购物车程序的面向对象设计
购物车程序的面向对象设计
1.人员分工:
| 姓名 | 任务 |
|---|---|
| 陈丹宇 | 编码规范、面向对象设计、功能设计 |
| 韦早辉 | 前期调查、博客制作 |
2.前期调查:
首先要登陆京东用户必须要有账号密码,所以用户的属性有:姓名,账号,密码,及收货地址:
登录了京东后搜索商品,然后找到商品,我们可以看见商品的名字,价格,如果心仪则加入购物车,所以商品的方法有:搜索,加入购物车;属性有:名字,价格


当我们加入购物车后我们可以看见商品的数量,总价,还有我们可以减少我们所加入购物车的商品的数量或者增加商品数量,然后进行结算,所以购物车的属性有:商品数量,总价;方法有:结算,增加、减少商品数量

3.系统结构图:
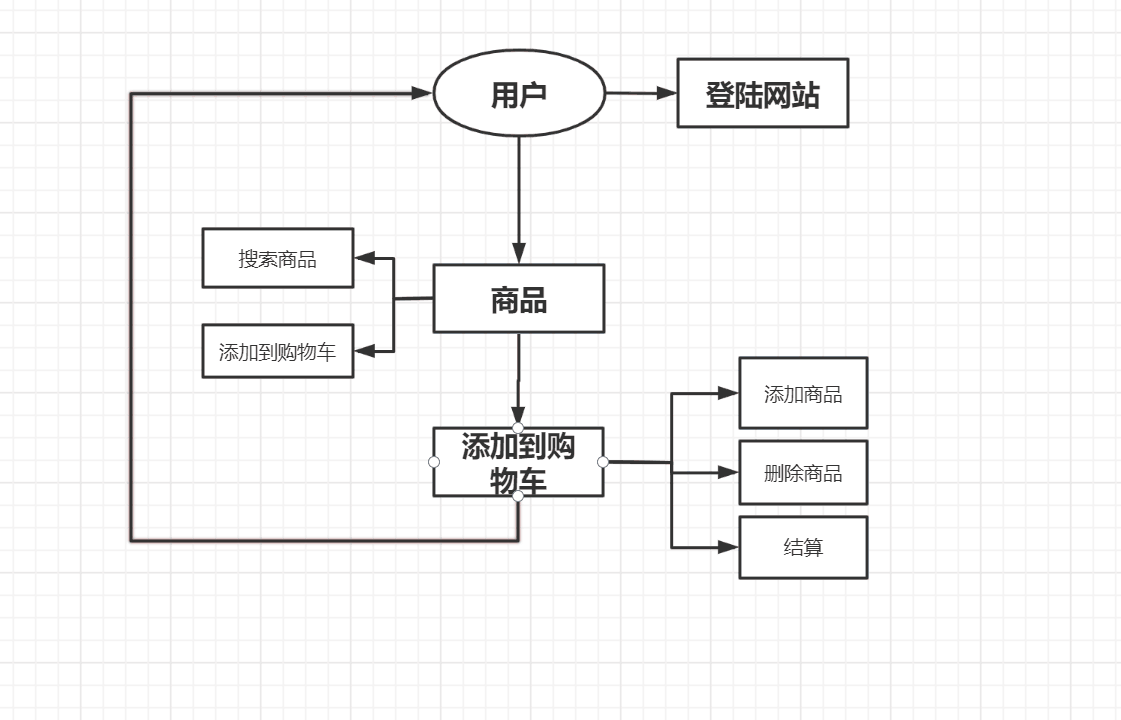
4.UML类图:

5.体现了面向对象的封装性:
在同一个包内调用Class文件
6.项目包结构与关键代码:
项目包结构

Product类
package Shoppingcart;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Product implements Comparable{
private Integer id;
private String name;
private double price;
public Product() {
}
public Product(Integer id, String name, double price) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Product product = (Product) o;
return Double.compare(product.price, price) == 0 &&
Objects.equals(id, product.id) &&
Objects.equals(name, product.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return this.id/10;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{" +
"商品编号:" + id +
", 商品名称:" + name + '\'' +
", 商品单价:" + price +
'}'+"\n";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
Product product = (Product)o;
int this_id = this.id;
int p_id = product.getId();
return this_id > p_id?1:-1;
}
}
ShoppingCar类
package Shoppingcart;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class ShoppingCar {
private Map<Product,Integer> cars;
private double totalPrice;
public ShoppingCar(){
cars = new HashMap<>();
}
//对外提供添加多个一类商品的方法
public void addProducts(Product p,Integer num){
if (num<=0){
System.out.println("商品数量不能小于1!");
return;
}
if (cars.containsKey(p)){
//如果能执行到这里说明购物车已经包含此商品了 这时需要累加 商品的数量
int productcount_before = cars.get(p);
int productcount_after = productcount_before + num;
cars.put(p,productcount_after);
System.out.println("添加商品成功!");
}else {
//程序执行到这里说明购物车中没有此商品 则添加
cars.put(p,num);
System.out.println("添加商品成功!");
}
double price = (p.getPrice())*num;
totalPrice = totalPrice + price;
}
//提供添加一个商品的方法
public void addProducts(Product product){
addProducts(product,1);
System.out.println("添加一个商品成功!");
}
//删除一类商品(指定数量)
public void removeProducts(Product product,Integer deletenum){
if (!cars.containsKey(product)){
System.out.println("您要删除的商品不存在!");
return;
}
//获取这个商品此时的数量 要删除的数量不能大于这个数量
int productNum = cars.get(product);
if (deletenum>productNum){
System.out.println("删除的商品数量不能大于已有的数量!");
return;
}
//程序能执行到这里说明满足上面的条件
//key重复 value覆盖
int afterDelete = productNum - deletenum;
//判断删除的数量是否的存在的数量相等 如果相等 则应连同商品删除
if (productNum == deletenum){
cars.remove(product);
System.out.println("删除商品成功!");
}else {
cars.put(product,afterDelete);
System.out.println("删除商品成功!");
}
//删去对应的价格
double price = (product.getPrice()) * deletenum;
totalPrice = totalPrice - price;
}
//某类商品全部删除
public void deleteClassProduct(Product product){
if (!cars.containsKey(product)){
System.out.println("该类商品不存在!");
return;
}
cars.remove(product);
System.out.println("该类删除商品成功!");
}
//删除某类商品其中的一个
public void deleteAproduct(Product product){
this.removeProducts(product,1);
}
//清空购物车
public void clearShoppingCar(){
if (cars.size()<=0){
System.out.println("您的购物车里没有任何商品哦~"+"\n");
return;
}
cars.clear();
totalPrice = 0.0;
System.out.println("清空购物车成功!");
}
//结账
public void checkOut() throws Exception{
if (cars.size()<=0){
System.out.println("您的购物车里没有任何商品哦~"+"\n");
return;
}else {
System.out.println("正在结账请稍后··········");
Thread.sleep(3000);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("\t\t购物详单:"+"\n\n");
sb.append("へへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへへ\n");
for (Map.Entry<Product,Integer> me : cars.entrySet()){
int num = me.getValue();
Product product = me.getKey();
int pid = product.getId();
String pname = product.getName();
double price = product.getPrice();
sb.append("\t\t商品编号:"+pid+"\t商品名称:"+pname+"\t商品单价:"+price+"\t商品数量:"+num+"\n");
}
sb.append("\n");
sb.append("\t\t\t\t\t总价:"+totalPrice+"\n\n");
sb.append("\t\t祝您购物愉快,欢迎下次光临!");
System.out.println(sb.toString());
clearShoppingCar();
}
}
//查看购物车
public void lookcar(){
if (cars.size()<=0){
System.out.println("您的购物车里没有任何商品哦~"+"\n");
return;
}else {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("\t\t您的购物车↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓:"+"\n\n");
for (Map.Entry<Product,Integer> me : cars.entrySet()){
int num = me.getValue();
Product product = me.getKey();
int pid = product.getId();
String pname = product.getName();
double price = product.getPrice();
sb.append("\t\t商品编号:"+pid+"\t商品名称:"+pname+"\t商品单价:"+price+"\t商品数量:"+num+"\n");
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
public Map<Product, Integer> getCars() {
return cars;
}
public void setCars(Map<Product, Integer> cars) {
this.cars = cars;
}
public double getTotalPrice() {
return totalPrice;
}
public void setTotalPrice(double totalPrice) {
this.totalPrice = totalPrice;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Shoppcar{" +
"cars=" + cars +
", totalPrice=" + totalPrice +
'}';
}
}
Test类
package Shoppingcart;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
static {
}
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception{
Product[] products = new Product[4];
Product p1 = new Product(100,"绿魔手机",9.9);
Product p2 = new Product(200,"1phone 14 proMax",8.8);
Product p3 = new Product(300,"8848太精手机",8848);
Product p4 = new Product(400,"菲尔普斯防水机",6.9);
products[0] = p1;
products[1] = p2;
products[2] = p3;
products[3] = p4;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("是否开始购物?(Y/N)");
String confirm = scanner.nextLine();
if (confirm.equals("Y") || confirm.equals("y")){
ShoppingCar shoppcar = new ShoppingCar();
System.out.println("\t\t商品信息如下:");
show();
while (true){
System.out.println("请输入您的选择:");
System.out.println("1:向购物车中添加商品");
System.out.println("2:从购物车中删除商品");
System.out.println("3:清空购物车");
System.out.println("4:查看购物车已有商品");
System.out.println("5:结账");
System.out.println("6:退出购物");
int choose = scanner.nextInt();
if (choose == 1){
System.out.println("请输入您要添加的商品的编号");
int productNum = scanner.nextInt();
Product p = getProduct(productNum,products);
if (p != null){
System.out.println("请输入要该类商品的添加数量");
int addCount = scanner.nextInt();
shoppcar.addProducts(p,addCount);
}else {
System.out.println("输入的商品编号有误!");
}
}
if (choose == 2){
System.out.println("请输入您要删除的商品的编号");
int productNum = scanner.nextInt();
Product p = getProduct(productNum,products);
if (p != null){
System.out.println("请输入要该类商品的删除数量");
int delCount = scanner.nextInt();
shoppcar.removeProducts(p,delCount);
}else {
System.out.println("输入的商品编号有误!");
}
}
if (choose == 3){
shoppcar.clearShoppingCar();
}if (choose == 4){
shoppcar.lookcar();
}
if (choose == 5){
shoppcar.checkOut();
}if (choose == 6){
System.out.println("您已退出购物,祝您生活愉快!");
break;
}
}
}
else {
System.exit(0);
}
}
public static void show(){
System.out.println("********************************************");
Product p1 = new Product(100,"绿魔手机",9.9);
Product p2 = new Product(200,"1phone 14 proMax",8.8);
Product p3 = new Product(300,"8848太精手机",8848);
Product p4 = new Product(400,"菲尔普斯防水机",6.9);
System.out.println(p1);
System.out.println(p2);
System.out.println(p3);
System.out.println(p4);
System.out.println("********************************************");
}
//传入一个商品编号 返回一个商品
public static Product getProduct(int num,Product[] products){
for (int i=0 ;i<products.length;i++){
int id = products[i].getId();
if (id == num){
return products[i];
}
}
return null;
}
}
总结
购物车的应用是我和小伙伴写的第一个程序,因此大部分是在模仿,代码层面第一次接触hashMap类,其中的大部分方法还是容易忘记,以及在Object中的默认方法是我们今后学习需要特别注意的地方。
最后感谢DanceDonkey博主的代码参考。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号