[LeetCode] 289. Game of Life_Medium tag: array
2021-08-21 23:58 Johnson_强生仔仔 阅读(56) 评论(0) 收藏 举报According to Wikipedia's article: "The Game of Life, also known simply as Life, is a cellular automaton devised by the British mathematician John Horton Conway in 1970."
The board is made up of an m x n grid of cells, where each cell has an initial state: live (represented by a 1) or dead (represented by a 0). Each cell interacts with its eight neighbors (horizontal, vertical, diagonal) using the following four rules (taken from the above Wikipedia article):
- Any live cell with fewer than two live neighbors dies as if caused by under-population.
- Any live cell with two or three live neighbors lives on to the next generation.
- Any live cell with more than three live neighbors dies, as if by over-population.
- Any dead cell with exactly three live neighbors becomes a live cell, as if by reproduction.
The next state is created by applying the above rules simultaneously to every cell in the current state, where births and deaths occur simultaneously. Given the current state of the m x n grid board, return the next state.
Example 1:
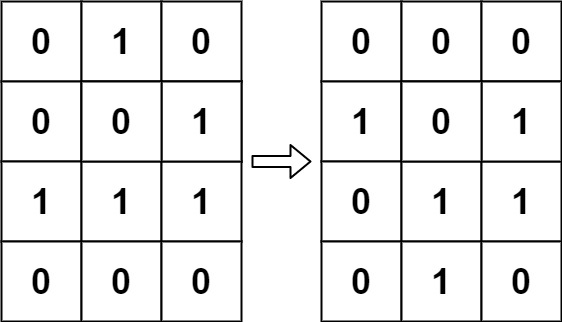
Input: board = [[0,1,0],[0,0,1],[1,1,1],[0,0,0]] Output: [[0,0,0],[1,0,1],[0,1,1],[0,1,0]]
Example 2:
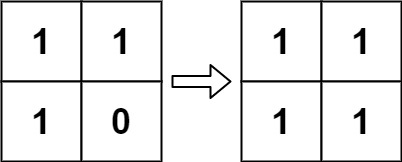
Input: board = [[1,1],[1,0]] Output: [[1,1],[1,1]]
Constraints:
m == board.lengthn == board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 25board[i][j]is0or1.
Follow up:
- Could you solve it in-place? Remember that the board needs to be updated simultaneously: You cannot update some cells first and then use their updated values to update other cells.
- In this question, we represent the board using a 2D array. In principle, the board is infinite, which would cause problems when the active area encroaches upon the border of the array (i.e., live cells reach the border). How would you address these problems?
Ideas:
1. T: O(m * n) S: O(m * n), 建一个新的array,然后不停更新, 最后将新的array来copy到旧array里面
2. T: O(m * n) S: O(1), 将原本是live的 + 100, 原本是dead的 - 100, 再加上num of neigs, 得到新的val; 再将2 D array 扫一次, 更新value
Code:
class Solution: def gameOfLife(self, board: List[List[int]]) -> None: """ Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead. """ self.board = board self.m = len(board) self.n = len(board[0]) for i in range(self.m): for j in range(self.n): self.getNumLiveNeigs(i, j) for i in range(self.m): for j in range(self.n): self.updateCell(i, j) def updateCell(self, i, j): val = self.board[i][j] if (val < 0 and val + 100 == 3) or (val > 0 and 2 <= val - 101 <= 3) : self.board[i][j] = 1 else: self.board[i][j] = 0 def getNumLiveNeigs(self, i, j): liveNeigs = 0 for d1, d2 in [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1), (-1, -1), (-1, 1), (1, -1), (1, 1)]: nr, nc = i + d1, j + d2 if 0 <=nr < self.m and 0 <= nc < self.n and self.board[nr][nc] > 0: liveNeigs += 1 temp = 100 if self.board[i][j] == 1 else - 100 self.board[i][j] += liveNeigs + temp
3. Follow up: what if matrix is so big.
- 因为每个cell只需要上面row 和下面row, 所以可以考虑3 行row 来处理, 然后再不停更新row
- 如果有很多都是dead cell;可能比较浪费空间, 那么可以考虑 1. 建一个set, 放所有的live cell positions; 2. 建一个dict,将所有live cell及他们的neigb的number of neigbs 都得到 3. 根据num neigbs == 3 or num == 2 and (i, j) in live set 来得到新的live set(就是在update next 之后应该要live的positions set); 4. 最后来update matrix
Note: 第2步是真的腻害并且简洁
Code:
class Solution: def gameOfLife(self, board: List[List[int]]) -> None: """ Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead. """ # 1. get the live cells , put them in live set live = {(i, j) for i, row in enumerate(board) for j, live in enumerate(row) if live} # 2. get the live cells and all the neigbs, the value of each cell is the num of live neigbs. ctr = collections.Counter((I, J) for i, j in live for I in range(i-1, i+2) for J in range(j-1, j+2) if I != i or J != j) # 3. get the set that it should be live after applying the rules live_next = {ij for ij in ctr if ctr[ij] == 3 or ctr[ij] == 2 and ij in live} # 4. update the cells in original array for i, row in enumerate(board): for j in range(len(row)): row[j] = int((i, j) in live_next)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号