2023省选武汉联测8
T1 Mix
非常难写的数据结构。
目前这道题有两种做法,一种是线段树上打 lazy 标记维护历史版本和,一种是平衡树维护增量转化为二维数点用扫描线解决,两种做法最大的差异是是否存在 lazy 标记,这里只讲解第二种做法。
首先考虑固定区间 \(r\) ,求解所有 \(l\) 所对应的答案,发现这是一个经典套路,直接线段树上二分 + 区间覆盖即可。考虑同时维护 mex 和 mix ,如果使用线段树维护,比较方便的写法是矩阵乘,但矩阵乘常数很大,因此需要用 lazy 标记代替(实质上是矩阵乘的手动展开),这非常麻烦,为了避开使用 lazy 标记,我们选择维护两棵平衡树,第一棵维护所有 \(l\) 对应的 mex ,第二棵维护所有 \(l\) 对应的 mix ,考虑将右端点移动到 \(r-1\) 后平衡树的变化,设 \(r-1\) 前面第一次出现 \(a_{r-1}\) 的位置为 \(pre\) ,简单画图:
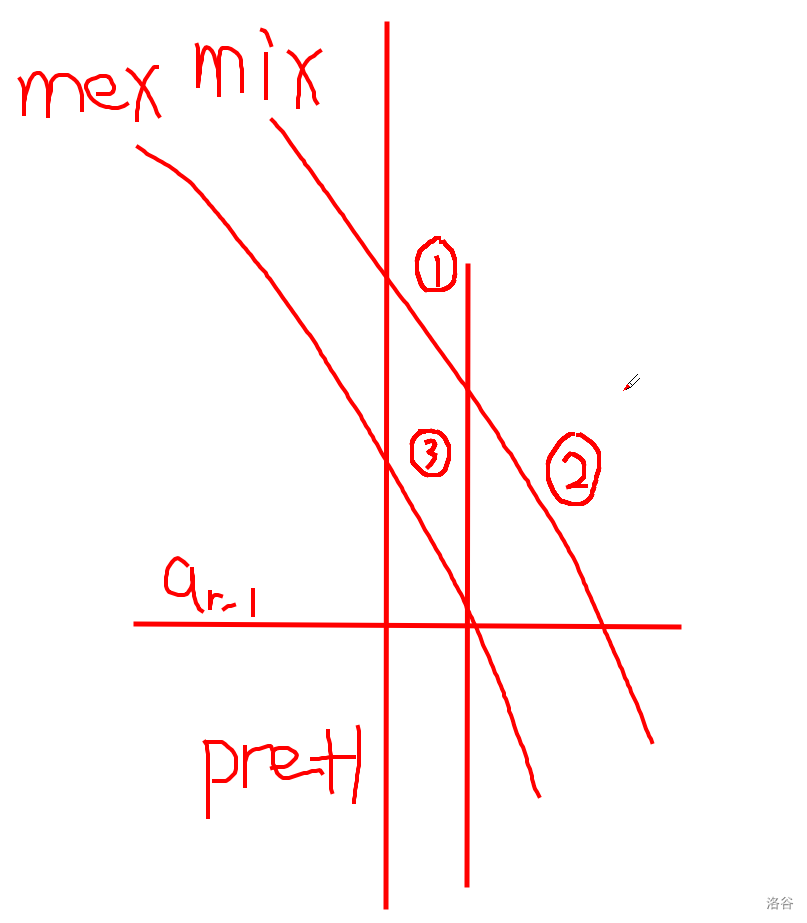
发现我们需要做的操作就是将 mix 和 mex 平衡树按照上图位置分裂为 \(3\) 部分,然后将 \(2,3\) 部分做区间覆盖,用 \(3\) 部分代替 \(1\) 部分,类似珂朵莉树,我们将值相同的区间进行合并,容易发现这样维护节点总数为 \(O(n)\) ,可以保证时间复杂度。
考虑维护四元组 \((tim,l,r,w)\) 表示当右端点从 \(tim-1\) 移动到 \(tim\) 时,左端点位于 \([l,r]\) 的部分 mix 值会增加 \(w\) ,发现可以用上述平衡树来找到所有的四元组,也就是暴力扫 \(1,2,3\) 中的每个节点,发现一个节点只会被扫一次,因此上述四元组的个数为 \(O(n)\) 个。
比较显然上述四元组可以被差分为三元组 \((tim,y,w)\) 表示当右端点从 \(tim-1\) 移动到 \(tim\) 时,左端点位于 \([1,y]\) 的部分 mix 值会增加 \(w\) ,将三元组放到二维平面上,发现点 \((tim,y)\) 会对如下区间产生 \(w\) 的贡献:
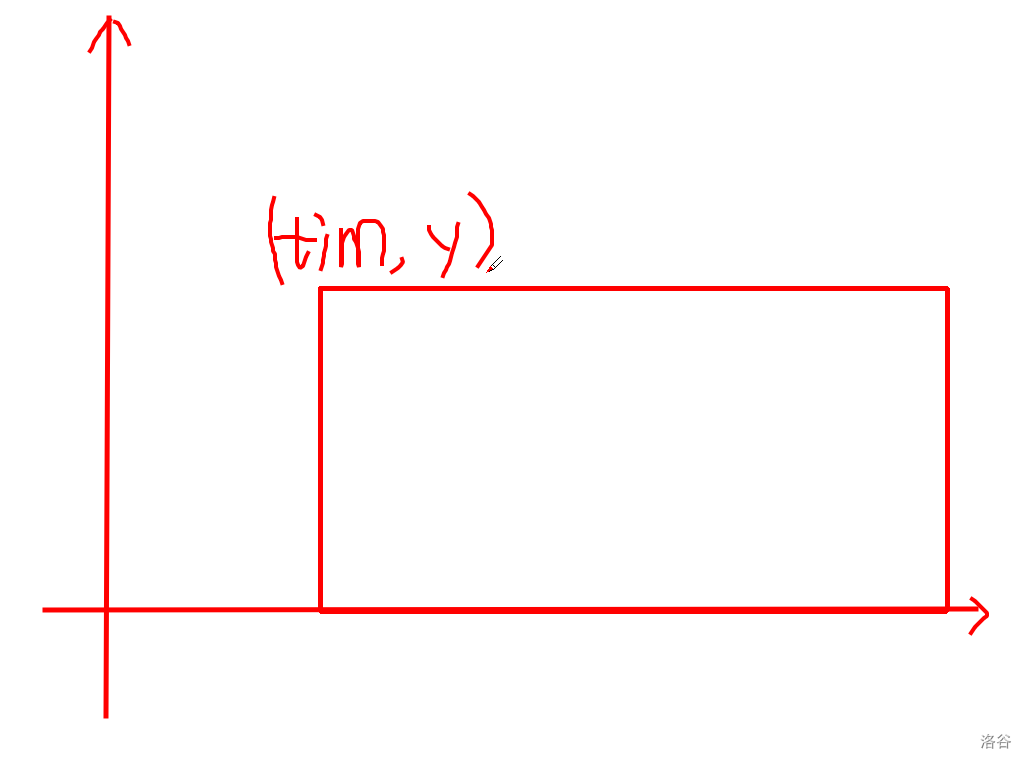
由于一次询问构成一个矩形,因此问题为矩形内的权值和,可以用扫描线解决。
code
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <random>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
const int max1 = 2e5, max2 = 1e6;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, q, a[max1 + 5];
int v[2][max1 + 5];
bool vis[max1 + 5];
int pos[max1 + 5], pre[max1 + 5];
struct Option
{
int tim, l, r, d;
Option () {}
Option ( int __tim, int __l, int __r, int __d )
{ tim = __tim, l = __l, r = __r, d = __d; }
}opt[max1 * 15 + 5];
int len;
struct Easy_Option
{
int tim, pos, d;
Easy_Option () {}
Easy_Option ( int __tim, int __pos, int __d )
{ tim = __tim, pos = __pos, d = __d; }
}easy_opt[max1 * 30 + 5];
int cnt;
struct Question
{ int l, r, id; } qus[max2 + 5];
bool Cmp1 ( const Question &A, const Question &B )
{ return A.l < B.l; }
bool Cmp2 ( const Question &A, const Question &B )
{ return A.r < B.r; }
long long ans[max2 + 5];
struct FHQ_Treap
{
#define lson(now) tree[now].son[0]
#define rson(now) tree[now].son[1]
struct Struct_FHQ_Treap
{
int son[2], rd;
int L, R, minL, maxR, val, minval;
}tree[max1 * 15 + 5];
int root[2], total;
int s[2][max1 + 5], top[2];
void Push_Up ( int now )
{
tree[now].minL = min(tree[lson(now)].minL, tree[now].L);
tree[now].maxR = max(tree[rson(now)].maxR, tree[now].R);
tree[now].minval = min(tree[now].val, min(tree[lson(now)].minval, tree[rson(now)].minval));
return;
}
int Build ( int l, int r, int b[] )
{
if ( l > r )
return 0;
int now = ++total, mid = l + r >> 1;
tree[now].rd = rand();
tree[now].L = tree[now].R = mid, tree[now].val = b[mid];
lson(now) = Build(l, mid - 1, b);
rson(now) = Build(mid + 1, r, b);
Push_Up(now);
return now;
}
void Build ()
{
lson(0) = rson(0) = 0;
tree[0].minL = inf, tree[0].maxR = -inf;
tree[0].minval = inf;
total = 0;
root[0] = Build(1, n, v[0]);
root[1] = Build(1, n, v[1]);
return;
}
void Split_Kth ( int now, int k, int &x, int &y )
{
if ( !now )
{ x = y = 0; return; }
if ( tree[now].L - 1 >= k )
y = now, Split_Kth(lson(now), k, x, lson(y));
else if ( tree[now].R <= k )
x = now, Split_Kth(rson(now), k, rson(x), y);
else
{
int clone = ++total;
tree[clone].rd = rand();
tree[clone].L = k + 1, tree[clone].R = tree[now].R;
tree[now].R = k;
tree[clone].val = tree[now].val;
lson(clone) = 0, rson(clone) = rson(now);
rson(now) = 0;
Push_Up(clone);
x = now, y = clone;
}
Push_Up(now);
return;
}
void Split_Val ( int now, int val, int &x, int &y )
{
if ( !now )
{ x = y = 0; return; }
if ( min(tree[lson(now)].minval, tree[now].val) > val )
x = now, Split_Val(rson(now), val, rson(x), y);
else
y = now, Split_Val(lson(now), val, x, lson(y));
Push_Up(now);
return;
}
int Merge ( int x, int y )
{
if ( !x || !y )
return x | y;
if ( tree[x].rd > tree[y].rd )
{
rson(x) = Merge(rson(x), y);
Push_Up(x);
return x;
}
lson(y) = Merge(x, lson(y));
Push_Up(y);
return y;
}
void Dfs ( int now, int id )
{
if ( !now )
return;
Dfs(lson(now), id);
s[id][++top[id]] = now;
Dfs(rson(now), id);
return;
}
void Delta ( int tim, int x, int y )
{
int pre = tree[x].minL - 1;
top[0] = top[1] = 0;
Dfs(x, 0);
Dfs(y, 1);
int now[2] = { 1, 1 };
while ( now[0] <= top[0] || now[1] <= top[1] )
{
if ( now[0] <= top[0] && ( now[1] > top[1] || tree[s[0][now[0]]].R <= tree[s[1][now[1]]].R ) )
{
if ( pre + 1 <= tree[s[0][now[0]]].R )
opt[++len] = Option(tim, pre + 1, tree[s[0][now[0]]].R, tree[s[1][now[1]]].val - tree[s[0][now[0]]].val);
pre = tree[s[0][now[0]]].R;
++now[0];
}
else
{
if ( pre + 1 <= tree[s[1][now[1]]].R )
opt[++len] = Option(tim, pre + 1, tree[s[1][now[1]]].R, tree[s[1][now[1]]].val - tree[s[0][now[0]]].val);
pre = tree[s[1][now[1]]].R;
++now[1];
}
}
return;
}
void Update ( int now, int pre, int val )
{
int x, y, z, tmp;
Split_Kth(root[1], pre, x, y);
Split_Val(y, val, y, z);
tmp = y;
if ( y )
{
tree[++total].rd = rand();
lson(total) = rson(total) = 0;
tree[total].L = tree[total].minL = tree[y].minL;
tree[total].R = tree[total].maxR = tree[y].maxR;
tree[total].val = tree[total].minval = val;
root[1] = Merge(x, Merge(total, z));
}
else
root[1] = Merge(x, z);
Split_Kth(root[0], pre, x, y);
Split_Val(y, val, y, z);
if ( y )
{
int w1, w2;
Split_Kth(y, max(pre, tree[tmp].maxR), w1, w2);
if ( tmp )
Delta(now, tmp, w1);
if ( w2 )
{
tree[++total].rd = rand();
lson(total) = rson(total) = 0;
tree[total].L = tree[total].minL = tree[w2].minL;
tree[total].R = tree[total].maxR = tree[w2].maxR;
tree[total].val = tree[total].minval = val;
Delta(now, total, w2);
y = Merge(tmp, total);
}
else
y = tmp;
root[0] = Merge(x, Merge(y, z));
}
else
root[0] = Merge(x, z);
Split_Kth(root[0], now - 1, root[0], x);
opt[++len] = Option(now, now, now, 1);
Split_Kth(root[1], now - 1, root[1], x);
return;
}
}Tree;
struct Data
{
long long sum1, sum2, sum3, sum4;
Data () {}
Data ( long long __sum1, long long __sum2, long long __sum3, long long __sum4 )
{ sum1 = __sum1, sum2 = __sum2, sum3 = __sum3, sum4 = __sum4; }
Data operator + ( const Data &A ) const
{ return Data(sum1 + A.sum1, sum2 + A.sum2, sum3 + A.sum3, sum4 + A.sum4); }
Data operator - ( const Data &A ) const
{ return Data(sum1 - A.sum1, sum2 - A.sum2, sum3 - A.sum3, sum4 - A.sum4); }
};
struct Bit_Tree
{
#define lowbit(now) ( now & -now )
Data tree[max1 + 5];
void Clear ()
{
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
tree[i] = Data(0, 0, 0, 0);
return;
}
void Insert ( int now, const Data &x )
{
while ( now <= n )
{
tree[now] = tree[now] + x;
now += lowbit(now);
}
return;
}
Data Query ( int now )
{
Data res = Data(0, 0, 0, 0);
while ( now )
{
res = res + tree[now];
now -= lowbit(now);
}
return res;
}
Data Query ( int L, int R )
{
return Query(R) - Query(L - 1);
}
}Bit;
int main ()
{
freopen("mix.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("mix.out", "w", stdout);
scanf("%d%d", &n, &q);
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
int mex = 0, mix = 1;
for ( int i = n; i >= 1; i -- )
{
vis[a[i]] = true;
while ( vis[mex] )
++mex;
if ( mix == mex )
++mix;
while ( vis[mix] )
++mix;
v[0][i] = mix, v[1][i] = mex;
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
pre[i] = pos[a[i]];
pos[a[i]] = i;
}
Tree.Build();
for ( int i = n; i >= 1; i -- )
Tree.Update(i, pre[i], a[i]);
for ( int i = 1; i <= len; i ++ )
{
easy_opt[++cnt] = Easy_Option(opt[i].tim, opt[i].r, opt[i].d);
if ( opt[i].l - 1 )
easy_opt[++cnt] = Easy_Option(opt[i].tim, opt[i].l - 1, -opt[i].d);
}
reverse(easy_opt + 1, easy_opt + 1 + cnt);
for ( int i = 1; i <= q; i ++ )
scanf("%d%d", &qus[i].l, &qus[i].r), qus[i].id = i;
Bit.Clear();
sort(qus + 1, qus + 1 + q, Cmp1);
int now = 1;
for ( int i = 1; i <= q; i ++ )
{
while ( now <= cnt && easy_opt[now].tim < qus[i].l )
{
Bit.Insert(easy_opt[now].pos, Data(easy_opt[now].d, 1LL * easy_opt[now].tim * easy_opt[now].d, 1LL * easy_opt[now].pos * easy_opt[now].d, 1LL * easy_opt[now].tim * easy_opt[now].pos * easy_opt[now].d));
++now;
}
Data tmp = Bit.Query(qus[i].r + 1, n);
ans[qus[i].id] += 1LL * tmp.sum1 * ( qus[i].r - qus[i].l + 1 ) * ( qus[i].r - qus[i].l + 1 );
tmp = Bit.Query(qus[i].r + 1, n);
ans[qus[i].id] -= 1LL * ( qus[i].r + 1 ) * ( qus[i].r - qus[i].l + 1 ) * tmp.sum1 - 1LL * ( qus[i].r - qus[i].l + 1 ) * tmp.sum2;
tmp = Bit.Query(qus[i].l, qus[i].r);
ans[qus[i].id] += 1LL * ( qus[i].r - qus[i].l + 1 ) * tmp.sum3 - 1LL * ( qus[i].r - qus[i].l + 1 ) * ( qus[i].l - 1 ) * tmp.sum1;
tmp = Bit.Query(qus[i].l, qus[i].r);
ans[qus[i].id] -= 1LL * ( qus[i].r + 1 ) * tmp.sum3 - 1LL * ( qus[i].r + 1 ) * ( qus[i].l - 1 ) * tmp.sum1 - tmp.sum4 + 1LL * ( qus[i].l - 1 ) * tmp.sum2;
}
Bit.Clear();
sort(qus + 1, qus + 1 + q, Cmp2);
now = 1;
for ( int i = 1; i <= q; i ++ )
{
while ( now <= cnt && easy_opt[now].tim <= qus[i].r )
{
Bit.Insert(easy_opt[now].pos, Data(easy_opt[now].d, 1LL * easy_opt[now].tim * easy_opt[now].d, 1LL * easy_opt[now].pos * easy_opt[now].d, 1LL * easy_opt[now].tim * easy_opt[now].pos * easy_opt[now].d));
++now;
}
Data tmp = Bit.Query(qus[i].r + 1, n);
ans[qus[i].id] += 1LL * ( qus[i].r + 1 ) * ( qus[i].r - qus[i].l + 1 ) * tmp.sum1 - 1LL * ( qus[i].r - qus[i].l + 1 ) * tmp.sum2;
tmp = Bit.Query(qus[i].l, qus[i].r);
ans[qus[i].id] += 1LL * ( qus[i].r + 1 ) * tmp.sum3 - 1LL * ( qus[i].r + 1 ) * ( qus[i].l - 1 ) * tmp.sum1 - tmp.sum4 + 1LL * ( qus[i].l - 1 ) * tmp.sum2;
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= q; i ++ )
printf("%lld\n", ans[i]);
return 0;
}
T2 梦
按照题解进行模拟。
首先找到树的一个重心作为根,如果当前 \(x\) 和 \(y\) 均不为根并且 \(x\) 子树与 \(y\) 子树同构,那么让 \(x\) 和 \(y\) 同时向上跳。此处定义子树同构为 \(x\) 和 \(y\) 的度数相同,父边编号相同,并且出边编号相同的儿子同构。
考虑最终 \(x,y\) 的位置,不妨设 \(siz_x\ge siz_y\) ,考虑下面几种情况:
-
\(x=y=root\) ,显然可以直接返回答案;
-
\(x=root,y\ne root\) ,如果 \(x\) 和 \(y\) 度数相同,并且以 \(x\) 为根除去 \(y\) 方向上的子树与以 \(y\) 为根的子树同构,那么 \(1+\sum_{v\not\to y}siz_v=siz_y\le \tfrac{n}{2}\) ,由于 \(1+\sum_{v}siz_v=n\) ,因此 \(y\) 为 \(x\) 的一棵子树,容易判断此时无解,其他情况有解。
-
\(x\ne y\ne root\) ,此时一定有解。
考虑构造一组可行解,不妨设 \(siz_x\ge siz_y\) ,如果 \(x,y\) 的度数不同,可以直接返回答案,如果 \(x,y\) 的父边编号不同,那么让 \(x\) 移动到父亲节点, \(y\) 一定向子树内移动,此时 \(x,y\) 一定不同构,否则,移动到任意不同构的子树即可。
考虑特殊情况 \(x=root\) ,发现此时不一定存在满足 \(siz_x\ge siz_y\) 的不同构的子树,但是容易发现此时一定存在 \(siz_x\le siz_y\) 的不同构的子树,仍然可以递归进行构造。
发现 \(\min(siz_x,siz_y)\) 单调递减,容易证明此时一定有解,第一部分移动了 \(\tfrac{n}{2}-1\) 次,第二部分移动了 \(\tfrac{n}{2}\) 次,可以通过本题。
code
#include "dream.h"
#include <map>
#include <utility>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int max1 = 2e5;
vector <int> tmp[max1 + 5];
int siz[max1 + 5], root;
int id[max1 + 5], father[max1 + 5];
map < pair <int, int>, bool > Map;
void Get_Size ( int now, int fa )
{
siz[now] = 1;
for ( auto v : tmp[now] )
{
if ( v == fa )
continue;
Get_Size(v, now);
siz[now] += siz[v];
}
return;
}
void Get_Root ( int now, int fa, int sum )
{
bool is_root = true;
for ( auto v : tmp[now] )
{
if ( v == fa )
continue;
Get_Root(v, now, sum);
if ( siz[v] > sum >> 1 )
is_root = false;
}
if ( sum - siz[now] > sum >> 1 )
is_root = false;
if ( is_root )
root = now;
return;
}
void Get_Father ( int now, int fa )
{
id[now] = -1, father[now] = fa;
for ( unsigned int i = 0; i < tmp[now].size(); i ++ )
{
int v = tmp[now][i];
if ( v == fa )
id[now] = i;
else
Get_Father(v, now);
}
return;
}
bool Check ( int x, int fx, int y, int fy )
{
if ( tmp[x].size() != tmp[y].size() )
return false;
int len = tmp[x].size();
for ( int i = 0; i < len; i ++ )
{
int v1 = tmp[x][i], v2 = tmp[y][i];
if ( v1 == fx || v2 == fy )
{
if ( v1 == fx && v2 == fy )
continue;
return false;
}
if ( !Check(v1, x, v2, y) )
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool Same ( int x, int fx, int y, int fy )
{
if ( x > y )
swap(x, y), swap(fx, fy);
if ( Map.find(make_pair(x, y)) != Map.end() )
return Map[make_pair(x, y)];
if ( id[x] != id[y] || siz[x] != siz[y] || tmp[x].size() != tmp[y].size() )
{ Map[make_pair(x, y)] = false; return false; }
int len = tmp[x].size();
for ( int i = 0; i < len; i ++ )
{
if ( i == id[x] )
continue;
if ( !Same(tmp[x][i], x, tmp[y][i], y) )
{ Map[make_pair(x, y)] = false; return false; }
}
Map[make_pair(x, y)] = true;
return true;
}
int Solve ( int x, int y, int deg )
{
if ( x == y )
return x;
if ( tmp[x].size() != tmp[y].size() )
{
if ( tmp[x].size() == deg )
return x;
return y;
}
int len = tmp[x].size();
for ( int i = 0; i < len; i ++ )
{
int v1 = tmp[x][i], v2 = tmp[y][i];
if ( min(siz[v1], siz[v2]) < min(siz[x], siz[y]) && !Same(v1, father[v1], v2, father[v2]) )
return Solve(v1, v2, move(i));
}
}
int dream ( int num, int q, int n, int deg, int x, int y, const vector <int> *edge )
{
++x, ++y;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
tmp[i] = edge[i - 1];
for ( unsigned int j = 0; j < tmp[i].size(); j ++ )
++tmp[i][j];
}
Get_Size(1, 0);
Get_Root(1, 0, n);
Get_Size(root, 0);
Get_Father(root, 0);
Map.clear();
while ( x != root && y != root )
{
if ( !Same(x, father[x], y, father[y]) )
break;
deg = move(id[x]);
x = father[x];
y = father[y];
}
if ( siz[x] < siz[y] )
swap(x, y);
if ( x == root && y == root )
return root - 1;
else if ( x == root && father[y] == x && Check(x, y, y, x) )
return -1;
return Solve(x, y, deg) - 1;
}
T3 不平衡度
设 \(f_i\) 表示平衡度小于等于 \(i\) 的方案数,考虑加入以 \(x\) 为根的子树的贡献,发现这个贡献只与节点 \(x\) 的左右儿子数量有关,设左儿子大小为 \(n\) ,右儿子大小为 \(m\) ,当前枚举的平衡度最大值为 \(k\) ,这相当于从 \((0,0)\) 走到 \((n,m)\) 且不经过直线 \(y=x+k+1\) 和 \(y=x-k-1\) 的方案数,那么有经典结论 \(ans=\binom{n+m}{n}-\sum_{i=1}^{\infty}(-1)^i(\binom{n+m}{n+i(k+1)}+\binom{n+m}{n-i(k+1)})\) 。(显然我不会证明)
发现以 \(x\) 为根的节点贡献的下界为 \(|n-m|\) ,由于 \(\max(n,m)\) 以上的贡献完全相同,因此可以用类似差分的方法进行维护,发现枚举的范围为 \(|n-m|\to\max(n,m)\) ,这个大小不超过 \(x\) 大小的一半,因此会产生 \(\log\) 的复杂度,由于存在调和级数,因此总复杂度为 \(O(n\log^2 n)\) 。
code
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int max1 = 1 << 20;
const int mod = 998244353;
int n, L[max1 + 5], R[max1 + 5];
int inv[max1 + 5], fac[max1 + 5], ifac[max1 + 5];
int siz[max1 + 5], f[max1 + 5], g[max1 + 5];
void Dfs ( int now )
{
if ( !now )
return;
Dfs(L[now]), Dfs(R[now]);
siz[now] = siz[L[now]] + siz[R[now]] + 1;
return;
}
int C ( int n, int m )
{
if ( n < m || n < 0 || m < 0 )
return 0;
return 1LL * fac[n] * ifac[n - m] % mod * ifac[m] % mod;
}
int Solve ( int n, int m, int k )
{
if ( n > m )
swap(n, m);
int ans = C(n + m, n);
for ( int i = 1; i * ( k + 1 ) <= m; i ++ )
{
if ( i & 1 )
ans = ( ( ans - C(n + m, n + i * ( k + 1 )) + mod ) % mod - C(n + m, n - i * ( k + 1 )) + mod ) % mod;
else
ans = ( ( ans + C(n + m, n + i * ( k + 1 )) ) % mod + C(n + m, n - i * ( k + 1 )) ) % mod;
}
return ans;
}
int main ()
{
freopen("imbalance.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("imbalance.out", "w", stdout);
scanf("%d", &n);
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
scanf("%d%d", &L[i], &R[i]);
inv[1] = 1;
for ( int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ )
inv[i] = 1LL * ( mod - mod / i ) * inv[mod % i] % mod;
fac[0] = 1, ifac[0] = inv[1];
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
fac[i] = 1LL * fac[i - 1] * i % mod,
ifac[i] = 1LL * ifac[i - 1] * inv[i] % mod;
Dfs(1);
for ( int i = 0; i <= n; i ++ )
f[i] = g[i] = 1;
int lim = 0, ans = 0;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
int down = abs(siz[L[i]] - siz[R[i]]), up = max(siz[L[i]], siz[R[i]]);
lim = max(lim, down);
for ( int j = down; j < up; j ++ )
f[j] = 1LL * f[j] * Solve(siz[L[i]], siz[R[i]], j) % mod;
g[up] = 1LL * g[up] * Solve(siz[L[i]], siz[R[i]], up) % mod;
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
g[i] = 1LL * g[i - 1] * g[i] % mod;
f[lim - 1] = 0;
for ( int i = lim; i <= n; i ++ )
f[i] = 1LL * f[i] * g[i] % mod, ans = ( ans + 1LL * ( f[i] - f[i - 1] + mod ) * i ) % mod;
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号