.前言
题目集 8 和题目集 9 的题目数量分别为 3 题和 3 题,总题量为 6 题。题目集 8 的难度适中,而题目集 9 的难度相对较高。这两次题目集主要围绕面向对象编程的核心概念展开,涵盖了继承、多态、抽象类、异常处理等重要知识点。通过这三次作业,我学会更熟练地使用抽象类,包含类的容器类,在Main函数中定义方法,以及类之间的相互调用。总体来说题目的难度不大,但每一次的作业迭代,都可以让我有更成熟的对类的设计思想。
作业设计与分析
题目集八
7-41 NCHU_点线面问题重构(继承与多态)
题目
7-41 NCHU_点线面问题重构(继承与多态)
在“点与线(类设计)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,以实现继承与多态的技术性需求。
- 对题目中的点Point类和线Line类进行进一步抽象,定义一个两个类的共同父类Element(抽象类),将display()方法在该方法中进行声明(抽象方法),将Point类和Line类作为该类的子类。
- 再定义一个Element类的子类面Plane,该类只有一个私有属性颜色color,除了构造方法和属性的getter、setter方法外,display()方法用于输出面的颜色,输出格式如下:The Plane's color is:颜色
- 在主方法内,定义两个Point(线段的起点和终点)对象、一个Line对象和一个Plane对象,依次从键盘输入两个Point对象的起点、终点坐标和颜色值(Line对象和Plane对象颜色相同),然后定义一个Element类的引用,分别使用该引用调用以上四个对象的display()方法,从而实现多态特性。示例代码如下:
![图形用户界面, 应用程序
AI 生成的内容可能不正确。]()
源代码
import java.util.Scanner;
abstract class Element
{
public void display()
{
}
}
class Point extends Element
{
private double x;
private double y;
public Point(double x,double y)
{
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
public double Getx()
{
return x;
}
public double Gety()
{
return y;
}
}
class Line extends Element
{
private Point p1;
private Point p2;
private String color;
public Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color)
{
this.p1=p1;
this.p2=p2;
this.color=color;
}
public void p1()
{
System.out.printf("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:\n");
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",p1.Getx(),p1.Gety());
}
public void p2()
{
System.out.printf("The line's end point's Coordinate is:\n");
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",p2.Getx(),p2.Gety());
}
public void print()
{
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",p1.Getx(),p1.Gety());
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",p2.Getx(),p2.Gety());
}
public void display()
{
System.out.printf("The line's color is:%s\n",color);
}
public void length()
{
double d=Math.sqrt ((p1.Getx()-p2.Getx())*(p1.Getx()-p2.Getx())+(p1.Gety()- p2.Gety())*(p1.Gety()- p2.Gety()));
System.out.printf("The line's length is:%.2f\n",d);
}
}
class Plane extends Element
{
private String color;
public Plane(String color)
{
this.color=color;
}
public void display()
{
System.out.printf("The Plane's color is:%s\n",color);
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
double x1=scanner.nextDouble();
double y1=scanner.nextDouble();
double x2=scanner.nextDouble();
double y2=scanner.nextDouble();
scanner.nextLine();
String color=scanner.nextLine();
if(x1<=0||x1>200||y1<=0||y1>200||x2<=0||x2>200||y2<=0||y2>200)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return;
}
Point p1=new Point(x1,y1);
Point p2=new Point(x2,y2);
Line line=new Line(p1,p2,color);
Plane plane=new Plane(color);
line.print();
line.display();
line.p1();
line.p2();
line.length();
plane.display();
scanner.close();
}
}
设计
1.设计思路
1. 抽象父类 Element 的设计
题目要求将 Point 和 Line 类进一步抽象,因此创建了共同父类 Element,并将 display() 方法声明为抽象方法:

- 作用:通过抽象方法定义统一接口,确保所有子类必须实现 display(),从而支持多态调用。
2. 子类 Point 的实现
Point 类继承 Element,并实现 display() 方法以输出坐标:

3. 子类 Line 的实现
Line 类表示线段,包含起点、终点和颜色属性,并在 display() 中输出完整信息:

- 关键点:
- 组合关系:Line 包含两个 Point 对象(起点和终点)。
- 多态调用:在 display() 中通过 p1.display() 和 p2.display() 间接调用 Point 类的方法,体现多态性。
- 代码优化:原代码中的 p1()、p2() 和 length() 方法可合并到 display() 中,避免功能分散。
4. 子类 Plane 的实现

- 关键点:简单实现 display() 输出颜色信息。
5. 多态特性的实现
在 Main 类中,通过 Element 类型的引用变量依次指向不同子类对象,调用 display() 方法:

多态的核心:通过父类引用调用子类重写的方法,实现运行时动态绑定。
6. 输入验证与错误处理
原代码中已包含坐标范围验证:

- 作用:确保输入的坐标在有效范围内(1-200),否则终止程序。
2.类图

3.代码规模
共计118行

4.复杂度分析
7-42 NCHU_雨刷程序功能扩展设计
题目
7-42 NCHU_雨刷程序功能扩展设计
在给定的汽车手动风挡玻璃雨刷程序的基础上,对程序进行重构(Refactoring),使得程序可以对功能进行扩展。
- 附件1:
附件1.pdf - 作业指导书:
OO第九周作业题目说明(雨刷问题).pdf
输入格式:
输入共2行,第一行为一个整型数字,取值范围为[1,2],其中1代表表1所描述的雨刷系统,2代表表2所描述的雨刷系统;第二行为若干个用一个或多个空格分开且以数字0结束的整型数字,取值范围为[1,4],其中1代表控制杆升档操作、2代表控制杆降档操作、3代表刻度盘升刻度操作、4代表刻度盘降刻度操作、0代表操作结束(输入时只要遇到0即认为输入结束)。
输出格式:
程序的输出行数根据每一次对控制杆/刻度盘操作次数而定,每一次对控制杆/刻度盘进行了操作,则输出一行数据。格式为:操作类型/控制杆当前档位/刻度盘当前刻度/雨刷当前速度
其中,操作类型共四种,分别为Lever up、Lever down、Dial up、Dial down;控制杆当前档位显示中文内容,例如停止、间歇、低速、高速、超高速(表2);刻度盘当前刻度显示为数值,例如1、2、3、4、5(4、5见表2);雨刷当前速度显示为整型数值。
源代码
import java.util.Scanner;
class Lever {
private int pos;
private int systemType;
public Lever(int pos, int systemType) {
this.pos = pos;
this.systemType = systemType;
}
public int getPos() {
return pos;
}
// 对控制杆升档操作进行界限判断
public void leverUp() {
if (systemType == 1) {
if (pos < 4) {
pos++;
}
} else if (systemType == 2) {
if (pos < 5) {
pos++;
}
}
}
// 对控制杆降档操作进行界限判断
public void leverDown() {
if (pos > 1) {
pos--;
}
}
}
class Dial {
private int pos;
private int systemType;
public Dial(int pos, int systemType) {
this.pos = pos;
this.systemType = systemType;
}
public int getPos() {
return pos;
}
// 对刻度盘升刻度操作进行界限判断
public void dialUp() {
if (systemType == 1) {
if (pos < 3) {
pos++;
}
} else if (systemType == 2) {
if (pos < 5) {
pos++;
}
}
}
// 对刻度盘降刻度操作进行界限判断
public void dialDown() {
if (pos > 1) {
pos--;
}
}
}
class Brush {
private int speed;
public Brush(int speed) {
this.speed = speed;
}
public int getSpeed() {
return speed;
}
public void setSpeed(int speed) {
this.speed = speed;
}
}
class Agent {
private Lever lever;
private Dial dial;
private Brush brush;
private int systemType;
public Agent(Lever lever, Dial dial, Brush brush, int systemType) {
this.lever = lever;
this.dial = dial;
this.brush = brush;
this.systemType = systemType;
}
public Lever getLever() {
return lever;
}
public Dial getDial() {
return dial;
}
public Brush getBrush() {
return brush;
}
public String getLeverPositionName() {
int pos = lever.getPos();
switch (pos) {
case 1:
return "停止";
case 2:
return "间歇";
case 3:
return "低速";
case 4:
return "高速";
case 5:
return "超高速";
default:
return "";
}
}
public void dealSpeed() {
int speed = 0;
int leverPos = lever.getPos();
int dialPos = dial.getPos();
switch (leverPos) {
case 1:
speed = 0;
break;
case 2:
if (systemType == 1) {
switch (dialPos) {
case 1:
speed = 4;
break;
case 2:
speed = 6;
break;
case 3:
speed = 12;
break;
}
} else {
switch (dialPos) {
case 1:
speed = 4;
break;
case 2:
speed = 6;
break;
case 3:
speed = 12;
break;
case 4:
speed = 15;
break;
case 5:
speed = 20;
break;
}
}
break;
case 3:
speed = 30;
break;
case 4:
speed = 60;
break;
case 5:
if (systemType == 2) {
speed = 90;
break;
}
}
brush.setSpeed(speed);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int systemType;
if (input.hasNextInt()) {
systemType = input.nextInt();
if (systemType < 1 || systemType > 2) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return;
}
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return;
}
Lever lever = new Lever(1, systemType);
Dial dial = new Dial(1, systemType);
Brush brush = new Brush(0);
Agent agent = new Agent(lever, dial, brush, systemType);
boolean hasValidInput = false;
while (input.hasNext()) { // 使用 hasNext 替代 hasNextInt,以便更全面检查输入
String inputStr = input.next(); // 先读取为字符串
if (isNumeric(inputStr)) { // 判断字符串是否为数字
int choice = Integer.parseInt(inputStr);
if (choice == 0) {
break;
}
if (choice < 1 || choice > 4) {
continue;
}
hasValidInput = true;
String operationType = "";
switch (choice) {
case 1:
operationType = "Lever up";
agent.getLever().leverUp();
break;
case 2:
operationType = "Lever down";
agent.getLever().leverDown();
break;
case 3:
operationType = "Dial up";
agent.getDial().dialUp();
break;
case 4:
operationType = "Dial down";
agent.getDial().dialDown();
break;
}
agent.dealSpeed();
String leverPosition = agent.getLeverPositionName();
int dialPos = agent.getDial().getPos();
int speed = agent.getBrush().getSpeed();
System.out.println(operationType + "/" + leverPosition + "/" + dialPos + "/" + speed);
} else {
continue; // 如果不是数字,跳过本次循环
}
}
if (hasValidInput) {
}
input.close();
}
// 判断字符串是否为数字的方法
public static boolean isNumeric(String str) {
try {
Double.parseDouble(str);
return true;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
return false;
}
}
}
设计
1,设计思路
程序核心功能理解
该程序模拟了汽车雨刷控制系统,包含两种雨刷系统(系统 1 和系统 2),通过控制杆和刻度盘操作来调节雨刷速度。主要操作类型有控制杆升档、降档,刻度盘升刻度、降刻度,每种操作都会影响雨刷的速度。

初始设计架构分析
- 类的划分:原程序将系统划分为四个主要类:
- Lever类:处理控制杆操作和档位管理。
- Dial类:处理刻度盘操作和刻度管理。
- Brush类:管理雨刷速度。
- Agent类:协调其他类的操作,根据控制杆和刻度盘状态计算雨刷速度。
- 核心逻辑:
- 控制杆有不同档位(如停止、间歇、低速、高速等)。
- 刻度盘有不同刻度值,影响间歇档位下的雨刷速度。
- 雨刷速度根据控制杆档位和刻度盘刻度计算得出。
重构的关键改进点
- 扩展性设计:
- 使用策略模式或工厂模式可以更好地处理不同雨刷系统的差异,避免大量的条件判断。
- 将雨刷速度计算逻辑抽象成接口,不同系统实现不同的计算策略。
- 代码优化:
- 原程序中存在重复的条件判断(如系统类型判断),可通过多态或配置文件消除。
- dealSpeed方法中的嵌套 switch 语句可通过查表法或策略模式简化。
- 用户输入处理:
- 输入验证和处理逻辑分离,提高代码清晰度。
- 使用更健壮的输入处理机制,确保程序对异常输入的容错性。
2.类图

3.代码规模
共计264行
复杂度分析
S
7-43 NCHU_航空货运管理系统(类设计)
题目
7-43 NCHU_航空货运管理系统(类设计)
分数 60
中等
全屏浏览
切换布局
作者 段喜龙
单位 南昌航空大学
航空快递以速度快、安全性高成为急件或贵重物品的首选。本题目要求对航空货运管理系统进行类设计,具体说明参看说明文件。
OO第九周作业题目说明.pdf
输入格式:
按如下顺序分别输入客户信息、货物信息、航班信息以及订单信息。
客户编号
客户姓名
客户电话
客户地址
运送货物数量
[货物编号
货物名称
货物宽度
货物长度
货物高度
货物重量
]//[]内的内容输入次数取决于“运送货物数量”,输入不包含“[]”
航班号
航班起飞机场
航班降落机场
航班日期(格式为YYYY-MM-DD)
航班最大载重量
订单编号
订单日期(格式为YYYY-MM-DD)
发件人地址
发件人姓名
发件人电话
收件人地址
收件人姓名
收件人电话
输出格式:
- 如果订单中货物重量超过航班剩余载重量,程序输出The flight with flight number:航班号 has exceeded its load capacity and cannot carry the order. ,程序终止运行。
- 如果航班载重量可以承接该订单,输出如下:
客户:姓名(电话)订单信息如下:
-----------------------------------------
航班号:
订单号:
订单日期:
发件人姓名:
发件人电话:
发件人地址:
收件人姓名:
收件人电话:
收件人地址:
订单总重量(kg):
微信支付金额:
货物明细如下:
-----------------------------------------
明细编号 货物名称 计费重量 计费费率 应交运费
1 ...
2 ...
注:输出中实型数均保留1位小数。
源代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Customer {
private String customerId;
private String name;
private String phone;
private String address;
public Customer(String customerId, String name, String phone, String address) {
this.customerId = customerId;
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
this.address = address;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public String getPhone()
{
return phone;
}
}
class Cargo {
private String cargoId;
private String name;
private double width;
private double length;
private double height;
private double weight;
public Cargo(String cargoId, String name, double width, double length, double height, double weight) {
this.cargoId = cargoId;
this.name = name;
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
}
public double getVolumeWeight() {
return (width * length * height) / 6000;
}
public double getWeight() {
return Math.max(weight, getVolumeWeight());
}
public double getRate() {
double chargeableWeight = getWeight();
if (chargeableWeight < 20) {
return 35;
} else if (chargeableWeight < 50) {
return 30;
} else if (chargeableWeight < 100) {
return 25;
}else
{
return 15;
}
}
public double getFreight() {
return getWeight() * getRate();
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public double getChargeableWeightValue()
{
return getWeight();
}
}
class Flight
{
private String flightNumber;
private String departureAirport;
private String arrivalAirport;
private String date;
private double maxLoad;
private double remainingLoad;
public Flight(String flightNumber, String departureAirport, String arrivalAirport, String date, double maxLoad) {
this.flightNumber = flightNumber;
this.departureAirport = departureAirport;
this.arrivalAirport = arrivalAirport;
this.date = date;
this.maxLoad = maxLoad;
this.remainingLoad = maxLoad;
}
public boolean canCarry(double weight) {
return remainingLoad >= weight;
}
public void carry(double weight) {
remainingLoad -= weight;
}
public String getFlightNumber() {
return flightNumber;
}
}
class Order {
private String orderId;
private String orderDate;
private String senderAddress;
private String senderName;
private String senderPhone;
private String receiverAddress;
private String receiverName;
private String receiverPhone;
private Flight flight;
private List<Cargo> cargos;
public Order(String orderId, String orderDate, String senderAddress, String senderName, String senderPhone,
String receiverAddress, String receiverName, String receiverPhone, Flight flight, List<Cargo> cargos) {
this.orderId = orderId;
this.orderDate = orderDate;
this.senderAddress = senderAddress;
this.senderName = senderName;
this.senderPhone = senderPhone;
this.receiverAddress = receiverAddress;
this.receiverName = receiverName;
this.receiverPhone = receiverPhone;
this.flight = flight;
this.cargos = cargos;
}
public double getTotalWeight() {
double totalWeight = 0;
for (Cargo cargo : cargos) {
totalWeight += cargo.getWeight();
}
return totalWeight;
}
public double getTotalCost() {
double totalCost = 0;
for (Cargo cargo : cargos) {
totalCost += cargo.getFreight();
}
return totalCost;
}
public boolean canBeCarried() {
return flight.canCarry(getTotalWeight());
}
public void carryOrder() {
flight.carry(getTotalWeight());
}
public String getOrderId() {
return orderId;
}
public String getOrderDate() {
return orderDate;
}
public String getSenderAddress() {
return senderAddress;
}
public String getSenderName() {
return senderName;
}
public String getSenderPhone() {
return senderPhone;
}
public String getReceiverAddress() {
return receiverAddress;
}
public String getReceiverName() {
return receiverName;
}
public String getReceiverPhone() {
return receiverPhone;
}
public String getFlightNumber() {
return flight.getFlightNumber();
}
public List<Cargo> getCargos() {
return cargos;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String customerId = scanner.nextLine();
String customerName = scanner.nextLine();
String customerPhone = scanner.nextLine();
String customerAddress = scanner.nextLine();
Customer customer = new Customer(customerId, customerName, customerPhone, customerAddress);
int cargoCount = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine());
List<Cargo> cargos = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < cargoCount; i++) {
String cargoId = scanner.nextLine();
String cargoName = scanner.nextLine();
double width = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
double length = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
double height = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
double weight = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
cargos.add(new Cargo(cargoId, cargoName, width, length, height, weight));
}
String flightNumber = scanner.nextLine();
String departureAirport = scanner.nextLine();
String arrivalAirport = scanner.nextLine();
String flightDate = scanner.nextLine();
double maxLoad = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
Flight flight = new Flight(flightNumber, departureAirport, arrivalAirport, flightDate, maxLoad);
String orderId = scanner.nextLine();
String orderDate = scanner.nextLine();
String senderAddress = scanner.nextLine();
String senderName = scanner.nextLine();
String senderPhone = scanner.nextLine();
String receiverAddress = scanner.nextLine();
String receiverName = scanner.nextLine();
String receiverPhone = scanner.nextLine();
Order order = new Order(orderId, orderDate, senderAddress, senderName, senderPhone,
receiverAddress, receiverName, receiverPhone, flight, cargos);
if (!order.canBeCarried()) {
System.out.printf("The flight with flight number:%s has exceeded its load capacity and cannot carry the order.\n", flightNumber);
return;
}
order.carryOrder();
System.out.printf("客户:%s(%s)订单信息如下:\n", customer.getName(), customer.getPhone());
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.printf("航班号:%s\n", order.getFlightNumber());
System.out.printf("订单号:%s\n", order.getOrderId());
System.out.printf("订单日期:%s\n", order.getOrderDate());
System.out.printf("发件人姓名:%s\n", order.getSenderName());
System.out.printf("发件人电话:%s\n", order.getSenderPhone());
System.out.printf("发件人地址:%s\n", order.getSenderAddress());
System.out.printf("收件人姓名:%s\n", order.getReceiverName());
System.out.printf("收件人电话:%s\n", order.getReceiverPhone());
System.out.printf("收件人地址:%s\n", order.getReceiverAddress());
System.out.printf("订单总重量(kg):%.1f\n", order.getTotalWeight());
System.out.printf("微信支付金额:%.1f", order.getTotalCost());
System.out.printf("\n\n货物明细如下:\n");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.printf("明细编号\t货物名称\t计费重量\t计费费率\t应交运费");
int index = 1;
for (Cargo cargo : order.getCargos())
{
System.out.printf("\n%d\t%s\t%.1f\t%.1f\t%.1f", index++, cargo.getName(),
cargo.getChargeableWeightValue(), cargo.getRate(), cargo.getFreight());
}
}
}
设计
设计思路
系统设计思路
- 类设计
- Customer:存储客户基本信息
- Cargo:计算货物计费重量和运费(实际重量 vs 体积重量取大值,分四级费率)
- Flight:管理航班载重,检查订单是否可装载
- Order:整合货物、航班信息,计算总费用,验证载重
- 核心流程
- 输入客户→货物→航班→订单信息
- 订单总重量 = 所有货物计费重量之和
- 检查航班剩余载重,超重则终止
- 输出订单详情(含货物明细、总费用)
- 关键点
- 重量计算:体积重量 = 长 × 宽 × 高 / 6000,计费重量取实际重量与体积重量较大值
- 费率分级:<20kg (35 元)、20-49kg (30 元)、50-99kg (25 元)、≥100kg (15 元)
- 载重验证:订单创建时自动检查航班剩余载重
2.类图
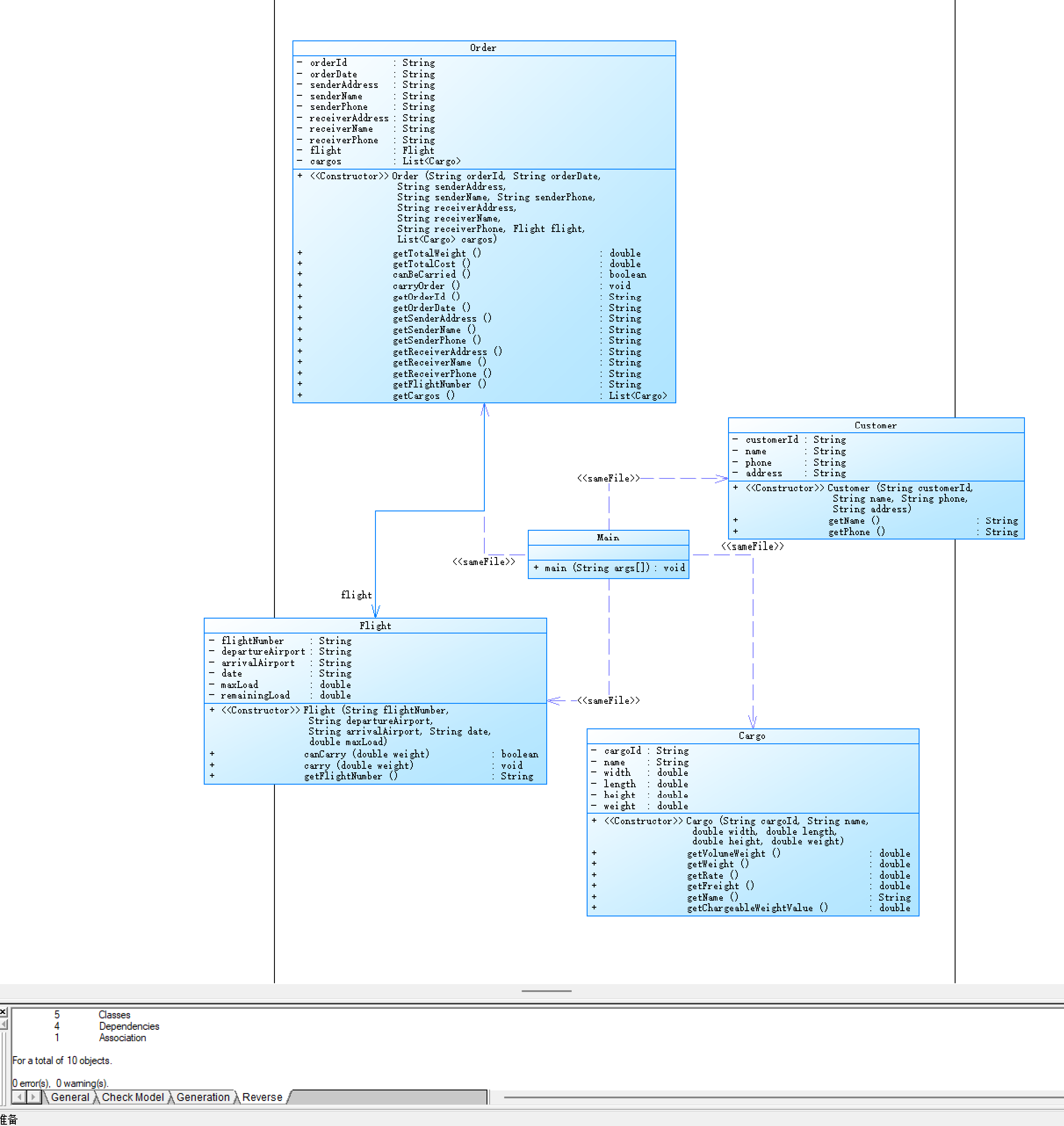
3.代码规模

4.复杂度分析

整体指标
- 代码规模:文件共 276 行,包含 183 条语句 。规模不算特别大,但语句数较多也意味着逻辑有一定复杂性。
- 分支语句占比:分支语句占 4.9% ,表明代码中条件判断逻辑不算特别多,但也存在一定数量的条件控制逻辑。
- 方法调用语句数:有 60 条方法调用语句 ,说明代码中各模块间交互频繁,体现了一定的模块化程度,但也可能导致调用关系复杂。
- 注释占比:注释占比为 0.0% ,这是比较严重的问题,缺乏注释会极大增加代码阅读和理解难度,不利于代码维护。
- 类和接口数量:有 5 个类和接口 ,类数量不算多,但结合平均每个类 6.00 个方法来看,类的功能可能较为丰富。
- 平均方法数:每个类平均有 6.00 个方法 ,意味着类的功能相对集中,需要审视类的职责是否单一。
- 平均每个方法的语句数:平均每个方法有 3.97 条语句 ,方法语句数不算多,但要结合方法复杂度综合判断。
方法复杂度相关
- 最复杂方法:Cargo.getRate() 复杂度为 5 ,是最复杂的方法。这可能意味着该方法内部包含较多条件判断、循环或复杂计算逻辑,需要重点关注和优化,比如考虑拆分其中的逻辑。
- 最大复杂度:整体最大复杂度为 5 ,说明代码中存在较为复杂的逻辑片段,可能需要进一步梳理和重构。
- 平均复杂度:平均复杂度为 1.30 ,说明大部分方法复杂度尚可,但个别高复杂度方法会影响整体维护难度。
深度相关指标
- 最深代码块行数:最深代码块有 57 行 ,这可能表示存在较长且逻辑复杂的代码片段,需要检查是否能对其进行功能拆分。
- 最大代码块深度:最大代码块深度为 3 ,平均代码块深度为 1.69 ,说明代码存在一定的嵌套层次,嵌套会增加代码理解难度,可考虑优化条件和循环结构来降低嵌套。
改进建议
- 添加注释:务必增加注释,对关键逻辑、方法作用、参数含义等进行说明,提高代码可读性。
- 重构高复杂度方法:针对 Cargo.getRate() 等高复杂度方法,进行逻辑拆分和优化,使其功能更清晰、单一。
- 优化代码结构:检查类的职责是否单一,避免一个类承担过多功能,同时梳理方法调用关系,提高代码的可维护性。
题目集九
7-1 NCHU_魔方问题
题目
- 问题描述:本问题中的魔方有两种,一种是正方体魔方,一种是正三棱锥魔方,其中,正方体或正三棱锥魔方是由单元正方体或正三棱锥组成,单元正方体或正三棱锥的个数由阶数(即层数)决定,即魔方边长=阶数*单元边长。输入格式:
- 第一部分:正方体魔方颜色、阶数、单元正方体边长,以空格或回车分隔;
- 第二部分:正三棱锥魔方颜色、阶数、单元正三棱锥边长,以空格或回车分隔。
- 输出格式:
- 正方体魔方颜色
- 正方体魔方表面积
- 正方体魔方体积
- 正三棱锥魔方颜色
- 正三棱锥魔方表面积
正三棱锥魔方体积 - 注:小数点保留两位
源代码
import java.util.Scanner;
abstract class Solid {
private double side;
public Solid(double side) {
this.side = side;
}
public double getSide() {
return side;
}
public void setSide(double side) {
this.side = side;
}
abstract public double getArea();
abstract public double getVolume();
}
class RegularPyramid extends Solid {
public RegularPyramid(double side) {
super(side);
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return Math.sqrt(3) * getSide() * getSide();
}
@Override
public double getVolume() {
return (Math.sqrt(2) / 12) * getSide() * getSide() * getSide();
}
}
class Cube extends Solid {
public Cube(double side) {
super(side);
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return 6 * getSide() * getSide();
}
@Override
public double getVolume() {
return getSide() * getSide() * getSide();
}
}
abstract class RubikCube extends Solid {
private String color;
private int layer;
private Solid solid;
public RubikCube(String color, int layer, Solid solid) {
super(solid.getSide() * layer); // 总边长 = 层数 * 单元边长
this.color = color;
this.layer = layer;
this.solid = solid;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public int getLayer() {
return layer;
}
public Solid getSolid() {
return solid;
}
}
class SquareCube extends RubikCube {
public SquareCube(String color, int layer, Solid solid) {
super(color, layer, solid);
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
double totalSide = getLayer() * getSolid().getSide();
return 6 * totalSide * totalSide;
}
@Override
public double getVolume() {
double totalSide = getLayer() * getSolid().getSide();
return totalSide * totalSide * totalSide;
}
}
class RegularPyramidCube extends RubikCube {
public RegularPyramidCube(String color, int layer, Solid solid) {
super(color, layer, solid);
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
double totalSide = getLayer() * getSolid().getSide();
return Math.sqrt(3) * totalSide * totalSide;
}
@Override
public double getVolume() {
double totalSide = getLayer() * getSolid().getSide();
return (Math.sqrt(2) / 12) * totalSide * totalSide * totalSide;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String color = input.next();
int layer = input.nextInt();
double side = input.nextDouble();
RubikCube cube1 = new SquareCube(color, layer, new Cube(side));
color = input.next();
layer = input.nextInt();
side = input.nextDouble();
RubikCube cube2 = new RegularPyramidCube(color, layer, new RegularPyramid(side));
display(cube1);
display(cube2);
input.close();
}
public static void display(RubikCube cube) {
System.out.println(cube.getColor());
System.out.printf("%.2f\n", cube.getArea());
System.out.printf("%.2f\n", cube.getVolume());
}
}
设计
1.设计思路
- 类层次结构
- 抽象类 Solid:定义单元几何体(正方体 / 正三棱锥)的边长side,以及抽象方法getArea()(表面积)和getVolume()(体积)。
- 具体子类 Cube/RegularPyramid:继承Solid,分别实现正方体和正三棱锥的表面积与体积计算(基于单元边长)。
- 魔方抽象类 RubikCube
- 定义魔方公共属性:颜色color、阶数layer、关联的单元几何体solid。
- 总边长 = 阶数 × 单元边长(通过layer * solid.getSide()计算)。
- 具体魔方子类
- SquareCube(正方体魔方):
- 表面积 = 6 × 总边长²(正方体表面积公式)。
- 体积 = 总边长³(正方体体积公式)。
- RegularPyramidCube(正三棱锥魔方):
- 表面积 = √3 × 总边长²(正三棱锥侧面积公式,假设底面不外露)。
- 体积 = (√2/12) × 总边长³(正三棱锥体积公式)。
- SquareCube(正方体魔方):
- 多态实现
- 通过display(RubikCube cube)方法统一输出魔方信息,利用子类重写的getArea()和getVolume()实现多态计算。
- 输入输出逻辑
- 读取输入数据,创建两种魔方实例,调用display方法输出颜色、表面积(保留两位小数)、体积(保留两位小数)。
2.类图

3.代码规模

复杂度分析
S
7-2 NCHU_点线面问题再重构(容器类)
题目
在“点与线(继承与多态)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,增加容器类保存点、线、面对象,并对该容器进行相应增、删、遍历操作。
- 在原有类设计的基础上,增加一个GeometryObject容器类,其属性为ArrayList<Element>类型的对象(若不了解泛型,可以不使用<Element>)
- 增加该类的add()方法及remove(int index)方法,其功能分别为向容器中增加对象及删除第index - 1(ArrayList中index>=0)个对象
- 在主方法中,用户循环输入要进行的操作(choice∈[0,4]),其含义如下:
- 1:向容器中增加Point对象
- 2:向容器中增加Line对象
- 3:向容器中增加Plane对象
- 4:删除容器中第index - 1个数据,若index数据非法,则无视此操作
源代码
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
abstract class Element
{
public void display()
{
}
}
class Point extends Element
{
private double x;
private double y;
public Point(double x,double y)
{
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
public double Getx()
{
return x;
}
public double Gety()
{
return y;
}
public void display()
{
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",x,y);
}
}
class Line extends Element
{
private Point p1;
private Point p2;
private String color;
public Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color)
{
this.p1=p1;
this.p2=p2;
this.color=color;
}
public void display()
{
System.out.printf("The line's color is:%s\n",color);
System.out.printf("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:\n");
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",p1.Getx(),p1.Gety());
System.out.printf("The line's end point's Coordinate is:\n");
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",p2.Getx(),p2.Gety());
double dx = p2.Getx() - p1.Getx();
double dy = p2.Gety() - p1.Gety();
double length = Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
System.out.printf("The line's length is:%.2f\n", length);
}
}
class Plane extends Element
{
private String color;
public Plane(String color)
{
this.color=color;
}
public void display()
{
System.out.printf("The Plane's color is:%s\n",color);
}
}
class GeometryObject
{
private static ArrayList<Element> object = new ArrayList<>();
public GeometryObject()
{
}
public static void add(Element element)
{
object.add(element);
}
public static void remove(int n)
{
if(n>=0&&n<object.size())
{
object.remove(n);
}
}
public static ArrayList<Element> Get()
{
return object;
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
int choice=scanner.nextInt();
if(choice==0)
{
break;
}
switch(choice) {
case 1:
double x=scanner.nextDouble();
double y=scanner.nextDouble();
Point p=new Point(x,y);
GeometryObject.add(p);
break;
case 2:
double x1=scanner.nextDouble();
double y1=scanner.nextDouble();
double x2=scanner.nextDouble();
double y2=scanner.nextDouble();
scanner.nextLine();
String Lcolor=scanner.nextLine();
Point p1=new Point(x1,y1);
Point p2=new Point(x2,y2);
Line l=new Line(p1,p2,Lcolor);
GeometryObject.add(l);
break;
case 3://insert Plane object into list
scanner.nextLine();
String Pcolor=scanner.nextLine();
Plane plane=new Plane(Pcolor);
GeometryObject.add(plane);
break;
case 4://delete index - 1 object from list
int n=scanner.nextInt();
GeometryObject.remove(n-1);
break;
}
}
ArrayList<Element> e=GeometryObject.Get();
for(int i=0;i<e.size();i++)
{
e.get(i).display();
}
scanner.close();
}
}
设计
1.设计思路
- 类层次结构
- 抽象类 Element:作为点、线、面的基类,定义display()抽象方法(所有子类需重写)。
- 具体子类 Point/Line/Plane:
- Point:存储坐标 (x,y),重写display()输出坐标。
- Line:包含两个端点(Point 对象)和颜色,重写display()输出颜色、端点坐标及长度。
- Plane:存储颜色,重写display()输出颜色。
- 容器类 GeometryObject
- 使用ArrayList<Element>存储所有几何对象,实现:
- add(Element element):向列表添加对象。
- remove(int index):根据索引(从 0 开始)删除对象,索引非法时忽略。
- 使用ArrayList<Element>存储所有几何对象,实现:
- 核心流程
- 输入处理:
- 循环读取操作指令(1-4),根据指令类型创建对应对象(Point/Line/Plane)或执行删除操作。
- 注意:输入 Line 和 Plane 的颜色时需处理换行符,避免读取错误。
- 删除逻辑:用户输入的删除位置index(从 1 开始)需转换为列表索引index-1,并校验索引是否合法(≥0 且 < 列表长度)。
- 输出遍历:输入结束后,遍历容器中的所有对象,调用display()方法输出结果。
- 输入处理:
- 关键点
- 多态性:通过基类 Element 引用子类对象,统一调用display()实现差异化输出。
- 容器操作:利用 ArrayList 的动态特性,实现灵活的增删操作,确保索引校验的健壮性。
2.类图

3.代码规模

4,复杂度分析
s
复杂度分析
S
7-3 NCHU_航空货运管理系统(继承与多态)
题目
航空快递以速度快、安全性高成为急件或贵重物品的首选。本题目要求对航空货运管理系统进行类设计,具体说明参看说明文件。
OO第十二周作业题目说明.pdf
输入格式:
按如下顺序分别输入客户信息、货物信息、航班信息以及订单信息。
客户类型[可输入项:Individual/Corporate]
客户编号
客户姓名
客户电话
客户地址
货物类型[可输入项:Normal/Expedite/Dangerous]
运送货物数量
[货物编号
货物名称
货物宽度
货物长度
货物高度
货物重量
]//[]内的内容输入次数取决于“运送货物数量”,输入不包含“[]”
航班号
航班起飞机场
航班降落机场
航班日期(格式为YYYY-MM-DD)
航班最大载重量
订单编号
订单日期(格式为YYYY-MM-DD)
发件人地址
发件人姓名
发件人电话
收件人地址
收件人姓名
收件人电话
支付方式[可输入项:Wechat/ALiPay/Cash]
输出格式:
- 如果订单中货物重量超过航班剩余载重量,程序输出The flight with flight number:航班号 has exceeded its load capacity and cannot carry the order. ,程序终止运行。
- 如果航班载重量可以承接该订单,输出如下:
客户:姓名(电话)订单信息如下:
-----------------------------------------
航班号:
订单号:
订单日期:
发件人姓名:
发件人电话:
发件人地址:
收件人姓名:
收件人电话:
收件人地址:
订单总重量(kg):
[微信/支付宝/现金]支付金额:
货物明细如下:
-----------------------------------------
明细编号 货物名称 计费重量 计费费率 应交运费
1 ...
2 ...
源代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Scanner;
abstract class Customer {
private String customerId;
private String name;
private String phone;
private String address;
public Customer(String customerId, String name, String phone, String address) {
this.customerId = customerId;
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
this.address = address;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public String getCustomerId() {
return customerId;
}
abstract public double getDiscount();
}
class InCustomer extends Customer {
public InCustomer(String customerId, String name, String phone, String address) {
super(customerId, name, phone, address);
}
@Override
public double getDiscount() {
return 0.9;
}
}
class CoCustomer extends Customer {
public CoCustomer(String customerId, String name, String phone, String address) {
super(customerId, name, phone, address);
}
@Override
public double getDiscount() {
return 0.8;
}
}
abstract class Cargo {
private String cargoId;
private String name;
private double width;
private double length;
private double height;
private double weight;
public Cargo(String cargoId, String name, double width, double length, double height, double weight) {
this.cargoId = cargoId;
this.name = name;
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
}
// 为私有属性添加getter方法
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public abstract double getVolumeWeight();
public abstract double getWeightForRate();
public abstract double getRate();
public abstract double getFreight();
public abstract double getChargeableWeightValue();
}
class NormalCargo extends Cargo {
public NormalCargo(String cargoId, String name, double width, double length, double height, double weight) {
super(cargoId, name, width, length, height, weight);
}
@Override
public double getVolumeWeight() {
return (getWidth() * getLength() * getHeight()) / 6000;
}
@Override
public double getWeightForRate() {
return Math.max(getWeight(), getVolumeWeight());
}
@Override
public double getRate() {
double chargeableWeight = getWeightForRate();
if (chargeableWeight < 20) {
return 35;
} else if (chargeableWeight < 50) {
return 30;
} else if (chargeableWeight < 100) {
return 25;
} else {
return 15;
}
}
@Override
public double getFreight() {
return getWeightForRate() * getRate();
}
@Override
public double getChargeableWeightValue() {
return getWeightForRate();
}
}
class ExpediteCargo extends Cargo {
public ExpediteCargo(String cargoId, String name, double width, double length, double height, double weight) {
super(cargoId, name, width, length, height, weight);
}
@Override
public double getVolumeWeight() {
return (getWidth() * getLength() * getHeight()) / 6000;
}
@Override
public double getWeightForRate() {
return Math.max(getWeight(), getVolumeWeight());
}
@Override
public double getRate() {
double chargeableWeight = getWeightForRate();
if (chargeableWeight < 20) {
return 60;
} else if (chargeableWeight < 50) {
return 50;
} else if (chargeableWeight < 100) {
return 40;
} else {
return 30;
}
}
@Override
public double getFreight() {
return getWeightForRate() * getRate();
}
@Override
public double getChargeableWeightValue() {
return getWeightForRate();
}
}
class DangerousCargo extends Cargo {
public DangerousCargo(String cargoId, String name, double width, double length, double height, double weight) {
super(cargoId, name, width, length, height, weight);
}
@Override
public double getVolumeWeight() {
return (getWidth() * getLength() * getHeight()) / 6000;
}
@Override
public double getWeightForRate() {
return Math.max(getWeight(), getVolumeWeight());
}
@Override
public double getRate() {
double chargeableWeight = getWeightForRate();
if (chargeableWeight < 20) {
return 80;
} else if (chargeableWeight < 50) {
return 50;
} else if (chargeableWeight < 100) {
return 30;
} else {
return 20;
}
}
@Override
public double getFreight() {
return getWeightForRate() * getRate();
}
@Override
public double getChargeableWeightValue() {
return getWeightForRate();
}
}
class Flight {
private String flightNumber;
private String departureAirport;
private String arrivalAirport;
private String date;
private double maxLoad;
private double remainingLoad;
public Flight(String flightNumber, String departureAirport, String arrivalAirport, String date, double maxLoad) {
this.flightNumber = flightNumber;
this.departureAirport = departureAirport;
this.arrivalAirport = arrivalAirport;
this.date = date;
this.maxLoad = maxLoad;
this.remainingLoad = maxLoad;
}
public boolean canCarry(double weight) {
return remainingLoad >= weight;
}
public void carry(double weight) {
remainingLoad -= weight;
}
public String getFlightNumber() {
return flightNumber;
}
}
class Order {
private String orderId;
private String orderDate;
private String senderAddress;
private String senderName;
private String senderPhone;
private String receiverAddress;
private String receiverName;
private String receiverPhone;
private Flight flight;
private List<Cargo> cargos;
private String paymentMethod;
public Order(String orderId, String orderDate, String senderAddress, String senderName, String senderPhone,
String receiverAddress, String receiverName, String receiverPhone, Flight flight, List<Cargo> cargos, String paymentMethod) {
this.orderId = orderId;
this.orderDate = orderDate;
this.senderAddress = senderAddress;
this.senderName = senderName;
this.senderPhone = senderPhone;
this.receiverAddress = receiverAddress;
this.receiverName = receiverName;
this.receiverPhone = receiverPhone;
this.flight = flight;
this.cargos = cargos;
this.paymentMethod = paymentMethod;
}
public double getTotalWeight() {
double totalWeight = 0;
for (Cargo cargo : cargos)
{
totalWeight += cargo.getWeightForRate();
}
return totalWeight;
}
public double getTotalCost() {
double totalCost = 0;
for (Cargo cargo : cargos) {
totalCost += cargo.getFreight();
}
return totalCost;
}
public boolean canBeCarried() {
return flight.canCarry(getTotalWeight());
}
public void carryOrder() {
flight.carry(getTotalWeight());
}
public String getOrderId() {
return orderId;
}
public String getOrderDate() {
return orderDate;
}
public String getSenderAddress() {
return senderAddress;
}
public String getSenderName() {
return senderName;
}
public String getSenderPhone() {
return senderPhone;
}
public String getReceiverAddress() {
return receiverAddress;
}
public String getReceiverName() {
return receiverName;
}
public String getReceiverPhone() {
return receiverPhone;
}
public String getFlightNumber() {
return flight.getFlightNumber();
}
public List<Cargo> getCargos() {
return cargos;
}
public String getPaymentMethod() {
if (Objects.equals(paymentMethod, "ALiPay")) {
return "支付宝";
} else if (Objects.equals(paymentMethod, "Wechat")) {
return "微信";
} else {
return "现金";
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
try {
Customer customer = createCustomer(scanner);
List<Cargo> cargos = createCargos(scanner);
Flight flight = createFlight(scanner);
Order order = createOrder(scanner, flight, cargos);
if (!order.canBeCarried()) {
System.out.printf("The flight with flight number:%s has exceeded its load capacity and cannot carry the order.\n", flight.getFlightNumber());
return;
}
order.carryOrder();
printOrderDetails(order, customer);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("输入数据格式错误,请确保输入的数字符合要求。");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("发生未知错误:" + e.getMessage());
} finally {
scanner.close();
}
}
private static Customer createCustomer(Scanner scanner) {
String type = scanner.nextLine();
String customerId = scanner.nextLine();
String customerName = scanner.nextLine();
String customerPhone = scanner.nextLine();
String customerAddress = scanner.nextLine();
if (Objects.equals(type, "Individual")) {
return new InCustomer(customerId, customerName, customerPhone, customerAddress);
} else {
return new CoCustomer(customerId, customerName, customerPhone, customerAddress);
}
}
private static List<Cargo> createCargos(Scanner scanner) {
String cargoType = scanner.nextLine();
int cargoCount = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine());
List<Cargo> cargos = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < cargoCount; i++) {
String cargoId = scanner.nextLine();
String cargoName = scanner.nextLine();
double width = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
double length = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
double height = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
double weight = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
if (Objects.equals(cargoType, "Normal")) {
cargos.add(new NormalCargo(cargoId, cargoName, width, length, height, weight));
} else if (Objects.equals(cargoType, "Expedite")) {
cargos.add(new ExpediteCargo(cargoId, cargoName, width, length, height, weight));
} else {
cargos.add(new DangerousCargo(cargoId, cargoName, width, length, height, weight));
}
}
return cargos;
}
private static Flight createFlight(Scanner scanner) {
String flightNumber = scanner.nextLine();
String departureAirport = scanner.nextLine();
String arrivalAirport = scanner.nextLine();
String flightDate = scanner.nextLine();
double maxLoad = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
return new Flight(flightNumber, departureAirport, arrivalAirport, flightDate, maxLoad);
}
private static Order createOrder(Scanner scanner, Flight flight, List<Cargo> cargos) {
String orderId = scanner.nextLine();
String orderDate = scanner.nextLine();
String senderAddress = scanner.nextLine();
String senderName = scanner.nextLine();
String senderPhone = scanner.nextLine();
String receiverAddress = scanner.nextLine();
String receiverName = scanner.nextLine();
String receiverPhone = scanner.nextLine();
String paymentMethod = scanner.nextLine();
return new Order(orderId, orderDate, senderAddress, senderName, senderPhone,
receiverAddress, receiverName, receiverPhone, flight, cargos, paymentMethod);
}
private static void printOrderDetails(Order order, Customer customer) {
System.out.printf("客户:%s(%s)订单信息如下:\n", customer.getName(), customer.getPhone());
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.printf("航班号:%s\n", order.getFlightNumber());
System.out.printf("订单号:%s\n", order.getOrderId());
System.out.printf("订单日期:%s\n", order.getOrderDate());
System.out.printf("发件人姓名:%s\n", order.getSenderName());
System.out.printf("发件人电话:%s\n", order.getSenderPhone());
System.out.printf("发件人地址:%s\n", order.getSenderAddress());
System.out.printf("收件人姓名:%s\n", order.getReceiverName());
System.out.printf("收件人电话:%s\n", order.getReceiverPhone());
System.out.printf("收件人地址:%s\n", order.getReceiverAddress());
System.out.printf("订单总重量(kg):%.1f\n", order.getTotalWeight());
double total=0;
for(Cargo cargo : order.getCargos())
{
total=total+cargo.getFreight();
}
System.out.printf("%s支付金额:%.1f\n", order.getPaymentMethod(), total*customer.getDiscount());
System.out.printf("\n货物明细如下:\n");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.printf("明细编号\t货物名称\t计费重量\t计费费率\t应交运费\n");
int index = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < order.getCargos().size(); i++) {
Cargo cargo = order.getCargos().get(i);
if(i!=order.getCargos().size()-1) {
System.out.printf("%d\t%s\t%.1f\t%.1f\t%.1f\n", i + 1, cargo.getName(),
cargo.getChargeableWeightValue(), cargo.getRate(), cargo.getFreight());
}else {
System.out.printf("%d\t%s\t%.1f\t%.1f\t%.1f", i + 1, cargo.getName(),
cargo.getChargeableWeightValue(), cargo.getRate(), cargo.getFreight());
}
}
}
}
设计
1.设计思路
- 客户类设计(继承与多态)
- 抽象类 Customer:定义客户公共属性(编号、姓名、电话、地址)和抽象方法getDiscount()(获取折扣率)。
- 子类 InCustomer(个人客户):折扣率 0.9。
- 子类 CoCustomer(企业客户):折扣率 0.8。
- 货物类设计(继承与多态)
- 抽象类 Cargo:定义货物公共属性(编号、名称、尺寸、重量)和抽象方法(体积重量、计费重量、费率、运费等)。
- 子类 NormalCargo(普通货物):按普通费率计算(35/30/25/15 元 /kg)。
- 子类 ExpediteCargo(加急货物):按加急费率计算(60/50/40/30 元 /kg)。
- 子类 DangerousCargo(危险品):按危险品费率计算(80/50/30/20 元 /kg)。
- 核心业务逻辑
- 计费重量:取实际重量与体积重量(长 × 宽 × 高 / 6000)的较大值。
- 总费用计算:各货物运费之和 × 客户折扣率,运费 = 计费重量 × 对应费率。
- 航班载重验证:订单总计费重量超过航班剩余载重时终止程序。
- 订单与输出
- Order 类:整合客户、航班、货物信息,处理支付方式转换(如 ALiPay→支付宝)。
- 输出格式化:按固定格式输出订单详情、货物明细,数值保留 1 位小数,支持多态调用各货物的计算方法。
- 输入处理
- 按顺序读取客户类型、货物类型、航班信息、订单信息,根据类型创建对应子类对象。
- 处理可能的输入异常(如数字格式错误),确保程序健壮性。
2.类图

3.代码规模

4.复杂度分析

整体情况
- 行数与语句数:文件有 478 行,包含 224 条语句 。语句数一定程度上反映了代码规模,较多语句意味着代码实现的功能相对复杂。
- 分支语句占比:分支语句占比 7.1% ,说明代码中条件判断逻辑不算特别多,但仍有一定比例,会增加代码理解和维护难度。
- 方法调用语句数:有 43 条方法调用语句 ,体现了代码中各模块间的交互频繁程度,较多的方法调用意味着代码的模块化程度尚可,但也可能带来调用关系复杂的问题。
- 注释占比:注释仅占 0.2% ,注释过少不利于他人(甚至自己后续)理解代码逻辑,会增加代码维护难度。
- 类和接口数量:有 9 个类和接口 ,表明代码结构有一定复杂度,涉及多个不同职责的对象。
- 平均方法数:每个类平均有 5.89 个方法 ,说明类的功能相对丰富,但也可能存在类职责不够单一的情况。
- 平均每个方法的语句数:平均每个方法有 2.04 条语句 ,整体方法相对简洁,但结合总语句数多,说明方法数量较多。
方法复杂度
- 最复杂方法:ExpediteCargo.getRate() 复杂度为 5 ,是最复杂的方法。该方法可能包含较多条件判断或计算逻辑,需要重点关注和优化,比如检查是否可以拆分其中的逻辑到多个小方法中,提高可读性和可维护性。
- 最大复杂度:整体最大复杂度为 5 ,说明代码中存在部分较为复杂的逻辑片段,需要进一步审视这些高复杂度方法的实现逻辑。
- 平均复杂度:平均复杂度为 1.27 ,说明大部分方法复杂度不算高,但由于存在个别高复杂度方法,仍需关注整体方法复杂度的均衡性。
深度相关指标
- 最深代码块行数:最深代码块有 124 行 ,这可能意味着存在一个较长且逻辑复杂的代码片段,需要检查是否可以对其进行重构,拆分功能。
- 最大代码块深度:最大代码块深度为 3 ,平均代码块深度为 1.49 ,说明代码中存在一定嵌套层次,嵌套会使代码逻辑理解难度增加,可考虑优化条件判断和循环结构,降低嵌套深度。
改进建议
- 增加注释:补充关键逻辑、方法功能、参数意义等方面的注释,提高代码可读性。
- 重构高复杂度方法:针对如 ExpediteCargo.getRate() 等高复杂度方法,拆分复杂逻辑,使其功能更单一、清晰。
- 优化代码结构:检查类的职责是否单一,减少不必要的方法调用和嵌套,提高代码的可维护性。
总结
踩坑
问题一:题目集 8 中,Scanner读取数值后直接调用nextLine()可能读取到残留的换行符,导致颜色输入错误。
解决方案:统一使用nextLine()读取所有输入,再手动转换类型,并通过trim()去除空格。
问题二:题目集 9 中,初期遗漏Cargo子类的getChargeableWeightValue()方法,导致货物明细无法统一获取计费重量。
问题三:直接使用double计算运费时,出现精度误差(如2000.0 * 0.8变为1599.9999999999998)。
解决方案:改用BigDecimal进行精确计算,并通过setScale(1, RoundingMode.HALF_UP)保留一位小数。
问题:题目集 8 的Line类中,display方法同时处理颜色输出、坐标输出和长度计算,违反单一职责原则。
改进:将坐标输出逻辑封装到Point类的display方法中,Line类仅负责组合调用
结语
所学核心知识有,抽象与多态的本质,通过抽象类定义 “做什么”,子类实现 “怎么做”,实现 “接口统一,实现可变”。
以及类设计的五大原则:
单一职责原则:每个类仅负责单一功能(如Flight只管理载重,Order只处理订单流程)
里氏替换原则:子类可无缝替换父类,如CoCustomer可直接赋值给Customer引用。
依赖倒置原则:高层模块依赖抽象(如Order依赖Customer抽象类,而非具体子类)。
其中也考察也有很多思维的考察,例如魔法问题。
作业中包含了大量的迭代问题,对于设计程序的思维有显著提升。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号