使用Galaxy实现AES_CBC带干扰的加解密
在浏览一个网站的过程中,发现该网站与服务端之间http通信都是进行加密的,刚好最近在学习js逆向,就拿这个网站来试试,顺带看看如何使用Galaxy进行加解密。
在登录接口处设置断点调试,找到加密函数

定位加解密函数,获得干扰项位置
加密函数:

解密函数:

定位AES、CBC加密方式使用的KEY、IV
这里是通过断点调试,一步步的跟函数获得加密后的KEY和IV进行返推获得的KEY、IV。

实现加解密
安装Burp插件 Galaxy ,还要记得下载提供的脚本 GalaxyHttpHooker
因为已经知道了是aes cbs加密,但是其中添加了干扰内容,所以要修改原有的cbc加解密脚本:
增加对请求包进行【解密-加密】的函数,
从客户端发送--Burp拦截--去除干扰--解密--Burp中呈现或修改--加密--添加干扰--提交服务端
# 实现解密
def remove_request_noise(s):
# 删除 35:45(10字符)
return s[:35] + s[45:]
def get_request_data(content: bytes) -> bytes:
print("get_request_data:", content)
body_json: t.Dict = json.loads(content)
return base64.b64decode(remove_request_noise(body_json[JSON_KEY]))
# 实现加密
def add_request_noise(s: str) -> str:
"""在响应数据中添加混淆字符"""
# 添加中缀混淆(10个随机字符)
infix = ''.join(random.choices(string.ascii_lowercase, k=10))
if len(s) < 35:
raise ValueError("密文太短,无法插入干扰")
# 在索引 35 处插入 10 个随机小写字母
return s[:35] + infix + s[35:]
def to_request_data(content: bytes) -> bytes:
body_json = {}
base64_data = base64.b64encode(content).decode()
noisy_data = add_request_noise(base64_data)
body_json[JSON_KEY] = noisy_data
return json.dumps(body_json).encode()
增加对响应包进行【解密-加密】的函数
服务端返回--Burp拦截--去除干扰--解密--Burp中呈现或修改--加密--添加干扰--返回客户端
# 实现解密
def remove_response_noise(s):
# 删除 20:36(16字符)
return s[:20] + s[36:]
def get_response_data(content: bytes) -> bytes:
body = remove_response_noise(content)
return base64.b64decode((body))
# 实现加密
def add_response_noise(s: str) -> str:
"""在响应数据中添加混淆字符"""
# 添加中缀混淆(16个随机字符)
infix = ''.join(random.choices(string.ascii_lowercase, k=16))
if len(s) < 20:
raise ValueError("密文太短,无法插入干扰")
# 在索引 35 处插入 10 个随机小写字母
return s[:20] + infix + s[20:]
def to_response_data(contnet: bytes) -> bytes:
body = base64.b64encode(contnet).decode()
noisy_data = add_response_noise(body)
return noisy_data.encode()
完整的代码实现
import json
import base64
import typing as t
from fastapi import FastAPI
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad, unpad
from _base_classes import *
import random
import string
KEY = b""
IV = b""
JSON_KEY = "params"
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/hookRequestToBurp", response_model=RequestModel)
async def hook_request_to_burp(request: RequestModel):
"""HTTP请求从客户端到达Burp时被调用。在此处完成请求解密的代码就可以在Burp中看到明文的请求报文。"""
print(f"[+] hookRequestToBurp be called. request: {request.model_dump_json()}")
# 获取需要解密的数据
encrypted_data: bytes = get_request_data(request.content)
# 调用函数解密
data: bytes = decrypt(encrypted_data)
# 更新body为已解密的数据
request.content = data
return request
@app.post("/hookRequestToServer", response_model=RequestModel)
async def hook_request_to_server(request: RequestModel):
"""HTTP请求从Burp将要发送到Server时被调用。在此处完成请求加密的代码就可以将加密后的请求报文发送到Server。"""
print(f"[+] hookRequestToServer be called. request: {request.model_dump_json()}")
# 获取被解密的数据
data: bytes = request.content
# 调用函数加密回去
encryptedData: bytes = encrypt(data)
# 将已加密的数据转换为Server可识别的格式
body: bytes = to_request_data(encryptedData)
# 更新body
request.content = body
return request
def remove_request_noise(s):
# 删除 35:45(10字符)
return s[:35] + s[45:]
def get_request_data(content: bytes) -> bytes:
print("get_request_data:", content)
body_json: t.Dict = json.loads(content)
return base64.b64decode(remove_request_noise(body_json[JSON_KEY]))
def add_request_noise(s: str) -> str:
"""在响应数据中添加混淆字符"""
# 添加中缀混淆(10个随机字符)
infix = ''.join(random.choices(string.ascii_lowercase, k=10))
if len(s) < 35:
raise ValueError("密文太短,无法插入干扰")
# 在索引 35 处插入 10 个随机小写字母
return s[:35] + infix + s[35:]
def to_request_data(content: bytes) -> bytes:
body_json = {}
base64_data = base64.b64encode(content).decode()
noisy_data = add_request_noise(base64_data)
body_json[JSON_KEY] = noisy_data
return json.dumps(body_json).encode()
@app.post("/hookResponseToBurp", response_model=ResponseModel)
async def hook_response_to_burp(response: ResponseModel):
"""HTTP响应从Server到达Burp时被调用。在此处完成响应解密的代码就可以在Burp中看到明文的响应报文。"""
print(f"[+] hookResponseToBurp be called. response: {response.model_dump_json()}")
# 获取需要解密的数据
encryptedData: bytes = get_response_data(response.content)
# 调用函数解密
data: bytes = decrypt(encryptedData)
# 更新body
response.content = data
return response
@app.post("/hookResponseToClient", response_model=ResponseModel)
async def hook_response_to_client(response: ResponseModel):
"""HTTP响应从Burp将要发送到Client时被调用。在此处完成响应加密的代码就可以将加密后的响应报文返回给Client。"""
print(f"[+] hookResponseToClient be called. response: {response.model_dump_json()}")
# 获取被解密的数据
data: bytes = response.content
# 调用函数加密回去
encryptedData: bytes = encrypt(data)
# 将已加密的数据转换为Server可识别的格式
body: bytes = to_response_data(encryptedData)
# 更新body
response.content = body
return response
def remove_response_noise(s):
# 删除 20:36(16字符)
return s[:20] + s[36:]
def get_response_data(content: bytes) -> bytes:
body = remove_response_noise(content)
return base64.b64decode((body))
def add_response_noise(s: str) -> str:
"""在响应数据中添加混淆字符"""
# 添加中缀混淆(16个随机字符)
infix = ''.join(random.choices(string.ascii_lowercase, k=16))
if len(s) < 20:
raise ValueError("密文太短,无法插入干扰")
# 在索引 35 处插入 10 个随机小写字母
return s[:20] + infix + s[20:]
def to_response_data(contnet: bytes) -> bytes:
body = base64.b64encode(contnet).decode()
noisy_data = add_response_noise(body)
return noisy_data.encode()
def decrypt(content: bytes) -> bytes:
cipher = AES.new(KEY, AES.MODE_CBC, IV)
return unpad(cipher.decrypt(content), AES.block_size)
def encrypt(content: bytes) -> bytes:
cipher = AES.new(KEY, AES.MODE_CBC, IV)
return cipher.encrypt(pad(content, AES.block_size))
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 多进程启动
# uvicorn aes_cbc:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 25000 --workers 4
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=25000)
效果展示
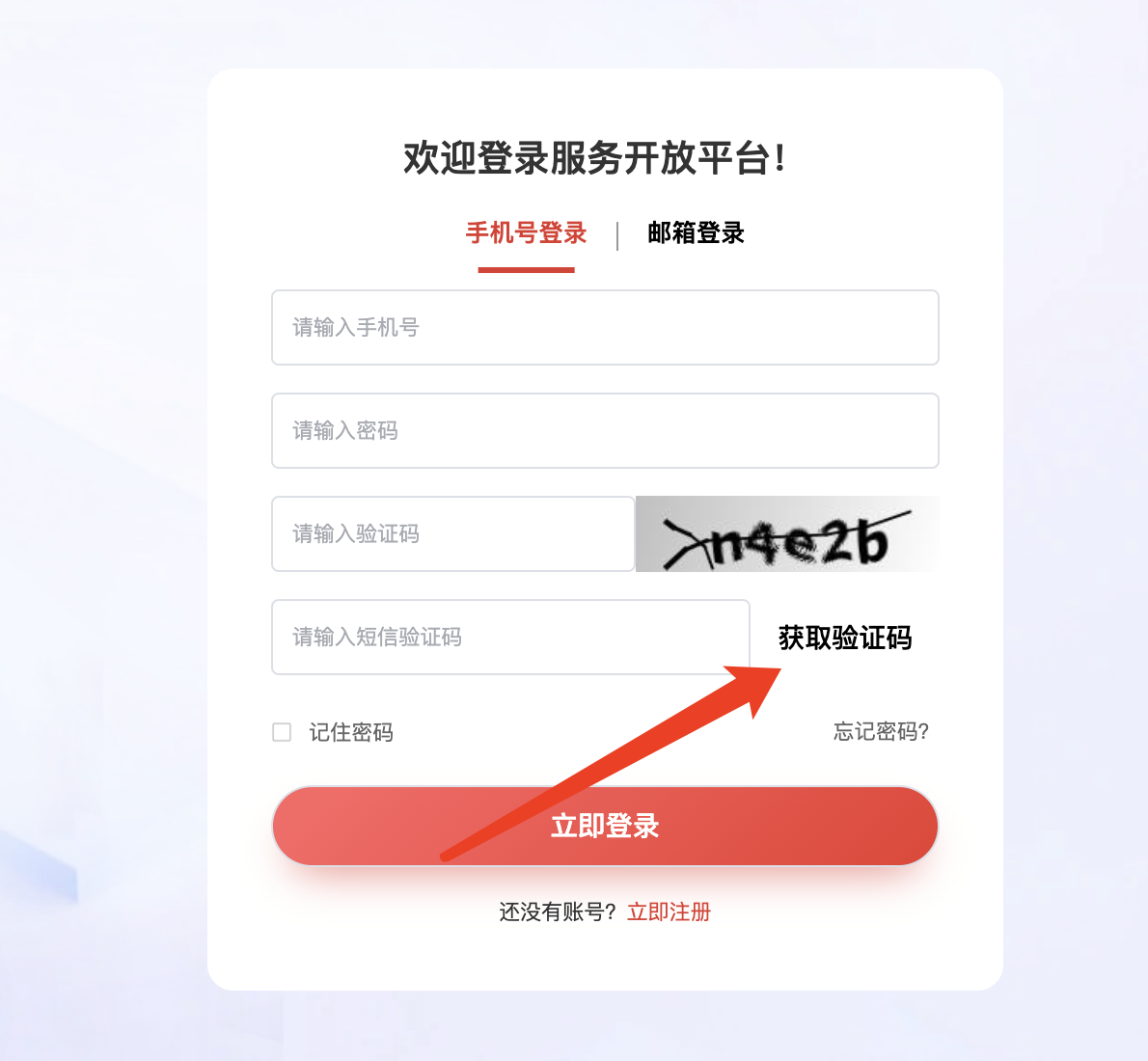
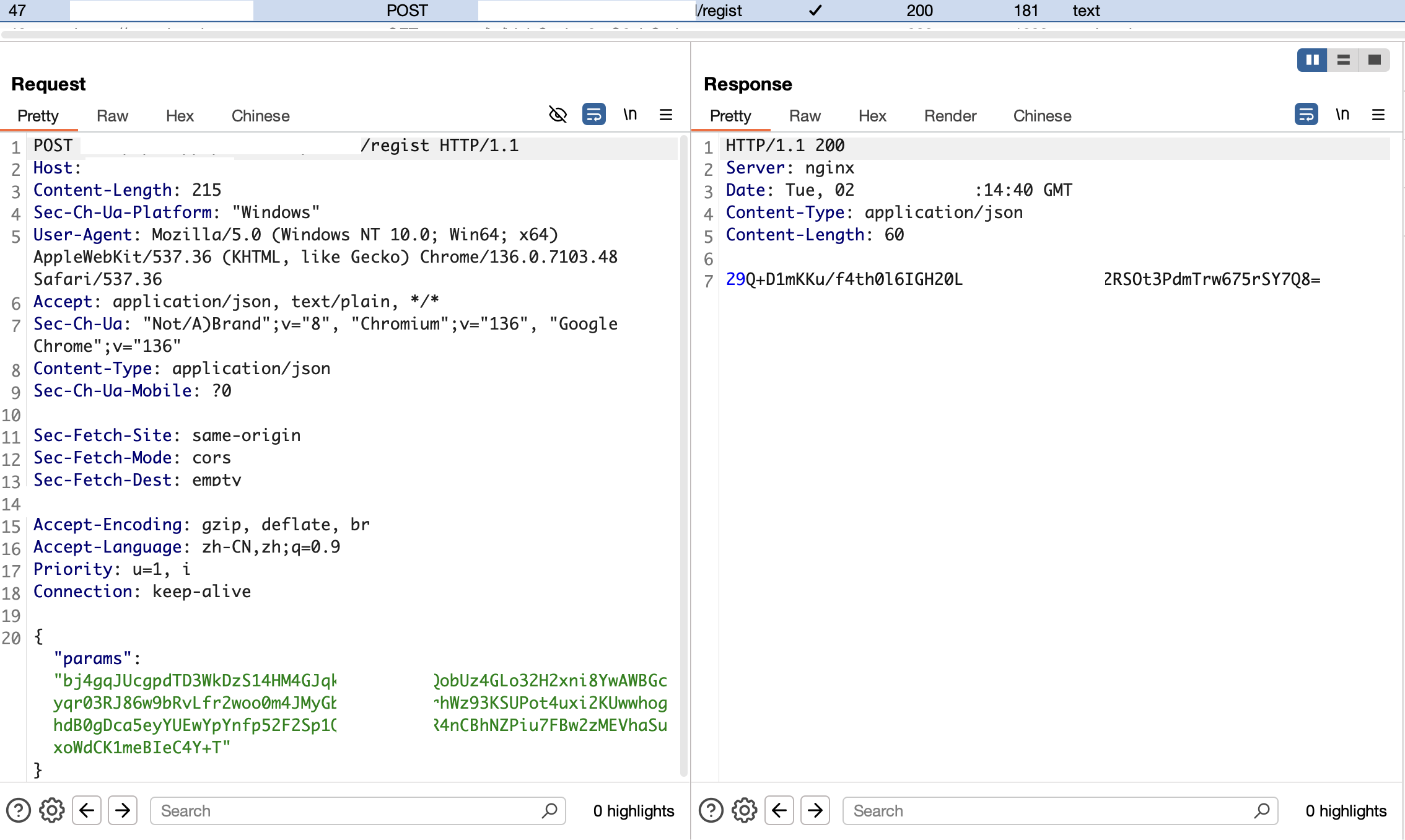
输入完成手机号、验证码,点击获取验证码时发送的是加密数据包,收到的也是加密数据包:
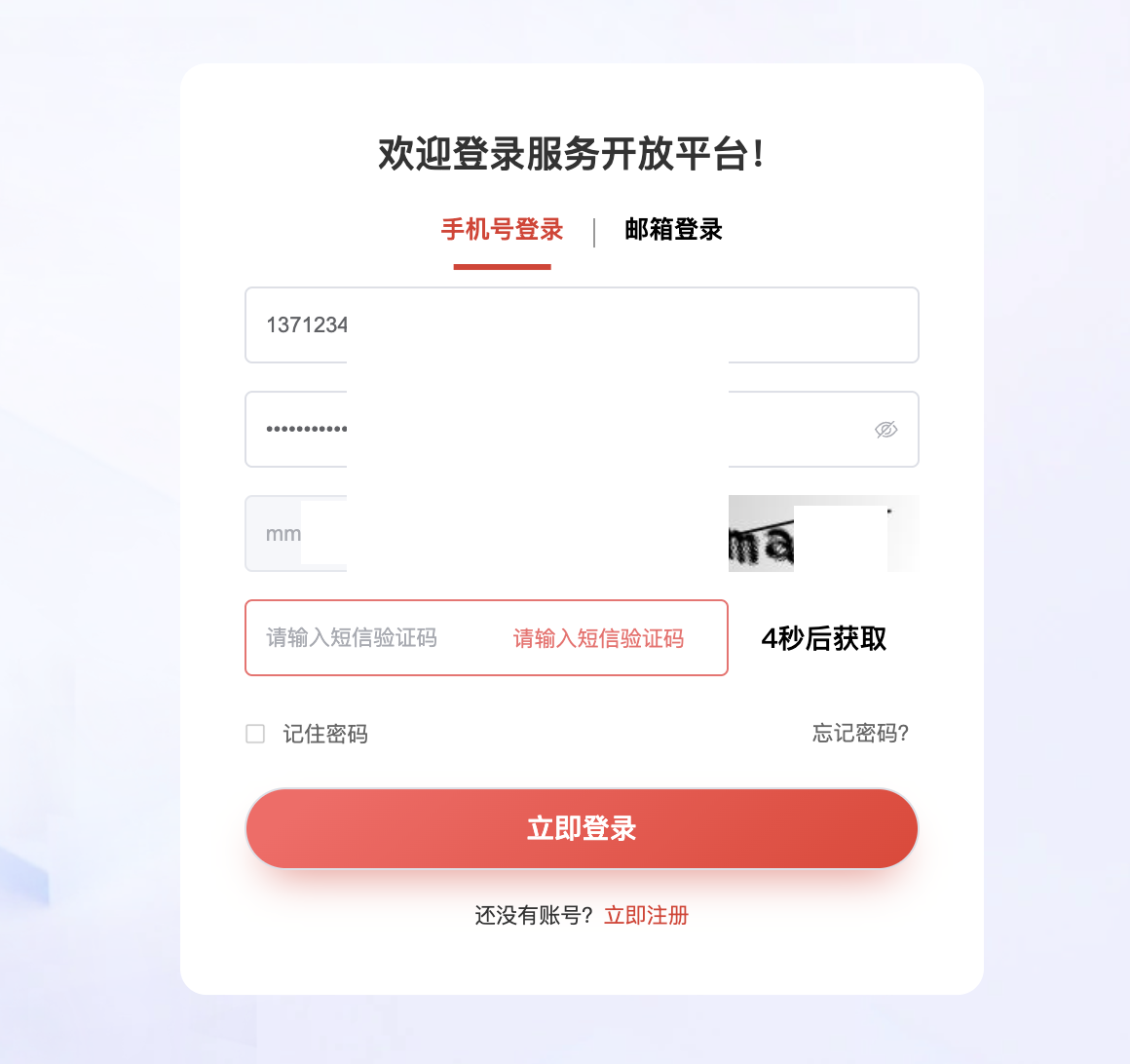
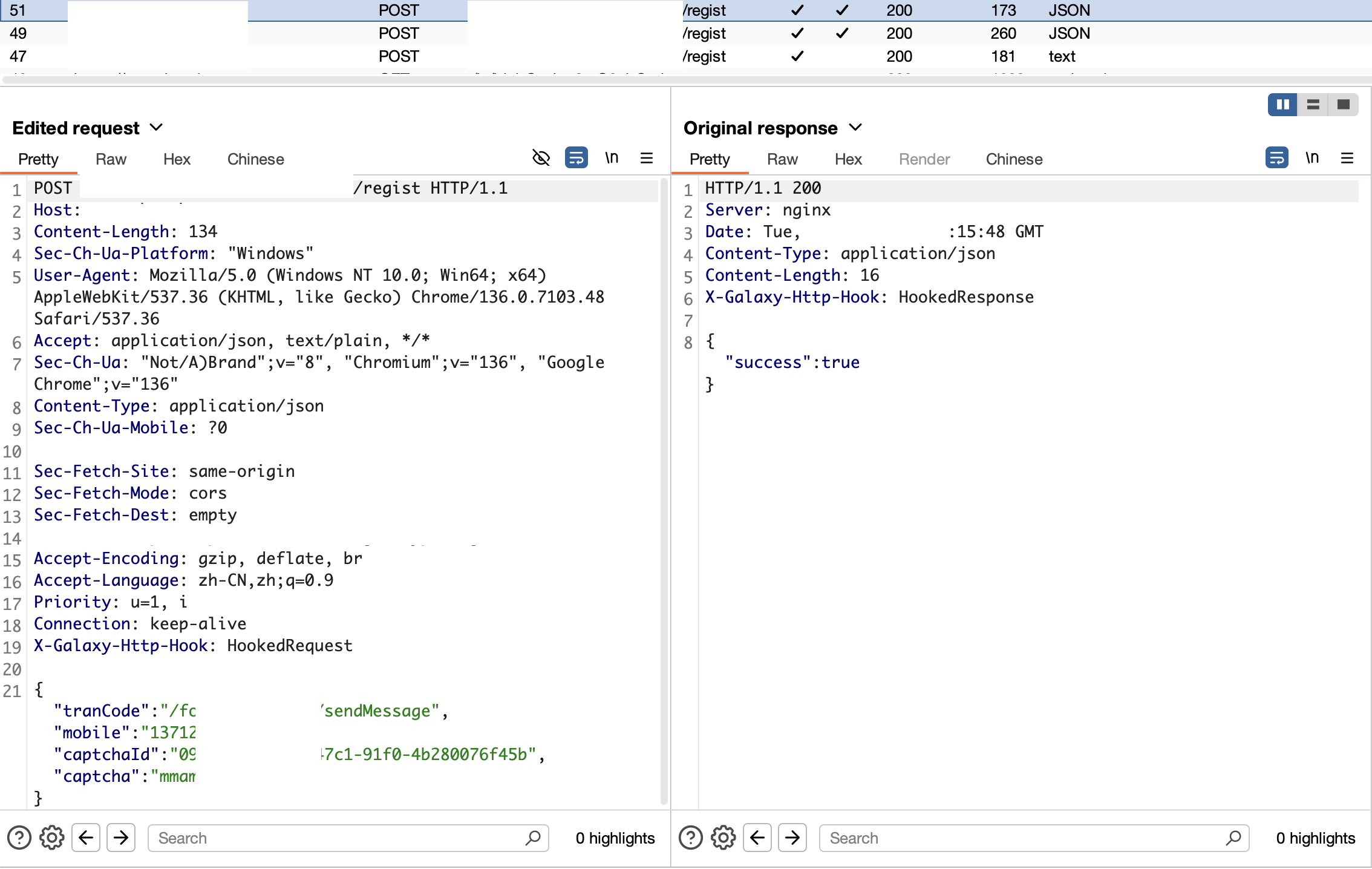
运行脚本,设置Galaxy好后,经过代理的流量就都是解密好的了。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号