Collections工具类
java.util.Collection 集合接口
java.util,Collections 集合工具类,方便集合的操作
1.
1 package Connection; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collections; 5 import java.util.List; 6 import java.util.TreeSet; 7 8 /* 9 * java.util.Collection 集合接口 10 * java.util,Collections 集合工具类,方便集合的操作 11 */ 12 public class CollectionsTest { 13 14 public static void main(String[] args){ 15 16 List<String>list=new ArrayList();//ArrayList是非线程安全的 17 18 Collections.synchronizedList(list);//变成线程安全的 19 20 list.add("abg"); 21 list.add("dbd"); 22 list.add("abc"); 23 24 System.out.println("未排序:"); 25 for(String l:list){ 26 System.out.println(l); 27 } 28 29 Collections.sort(list);//排序 30 31 System.out.println("排序:"); 32 for(String l:list){ 33 System.out.println(l); 34 } 35 36 37 } 38 39 }
运行结果:
未排序(没有按照定义的某种顺序输出,而是按照存进去的顺序输出的)
abg
dbd
abc
排序:(按照字符串的先后顺序输出)
abc
abg
dbd
注:这里的排序指的是按照定义的某种顺序,而不是按存进去的顺序.
2.对list集合元素排序,需要保证list集合中的元素实现了Comparable接口
(1)未实现Comparable接口
1 package Connection; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collections; 5 import java.util.List; 6 import java.util.TreeSet; 7 8 /* 9 * java.util.Collection 集合接口 10 * java.util,Collections 集合工具类,方便集合的操作 11 */ 12 public class CollectionsTest { 13 14 public static void main(String[] args){ 15 16 List<Student> st=new ArrayList<Student>(); 17 18 Student s1=new Student(10,"Tom"); 19 Student s2=new Student(9,"Jack"); 20 Student s3=new Student(9,"Tony"); 21 Student s4=new Student(18,"Tom"); 22 Student s5=new Student(16,"Tim"); 23 st.add(s1); 24 st.add(s2); 25 st.add(s3); 26 st.add(s4); 27 st.add(s5); 28 for(Student s:st){ 29 System.out.println(s.toString()); 30 } 31 } 32 33 } 34 class Student { 35 36 String name; 37 int age; 38 public Student(int age,String name){ 39 this.age=age; 40 this.name=name; 41 } 42 @Override 43 public String toString() { 44 return "年龄" + age + ", 姓名" + name ; 45 } 46 47 }
运行结果:
年龄10, 姓名Tom
年龄9, 姓名Jack
年龄9, 姓名Tony
年龄18, 姓名Tom
年龄16, 姓名Tim
这种输出是按照存进去的顺序直接输出,而不是按照我们想要的顺序输出。
若加上:
Collections.sort(st);
则会报错,显示:
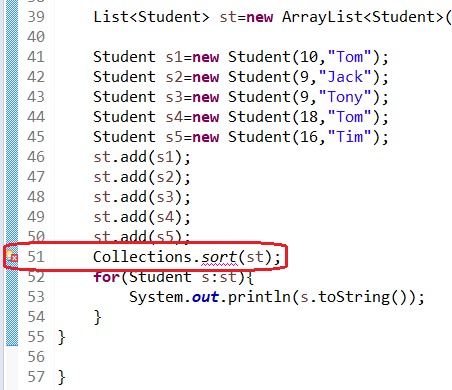
报错原因:

(2)实现Comparable接口
1 package Connection; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collections; 5 import java.util.List; 6 import java.util.TreeSet; 7 8 /* 9 * java.util.Collection 集合接口 10 * java.util,Collections 集合工具类,方便集合的操作 11 */ 12 public class CollectionsTest { 13 14 public static void main(String[] args){ 15 /* 16 List<String>list=new ArrayList();//ArrayList是非线程安全的 17 18 Collections.synchronizedList(list);//变成线程安全的 19 20 list.add("abg"); 21 list.add("dbd"); 22 list.add("abc"); 23 24 System.out.println("未排序:"); 25 for(String l:list){ 26 System.out.println(l); 27 } 28 29 Collections.sort(list);//排序 30 31 System.out.println("排序:"); 32 for(String l:list){ 33 System.out.println(l); 34 } 35 36 */ 37 38 39 List<Student> st=new ArrayList<Student>(); 40 41 Student s1=new Student(10,"Tom"); 42 Student s2=new Student(9,"Jack"); 43 Student s3=new Student(9,"Tony"); 44 Student s4=new Student(18,"Tom"); 45 Student s5=new Student(16,"Tim"); 46 st.add(s1); 47 st.add(s2); 48 st.add(s3); 49 st.add(s4); 50 st.add(s5); 51 Collections.sort(st); 52 for(Student s:st){ 53 System.out.println(s.toString()); 54 } 55 } 56 57 } 58 59 class Student implements Comparable<Student>{ 60 61 String name; 62 int age; 63 public Student(int age,String name){ 64 this.age=age; 65 this.name=name; 66 } 67 @Override 68 public String toString() { 69 return "年龄" + age + ", 姓名" + name ; 70 } 71 72 //重写CompareTo方法,按照年龄升序,如果年龄相同,比较名字 73 @Override 74 public int compareTo(Student s) { 75 if(this.age==s.age){ 76 return this.name.compareTo(s.name); 77 }else 78 return this.age-s.age; 79 } 80 81 82 } 83 84
运行结果:
年龄9, 姓名Jack
年龄9, 姓名Tony
年龄10, 姓名Tom
年龄16, 姓名Tim
年龄18, 姓名Tom
按照我们设定的顺序输出结果。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号