2.xv6启动流程
xv6启动流程
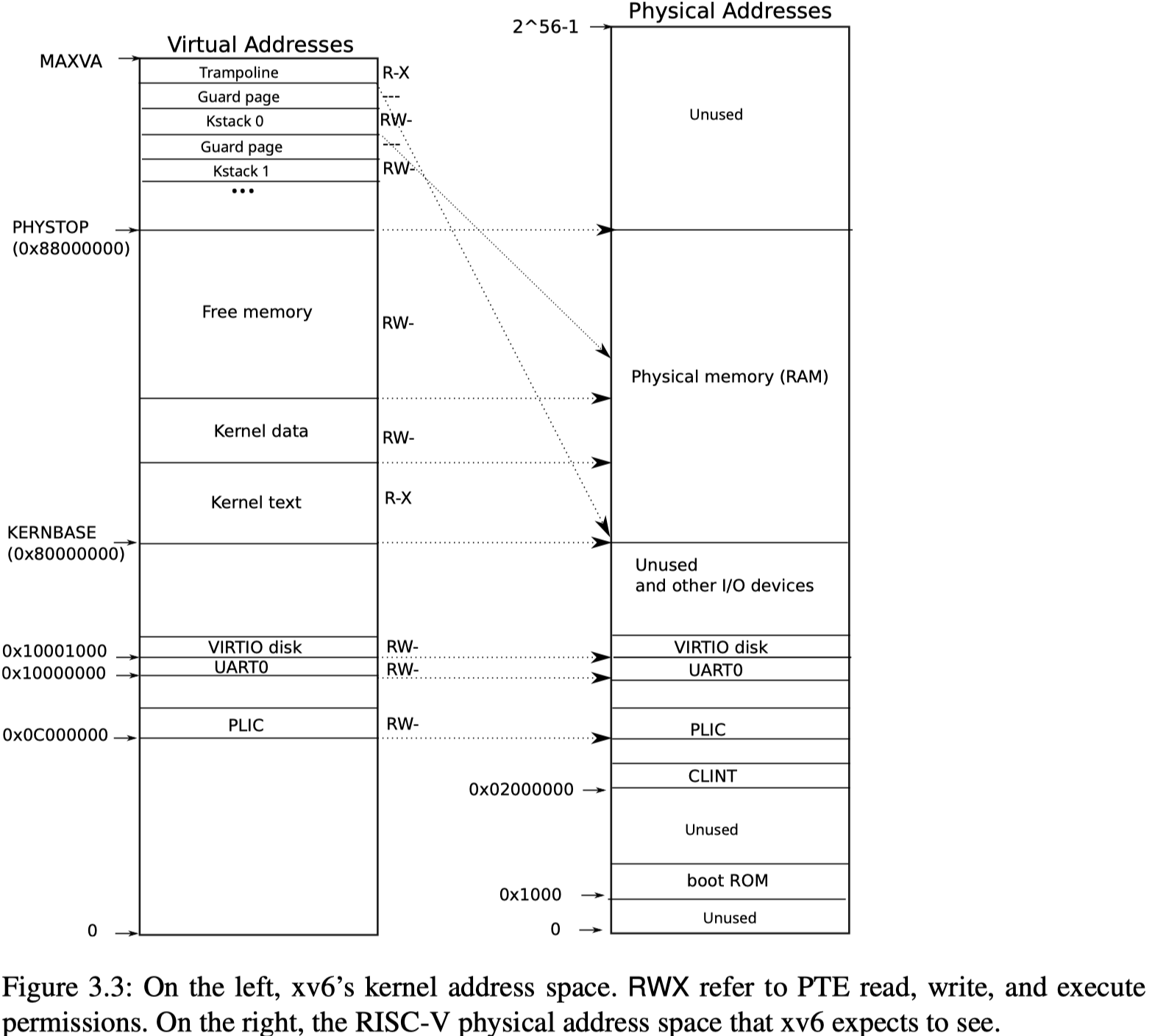
xv6内核地址空间
1 Riscv开机
riscv在启动时,pc被默认设置为0X1000,之后经过以下几条指令,跳转到0x80000000
-
在第一个shell,打开xv6 gdb模式
make qemu-gdb -
打开第二个shell,进行调试
riscv64-unknown-elf-gdb -
可以看到启动时,qemu就在
0X1000地址The target architecture is set to "riscv:rv64". warning: No executable has been specified and target does not support determining executable automatically. Try using the "file" command. 0x0000000000001000 in ?? () -
使用
layout asm查看汇编源码0x1000 auipc t0,0x0 0x1004 addi a2,t0,40 0x1008 csrr a0,mhartid 0x100c ld a1,32(t0) 0x1010 ld t0,24(t0) 0x1014 jr t0 -
执行到
0x1014时,使用info reg,可以看到t0此时的值等于0x80000000 -
从而跳转到
0x80000000
2. xv6编译
同时,xv6在编译时,会把引导程序放在0x80000000位置,从而成功进入系统
-
查看xv6中的
kernel/kernel.ld,可以看到. = 0x80000000;,这一行会将初始程序放置到0x80000000地址 -
使用
make qemu编译xv6 -
使用
riscv64-unknown-elf-objdump -d kernel/kernel反编译内核文件,可以看到kernel: file format elf64-littleriscv Disassembly of section .text: 0000000080000000 <_entry>: 80000000: 0001a117 auipc sp,0x1a 80000004: c7010113 add sp,sp,-912 # 80019c70 <stack0> 80000008: 6505 lui a0,0x1 8000000a: f14025f3 csrr a1,mhartid 8000000e: 0585 add a1,a1,1 80000010: 02b50533 mul a0,a0,a1 80000014: 912a add sp,sp,a0 80000016: 6d0050ef jal 800056e6 <start> -
_entry函数被放置在了0X80000000位置
2. kernel/entry.S
_entry:
# 设置内核栈指针
la sp, stack0 # sp<-stack0
li a0, 1024*4 # a0<-4096
csrr a1, mhartid # a1<-mhartid
addi a1, a1, 1 # a1<-a1+1
mul a0, a0, a1 # a0<-a0*a1
add sp, sp, a0 # sp<-sp+a0
call start # 最后跳转到kernel/start.c/start函数
-
la sp, stack0stack0定义在
kernel/start.cz中,xv6最多支持8个cpu,每个cpu的栈大小为4KB// maximum number of CPUs #define NCPU 8 // entry.S needs one stack per CPU. __attribute__ ((aligned (16))) char stack0[4096 * NCPU]; -
csrr a1, mhartid:-
csrr:CSR read
CSR:Control and Status Register,即控制和状态寄存器
CSRR就是读取控制和状态寄存器
-
mhartid[1]:Machine Hardware Thread ID,即硬件线程ID寄存器
-
所以这里就是获取硬件线程ID,并存储到a1中
-
hart(hardware thread,硬件线程):在软件层面看来,硬件线程就是一个独立的处理器。但实际上,它可能并不是一个完整的核心。因为CPU有超线程技术,超线程将一个处理器单元复用给多个硬件线程,每个硬件线程有自己独立的一套通用寄存器等上下文资源
-
2.1 功能解析
_entry的作用是设置栈指针
-
sp = stack0[0]的地址
-
a0 = 4096
-
a1 = mhartid,mhartid从0开始
-
a1 = a1 + 1 = mhartid + 1
-
a0 = a0 * a1 = 4096 * (mhartid + 1)
-
sp = sp + a0 = stack0[0] + a0 = stack0[0] + 4096 * (mhartid + 1)
当mhartid = 0时,sp = stack0[0] + 4096,这是因为栈是从高地址往低地址增长的,所以第一个栈的起始地址是stack0[4096],往stack0[0]增长
当mhartid = 1时,sp = stack0[0] + 4096 * 2,第二个栈的起始地址是stack0[8192],往stack0[4096]增长
其他的以此类推,就完成了栈指针的设置
3. kernel\start.c\start()
void start() {
// 将mstatus从机器模式设置为特权者模式
unsigned long x = r_mstatus();
x &= ~MSTATUS_MPP_MASK;
x |= MSTATUS_MPP_S;
w_mstatus(x);
// 将main函数地址写入mepc
w_mepc((uint64)main);
// 将satp设置为0,关闭页表,即关闭虚拟地址转换功能
w_satp(0);
// 把所有中断和异常委托给S-mode
w_medeleg(0xffff);
w_mideleg(0xffff);
// 打开中断
w_sie(r_sie() | SIE_SEIE | SIE_STIE | SIE_SSIE);
// configure Physical Memory Protection to give
// supervisor mode access to all of physical memory.
w_pmpaddr0(0x3fffffffffffffull);
w_pmpcfg0(0xf);
// ask for clock interrupts.
timerinit();
// 将hart_id存储到tp寄存器中
int id = r_mhartid();
w_tp(id);
// 切换到监督者模式,并跳转到main函数
asm volatile("mret");
}
- 当前计算机处于
M-Mode,即机器模式
3.1 mstatus
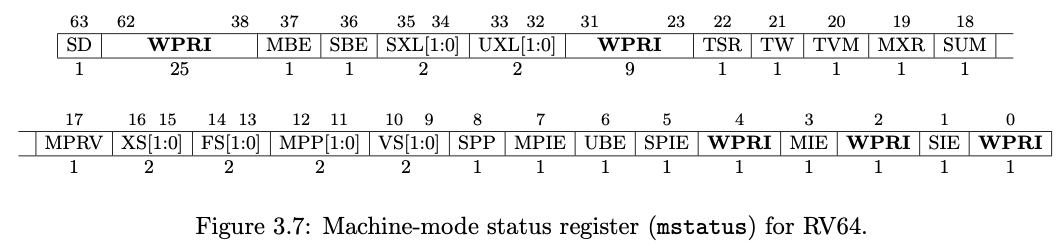
mstatus(Machine Status):是一个控制和状态寄存器CSR,存储处理器当前状态。包含以下位字段
- MPP (Machine Previous Privilege): 指示在发生异常或中断之前的特权级别,当使用
mret返回时,处理器会切换回原来的级别,在第11 12位00: User Mode01: Supervisor Mode11: Machine Mode
- MPIE (Machine Previous Interrupt Enable): 记录在发生异常或中断之前,中断是否被启用。
- MIE (Machine Interrupt Enable): 允许或禁止中断。当为1时,中断被启用。
- MIE (Machine Interrupt Enable): 记录中断是否被启用。
unsigned long x = r_mstatus();
x &= ~MSTATUS_MPP_MASK;
x |= MSTATUS_MPP_S;
w_mstatus(x);
-
unsigned long x = r_mstatus():读出mstatus的值 -
x &= ~MSTATUS_MPP_MASK:清除MPP的状态比如x = 1010 1011,其中第2,3位表示MPP状态,那么
MSTATUS_MPP_MASK = 0110 0000,~MSTATUS_MPP_MASK=1001 1111x &= ~MSTATUS_MPP_MASK=>1010 1011&1001 1111=1000 1011 -
x |= MSTATUS_MPP_S:设置MPP为监督者模式
这里我们将mstatus设置为监督者模式,之后跳回时,会切换到监督者模式
3.2 mepc
Machine Exception Program Counter:存储从内核返回用户态时的地址,指令执行操作如下
- 发生异常(中断、故障等)。
- 处理器将当前的PC值(即异常发生前正在执行的指令地址)写入
mepc寄存器。 - 进入内核处理异常
- 异常处理完毕后,返回到
mepc保存的地址,继续执行。
w_mepc((uint64)main);
但是我们这里并不是从用户态返回,而是利用这一特性,在内核返回时,跳转到main函数
3.3 satp
Supervisor Address Translation and Protection Register:监督地址转换和保护寄存器,用于控制和配置页表的地址。它定义了当前页表的位置和格式,以及一些与地址翻译和保护相关的信息,这里就是关闭页表功能
3.4 medeleg & mideleg
medeleg:Machine Exception Delegation Register:用于指定被委托给更低特权级别的异常,当异常发生时,如果该异常被委托,处理器会将该异常转交给更低特权级别的异常处理程序进行处理。 如果某个位被设置为 1,表示被委托。
mideleg:Machine Interrupt Delegation Register:和委托异常类似,用于委托中断
3.5 sie
sie:Supervisor Interrupt Enable :用于控制哪些中断可以在 Supervisor 模式下被启用或禁用。
-
SEIE (Supervisor External Interrupt Enable):
外部中断。当
SEIE位被设置为 1 时,允许外部中断在 Supervisor 模式下触发。 -
STIE (Supervisor Timer Interrupt Enable):
定时器中断。当
STIE位被设置为 1 时,允许定时器中断在 Supervisor 模式下触发。 -
SSIE (Supervisor Soft Interrupt Enable):
软中断。当
SSIE位被设置为 1 时,允许软中断在 Supervisor 模式下触发。
3.5 pmpaddr0 & pmpcfg0
和PMP有关,比较复杂
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/139695407
https://www.rvmcu.com/site/nuclei_n_isa/#8-n
3.6 timerinit
解析在下方
3.7 mhartid & tp
mhartid:之前讲过,就是硬件线程编号
tp:Thread Pointer,用于保存线程本地数据的指针,没有规定存什么,这里用来存线程编号
3.8 mret
只能在机器模式下执行,用于返回到调用之前的上下文环境,指令执行的操作如下:
- 从
mepc寄存器中取出先前保存的返回地址,加载到pc中。 - 切换回
mstatus中存储的之前的机器特权状态。
这个指令在异常处理或中断服务结束时使用,将处理器从机器模式切换回先前的模式,例如用户模式。这里我们是从机器模式切到监督者模式
4.kernel\start.ct\timerinit()
设置时钟中断
void timerinit()
{
// 获取CPU ID
int id = r_mhartid();
// ask the CLINT for a timer interrupt.
int interval = 1000000; // cycles; about 1/10th second in qemu.
*(uint64*)CLINT_MTIMECMP(id) = *(uint64*)CLINT_MTIME + interval;
// prepare information in scratch[] for timervec.
// scratch[0..2] : space for timervec to save registers.
// scratch[3] : address of CLINT MTIMECMP register.
// scratch[4] : desired interval (in cycles) between timer interrupts.
uint64 *scratch = &timer_scratch[id][0];
scratch[3] = CLINT_MTIMECMP(id);
scratch[4] = interval;
w_mscratch((uint64)scratch);
// set the machine-mode trap handler.
w_mtvec((uint64)timervec);
// enable machine-mode interrupts.
w_mstatus(r_mstatus() | MSTATUS_MIE);
// enable machine-mode timer interrupts.
w_mie(r_mie() | MIE_MTIE);
}
5. Kernel\main.c\main()
void main() {
if(cpuid() == 0){
// 对各个功能进行初始化
consoleinit();
printfinit();
printf("\n");
printf("xv6 kernel is booting\n");
printf("\n");
kinit(); // physical page allocator
kvminit(); // create kernel page table
kvminithart(); // turn on paging
procinit(); // process table
trapinit(); // trap vectors
trapinithart(); // install kernel trap vector
plicinit(); // set up interrupt controller
plicinithart(); // ask PLIC for device interrupts
binit(); // buffer cache
iinit(); // inode table
fileinit(); // file table
virtio_disk_init(); // emulated hard disk
userinit(); // first user process
__sync_synchronize();
started = 1;
} else {
while(started == 0)
;
__sync_synchronize();
printf("hart %d starting\n", cpuid());
kvminithart(); // turn on paging
trapinithart(); // install kernel trap vector
plicinithart(); // ask PLIC for device interrupts
}
scheduler();
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号