Linux 内核学习笔记(一)
操作系统与kernel
操作系统包括内核、设备驱动、boot loader、命令shell、别的用户接口等。
典型的内核里面有:中断handle、scheduler to share processor time、a memory management system to manage process address spaces、system services such as networking and interprocess communication.
kernel space 和 user space 是不同的。kernel 有更高的权限完全控制硬件,同时占用特定的user不能访问的memory。
应用application与kernel之间仅仅且只能通过system call进行交流。
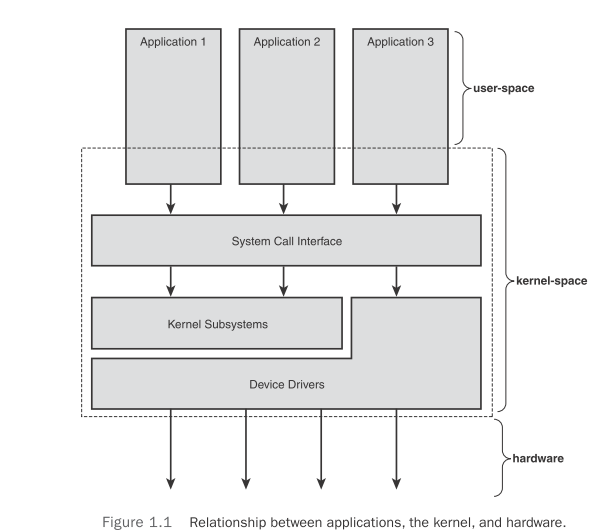
为了provide synchronization 内核可以禁用一个或多个中断。
在linux中,处理器在任何时刻都在做以下三个事情中的一个:
- 在user-space 执行代码in a process
- 在kernel-space,在process的语境下,执行特别的process;
- 在kernel-space,在interrupt语境下,不处理procee,但是处理interrupt。
The kernel source tree
可以在GitHub上可下载到。
linux kernel 代码的特点
- kernel不使用C library或者标准C header。(毕竟这些都是上层应用调用自己的库)
- kernel使用GNU C(内部内嵌了汇编和一些function)
- kernel自身没有memory protection;(如果user-application 突兀地进入了禁止内存去,kernel会生成错误提示设法去阻止,但是kernel自己进入了非法区域,谁能阻止他呢。所以说,kernel本身没有memory保护机制)
- kernel有一个小的pre-process的定长stack; (不要在kernel里面进行浮点运算,一般处理不太行)
- 因为外部的中断是异步中断,sysnchronization and concurrency(并发) are major concerns within the kernel;
- (linux是多用户多进程的,多个用户同时访问共同的资源(这叫并发)时,需要进行同步,防止竞争races)
- Linux is a preemptive (抢先的)multitasking operating system. Processes are scheduled and
rescheduled at the whim of the kernel’s process scheduler.The kernel must syn-
chronize between these tasks.
- portability is important.
Process
process(进程)是执行中的程序。有时又被成为task。
thread(线程)are the objects of activity within the process. Each thread includes a unique program counter,process stack ,and set of processor regiters. 对linux来说,a thread is just a special kind of process.
virtual processor: 给process一个假象,似乎它自己独自掌控processor,尽管可能有数百个进程process在同时工作;
virtual memory:让process划分和管理memory,似乎它自己拥有了all memory in the system.
使用fork()来在当前的process中产生新的process。原有的成为parent,新的process成为child。fork()函数这个system call返回两次。
The kernel stores the list of processes in a circular doubly linked list called the task list. Each element in the task list is a process descriptor of the type struct task_struct , which is defined in <linux/sched.h> . 所有的任务存放在task list里面。里面包含了process的一些描述一个process的所有information。 这也类似于一个指针array,指向实际需要执行的process代码处。
The system identifies processes by a unique process identification value or PID. (比如全局init()的初始化PID代码为1)
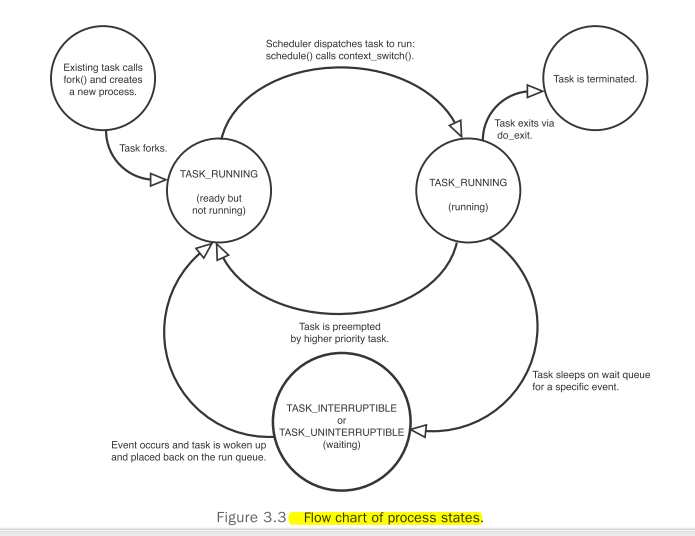
每一个process都有一个parent,有0或者多个child,不同child之间成为sibling。这些亲戚关系(family tree家谱)都存放在process descriptor 里面了。所以也就可以通过程序的方式获得不同process之间的关系了。
process creation
- fork()这也是system call。 fork出来的child除了PID(process ID)序号、特别的资源和数据(比如pending signal)不同外,其他的和parent是一模一样的;
- exec() 在地址空间加载一个新的程序,然后开始执行。The exec call is a way to basically replace the entire current process with a new program. 大多数时候fork()出来一个child紧接着就是执行exec()函数。
copy-on-write
parent 产生一个child之后,不是把数据也统统拷贝一份给child(可能是几十G的数据),而是把地址提供给child。这期间如果这段数据需要被更改,那么就把这一部分需要更改的数据拷贝一份给child,防止parent那边被改动。也就是需要改动啥,拷贝啥,不需要修改的数据仅仅保留数据地址即可。这极大地提高了效率。
另外这也适用于不同sibling从parent继承的相同一段数据段。
A page table is the data structure used by a virtual memory system in a computer operating system to store the mapping between virtual addresses and physical addresses.
forking
fork()是通过clone()这个system call来实现的。
v-fork()
和fork()类似,区别在于生成了child之后,parent被封锁,必须等待child执行exec(),或者exits。或者说v-fork()有一点过时,它需要完全复制parent的memory,而不是采用先进的copy-on-write。
thread
thread其实就是一个和其他许多processes共享特定资源的process。thead仅仅在需要共享资源(比如地址空间)的时候出现。
kernel thread也就是仅仅存在于kernel space的thread。 kernel thread的地址空间是null,这是它的特殊之处。kernel thread 只能通过另一个kernel thread来生成。第一个kernel thread是boot的时候生成的。它主要完成两件工作:flush、ksoftirqd。
termination
一般process自己终止。通过exit()system call来完成的。一个process结束之后,kernel释放它的资源,并且通知他的parent。之后将这个结束process的信息从process descriptor 里面清除干净。
有一个wait4()的system call,类似于在中断来临时,等待暂停手头工作。
当一个parent程序先exit了,那么他的child就需要进行一个过程:reparent。为其找到新的parent。
参考:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/4856255/the-difference-between-fork-vfork-exec-and-clone
本文作者:LT_Rock
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/LT-Rock/p/13524756.html
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明出处!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号