后端笔记02-Properties
SpringBoot2-properties
演示获取配置文件的自定义配置,以及多环境下的配置文件信息的获取
pmx.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<!--在 META-INF/additional-spring-configuration-metadata.json 中配置可以去除 application.yml 中自定义配置的 红线警告,并且为自定义配置添加 hint 提醒-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
ApplicationProperty.java
通过@Value读取配置文件
/**
* Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
* User: KingRainGrey
* Date: 2020/8/21
*/
@Data
@Component
public class ApplicationProperty {
@Value("${application.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${application.version}")
private String version;
}
@Component是通用注解,其他三个注解(@Service, @Controller, @Repository)是这个注解的拓展,并且具有了特定的功能。通过这些注解的分层管理,就能将请求处理,义务逻辑处理,数据库操作处理分离出来,为代码解耦,也方便了以后项目的维护和开发。所以我们在正常开发中,如果能用@Service, @Controller, @Repository其中一个标注这个类的定位的时候,就不要用@Component来标注。
@Component注解表明一个类会作为组件类,并告知Spring要为这个类创建bean。
@Bean注解告诉Spring这个方法将会返回一个对象,这个对象要注册为Spring应用上下文中的bean。通常方法体中包含了最终产生bean实例的逻辑。
@Component(@Controller、@Service、@Repository)通常是通过类路径扫描来自动侦测以及自动装配到Spring容器中。
@Bean注解通常是我们在标有该注解的方法中定义产生这个bean的逻辑。
@Component 作用于类,@Bean作用于方法。
@Component注解的类放入Spring容器中,可以用@Autowired来取用
DeveloperProperty.java
通过@ConfigurationProperties读取配置文件
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "developer")
@Component
public class DeveloperProperty {
private String name;
private String website;
private String qq;
private String phoneNumber;
}
@ConfigurationProperties的大致作用就是通过它可以把properties或者yml配置直接转成对象
@ConfigurationProperties的基本用法非常简单:我们为每个要捕获的外部属性提供一个带有字段的类。请注意以下几点:
- 前缀定义了哪些外部属性将绑定到类的字段上
- 根据 Spring Boot 宽松的绑定规则,类的属性名称必须与外部属性的名称匹配
- 我们可以简单地用一个值初始化一个字段来定义一个默认值
- 类本身可以是包私有的
- 类的字段必须有公共 setter 方法
参考
增加校验
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "developer")
@Component
@Validated
public class DeveloperProperty {
@NotNull
private String name;
@NotEmpty
private String website;
private String qq;
private String phoneNumber;
}
复杂属性类型
list set
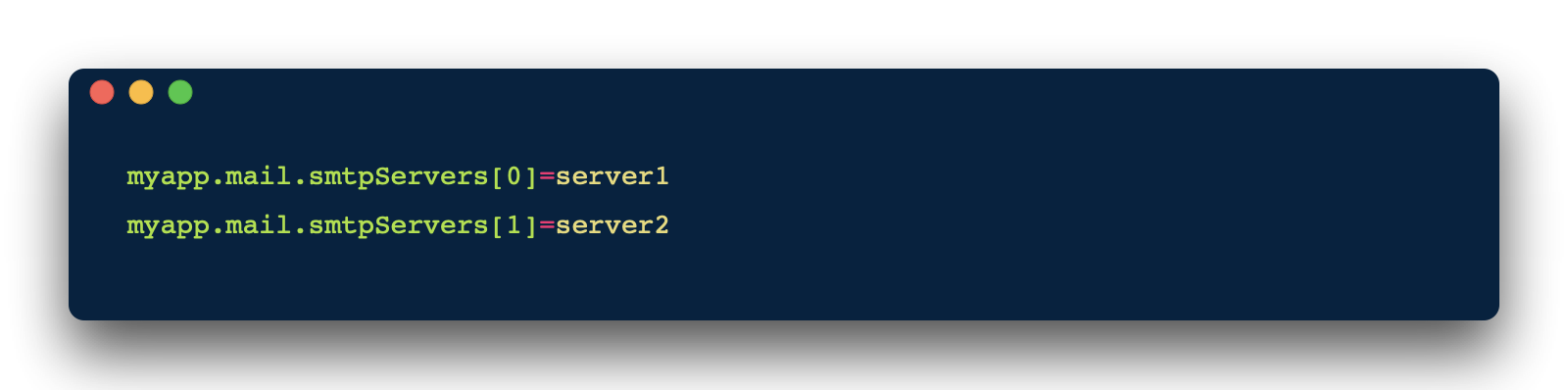

自定义类型
@Data
public class Weight {
private int w;
public Weight(char w) {
this.w = Integer.parseInt(w + "");
}
}
编写转化器
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter;
/**
* Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
* User: KingRainGrey
* Date: 2020/8/21
*/
public class WeightConverter implements Converter<String, Weight> {
@Override
public Weight convert(String s) {
return new Weight(s.toCharArray()[0]);
}
}
注册转化器
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationPropertiesBinding;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
* User: KingRainGrey
* Date: 2020/8/21
*/
@Configuration
public class PropertiesConfig {
@Bean
@ConfigurationPropertiesBinding
public WeightConverter weightConverter() {
return new WeightConverter();
}
}
Duration DataSize参考给出网址
配置文件
server:
port: 8055
servlet:
context-path: /study
spring:
profiles:
active: prod
application:
name: dev环境 @artifactId@
version: dev环境 @version@
developer:
name: dev环境 xkcoding
website: dev环境 http://xkcoding.com
qq: dev环境 237497819
phone-number: dev环境 17326075631
weight: 5kg
application:
name: prod环境 @artifactId@
version: prod环境 @version@
developer:
name: prod环境 xkcoding
website: prod环境 http://xkcoding.com
qq: prod环境 237497819
phone-number: prod环境 17326075631
weight: 5kg
测试控制器
@RestController
public class PropertyController {
private final ApplicationProperty applicationProperty;
private final DeveloperProperty developerProperty;
@Autowired
public PropertyController(ApplicationProperty applicationProperty, DeveloperProperty developerProperty) {
this.applicationProperty = applicationProperty;
this.developerProperty =developerProperty;
}
@GetMapping("/property")
public Dict index() {
return Dict.create().set("applicationProperty", applicationProperty).set("developerProperty", developerProperty);
}
}
Dict继承HashMap,其key为String类型,value为Object类型,通过实现BasicTypeGetter接口提供针对不同类型的get方法,同时提供针对Bean的转换方法,大大提高Map的灵活性。
基本使用
Dict dict = Dict.create()
.set("key1", 1)//int
.set("key2", 1000L)//long
.set("key3", DateTime.now());//Date
测试结果
{
"applicationProperty": {
"name": "prod环境 properties",
"version": "prod环境 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT"
},
"developerProperty": {
"name": "prod环境 xkcoding",
"website": "prod环境 http://xkcoding.com",
"qq": "prod环境 237497819",
"phoneNumber": "prod环境 17326075631",
"weight": {
"w": 5
},
"frozen": false,
"advisors": [
{
"order": 2147483647,
"advice": {},
"pointcut": {
"classFilter": {},
"methodMatcher": {
"runtime": false
}
},
"perInstance": true
}
],
"targetSource": {
"target": {
"name": "prod环境 xkcoding",
"website": "prod环境 http://xkcoding.com",
"qq": "prod环境 237497819",
"phoneNumber": "prod环境 17326075631",
"weight": {
"w": 5
}
},
"static": true,
"targetClass": "com.study.properties.property.DeveloperProperty"
},
"targetClass": "com.study.properties.property.DeveloperProperty",
"exposeProxy": false,
"preFiltered": false,
"proxiedInterfaces": [],
"proxyTargetClass": true
}
}
搬运自我的 Git:https://github.com/miles-rush/StudyNote
SpringBoot-Demo:https://github.com/xkcoding/spring-boot-demo 的学习笔记


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号