HashSet
1 package ListSetMapTest; 2 3 import java.util.HashSet; 4 import java.util.Set; 5 6 public class HashSetTest { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args){ 9 Set<Student> s=new HashSet(); 10 s.add(new Student(1,"Tom",15)); 11 s.add(new Student(1,"Tom",15)); 12 s.add(new Student(1,"Animy",12)); 13 s.add(new Student(1,"Tom",11)); 14 s.add(new Student(2,"Tom",15)); 15 s.add(new Student(3,"Jack",13)); 16 17 for(Student st:s){ 18 System.out.println(st+"------->"+st.hashCode()); 19 } 20 21 } 22 23 } 24 25 class Student{ 26 int no; 27 String name; 28 int age; 29 30 public Student(int no, String name, int age) { 31 this.no = no; 32 this.name = name; 33 this.age = age; 34 } 35 36 @Override 37 public String toString() { 38 return "学号: " + no + "姓名: " + name + "年龄: " + age ; 39 } 40 41 42 43 44 }
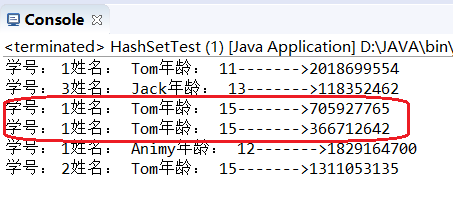
Set集合中不能保存相同的内容,这里值相同但是没有覆盖的原因是两者的哈希值不同,这与HashSet的设计理念不服,因为HashSet是HashMap的key部分,key部分必须唯一。key和value是一一对应的。
只重写equals()方法:
1 package ListSetMapTest; 2 3 import java.util.HashSet; 4 import java.util.Set; 5 6 public class HashSetTest { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args){ 9 Set<Student> s=new HashSet(); 10 s.add(new Student(1,"Tom",15)); 11 s.add(new Student(1,"Tom",15)); 12 s.add(new Student(1,"Animy",12)); 13 s.add(new Student(1,"Tom",11)); 14 s.add(new Student(2,"Tom",15)); 15 s.add(new Student(3,"Jack",13)); 16 17 for(Student st:s){ 18 System.out.println(st+"------->"+st.hashCode()); 19 } 20 21 } 22 23 } 24 25 class Student{ 26 int no; 27 String name; 28 int age; 29 30 public Student(){ 31 32 } 33 public Student(int no, String name, int age) { 34 this.no = no; 35 this.name = name; 36 this.age = age; 37 } 38 39 @Override 40 public String toString() { 41 return "学号: " + no + "姓名: " + name + "年龄: " + age ; 42 } 43 44 //重写equals()方法 45 @Override 46 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 47 if(!(obj instanceof Student)){ 48 return false; 49 } 50 Student s = (Student)obj; 51 if(this==s){ 52 return true; 53 } 54 if(this.name .equals(s.name)&&this.no==s.no&&this.age==s.age){ 55 return true; 56 }else 57 return false; 58 } 59 60 61 62 63 64 }
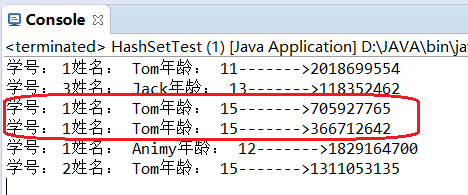
equals()和hashCode()方法都重写
1 package ListSetMapTest; 2 3 import java.util.HashSet; 4 import java.util.Set; 5 6 public class HashSetTest { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args){ 9 Set<Student> s=new HashSet(); 10 s.add(new Student(1,"Tom",15)); 11 s.add(new Student(1,"Tom",15)); 12 s.add(new Student(1,"Animy",12)); 13 s.add(new Student(1,"Tom",11)); 14 s.add(new Student(2,"Tom",15)); 15 s.add(new Student(3,"Jack",13)); 16 17 for(Student st:s){ 18 System.out.println(st+"------->"+st.hashCode()); 19 } 20 21 } 22 23 } 24 25 class Student{ 26 int no; 27 String name; 28 int age; 29 30 public Student(){ 31 32 } 33 public Student(int no, String name, int age) { 34 this.no = no; 35 this.name = name; 36 this.age = age; 37 } 38 39 @Override 40 public String toString() { 41 return "学号: " + no + "姓名: " + name + "年龄: " + age ; 42 } 43 44 45 @Override 46 public int hashCode() { 47 final int prime = 31; 48 int result = 1; 49 result = prime * result + age; 50 result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode()); 51 result = prime * result + no; 52 return result; 53 } 54 55 56 @Override 57 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 58 if(!(obj instanceof Student)){ 59 return false; 60 } 61 Student s = (Student)obj; 62 if(this==s){ 63 return true; 64 } 65 if(this.name .equals(s.name)&&this.no==s.no&&this.age==s.age){ 66 return true; 67 }else 68 return false; 69 } 70 71 72 73 74 75 }
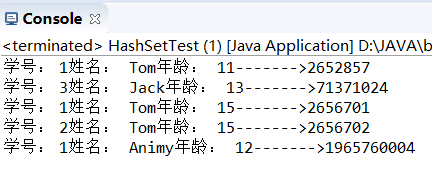
相同的值被覆盖



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号