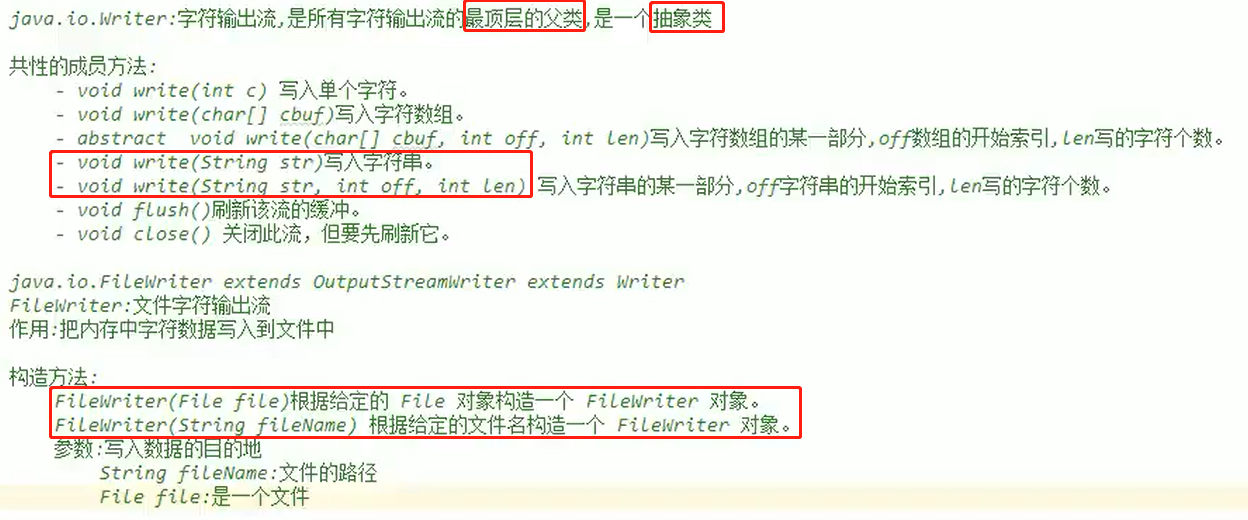
I/O
1.输入输出都是相对内存和硬盘来说的
内存 ==> 硬盘:输出流,写入操作
硬盘 ==> 内存:输入流,读取操作
字节流:
InputStream FileInputStream BufferedInputStream InputStreamReader(从字节流到字符流的桥:它读取字节,并使用指定的charset将其解码为字符)
OutputStream FileOutputStream BufferedOutputStream OutputStreamWriter(从字节流到字符流的桥:向其写入的字符编码成使用指定的字节charset )
字符流
Reader FileReader BufferedReader
Writer FileWriter BufferedWriter
注意:关闭流资源一般放在finally 里面(fos.close(),而由于在开始的时候fos是赋值为null的,如果创建失败,那么就会引发NullPointException,所以在关闭资源的时候要注意先判断(if(fos!=null){fos.close() })

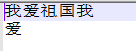
public static void main(String[] args) { try(FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\7_Joyce\\e.txt");){ byte[] bytes = "我爱祖国".getBytes(); byte[] bytes1 = new byte[] {(byte) 206,(byte) 210}; // System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));//[-50, -46, -80, -82, -41, -26, -71, -6] fos.write(bytes); fos.write(bytes1); fos.write("\r\n".getBytes()); fos.write("爱".getBytes()); }catch(IOException ex) { System.out.println(ex); } }

字节流:
OutputStream:
FileOutputStream:(创建一个实例对象就会创建一个空的文件)
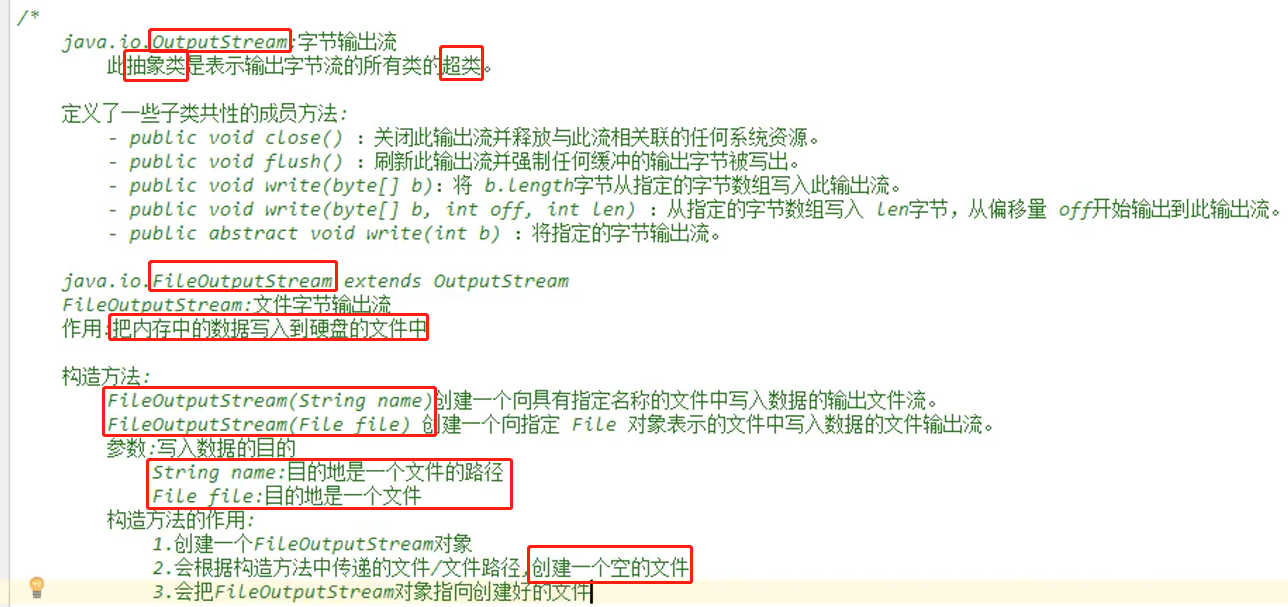

1.一次写入一个字符:
public void write(int b) throws IOException
public class TestFileOutputStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 创建一个对象的时候就会直接创建好这个文件 // 创建对象的时候需要捕获一个FileNotFoundException FileOutputStream fos = fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\7_Joyce\\a.txt"); // write方法会需要捕获一个IOException fos.write(97);// 会在文件中写入字符‘a’ fos.close(); } }

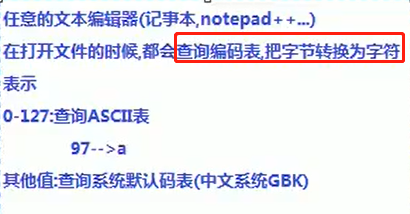
2.一次性写入多个字符:
String 类里面有一个方法:getBytes()可以把字符串转换成byte数组.
public void write(byte[] b)throws IOException
将b.length字节写入此输出流。
public void write(byte[] b,int off,int len)throws IOException
从指定的byte阵列写入len字节,从偏移量off开始输出到此输出流。

public class FileOutputStreamWriteString { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\7_Joyce\\b.txt"); byte[] bytes = "我爱祖国".getBytes(); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));//[-50, -46, -80, -82, -41, -26, -71, -6] fos.write(bytes); fos.close(); } }
3.数据的追加写入:
FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append) 创建文件输出流以写入由指定的 File对象表示的文件。
FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append) 创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件。
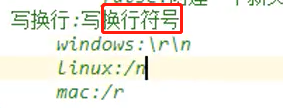
fos.write("\r\n".getBytes());
InputStream:

FileInputStream:
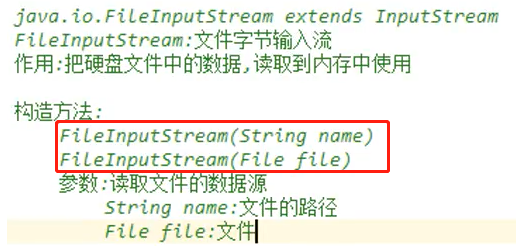

一次读取一个字节:
public int read() throws IOException 从该输入流读取下一个数据字节。 值字节作为int返回为0到255
 读取到的是一个一个的ASCII码值://97 98 99 100 13 10 104 101 108 108 111
读取到的是一个一个的ASCII码值://97 98 99 100 13 10 104 101 108 108 111
public class FileInputStreamDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\7_Joyce\\a.txt"); int len = 0; while((len = fis.read())!=-1) { System.out.print(len+" "); //97 98 99 100 13 10 104 101 108 108 111 } fis.close(); } }
一次读取多个字节:
public int read(byte[] b) throws IOException //返回的是字节数 读取到的字节存储在byte 数组中。
从该输入流读取最多b.length字节的数据到字节数组。 此方法将阻塞,直到某些输入可用。

public class FileInputStreamMoreByte { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\7_Joyce\\b.txt"); byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];//存储读取到的多个字节 int len = 0;//记录每次读取到的有效的字节个数 while((len = fis.read(bytes))!=-1) { System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len)); } } }
文件的复制:
public class CopyFile { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //先判断路径是否存在 不存在则创建 File file = new File("D:\\7_Joyce\\Destination\\"); if(!file.exists()) { if(!file.mkdir()) { System.out.println("创建文件夹失败!"); } } File sourceFile = new File("D:\\7_Joyce\\Source\\20201122.txt"); File destinationFile = new File("D:\\7_Joyce\\Destination\\20201122.txt"); copyFile(sourceFile,destinationFile); } private static void copyFile(File sourceFile,File destFile) throws IOException { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(sourceFile); //会自动创建一个空文件 只要文件路径存在 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile); int len = 0; /* //一边读一边写 一个字节一个字节地读 会比较慢 while((len=fis.read())!=-1) { fos.write(len); }*/ byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; while((len = fis.read(bytes))!=-1) { fos.write(bytes,0,len); } fos.close(); fis.close(); } }
字符流(按照字符读取)
Reader: 输入流
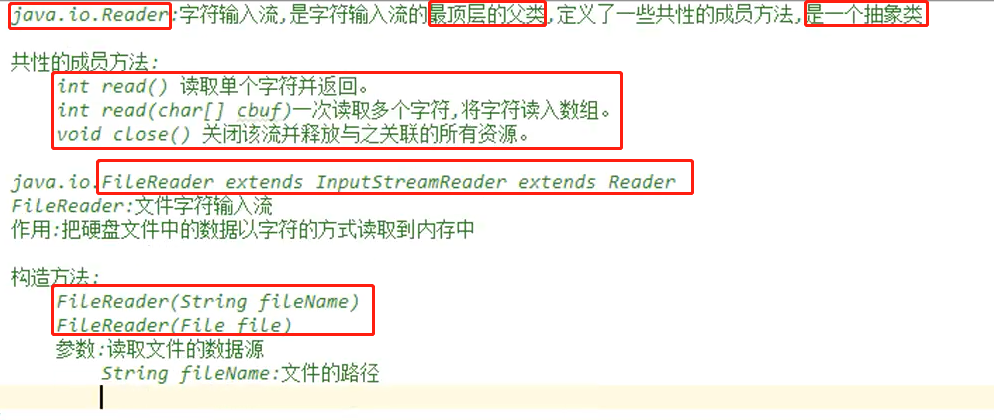
读取方式和字节流一样。
public class FileReaderDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileReader fr = new FileReader("D:\\7_Joyce\\b.txt"); int len = 0; int count = 0; //一个一个字符地读 /*while((len=fr.read())!=-1) { System.out.print((char)len);//我爱祖国 我爱人民 count++; } System.out.println("Count:"+count);//10*/ char[] chars = new char[1024]; while((len=fr.read(chars))!=-1) { System.out.println(new String(chars,0,len)); count++; } System.out.println(count);
fr.close(); } }
Writer:输出流



public class FileWriterDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("D:\\7_Joyce\\c.txt"); fw.write(97); //如果不调用 flush() 或者close() 方法,则没法把内存缓冲区的数据写入到文件 fw.flush(); fw.close(); } }

public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("D:\\7_Joyce\\d.txt"); char[] chars = new char[] {'a','b','c','d'}; fw.write(chars);//abcd String str = "我爱祖国,我爱人民!"; //我爱祖国,我爱人民! fw.write(str); fw.write("\r\n"); fw.write("hello world!"); fw.close(); }
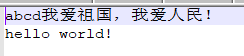
数据的追加写入和换行:

缓冲流

字节缓冲流
BufferedOutputStream
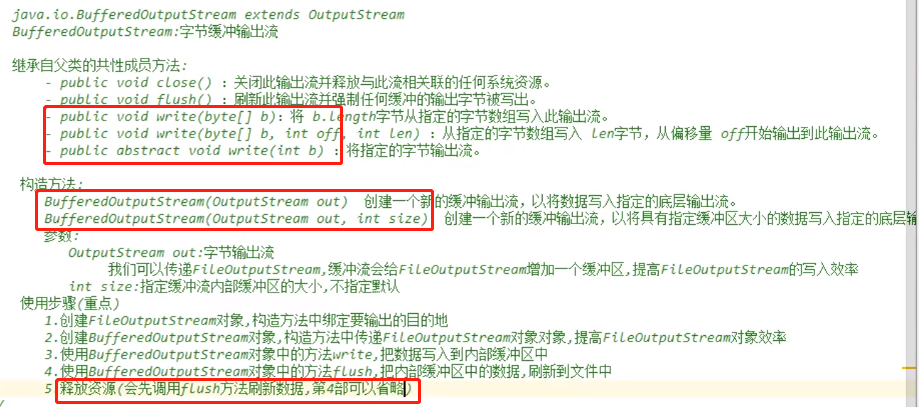
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\7_Joyce\\eclipse-workspace\\" + "Jave 基础\\src\\com\\Joyce\\IO\\BufferedOutputStream\\a.txt"); BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); bos.write("利用缓冲输出流写入文件!".getBytes()); bos.close(); }
BufferedInputStream

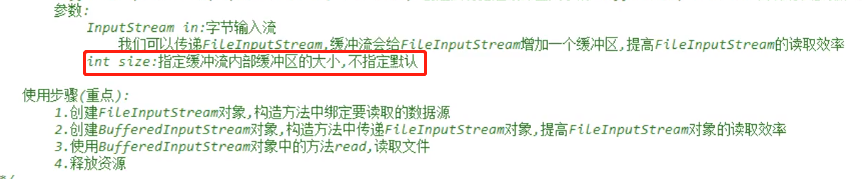
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("C:\\0_Joyce\\Eclipse\\a.txt")); int len; while((len =bis.read())!=-1) { System.out.print(len+ " ");//228 189 160 229 165 189 13 10 72 101 108 108 111 utf-8 编码 } bis.close();//只需要关闭缓存输入流 }
一次性读多个字节:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("C:\\0_Joyce\\Eclipse\\a.txt")); byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int len; while((len =bis.read(bytes))!=-1) { System.out.print(new String(bytes,0,len)); } bis.close(); }
字符缓冲流
BufferedWriter
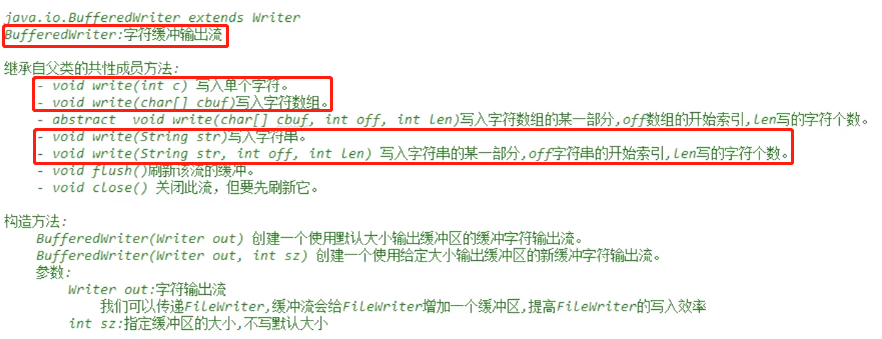

public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("C:\\0_Joyce\\Eclipse\\b.txt")); //bw.write(("使用字符缓冲流写入!").toCharArray()); bw.write("使用字符缓冲流写入!"); bw.newLine();//换行 bw.write("Hello World"); bw.close(); }
BufferedReader

public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("C:\\0_Joyce\\Eclipse\\b.txt")); String readLine; while((readLine = br.readLine())!=null) { System.out.println(readLine); } }
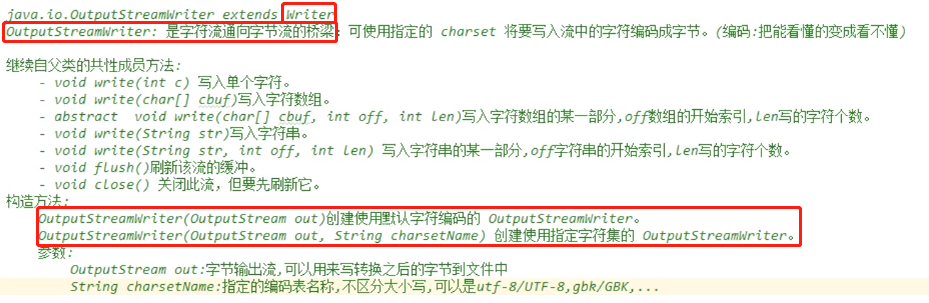
字符字节转换流:
OutputStreamWriter(其下有一个子类是FileWriter)
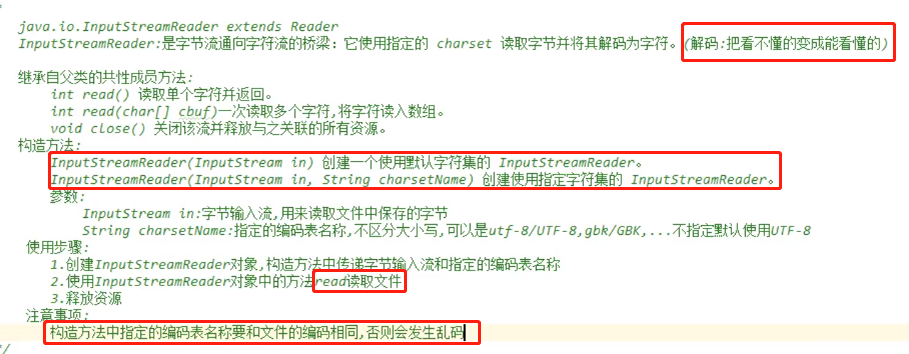
InputStreamReader
序列化与反序列化:

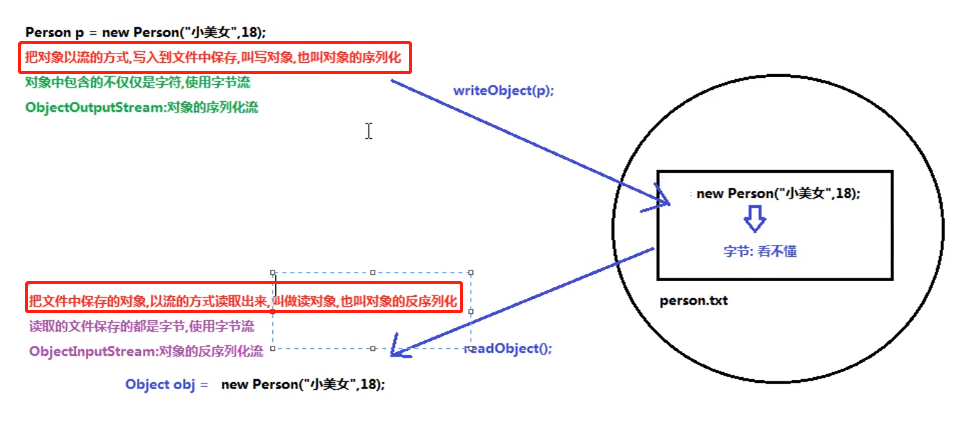
序列化:
ObjectOutputStream


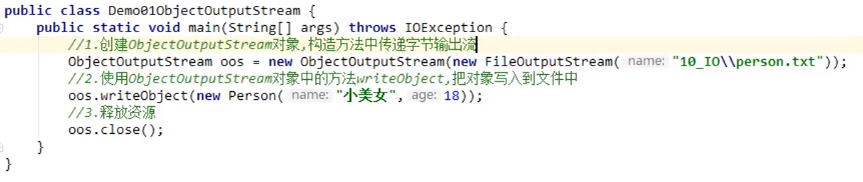
反序列化:
ObjectInputStream:
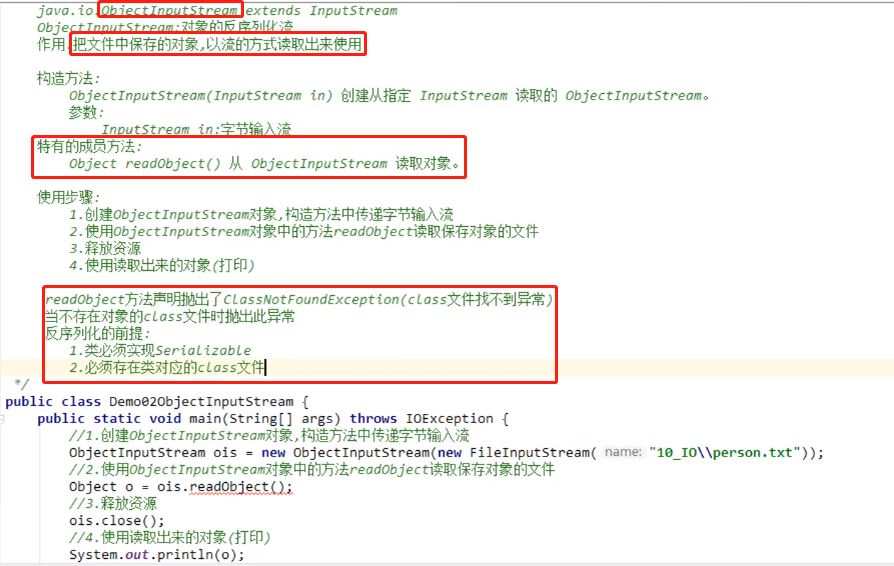








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号