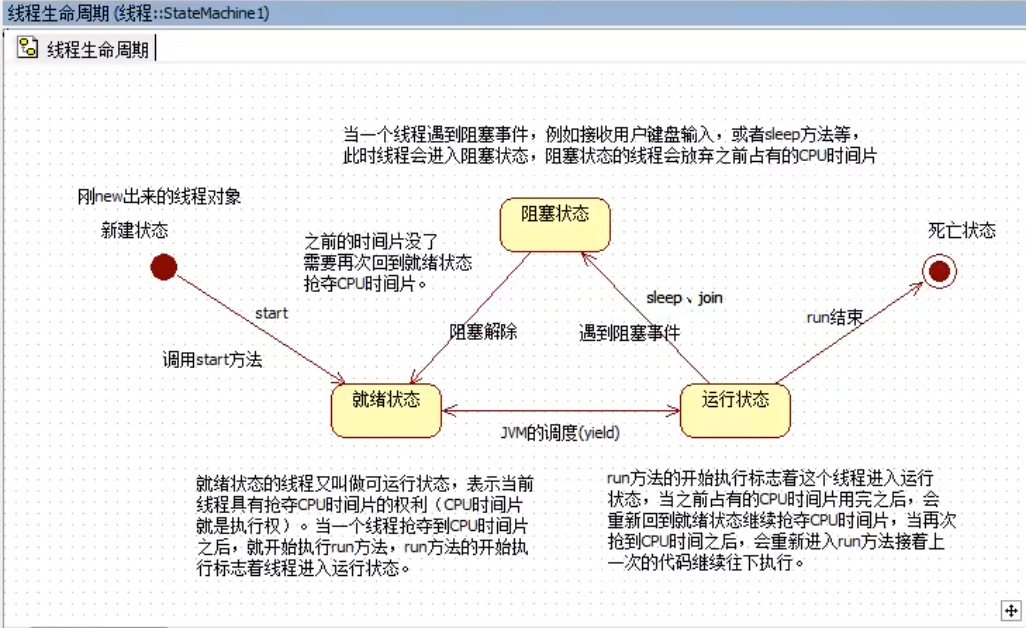
关于线程的调度
1.常见的线程调度模型
(1)抢占式调度模型
哪个线程的优先级比较高,抢到的CPU时间片的概率就大。java采用的就是抢占式调度模型。
(2) 均分式调度模型
平均分配CPU时间片,每个线程占有的CPU时间片长度一样,平均分配,一切平等。有一些编程语言采用的是这种方式。
2.java中提供了哪些方法和线程调度有关系的?
2.1 实例方法
(1)void setPriority(int newPriority) 设置线程的优先级
(2)int getPriority() 获取线程优先级
最低优先级:1;最高优先级:10;默认优先级:5
优先级高的获取CPU时间片很大概率会多一些
(3)void join() 合并线程
class MyThread1 extends Thread{ public void doSome(){ Mythread2 t=new MyThread2(); t.join(); //当前线程进入阻塞,t线程执行,直到t线程结束,当前线程才可以继续。(相当于把多线程变成单线程) } } class MyThread2 extends Thread{ }
2.2 静态方法
static void yield() 让位方法:暂停当前正在执行的线程对象,并执行其他线程
注:yield()方法不是阻塞方法,yield()方法的执行会让当前线程从“运行状态”回到“就绪状态”,但是回到就绪之后有可能会再次抢到
3. 代码延时
(1)
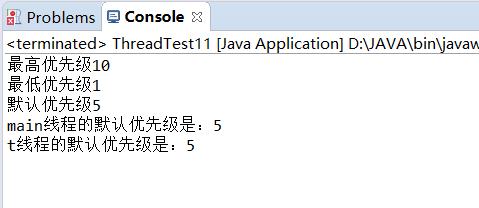
1 package XianChengFenXi; 2 3 /* 4 * 关于线程的优先级 5 */ 6 public class ThreadTest11 { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args){ 9 10 System.out.println("最高优先级"+Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); 11 System.out.println("最低优先级"+Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); 12 System.out.println("默认优先级"+Thread.NORM_PRIORITY); 13 14 //获取当前线程对象,获取当前线程的优先级 15 Thread currentThread=Thread.currentThread(); 16 currentThread.getName(); 17 //currentThread.setPriority(1); //将主线程的优先级设为1 18 19 //main线程的默认优先级是:5 20 System.out.println(currentThread.getName()+"线程的默认优先级是:"+currentThread.getPriority()); 21 22 Thread t=new Thread(new MyRunnable5()); 23 t.setName("t"); 24 t.start(); 25 26 27 } 28 29 } 30 31 class MyRunnable5 implements Runnable{ 32 public void run(){ 33 //获取线程的优先级,默认优先级也是5 34 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程的默认优先级是:"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); 35 36 } 37 }
运行结果:
(2)优先级设置及测试
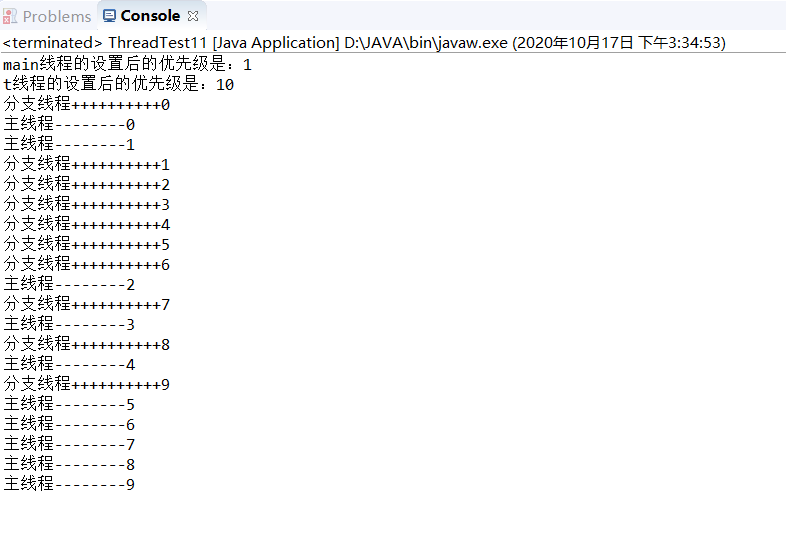
1 package XianChengFenXi; 2 3 /* 4 * 关于线程的优先级 5 */ 6 public class ThreadTest11 { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args){ 9 10 //获取当前线程对象,获取当前线程的优先级 11 Thread currentThread=Thread.currentThread(); 12 currentThread.setPriority(1); //将主线程的优先级设为1 13 14 Thread t=new Thread(new MyRunnable5()); 15 t.setName("t"); 16 t.setPriority(10); //将分支线程的优先级设为10 17 t.start(); 18 System.out.println(currentThread.getName()+"线程的设置后的优先级是:"+currentThread.getPriority()); 19 for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ 20 System.out.println("主线程--------"+i); 21 } 22 23 } 24 25 } 26 27 class MyRunnable5 implements Runnable{ 28 public void run(){ 29 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程的设置后的优先级是:"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); 30 for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ 31 System.out.println("分支线程++++++++++"+i); 32 } 33 34 35 } 36 }
运行结果:
(3)让位测试
1 package XianChengFenXi; 2 3 4 /* 5 * 让位:将当前线程暂停,使其回到就绪状态,让给其他线程 6 */ 7 public class ThreadTest12 { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args){ 10 Thread t=new Thread(new MyRunnable6()); 11 t.setName("t"); 12 t.start(); 13 for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){ 14 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"------"+i); 15 } 16 } 17 18 } 19 20 class MyRunnable6 implements Runnable{ 21 22 public void run(){ 23 for(int i=1;i<=100;i++){ 24 //每10个让位1次 25 if(i%10==0){ 26 Thread.yield(); //当前线程暂停一下,让位给主线程 27 } 28 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"------"+i); 29 } 30 31 } 32 }
运行结果:




注:分支线程当运行到10的倍数让位给主线程,并不代表着到10了一定会运行主线程,因为分支线程虽然让位了,但是它还是会和主线程去竞争
(4)线程合并测试
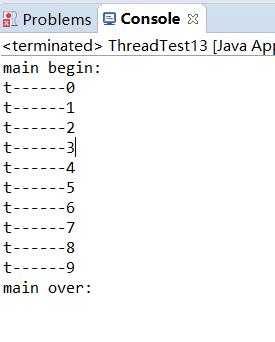
1 package XianChengFenXi; 2 3 public class ThreadTest13 { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 System.out.println("main begin:"); 6 7 Thread t=new Thread(new MyRunnable7()); 8 t.setName("t"); 9 t.start(); 10 11 //合并线程 12 13 try { 14 t.join(); 15 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 16 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 17 e.printStackTrace(); 18 } //将t合并到当前线程中,当前线程受阻塞,t线程开始执行,一直到结束 19 System.out.println("main over:"); 20 21 } 22 23 } 24 25 class MyRunnable7 implements Runnable{ 26 public void run(){ 27 for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ 28 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"------"+i); 29 } 30 } 31 }
运行结果:
注:合并的意思不是字面上的“将两个栈合并”,栈没有消失,而是两个栈之间发生了等待关系



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号