DDL,DML,子查询,各种表连接,rownum,rowid

DML: insert/update/delete
Insert语句:

动态输入插入数据:表名、字段名、值 前都可以加&来动态输入值

批量插入数据:
1.创建新表(批量插入数据之前此表不存在)
把emp中所有的数据都插入到新表:create table mytab as select * from emp;
插入部分数据:create table mytab1 as select ename,job,sal from emp where sal <6000;
如果只要表结构不要表数据:create table mytab2 as select * from emp where 1=0;
2.在旧表中插入数据(表已经存在)
insert into mytab3(ename,job,sal) select ename,job,sal from emp where sal >2000;
3.使用事务 begin.....end /
begin
insert into mytab4 values('hello','analyst',5000);
insert into mytab4 values('hello','clerk',4000);
end;
delete 语句: 删除表用drop table 表名
删除所有的数据: 1. delete from 表名 可以使用rollback 回退 2.truncate table 表名 不可以回退 原因:只有DML语句可以回退
两者的区别:
1.delete 可以回退,truncate 不可以回退
2.对于小数据量,delete删除比truncate快,但是对于大数据量,truncate效率高,原因:delete是一行一行的删除,而truncate是直接先删除整张表然后再新建一张空表(如何查看执行时间 set timing on/off)
3.delete 会产生碎片,而truncate不会,如果碎片太多,需要整理碎片:a. alter table 表名 move b.导入导出
4.delete不会释放空间(换了个地方存储数据[undo空间]),truncate会
5.delete 支持闪回,truncate 不支持闪回
删除选定行:delete from 表名 where .....
update 语句:
update 表名 set 字段名1 = value1,字段名2 = value2.....where.... 不加where则会全部修改
DDL: create/drop/truncate/alter table
CREATE语句:
create table 表名(
字段名 类型,
字段名 类型
)
create table person(
id number(4) not null primary key,
name varchar2(20),
age number(3)
)

修改表:alter
1.增加列名: alter table 表名 add 字段名 类型 alter table person add address varchar2(30);
2.修改列:修改列的长度/类型:alter table 表名 modify 字段名 类型 : alter table person modify address varchar2(40);
注意:blob和clob不能修改 -->非要改,先删除再增加
1.BLOB
BLOB全称为二进制大型对象(Binary Large Object)。它用于存储数据库中的大型二进制对象。可存储的最大大小为4G字节
2.CLOB
CLOB全称为字符大型对象(Character Large Object)。它与LONG数据类型类似,只不过CLOB用于存储数据库中的大型单字节字符数据块,不支持宽度不等的字符集。可存储的最大大小为4G字节
通常像图片、文件、音乐等信息就用BLOB字段来存储,先将文件转为二进制再存储进去。而像文章或者是较长的文字,就用CLOB存储,这样对以后的查询更新存储等操作都提供很大的方便。
3.删除列:alter table 表名 drop column 列名 :alter table person drop column address;
4.修改列名 alter table 表名 rename column 列名 to 新列名 alter table person rename column email to emailNew;
删除表:
drop table 表名: 可以回退 ,删除的表放在了回收站, drop table 表名 purge: 不进回收站,删除并清空
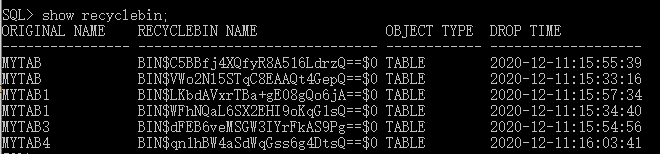
查看回收站:show recyclebin select * from tab: 表以及回收站的表
还原回收站:purge recyclebin;
清空回收站:闪回
表连接:
内连接:多张表通过相同字段进行连接,只显示匹配成功的数据
1.select * from emp e,dept d where e.deptno = d.deptno;
2.select * from emp e inner join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno
外连接:
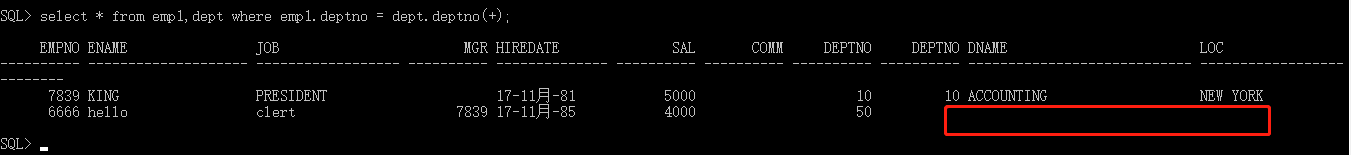
左外连接:以左表为基准(左表的数据全部显示),去匹配右表的数据,如果匹配成功,则全部显示,匹配不成功,则显示部分(无数据部分用null填充)
1.Oracle独有的写法:select * from emp1,dept where emp1.deptno = dept.deptno(+);
2.select * from emp1 left join dept on emp1.deptno=dept.deptno;
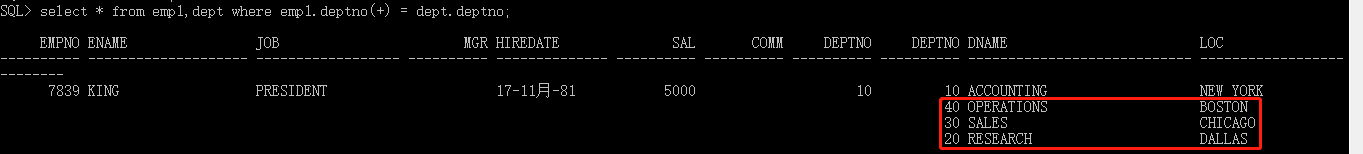
右外连接 :以左表为基准(右表的数据全部显示),去匹配左表的数据,如果匹配成功,则全部显示,匹配不成功,则显示部分(无数据部分用null填充)
1.Oracle独有的写法:select * from emp1,dept where emp1.deptno(+) = dept.deptno
2.select * from emp1 right join dept on emp1.deptno=dept.deptno;
全连接: 左外加右外再去重
select * from emp1 full join dept on emp1.deptno = dept.deptno;
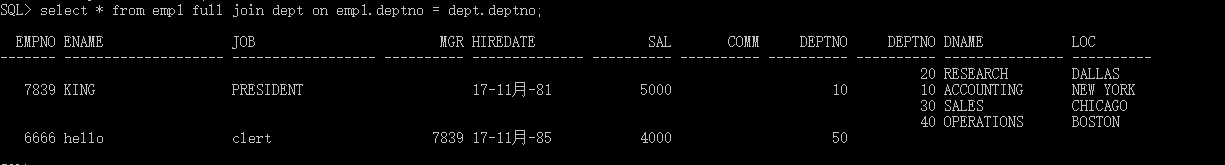
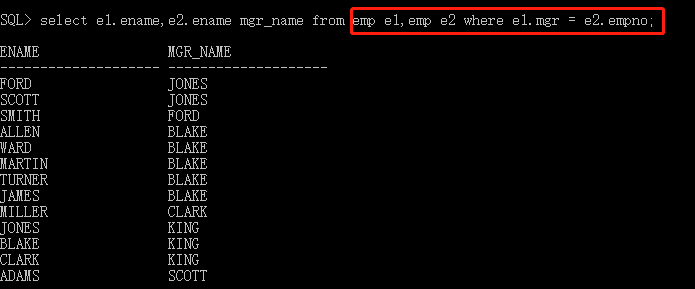
自连接:
查找员工的经理的名字:select e1.ename,e2.ename mgr_name from emp e1,emp e2 where e1.mgr = e2.empno;
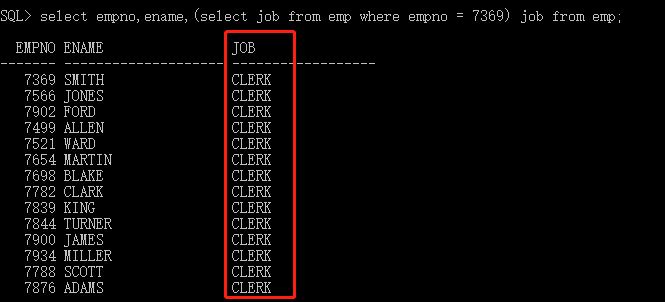
子查询:
1.子查询可以出现的位置:where、select、having、from 但是不能出现再group by 里面
select后面 表示单行列(常量列),只能由一个值
select empno,ename,(select job from emp where empno = 7369) job from emp;
select empno,ename,'CLARK' from emp;
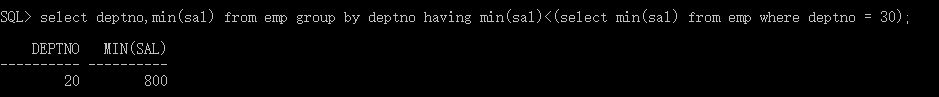
havind 后面 查询最低工资比30号部分最低工资还低的部分
select deptno,min(sal) from emp group by deptno having min(sal)<(select min(sal) from emp where deptno = 30);
from 后面:相当于修改了表结构
2.子查询中的null
单行操作符(=,>,<,!=,...) 多行操作符(in,not in)
in():这里面不能写null,因为null需要写is null 而不能 = null;
value in(A,B,null) 表示: value=A or value=B or value = null,那么value =null的值是搜索不到的。
not in(A,B,null):value!=A and value!=B and value !=null,这个是搜索不到数据的 null自身的特性,如果!=null则无法查询出任何数据,要用 is null, is not null;
子查询的结果中不要有null;如果有则先进行排空
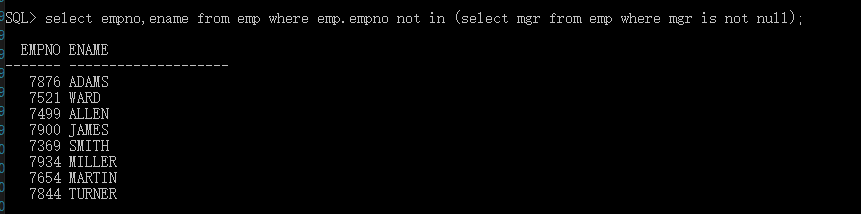
查询不是领导的员工信息: select empno,ename from emp where emp.empno not in (select mgr from emp where mgr is not null);
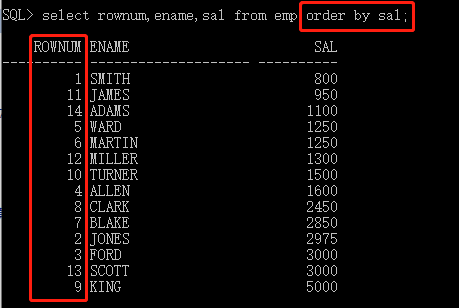
3.一般不在子查询中排序(排序没啥用),除非TOP-N问题(分页)
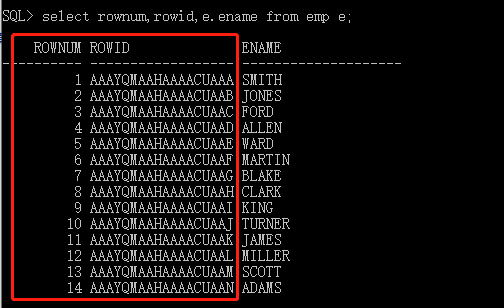
rownum 和rowid:



1. Top-n 问题解决:
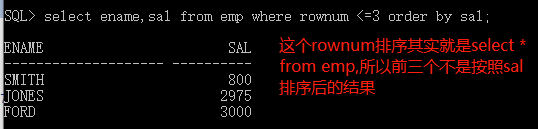
所以不能直接select ename,sal from emp where rownum <=3 order by sal;
top-n 前n个数据:
select rownum,....from (子查询里面需要order by) where rownum<=n;
查询薪资最高的前三个人:
select rownum,ename,sal from (select ename,sal from emp order by sal desc ) where rownum <=3;
2.用来删除重复数据:

如何一次性删除所有的重复的数据:

delete from mystudent where rowid not in(select min(rowid) from mystudent group by stuno)

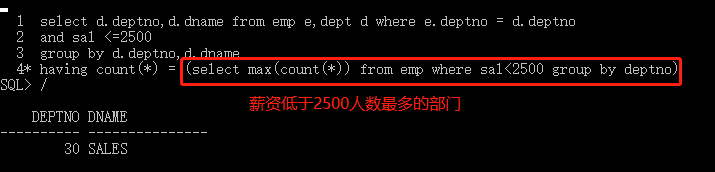
select d.deptno,d.dname from emp e,dept d where e.deptno = d.deptno
and sal <=2500
group by d.deptno,d.dname
having count(*) = (select max(count(*)) from emp where sal<2500 group by deptno)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号