Java中的锁——Lock
(已迁移)
lock与synchronized的区别:
1、Lock是一个接口,synchronized是关键字。前者可以程序员自己DIY功能,实现自定义同步组件;后者是JVM来维护的。
2、Lock需要手动加解锁,synchronized自动完成加解锁。
3、synchronized修饰的代码执行异常时,自动释放线程占有的锁,不会出现死锁;Lock异常时需在finally中unlock(),否则死锁。
4、Lock可以让线程“在等待锁的过程中(即阻塞时)”响应中断,如tryLock;而synchronized“在等待锁的过程中(即阻塞时)”无法响应中断。
5、synchronized只能是非公平锁,而Lock可公平可非公平。
6、Lock可实现读写锁。
7、Lock锁的范围有局限性,仅适用于代码块范围,而Synchronized可以锁住代码块,对象实例,类。
8、Lock可以绑定条件,实现分组唤醒需要的线程;synchronized要么随机唤醒一个,要么唤醒全部线程。
1 public interface Lock { 2 void lock(); 3 void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException; 4 boolean tryLock(); 5 boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException; 6 void unlock(); 7 Condition newCondition(); 8 }
1 Lock lock = new LockImpl; // new 一个Lock的实现类 2 lock.lock(); // 加锁 3 try{ 4 //todo 5 }catch(Exception ex){ 6 // todo 7 }finally{ 8 lock.unlock(); //释放锁 9 }
-- lock()方法,如果锁被其他线程获取,则进行等待。
lock的错误使用方法:
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.List; 3 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; 4 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 5 6 public class ApplicationDemo { 7 private List<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); 8 9 public static void main(String[] args){ 10 ApplicationDemo applicationDemo = new ApplicationDemo(); 11 12 Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { 13 @Override 14 public void run() { 15 applicationDemo.insert(Thread.currentThread()); 16 } 17 }); 18 Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { 19 @Override 20 public void run() { 21 applicationDemo.insert(Thread.currentThread()); 22 } 23 }); 24 25 thread1.start(); 26 thread2.start(); 27 } 28 29 private void insert(Thread thread){ 30 Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 31 lock.lock(); 32 try{ 33 System.out.println(thread.getName() + " get lock"); 34 thread.sleep(1000); 35 }catch(Exception e){ 36 //... 37 }finally{ 38 System.out.println(thread.getName() + " unlock the lock"); 39 lock.unlock(); 40 } 41 } 42 }
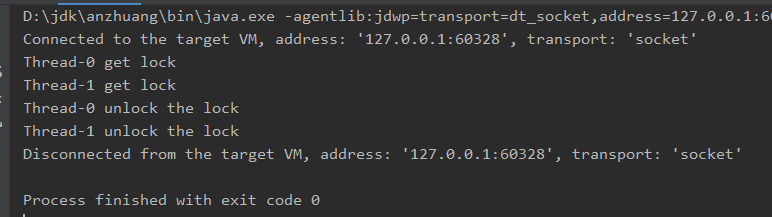
错误原因:
insert方法中lock变量为局部变量,每个线程获取到的是不同的锁,所以不会发生冲突。
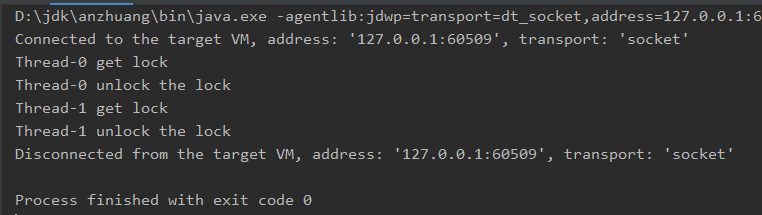
lock正确使用方式:
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.List; 3 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; 4 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 5 6 public class ApplicationDemo { 7 private List<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); 8 private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 9 10 public static void main(String[] args){ 11 ApplicationDemo applicationDemo = new ApplicationDemo(); 12 13 Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { 14 @Override 15 public void run() { 16 applicationDemo.insert(Thread.currentThread()); 17 } 18 }); 19 Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { 20 @Override 21 public void run() { 22 applicationDemo.insert(Thread.currentThread()); 23 } 24 }); 25 26 thread1.start(); 27 thread2.start(); 28 } 29 30 private void insert(Thread thread){ 31 lock.lock(); 32 try{ 33 System.out.println(thread.getName() + " get lock"); 34 thread.sleep(1000); 35 }catch(Exception e){ 36 //... 37 }finally{ 38 System.out.println(thread.getName() + " unlock the lock"); 39 lock.unlock(); 40 } 41 } 42 }
-- tryLock()方法,有返回值,尝试获取锁,获取成功返回true,获取失败(即锁被其他线程获取),返回false。也就是说,该方法无论能否拿到锁,都立即返回,不会拿不到锁的时候一直处于等待状态。
1 Lock lock = ...; 2 if(lock.tryLock()) { 3 try{ 4 //处理任务 5 }catch(Exception ex){ 6 7 }finally{ 8 lock.unlock(); //释放锁 9 } 10 }else { 11 //如果不能获取锁,则直接做其他事情 12 }
1 public class Test { 2 private ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 3 private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); //注意这个地方 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 final Test test = new Test(); 6 7 new Thread(){ 8 public void run() { 9 test.insert(Thread.currentThread()); 10 }; 11 }.start(); 12 13 new Thread(){ 14 public void run() { 15 test.insert(Thread.currentThread()); 16 }; 17 }.start(); 18 } 19 20 public void insert(Thread thread) { 21 if(lock.tryLock()) { 22 try { 23 System.out.println(thread.getName()+"得到了锁"); 24 for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { 25 arrayList.add(i); 26 } 27 } catch (Exception e) { 28 // TODO: handle exception 29 }finally { 30 System.out.println(thread.getName()+"释放了锁"); 31 lock.unlock(); 32 } 33 } else { 34 System.out.println(thread.getName()+"获取锁失败"); 35 } 36 } 37 }
1 Thread-0得到了锁 2 Thread-1获取锁失败 3 Thread-0释放了锁
-- lockInterruptibly()方法,可以在线程“等待获取锁”时响应中断,抛出InterruptedException异常。
1 public void method() throws InterruptedException { 2 lock.lockInterruptibly(); 3 try { 4 //..... 5 } 6 finally { 7 lock.unlock(); 8 } 9 }
1 public class Test { 2 private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Test test = new Test(); 5 MyThread thread1 = new MyThread(test); 6 MyThread thread2 = new MyThread(test); 7 thread1.start(); 8 thread2.start(); 9 10 try { 11 Thread.sleep(2000); 12 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 } 15 thread2.interrupt(); 16 } 17 18 public void insert(Thread thread) throws InterruptedException{ 19 lock.lockInterruptibly(); //注意,如果需要正确中断等待锁的线程,必须将获取锁放在外面,然后将InterruptedException抛出 20 try { 21 System.out.println(thread.getName()+"得到了锁"); 22 long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); 23 for( ; ;) {24 if(System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime >= Integer.MAX_VALUE) 25 break; 26 //插入数据 27 } 28 } 29 finally { 30 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行finally"); 31 lock.unlock(); 32 System.out.println(thread.getName()+"释放了锁"); 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 37 class MyThread extends Thread { 38 private Test test = null; 39 public MyThread(Test test) { 40 this.test = test; 41 } 42 @Override 43 public void run() { 44 45 try { 46 test.insert(Thread.currentThread()); 47 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 48 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"被中断"); 49 } 50 } 51 }
运行后发现,子线程可正常被中断。
-- ReentrantLock
可重入锁,即支持一个线程对相同资源重复加锁。实现可重入需解决两个问题:
1、锁需要去识别获取锁的线程是否为当前占据锁的线程,如果是,则可再次成功获取。
2、同一线程对同一资源锁的获取与释放,通过计数的方式来实现。
-- ReadWriteLock读写锁的接口,里面只定义了两个方法,一个用来获取读锁,一个用来获取写锁,即实现两个分开的锁,可分配给多个线程。
1 public interface ReadWriteLock { 2 /** 3 * Returns the lock used for reading. 4 * 5 * @return the lock used for reading. 6 */ 7 Lock readLock(); 8 9 /** 10 * Returns the lock used for writing. 11 * 12 * @return the lock used for writing. 13 */ 14 Lock writeLock(); 15 }
-- ReentrantReadWriteLock
实现了ReadWriteLock接口的类。
写锁只能一个线程获取;读锁可多个线程获取;有线程读时,写锁等待;有线程写时,读锁等待。
对于synchronized:
1 public class Test { 2 private ReentrantReadWriteLock rwl = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); 3 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 final Test test = new Test(); 6 7 new Thread(){ 8 public void run() { 9 test.get(Thread.currentThread()); 10 }; 11 }.start(); 12 13 new Thread(){ 14 public void run() { 15 test.get(Thread.currentThread()); 16 }; 17 }.start(); 18 19 } 20 21 public synchronized void get(Thread thread) { 22 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 23 while(System.currentTimeMillis() - start <= 1) { 24 System.out.println(thread.getName()+"正在进行读操作"); 25 } 26 System.out.println(thread.getName()+"读操作完毕"); 27 } 28 }
1 Thread-0正在进行读操作 2 Thread-0正在进行读操作 3 Thread-0正在进行读操作 4 Thread-0正在进行读操作 5 Thread-0正在进行读操作 6 Thread-0正在进行读操作 7 Thread-0正在进行读操作 8 Thread-0正在进行读操作 9 Thread-0正在进行读操作 10 Thread-0正在进行读操作 11 Thread-0正在进行读操作 12 Thread-0正在进行读操作 13 Thread-0正在进行读操作 14 Thread-0正在进行读操作 15 Thread-0正在进行读操作 16 Thread-0正在进行读操作 17 Thread-0正在进行读操作 18 Thread-0正在进行读操作 19 Thread-0正在进行读操作 20 Thread-0正在进行读操作 21 Thread-0正在进行读操作 22 Thread-0正在进行读操作 23 Thread-0正在进行读操作 24 Thread-0正在进行读操作 25 Thread-0正在进行读操作 26 Thread-0正在进行读操作 27 Thread-0正在进行读操作 28 Thread-0正在进行读操作 29 Thread-0读操作完毕 30 Thread-1正在进行读操作 31 Thread-1正在进行读操作 32 Thread-1正在进行读操作 33 Thread-1正在进行读操作 34 Thread-1正在进行读操作 35 Thread-1正在进行读操作 36 Thread-1正在进行读操作 37 Thread-1正在进行读操作 38 Thread-1正在进行读操作 39 Thread-1正在进行读操作 40 Thread-1正在进行读操作 41 Thread-1正在进行读操作 42 Thread-1正在进行读操作 43 Thread-1正在进行读操作 44 Thread-1正在进行读操作 45 Thread-1正在进行读操作 46 Thread-1正在进行读操作 47 Thread-1正在进行读操作 48 Thread-1正在进行读操作 49 Thread-1正在进行读操作 50 Thread-1正在进行读操作 51 Thread-1正在进行读操作 52 Thread-1正在进行读操作 53 Thread-1正在进行读操作 54 Thread-1正在进行读操作 55 Thread-1正在进行读操作 56 Thread-1正在进行读操作 57 Thread-1正在进行读操作 58 Thread-1正在进行读操作 59 Thread-1正在进行读操作 60 Thread-1正在进行读操作 61 Thread-1正在进行读操作 62 Thread-1正在进行读操作 63 Thread-1正在进行读操作 64 Thread-1正在进行读操作 65 Thread-1正在进行读操作 66 Thread-1正在进行读操作 67 Thread-1正在进行读操作 68 Thread-1正在进行读操作 69 Thread-1正在进行读操作 70 Thread-1正在进行读操作 71 Thread-1正在进行读操作 72 Thread-1正在进行读操作 73 Thread-1读操作完毕
对于读写锁:
1 public class Test { 2 private ReentrantReadWriteLock rwl = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); 3 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 final Test test = new Test(); 6 7 new Thread(){ 8 public void run() { 9 test.get(Thread.currentThread()); 10 }; 11 }.start(); 12 13 new Thread(){ 14 public void run() { 15 test.get(Thread.currentThread()); 16 }; 17 }.start(); 18 19 } 20 21 public void get(Thread thread) { 22 rwl.readLock().lock(); 23 try { 24 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 25 26 while(System.currentTimeMillis() - start <= 1) { 27 System.out.println(thread.getName()+"正在进行读操作"); 28 } 29 System.out.println(thread.getName()+"读操作完毕"); 30 } finally { 31 rwl.readLock().unlock(); 32 } 33 } 34 }
1 Thread-0正在进行读操作 2 Thread-0正在进行读操作 3 Thread-1正在进行读操作 4 Thread-0正在进行读操作 5 Thread-1正在进行读操作 6 Thread-0正在进行读操作 7 Thread-1正在进行读操作 8 Thread-1正在进行读操作 9 Thread-1正在进行读操作 10 Thread-1正在进行读操作 11 Thread-1正在进行读操作 12 Thread-1正在进行读操作 13 Thread-0正在进行读操作 14 Thread-0正在进行读操作 15 Thread-0正在进行读操作 16 Thread-0正在进行读操作 17 Thread-1正在进行读操作 18 Thread-1正在进行读操作 19 Thread-1正在进行读操作 20 Thread-1正在进行读操作 21 Thread-0正在进行读操作 22 Thread-1正在进行读操作 23 Thread-1正在进行读操作 24 Thread-0正在进行读操作 25 Thread-1正在进行读操作 26 Thread-1正在进行读操作 27 Thread-0正在进行读操作 28 Thread-1正在进行读操作 29 Thread-1正在进行读操作 30 Thread-1正在进行读操作 31 Thread-0正在进行读操作 32 Thread-1正在进行读操作 33 Thread-1正在进行读操作 34 Thread-0正在进行读操作 35 Thread-1正在进行读操作 36 Thread-0正在进行读操作 37 Thread-1正在进行读操作 38 Thread-0正在进行读操作 39 Thread-1正在进行读操作 40 Thread-0正在进行读操作 41 Thread-1正在进行读操作 42 Thread-0正在进行读操作 43 Thread-1正在进行读操作 44 Thread-0正在进行读操作 45 Thread-1正在进行读操作 46 Thread-0正在进行读操作 47 Thread-1正在进行读操作 48 Thread-0读操作完毕 49 Thread-1读操作完毕
-- 公平锁
即按先来后到的顺序让等待的线程获取锁;synchronized就是典型的非公平锁;非公平锁容易造成“饥饿”现象。
ReentrantLock和ReentrantWriteLock默认为非公平锁,若改为公平锁:
1 ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true);
-- Condition条件
1 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; 2 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; 3 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 4 5 public class ShareResource { 6 private volatile int num = 1; 7 private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 8 private Condition conditionA = lock.newCondition(); 9 private Condition conditionB = lock.newCondition(); 10 private Condition conditionC = lock.newCondition(); 11 12 //A线程打印1~5 13 public void print5(){ 14 lock.lock(); 15 try{ 16 while(num != 1){ 17 conditionA.await(); 18 } 19 for(int i=0;i<5;++i){ 20 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + (i+1)); 21 } 22 num = 2; 23 conditionB.signal(); 24 25 }catch(InterruptedException e){ 26 e.printStackTrace(); 27 }finally{ 28 lock.unlock(); 29 } 30 } 31 32 //B线程打印1~10 33 public void print10(){ 34 lock.lock(); 35 try{ 36 while(num != 2){ 37 conditionB.await(); 38 } 39 for(int i=0;i<10;++i){ 40 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + (i+1)); 41 } 42 num = 3; 43 conditionC.signal(); 44 45 }catch(InterruptedException e){ 46 e.printStackTrace(); 47 }finally{ 48 lock.unlock(); 49 } 50 } 51 52 //C线程打印1~15 53 public void print15(){ 54 lock.lock(); 55 try{ 56 while(num != 3){ 57 conditionC.await(); 58 } 59 for(int i=0;i<15;++i){ 60 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + (i+1)); 61 } 62 num = 1; 63 conditionA.signal(); 64 65 }catch(InterruptedException e){ 66 e.printStackTrace(); 67 }finally{ 68 lock.unlock(); 69 } 70 } 71 } 72 73 74 public class ApplicationDemo { 75 public static void main(String[] args){ 76 /** 77 * 锁定多个条件Condition 78 * 多线程按顺序打印,实现A->B->C的线程执行顺序,循环执行3次 79 * */ 80 ShareResource shareResource = new ShareResource(); 81 82 Thread threadA = new Thread(new Runnable() { 83 @Override 84 public void run() { 85 for(int i=0;i<3;++i){ 86 shareResource.print5(); 87 } 88 } 89 },"A"); 90 91 Thread threadB = new Thread(new Runnable() { 92 @Override 93 public void run() { 94 for(int i=0;i<3;++i){ 95 shareResource.print10(); 96 } 97 } 98 },"B"); 99 100 Thread threadC = new Thread(new Runnable() { 101 @Override 102 public void run() { 103 for(int i=0;i<3;++i){ 104 shareResource.print15(); 105 } 106 } 107 },"C"); 108 109 threadA.start(); 110 threadB.start(); 111 threadC.start(); 112 } 113 }
(非原创,原文参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/dolphin0520/p/3923167.html)
(非原创,原文参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/dd09194b120b)
(非原创,原文参考:https://blog.csdn.net/lixinkuan328/article/details/94426872)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号