项目总结:超市管理系统1
超市管理系统需要结合多种学习知识点;
数据库连接,数据库表连接,更改表的内容(增删该查);用户输入进行密码加密添加到数据库;密码二次加密进行比对用户数据
创建连接数据库
/**
* MVC 三层架构
* M model 数据模型
* V view 视图层
* C controller 控制层 管理层 前段页面交互
*
* controller 控制层 用来和用户交互
* service 业务层 真整的业务处理
* dao 与DB交互的一层
*/
public class DbUtils {
public static Connection getConn() throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
//加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//获取连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(
//获取连接 jdbc协议名 mysql子协议名 127.0.0.1服务器IP地址 3306端口号 supermarket数据库名
"jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/metro","root", "123456");
return connection;
// localhost 等价 127.0.0.1 都是服务器IP地址
}
//sql语句 insert (增) delete(删) update(修) 一类操作 更新数据表的操作
public static int update(String sql,Object... paras) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
//1.获取数据库连接
Connection conn = getConn();
//2.执行sql语句(语句对象)用来执行sql语句 PreparedStatement 用于执行sql语句
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//给占位符赋值
if(paras != null && paras.length > 0){
for (int i = 0; i < paras.length; i++) {
//setObject 方法就是用来个占位符赋值的
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1,paras[i]);
}
}
//i代表受影响的行数
int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
preparedStatement.close();
conn.close();
return i;
}
// select 返回一个结果集
public static void query(String sql,Object... paras) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
//1.获取连接对象
Connection conn = getConn();
//2. 生成语句对象
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
System.out.println(preparedStatement);
//3.给占位符赋值
if(paras!= null && paras.length > 0){
for (int i = 0; i < paras.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1,paras[i]);
}
}
//4.执行select select 返回一个结果集
//ResultSet 结果集合
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//获取列的个数 字段的个数
int columnCount = resultSet.getMetaData().getColumnCount();
while (resultSet.next()) {
for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {
System.out.print(resultSet.getObject(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
resultSet.close();
preparedStatement.close();
conn.close();
}
}也可以将数据库连接中的IP端口数据库名称一起写在一个资源文件中,遵守开闭原则,只改连接信息不去动用原代码
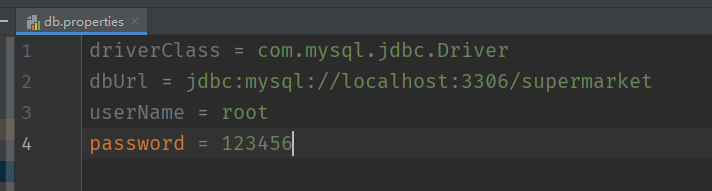
关闭资源;
resultSet.close();
preparedStatement.close();
conn.close();conn.close();
数据库查询表创建:
数据库中创建的是基本的超市系统
-- 商品信息表
CREATE TABLE t_st(
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,-- 商品唯一ID
name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, -- 商品名
type INT NOT NULL, -- 商品所属类型
sum INT NOT NULL, -- 商品数量
price FLOAT(4,2) NOT NULL, -- 商品单价
states INT,-- 商品状态
discount FLOAT(2,1), -- 商品折扣
creat datetime,
modify datetime
);
-- 商品类型表
CREATE TABLE t_bt(
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,-- 唯一ID
pid INT NOT NULL, -- 父类ID为0代表是1级目录
name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, -- 类名称
names INT NOT NULL, -- 是否是父类型 1是 0不是
states TINYINT NOT NULL, -- 0正常 1下架 2删除
creat datetime,
modify datetime
);
-- 会员管理
CREATE TABLE t_at(
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,-- 会员一ID
name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, -- 会员名
password VARCHAR(255), -- 密码
phone VARCHAR(255), -- 联系方式
integral FLOAT, -- 积分
balance FLOAT, -- 余额
creat datetime, -- 创建时间
modify datetime -- 修改时间
);
-- 订单信息表
CREATE TABLE t_dt(
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,-- 唯一ID
user INT NOT NULL,-- 用户ID
money DOUBLE,-- 订单总金额
time datetime,-- 下单时间
pay INT NOT NULL -- 支付类型
);
-- 订单详情表
CREATE TABLE t_tt(-- 订单详情ID
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,-- 唯一ID
form INT, -- 订单 与订单信息表订单ID有关系
goods INT, -- 购买商品 与商品信息表的商品编号有关系
sum INT NOT NULL-- 购买商品数量
);
创建与数据库中每个实体类对应的类型属性与方法,实现类
和对应的get set toString 方法,有参无参构造
/**
* 商品信息表
*/
public class Goods {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer type;//商品所属类型
private Integer sum;//库存数量
private Float price;//商品单价
private int states;//商品状态
private Float discount;//商品折扣
private Date creat;//创建时间
private Date modify;//更新时间
public Goods() {
}/**
* 订单详情表
*/
public class Details {
private Integer id;//详情表自增ID
private Integer form;//订单ID
private Integer goods;//购买商品
private Integer sum;//购买商品数量
public Details() {
}/**
* 购买商品
*/
public class GoodsVO {
private Goods goods;
private Integer buyNum;//当前商品总量
private BigDecimal price;//当前商品金额
public GoodsVO() {
}/**
* 订单信息
*/
public class Order {
private Integer user;//用户ID
private double money;//订单总金额
private Date time;//下单时间
private Integer pay;//支付类型
public Order() {
}
/**
* 购物车
*/
public class ShoppingCar {
private HashMap<Integer,GoodsVO> car;//购物车
private BigDecimal totalPrice;//总价格
public ShoppingCar(HashMap<Integer, GoodsVO> car, BigDecimal totalPrice) {
this.car = car;
this.totalPrice = totalPrice;
}
public ShoppingCar() {
}
/**
* 会员
*/
public class Vip {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String password;
private String phone;//联系电话
private Float integral;//积分
private Float balance;//余额
private Date creat;//创建时间
private Date modify;//修改时间
public Vip() {
}
在业务层service层
分别创建与超市管理系统相关的模板和继承方法实现(增删改查)
从上到下分别是:购物车、订单详情、商品信息、订单信息、购买业务、会员;(父类模板)
比如:
/**
* 订单详情表
*/
public interface DetailsService {
/**
* 添加详情表
*/
int addDetails(Details details);
/**
* 删除
*/
int removeDetails(int detailsId);
/**
* 修改
*/
int editDetails(Details details);
/**
* 查看
*/
List<Details> queryAllDetails();
/**
* 查看指定
*/
Details queryById(int detailsDi);
}
在DB交互层dao层
分别创建与超市管理系统相关的模板和继承方法实现(增删改查)
从上到下分别是:订单详情、商品信息、订单信息、会员;(父类模板)
比如:
/**
* 订单详情表
*/
public interface DetailsDao {
/**
* 添加
*/
int insertDetails(Details details) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException;
/**
* 删除
*/
int deleteDetails(int detailsId) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException;
/**
* 修改
*/
int updateDetails(Details details) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException;
/**
* 查看
*/
List<Details> selectAllDetails() throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException;
/**
* 指定查看
*/
Details selectById(int detailsId) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException;
}
在 impl文件中继承对应的父类
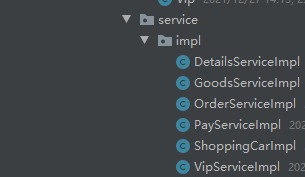
比如继承商品信息表,重写继承的方法:
service层去调用dao层
/**
* 订单详情表
*/
public class DetailsServiceImpl implements DetailsService {
private DetailsDao detailsDao = new DetailsDaoImpl();
/**
* 添加
* @param details
* @return
*/
@Override
public int addDetails(Details details) {
int i = 0;
try {
i = detailsDao.insertDetails(details);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return i;
}
/**
* 删除
* @param detailsId
* @return
*/
@Override
public int removeDetails(int detailsId) {
int i = 0;
try {
i = detailsDao.deleteDetails(detailsId);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return i;
}
/**
* 修改
* @param details
* @return
*/
@Override
public int editDetails(Details details) {
int i = 0;
try {
i = detailsDao.updateDetails(details);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return i;
}
/**
* 查看
* @return
*/
@Override
public List<Details> queryAllDetails() {
List<Details> list = null;
try {
list = detailsDao.selectAllDetails();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return list;
}
/**
* 更新
* @param detailsId
* @return
*/
@Override
public Details queryById(int detailsId) {
Details details = null;
try {
details = detailsDao.selectById(detailsId);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return details;
}
}
为什么说要在service层去调用dao层,经过询问李同学,听她的讲解我去网上查找的相应的答案,如下:
在service层去调用dao层,为的就是去提高dao层代码的复用性,相当于封装起来(将小的零件一个个拼接起来组成一个大的方便程序员使用的工具)



不用问我从哪里找来的,因为互联网的精神就是共享(手动狗头保命)
模拟系统中都添加了 : 商品管理、会员管理、信息表管理、详情表管理、购买商品; 每个管理都又逐个实现了增删该查(查找子类,指定查找)

.......
在主要的核心代码体现在购买购买商品中;
核心代码!!! ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
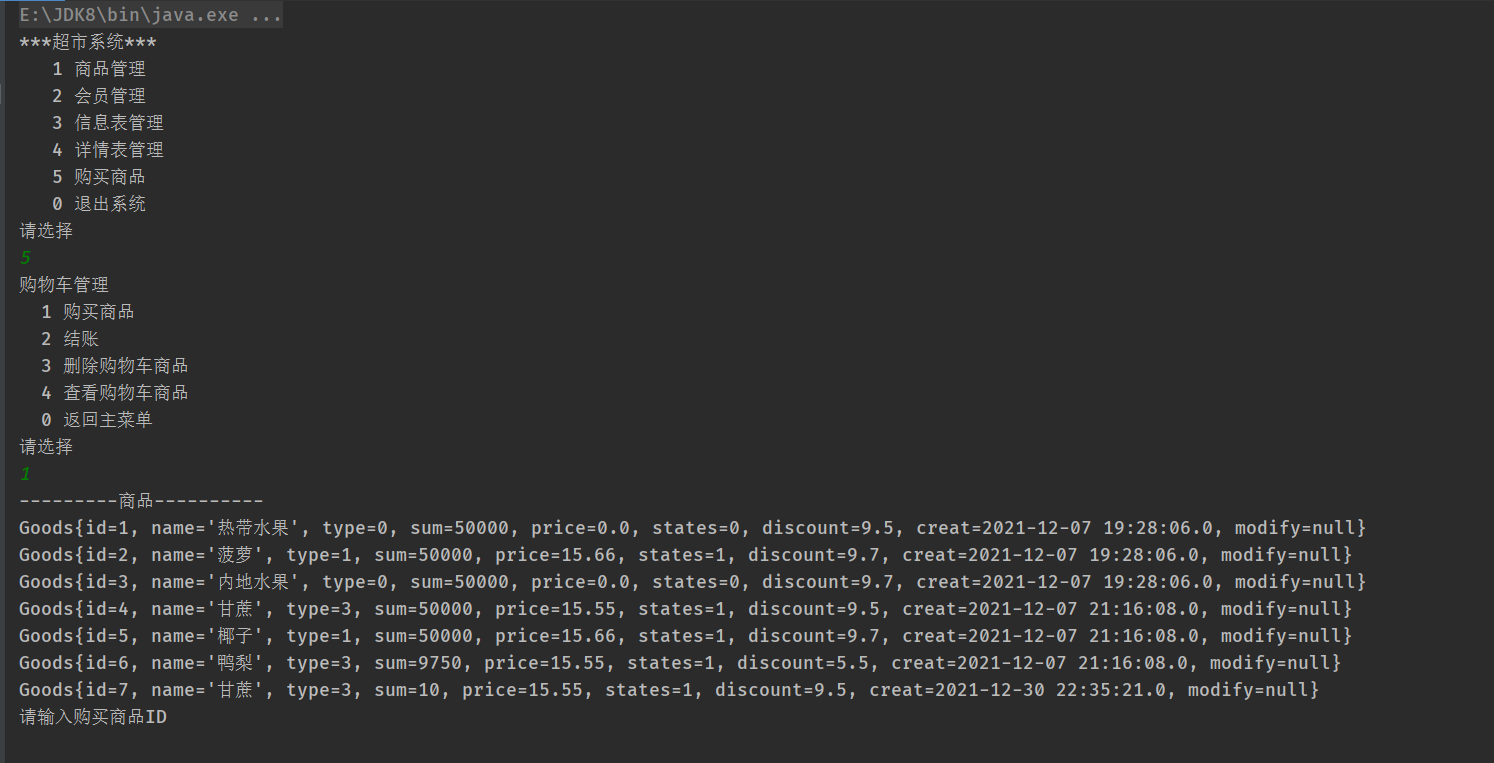
购买商品
/**
* 提示输出购买商品ID 然后将ID判断是否为空;如果不为空打印输出对应商品信息;提示购买数量,判断购买数量是否大于
* 库存数量;使用money计算总金额;
* 在goodsService方法中重写更新商品表的方法int goods1 = goodsService.updateStore(pid, sum)
* 将PID SUM传进goodsService.updateStore更新对应的商品数量 索引使用用户传进来的值
*
* @return
*/
public void buyGoods() {
String n = null;
int i = 0;
do {
System.out.println("---------商品----------");
List<Goods> list = goodsService.queryAllGoods();
list.forEach(k->{
System.out.println(k.toString());
});
System.out.println("请输入购买商品ID");
pid = scanner.nextInt();
goods = goodsService.queryById(pid);
if (goods == null) {
System.out.println("商品已经下架");
}
System.out.println(goods);
System.out.println("确定购买吗 y/n");
String num = scanner.next();
if (!("y".equalsIgnoreCase(num))) {
continue;
}
System.out.println("请输入购买数量");
sum = scanner.nextInt();
if (sum > goods.getSum()) {
System.out.println("库存不足 无法购买");
continue;
}
System.out.println("添加成功");
money = sum * goodsService.queryById(pid).getPrice();
BigDecimal price = BigDecimal.valueOf(money);
System.out.println("折算后价格为" + (money * goods.getDiscount() * 0.1));
moneys = money * goods.getDiscount() * 0.1;
GoodsVO goodsVO = new GoodsVO(goods,sum,price);
hashMap.put(i,goodsVO);
i++;
System.out.println("是否继续购买 Y/N");
n = scanner.next();
} while ("Y".equalsIgnoreCase(n));
}将数据库中的表中数据使用循环打印出来



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号