 53 }
6.归并排序算法
6.1 基本思想
归并排序是利用归并的思想实现的排序方法,该算法采用经典的分治策略(分治法将问题分成一些小的问题然后递归求解,而治的阶段则将分的阶段得到的各答案"修补"在一起,即分而治之)。
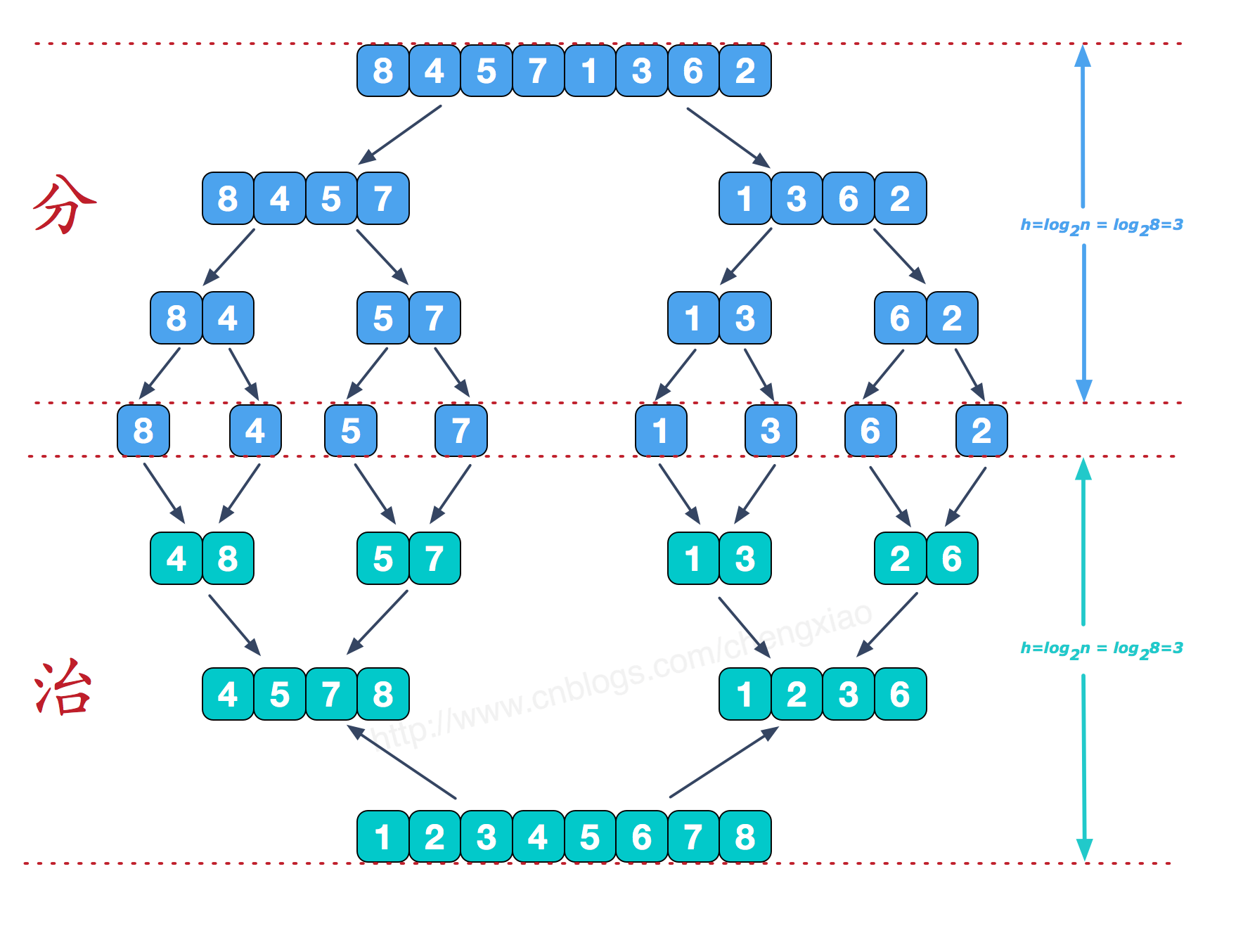
可以看到这种结构很像一棵完全二叉树,本文的归并排序采用递归去实现(也可采用迭代的方式去实现)。分阶段可以理解为就是递归拆分子序列的过程,递归深度为log2n。
6.2 合并相邻有序子序列
再来看看治阶段,我们需要将两个已经有序的子序列合并成一个有序序列,比如上图中的最后一次合并,要将[4,5,7,8]和[1,2,3,6]两个已经有序的子序列,合并为最终序列[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8],来看下实现步骤。

1 package PaiXu; 2 3 public class GuiBingDemo { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args){ 6 int[] a={8,9,1,7,2,3,5,4,6,0}; 7 int[] temp=new int[a.length]; 8 Sort(a,0,a.length-1,temp); 9 10 for(int data:a){ 11 System.out.print(data+" "); 12 } 13 14 } 15 16 17 public static void Sort(int[]a,int left,int right,int[] temp){ 18 if(left<right){ 19 int mid=(left+right)/2; 20 Sort(a,left,mid,temp); 21 Sort(a,mid+1,right,temp); 22 23 24 //将两个有序数组合并为一个有序数组 25 PaiXu(a,left,right,mid,temp); 26 } 27 } 28 29 30 public static void PaiXu(int[]a,int left,int right,int mid,int[] temp){ 31 int i=left; 32 int j=mid+1; 33 int index=0; 34 while(i<=mid&&j<=right){ 35 if(a[i]<a[j]){ 36 temp[index]=a[i]; 37 i++; 38 }else{ 39 temp[index]=a[j]; 40 j++; 41 } 42 index++; 43 } 44 45 while(i<=mid){ 46 temp[index]=a[i]; 47 index++; 48 i++; 49 } 50 51 while(j<=right){ 52 temp[index]=a[j]; 53 index++; 54 j++; 55 } 56 57 58 //将合并好后的临时数组复制到原数组a 59 index=0; 60 for(int k=left;k<=right;k++){ 61 a[k]=temp[index]; 62 index++; 63 } 64 65 } 66 }
运行结果:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
7.基数排序算法
基数排序适合于有不同位数的大小数字
7.1 核心思想
先找十个桶:0~9
第一轮按照元素的个位数排序
桶内分别存放上述数组元素的个位数,按照数组元素的顺序依次存放

之后,按照从左向右,从上到下的顺序依次取出元素,组成新的数组。
![]()
在新的数组中,进行第二轮,按照十位数排序,依次存放于桶中:
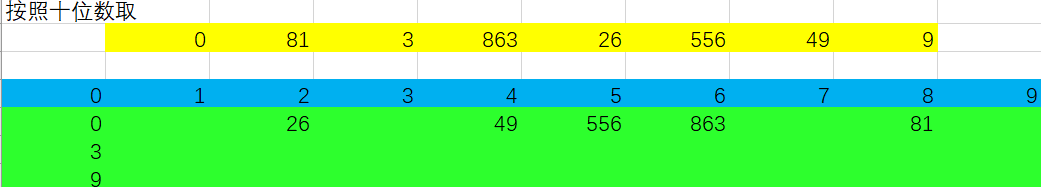
按照之前的顺序取出,组成新的数组。
进行第三轮,按照百位数排序:
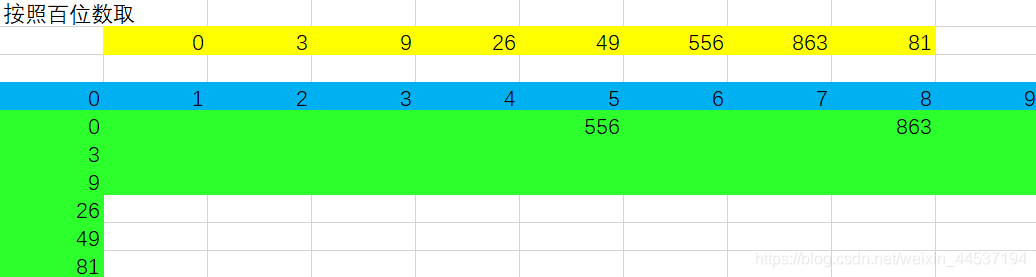
将百位数的元素取出之后,我们发现新的数组已经变成了有序数组
![]()
7.2 代码
1 package PaiXu; 2 3 public class JiShuDemo { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 int[] a={26,3,38,66,88,188,881,999,1,12,88,58,6006,9,0}; 6 Sort(a); 7 } 8 9 10 public static void Sort(int[] a){ 11 int le=getMax(a); 12 int[][]temp=new int[10][a.length];//用二维数组表示某个数存放在第几个桶的第几位 13 int []count=new int[10];//用来定位在某个桶中的哪一个位置 14 int index; 15 for(int i=0;i<le;i++){ 16 for(int j=0,n=1;j<a.length;j++,n*=10){ 17 index=(a[j]/n)%10; 18 19 //count[index]中index代表是哪个桶,而count[index]的值代表标号为index的桶中当前元素的位置,也即当前数据在标号为index的桶中的位置 20 temp[index][count[index]]=a[j]; 21 count[index]++; 22 } 23 24 //将各个桶中的数取出来 25 int l=0; 26 for(int m=0;m<10;m++){ 27 for(int k=0;k<count[m];k++){ 28 a[l]=temp[m][k]; 29 l++; 30 } 31 32 } 33 34 } 35 36 for(int data:a){ 37 System.out.print(data+" "); 38 } 39 40 } 41 42 public static int getMax(int[] a){ 43 //找出本组最大的数,并确定其位数 44 int max=a[0]; 45 for(int i=1;i<a.length;i++){ 46 if(max<a[i]){ 47 max=a[i]; 48 } 49 } 50 int le=(max+"").length();//获取最大数的位数 51 52 return le; 53 } 54 55 56 57 }
运行结果:
![]()
分析:在执行完一轮存取后,没有将count[index]清零,导致temp[index][count[index]]越界

这里写的也有问题
修改后的完整代码:
1 package PaiXu; 2 3 public class JiShuDemo { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 int[] a={26,3,38,66,88,188,881,999,1,12,88,58,6006,9,0}; 6 Sort(a); 7 } 8 9 10 public static void Sort(int[] a){ 11 int le=getMax(a); 12 int[][]temp=new int[10][a.length+1];//用二维数组表示某个数存放在第几个桶的第几位 13 int []count=new int[10];//用来定位在某个桶中的哪一个位置 14 int index; 15 for(int i=0,n=1;i<le;i++,n*=10){ 16 for(int j=0;j<a.length;j++){ 17 index=(a[j]/n)%10; 18 19 //count[index]中index代表是哪个桶,而count[index]的值代表标号为index的桶中当前元素的位置,也即当前数据在标号为index的桶中的位置 20 21 count[index]++; 22 temp[index][count[index]]=a[j]; 23 //count[index]++; 24 } 25 26 //将各个桶中的数取出来 27 int l=0; 28 for(int m=0;m<10;m++){ 29 for(int k=1;k<=count[m];k++){ 30 a[l]=temp[m][k]; 31 l++; 32 } 33 count[m]=0;//清零很重要,否则count[]的值会一直累加上去,导致第21行出现越界错误 34 35 } 36 37 } 38 39 for(int data:a){ 40 System.out.print(data+" "); 41 } 42 43 } 44 45 public static int getMax(int[] a){ 46 //找出本组最大的数,并确定其位数 47 int max=a[0]; 48 for(int i=1;i<a.length;i++){ 49 if(max<a[i]){ 50 max=a[i]; 51 } 52 } 53 int le=(max+"").length();//获取最大数的位数 54 55 return le; 56 } 57 58 59 60 }
运行结果:
![]()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号