数据采集第二次作业
作业1
爬取城市天气信息实验
(1)要求:在中国气象网(http://www.weather.com.cn)给定城市集的7日天气预报,并保存在数据库。
核心代码:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup, UnicodeDammit
import urllib.request
import csv
def fetch_weather(city, url):
try:
req = urllib.request.Request(url, headers={"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0"}) # 模拟浏览器
raw = urllib.request.urlopen(req).read()
html = UnicodeDammit(raw, ["utf-8", "gbk"]).unicode_markup # 自动解码为 Unicode 字符串
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml") # 解析 HTML
items = []
# 定位天气数据块
for li in soup.select("ul.t.clearfix li")[:7]:
# 提取具体字段
date = li.h1.text.strip() # 日期
weather = li.select_one("p.wea").text.strip() # 天气状况
tem = li.select_one("p.tem") # 温度
high = tem.select_one("span")
low = tem.select_one("i")
temp = (high.text if high else "") + "/" + low.text if low else ""
items.append([city, date, weather, temp])
return items
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ {city} 失败: {e}")
return [] # 处理异常
# 配置城市
cities = {
"深圳": "https://www.weather.com.cn/weather/101280601.shtml",
"福州": "https://www.weather.com.cn/weather/101230101.shtml"
}
# 收集所有数据
all_data = [["城市", "日期", "天气", "温度"]] # CSV 表头
for city, url in cities.items():
print(f"正在获取 {city} 天气...")
all_data.extend(fetch_weather(city, url))
结果:
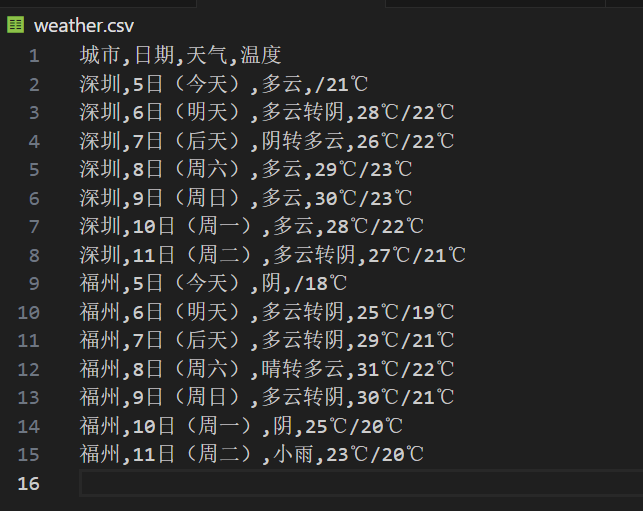
我的思路是先指定城市URL,再模拟浏览器请求获取天气页面,然后利用BeautifulSoup精准提取日期、天气和温度信息,结构化整理为7日预报数据,最后统一写入CSV文件。
(2)心得体会:
实践中学到网页编码处理与选择器定位技巧,深入了解了BeautifulSoup分析HTML页面的操作,也体会到爬虫需兼顾效率、健壮性与网站规则尊重。
作业2
爬取股票信息实验
(1)要求:用requests和API方法定向爬取股票相关信息,并存储在数据库中。
核心代码:
def fetch_page(self, page: int, pagesize: int = 20):
# 构造请求参数
params = {
'pn': page, # 页码
'pz': pagesize, # 每页数量
'po': 1, # 排序方式(1=升序,2=降序?此处固定为1)
'np': 1, # 是否返回分页信息(1=返回)
'fltt': 2, # 价格显示类型(2=显示百分比涨跌幅)
'invt': 2, # 股票类型(2=A股)
'fid': 'f3', # 排序字段(f3=涨跌幅)
'fs': 'm:0 t:6,m:0 t:80,m:1 t:2,m:1 t:23', # 筛选条件:
# m:0 t:6 → 沪A主板
# m:0 t:80 → 沪A科创板
# m:1 t:2 → 深A主板
# m:1 t:23 → 深A创业板
'fields': 'f12,f14,f2,f3,f4,f5,f6,f7,f15,f16,f17,f18' # 需要返回的字段
}
try:
# 发送 GET 请求
resp = requests.get(
self.base_url,
params=params,
headers=self.headers,
timeout=10 # 超时10秒
)
resp.raise_for_status() # 如果状态码不是200,抛出异常
text = resp.text
if text.startswith('jQuery'):
json_str = text[text.find('(') + 1:text.rfind(')')] # 提取括号内的 JSON 字符串并解析
data = json.loads(json_str)
else:
data = resp.json()
return data.get('data', {}).get('diff', []) # 提取股票数据列表(路径:data → diff)
except Exception as e:
print(f"第 {page} 页请求失败: {e}")
return [] # 异常处理
# 解析单条股票数据
def parse_stock(self, item):
now = datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') # 当前时间戳
return {
'stock_code': item.get('f12', ''), # 股票代码
'stock_name': item.get('f14', ''), # 股票名称
'current_price': item.get('f2'), # 当前价
'change_percent': item.get('f3'), # 涨跌幅(%)
'change_amount': item.get('f4'), # 涨跌额
'volume': item.get('f5'), # 成交量(单位:手)
'turnover': item.get('f6'), # 成交额(元)
'amplitude': item.get('f7'), # 振幅(%)
'high': item.get('f15'), # 最高价
'low': item.get('f16'), # 最低价
'open_price': item.get('f17'), # 开盘价
'close_price': item.get('f18'), # 昨收价
'update_time': now # 数据抓取时间
}
# 保存到 SQLite 数据库
def save_to_db(self, stocks):
with sqlite3.connect('stocks.db') as conn:
conn.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS stocks (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
stock_code TEXT NOT NULL,
stock_name TEXT NOT NULL,
current_price REAL,
change_percent REAL,
change_amount REAL,
volume REAL,
turnover REAL,
amplitude REAL,
high REAL,
low REAL,
open_price REAL,
close_price REAL,
update_time TEXT,
UNIQUE(stock_code, update_time)
)
''') # 创建表
conn.executemany('''
INSERT OR REPLACE INTO stocks
(stock_code, stock_name, current_price, change_percent, change_amount,
volume, turnover, amplitude, high, low, open_price, close_price, update_time)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
''', [tuple(s.values()) for s in stocks]) # 将每个字典转为元组
print(f"已保存 {len(stocks)} 条数据到数据库")
结果:
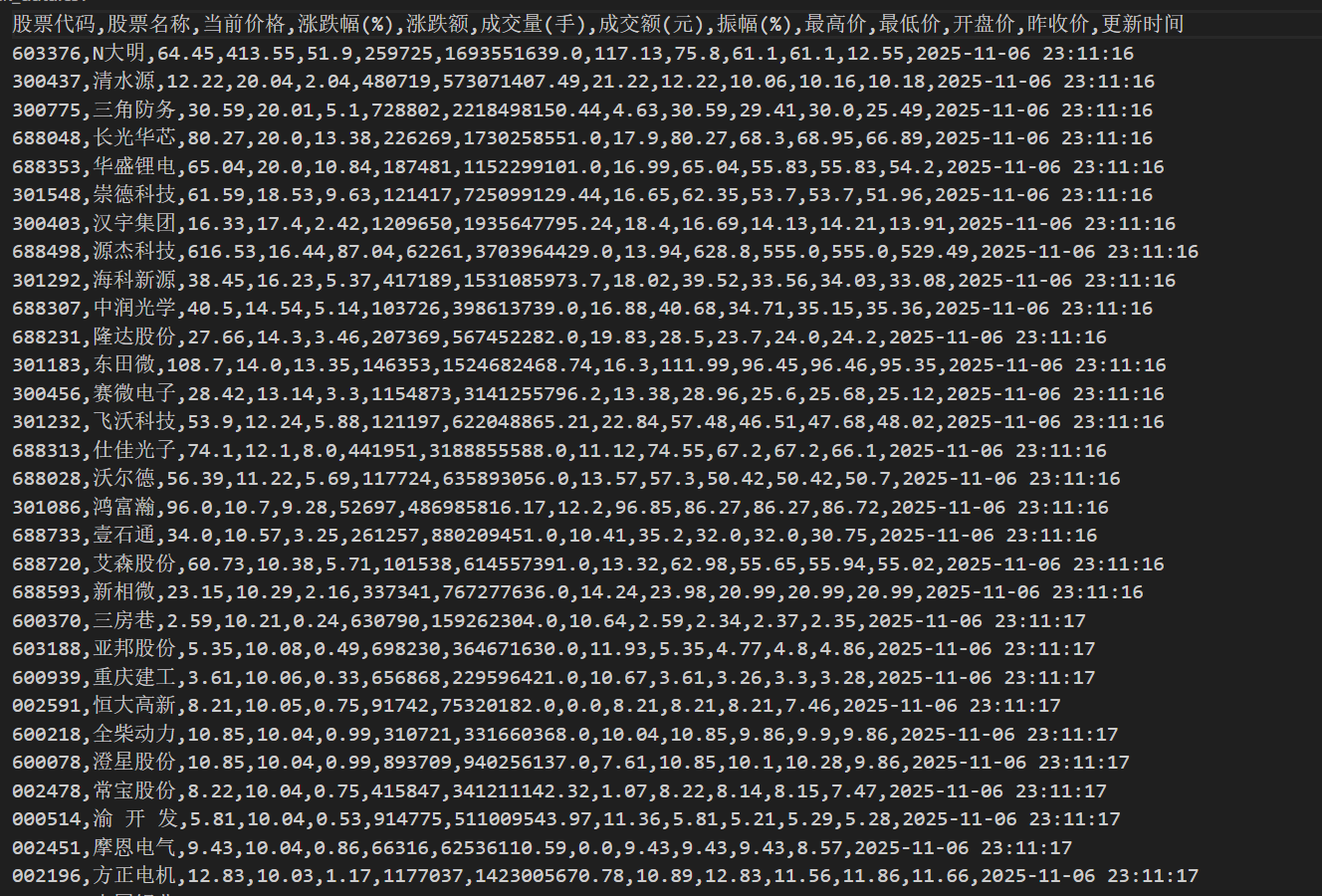
我的思路是先从利用东方财富网的公开接口获取原始响应,并对原始响应进行解析,通过params参数精确控制返回内容,提取结构化信息,再将原始字段(如 f12、f3 等)映射为语义清晰的中文键名(如 stock_code、change_percent),然后导入数据库,再格式化输出为csv和Excel文件。
(2)心得体会:
通过编写股票数据爬虫,我深入理解了API参数构造、JSONP响应处理及数据清洗流程。合理设置请求头和分页逻辑能有效提升稳定性,而字段映射与异常处理则保障了数据的完整性与程序的健壮性,为后续分析相似数据打下坚实基础。
作业3
爬取学校排名实验
(1)要求:爬取中国大学2021主榜(https://www.shanghairanking.cn/rankings/bcur/2021)所有院校信息,并存储在数据库中,同时将浏览器F12调试分析的过程录制Gif加入至博客中。
核心代码:
# 获取 API 数据
def fetch_rankings_via_api() :
url = "https://www.shanghairanking.cn/api/pub/v1/bcur?bcur_type=11&year=2021" # API地址
headers = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0'} # 模拟浏览器
try:
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=10) # 发送 HTTP 请求处理响应
response.raise_for_status() # 处理响应
# 解析 JSON 数据
rankings = response.json()['data']['rankings']
# 构建标准化的大学数据列表
return [
{
'ranking': i,
'univNameCn': item.get('univNameCn', 'N/A'),
'score': item.get('score', 0),
'province': item.get('province', '未知'),
'univCategory': item.get('univCategory', '未知')
}
for i, item in enumerate(rankings, 1)
]
except Exception as e:
print(f"获取数据失败: {e}")
return None # 处理异常
class UniversityDatabase:
def __init__(self, db_path='university_rankings.db'):
self.db_path = db_path
self.create_table()
# 创建数据表
def create_table(self):
with sqlite3.connect(self.db_path) as conn:
conn.execute("""
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS university_rankings_2021 (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
ranking INTEGER NOT NULL,
univ_name_cn TEXT NOT NULL,
score REAL NOT NULL,
province TEXT,
univ_category TEXT,
created_time TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
)
""")
# 插入数据
def insert_data(self, universities):
with sqlite3.connect(self.db_path) as conn:
# 使用 executemany 批量插入多条记录
try:
conn.executemany("""
INSERT INTO university_rankings_2021
(ranking, univ_name_cn, score, province, univ_category)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
""", [
(u['ranking'], u['univNameCn'], u['score'], u['province'], u['univCategory'])
for u in universities # 从每所大学的字典中提取对应字段,按顺序组成元组列表
])
print(f"成功插入 {len(universities)} 条数据")
except Exception as e:
print(f"数据插入失败: {e}")
raise
结果:
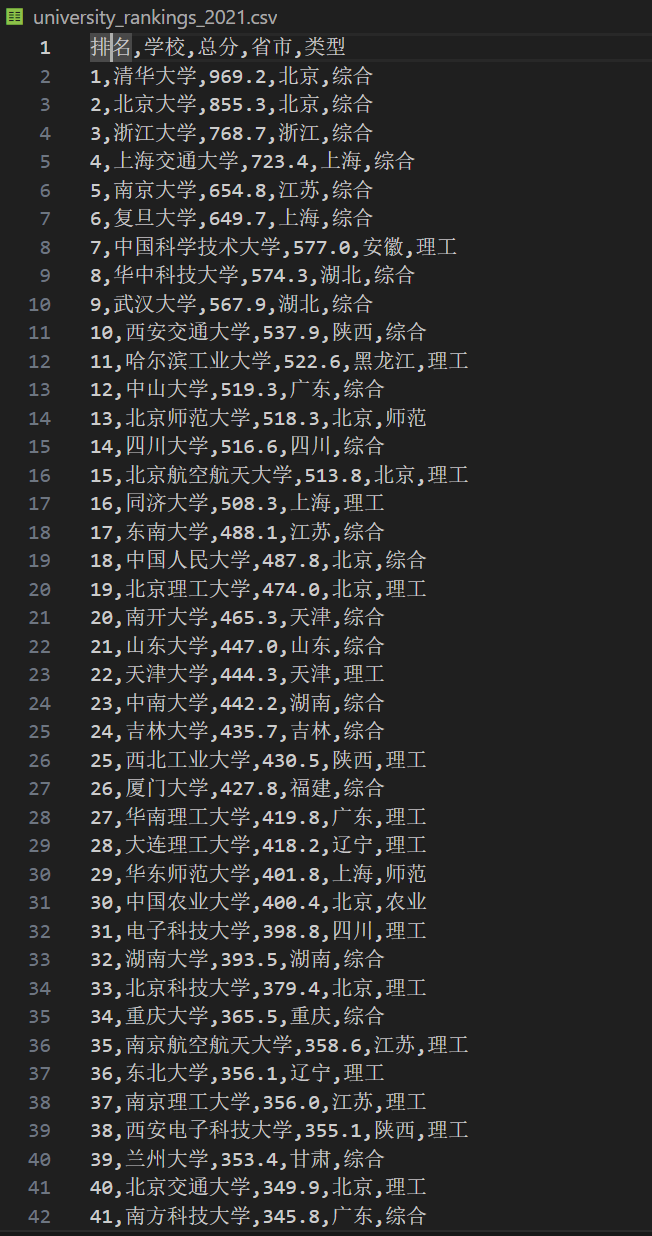
GIF:

我的思路是先利用API地址来获取JSON数据同时进行解析,再构建标准化的大学数据列表,然后根据构建的数据列表来创建数据表,同时使用 executemany 批量插入多条记录,最后格式化输出为CSV文件。
(2)心得体会:
本次实验通过分析软科官网的网络请求,精准定位到2021年中国大学排名的API接口,直接获取结构化数据。借助requests抓取、SQLite持久化存储,并用pandas导出CSV,高效完成数据采集全流程。实践让我掌握了基于开发者工具(F12)分析XHR请求的核心技巧,提升了对现代网站数据爬取的理解。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号