BZOJ 杂题选记(8.17 - 8.23)
P3457 POW-The Flood
当发现合并两个连通块会破坏一些性质时,可以考虑边合并边求出答案,贴一道相似思路以前也没做出来的题 Cave Paintings。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e3 + 5;
int h[N][N], n, m, way[4][2] = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}}, f[N * N], ans;
bool siz[N * N];
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
int getf(int u){ return u == f[u] ? u : f[u] = getf(f[u]); }
void merge(int u, int v){
u = getf(u), v = getf(v);
siz[u] |= siz[v];
f[v] = u;
}
void add(int u){
u = getf(u);
if(siz[u] == 0) siz[u] = 1, ++ans;
}
int cvt(int x, int y){ return m * (x - 1) + y; }
bitset<N * N> bk;
int main(){
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n * m; ++i) f[i] = i;
vector<pii> tmp;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
for(int j = 1; j <= m; ++j){
cin >> h[i][j];
tmp.push_back({i, j});
}
}
sort(tmp.begin(), tmp.end(), [](pii x, pii y){
return abs(h[x.first][x.second]) < abs(h[y.first][y.second]);
});
for(int i = 0; i < tmp.size(); ++i){
int x, y;
int j = i;
if(!bk[i]){
while(j < tmp.size() && abs(h[tmp[i].first][tmp[i].second]) == abs(h[tmp[j].first][tmp[j].second])){
tie(x, y) = tmp[j];
bk[j] = 1;
for(int k = 0; k < 4; ++k){
int xx = x + way[k][0], yy = y + way[k][1];
if(xx >= 1 && xx <= n && yy >= 1 && yy <= m && abs(h[xx][yy]) <= abs(h[x][y]))
merge(cvt(xx, yy), cvt(x, y));
}
++j;
}
}
tie(x, y) = tmp[i];
if(h[x][y] > 0)
add(cvt(x, y));
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
P3458 SKA-Rock Garden
如果我们记 \(a_i = \max(x_i, y_i)\),\(b_i = \min(x_i, y_i)\),那么第一问的答案就是 \(2 \times (\max{a_i} - \min{a_i} + \max{b_i} - \min{b_i})\)。这是因为如果我们让更大的坐标放一边,更小的坐标放一边之后。此时交换其中两个数,有可能让 \(\min{a_i}\) 减小,\(\max{b_i}\) 增大,那么答案要么不变,要么变劣。
还是考虑刚才大小分组的过程,现在虽然求出了一组可行解,但代价显然不一定最优。我们发现,只要最终方案的 \(\max{x_i}\) 等于 \(\max{a_i}\) 和 \(\max{b_i}\) 中的一个,\(\max{y_i}\) 等于另一个。并且 \(\min{x_i}\) 等于 \(\min{a_i}\) 和 \(\min{b_i}\) 中的一个,\(\min{y_i}\) 等于另一个的话,那么第一问的答案才不会变。充分性显然。必要性的话可以发现 \(\max{a_i}\) 一定会被取到, \(\min{b_i}\) 也一定会被取到。如果这俩在同一组,那么另一组的最大值 \(\ge \max{b_i}\),最小值 \(\le \min{a_i}\),就只有取等时第一问答案才不变。如果这俩不在同一组也可以类似地讨论,就不说了。
然后可以发现,我们可以钦定 \(\max x_i\),\(\min x_i\),\(\max y_i\),\(\min y_i\) 的值。然后带回去模拟,如果一对 \((x_i, y_i)\) 不满足条件,就尝试把他们交换并加上代价,如果交换后还不能满足,那就判断无解就行。同时,这样模拟下来,方案也出来了。
复杂度是 \(O(N)\) 的。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
typedef pair<ll, string> tp;
ll a[N], b[N], x[N], y[N], m[N], n, sum;
tp solve(int mxx, int mxy, int mnx, int mny){
int ans0 = sum;
string ans;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
if(x[i] >= mnx && x[i] <= mxx && y[i] >= mny && y[i] <= mxy) ans0 -= m[i], ans.push_back('0');
else{
if(y[i] >= mnx && y[i] <= mxx && x[i] >= mny && x[i] <= mxy) ans.push_back('1');
else return tp{1e9, ""};
}
}
return tp{ans0, ans};
}
signed main(){
cin >> n;
ll mxa = 0, mna = 1e9, mxb = 0, mnb = 1e9;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
cin >> x[i] >> y[i] >> m[i];
sum += m[i];
a[i] = max(x[i], y[i]);
b[i] = min(x[i], y[i]);
mxa = max(mxa, a[i]), mna = min(mna, a[i]), mxb = max(mxb, b[i]), mnb = min(mnb, b[i]);
}
cout << 2 * (mxa - mna + mxb - mnb) << ' ';
tp t = min({solve(mxa, mxb, mna, mnb), solve(mxb, mxa, mna, mnb), solve(mxa, mxb, mnb, mna), solve(mxb, mxa, mnb, mna)});
cout << t.first << '\n' << t.second;
return 0;
}
P3460 TET-Tetris Attack
这道题的贪心策略可能不唯一,但正解的贪心是实现起来最简洁的。
我们思考一下这个贪心的正确性。如果 \(a_i\) 是栈中最早的一对可以被删除的,对于下一对出现的可以被消去的 \(a_j\),如果有一个 \(a_j\) 在两个 \(a_i\) 之间,那么先放消哪个无所谓。否则,就必须先消去 \(a_i\) 了。
模拟的过程是 trival 的。(我什么时候才能做出来这种贪心啊)
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
int n, pos[N], a[N];
struct BIT{
int tr[N];
int lowbit(int x){ return x & (-x); }
void add(int x, int k){
for(int i = x; i <= 2 * n; i += lowbit(i))
tr[i] += k;
}
int qry(int x){
int ret = 0;
for(int i = x; i; i -= lowbit(i))
ret += tr[i];
return ret;
}
}tr;
int main(){
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(0);
cin >> n;
vector<int> ans;
for(int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; ++i){
int x; cin >> x;
tr.add(i, 1);
if(!pos[x]) pos[x] = i;
else{
// cout << tr.qry(pos[x]) << ' ' << tr.qry(i) << '\n';
for(int j = tr.qry(pos[x]); j < tr.qry(i) - 1; ++j)
ans.push_back(j);
tr.add(pos[x], -1), tr.add(i, -1);
}
}
cout << ans.size() << '\n';
for(int i : ans) cout << i << '\n';
return 0;
}
P6564 堆积木KLO
关键在于题意的转化吧,如果转化的不好写出来的就是二维的 dp,实际上也是可做的。注意到转移式:\(f_{i, j} = \max(f_{i - 1, j}, f_{i - 1, j - 1} + [A_i == j])\)。仔细思考一下,从 \(f_{i - 1, j}\) 相当于在平面上查询一个平行四边形的前缀最大值。 这个东西还是好维护的,贴一个题解的图。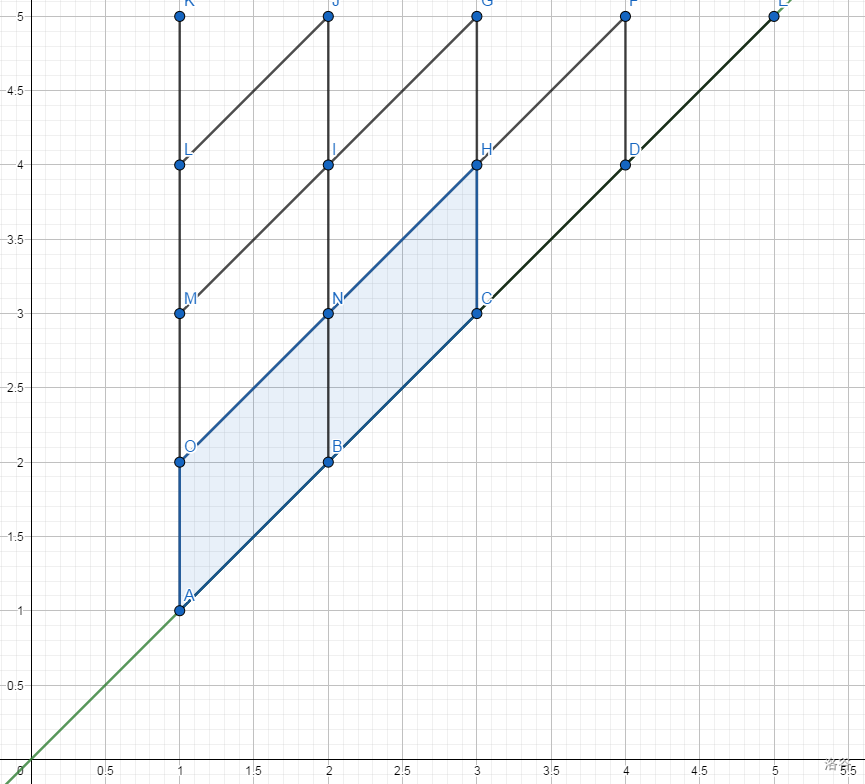
一个更好的方法基于一个重要的转化,先将 \(a_i > i\) 的点排除在外。发现如果 \(a_i = i\),考虑下一个满足 \(a_j = j\) 的 \(j\),一个 \(j\) 能被作为下一个当且仅当 \(j > i \land a_j - a_i \le j - i \land a_j > a_i\)。然后就可以用类似 LIS 的方法做了。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int a[N], n, d[N];
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> a[i];
vector<int> idx(n);
iota(idx.begin(), idx.end(), 1);
sort(idx.begin(), idx.end(), [&](int i, int j){
return (i - a[i] == j - a[j] ? (a[i] < a[j]) : (i - a[i] < j - a[j]));
});
memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof(d));
for(int i = 0; i < idx.size(); ++i){
if(a[idx[i]] > idx[i]) continue;
int x = a[idx[i]];
*lower_bound(d + 1, d + 1 + n, x) = x;
}
int ans = 1;
while(d[ans] != d[0]) ++ans;
cout << ans - 1;
return 0;
}
P3462 ODW-Weights
反悔贪心,注意一下贪心策略,先替换大的肯定更优,注意细节。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int w[N], n, m, nw[N][31], val[N], ans, a[32];
map<int, int> mp;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
cin >> w[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){
int x; cin >> x;
mp[x]++;
}
int cnt = 0;
for(auto it = mp.rbegin(); it != mp.rend(); ++it){
auto [key, num] = *it; ++cnt;
a[cnt] = key;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
int lst = w[i] - val[i];
if(lst >= key){
int k = min(lst / key, num);
num -= k;
ans += k;
nw[i][cnt] += k;
val[i] += k * key;
}
}
if(!num) continue;
for(int j = 1; j < cnt; ++j){
if(!num) break;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
if(nw[i][j] && num * key < a[j]){
nw[i][j]--;
nw[i][cnt] += num;
// cout << num << ' ' << ans << "!!!\n";
ans += num - 1;
val[i] += -a[j] + num * key;
num = 0;
break;
}
int k = a[j] / key, tmp = min(num / k, nw[i][j]);
num -= k * tmp;
nw[i][j] -= tmp;
nw[i][cnt] += tmp * k;
val[i] += -tmp * a[j] + tmp * k * key;
ans += -tmp + tmp * k;
}
}
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
P3468 ROB-Robinson
找到船宽度最大的一行和宽度最大的一列,把他们的交点叫做重心。如果能判断船的重心在 \((i,j)\) 时是否合法,那么就可以 bfs 的求出最小步数了。
暴力枚举重心可能在的 \(N^2\) 个点,单次检验用 bitset 的话也只能做到 \(O(\frac{N^4}{\omega})\)。
稍微想一下,如果对于每一行我们都取重心所在那一列的元素作为这一行的代表元。枚举每一行的这个点,然后再 \(N^2\) 的检验,这样可以做到 \(O(N^3)\)。
然后就不知道怎么做了,看了一下 claris 大佬的题解。因为重心有很好的性质,考虑重心在第 \(i\) 行左右移动,我们只需要知道第 \(j\) 列上下距离最近的障碍物,就可以 \(O(1)\) 求出在不碰到第 \(j\) 列的障碍物的条件下重心可以放置的一个区间。然后把这个区间标记一下,一次都没有被标记的就是可行的。
注意一下重心被移动到边界之后,仍需要一定的代价完全移出边界,这个代价的计算有一定的细节。
可能是比较短的一个代码实现。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef tuple<int, int, int> tpi;
const int N = 2e3 + 5;
char mp[N][N];
bool vis[N][N];
int n, lx = N, ly = N, rx, ry, cnti[N], cntj[N], x, y, l[2][N], r[2][N], way[4][2] = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
int obs[2][N], bk[N][N], cst[N][N];
void chmin(int &a, int b){ a = min(a, b); }
void chmax(int &a, int b){ a = max(a, b); }
int main(){
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(0);
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j){
cin >> mp[i][j];
if(mp[i][j] == 'r'){
cnti[i]++, cntj[j]++;
chmin(lx, i), chmax(rx, i);
chmin(ly, j), chmax(ry, j);
}
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
if(cnti[x] < cnti[i]) x = i;
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j)
if(cntj[y] < cntj[j]) y = j;
for(int i = lx; i <= rx; ++i){
int dx = x - i;
int fl = 0;
if(dx < 0) dx = -dx, fl = 1;
l[fl][dx] = N;
for(int j = ly; j <= ry; ++j){
if(mp[i][j] == 'r')
chmin(l[fl][dx], j), chmax(r[fl][dx], j);
}
l[fl][dx] = y - l[fl][dx];
r[fl][dx] = r[fl][dx] - y;
}
int len[2] = {x - lx, rx - x};
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j){
obs[0][0] = obs[1][n + 1] = N;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
obs[0][i] = (mp[i][j] == 'X' ? 0 : obs[0][i - 1] + 1);
for(int i = n; i >= 1; --i)
obs[1][i] = (mp[i][j] == 'X' ? 0 : obs[1][i + 1] + 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
int from = N, to = 0;
for(int k : {0, 1}){
if(obs[k][i] <= len[k]){
chmin(from, j - r[k][obs[k][i]]);
chmax(to, j + l[k][obs[k][i]]);
}
}
chmax(from, 1), chmin(to, n);
if(from <= to) bk[i][from]++, bk[i][to + 1]--;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j){
bk[i][j] += bk[i][j - 1];
cst[i][j] = 1e9;
if(i == 1 && j == 1)
for(int dx = 1; dx <= len[1]; ++dx)
chmin(cst[i][j], dx + r[1][dx] + 1);
if(i == 1 && j == n)
for(int dx = 1; dx <= len[1]; ++dx)
chmin(cst[i][j], dx + l[1][dx] + 1);
if(i == n && j == 1)
for(int dx = 1; dx <= len[0]; ++dx)
chmin(cst[i][j], dx + r[0][dx] + 1);
if(i == n && j == n)
for(int dx = 1; dx <= len[0]; ++dx)
chmin(cst[i][j], dx + l[0][dx] + 1);
if(i == 1) chmin(cst[i][j], rx - x + 1);
if(i == n) chmin(cst[i][j], x - lx + 1);
if(j == 1) chmin(cst[i][j], ry - y + 1);
if(j == n) chmin(cst[i][j], y - ly + 1);
}
}
queue<tpi> q;
q.push(tpi{x, y, 0});
vis[x][y] = 1;
int ans = 1e9;
while(!q.empty()){
int x, y, dist;
tie(x, y, dist) = q.front();
q.pop();
chmin(ans, dist + cst[x][y]);
for(int k = 0; k < 4; ++k){
int xx = x + way[k][0], yy = y + way[k][1];
if(xx >= 1 && xx <= n && yy >= 1 && yy <= n && !vis[xx][yy] && !bk[xx][yy]){
vis[xx][yy] = 1;
q.push(tpi{xx, yy, dist + 1});
}
}
}
if(ans == 1e9) cout << "NIE";
else cout << ans;
return 0;
}
P3479 GAS-Fire Extinguishers
可能见过可能没见过的一个贪心。
策略是:
- 能不放就不放,万不得已时才放一个,这样我们放的都是相对深度比较浅的那些祖先点。
- 我们总让灭火器去覆盖离他最远的点。
实际上这两者的最优性理解起来是很相似的。有点像找圆心(
实现的话,用到了类似这道题的思路 Delegation P。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
vector<int> e[N];
int n, s, k, f[N][25], g[N][25], ans;
void dfs(int u, int fa){
f[u][0] = 1;
for(int v : e[u]){
if(v != fa){
dfs(v, u);
for(int j = 0; j <= k - 1; ++j){
f[u][j + 1] += f[v][j];
g[u][j + 1] += g[v][j];
}
}
}
int tmp = (f[u][k] + s - 1) / s;
g[u][0] = tmp * s - f[u][k];
f[u][k] = 0;
ans += tmp;
for(int i = k; i >= 0; --i){
int j = k - i, d = min(f[u][i], g[u][j]);
f[u][i] -= d;
g[u][j] -= d;
}
for(int i = 0; i <= k - 1; ++i){
int j = k - 1 - i, d = min(f[u][i], g[u][j]);
f[u][i] -= d;
g[u][j] -= d;
}
}
signed main(){
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(0);
cin >> n >> s >> k;
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i){
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
e[u].push_back(v);
e[v].push_back(u);
}
dfs(1, 0);
for(int i = 0; i <= k; ++i){
for(int j = 0; j <= k - i; ++j){
int d = min(f[1][i], g[1][j]);
f[1][i] -= d, g[1][j] -= d;
}
}
int tot = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= k; ++i) tot += f[1][i];
cout << ans + (tot + s - 1) / s;
return 0;
}
P3481 PRZ-Algorithm Speedup
考虑 \(x\), \(y\) 中的哪些子串会被遍历到,这个数量是 \(O(NV)\) 的。然后就貌似就可以直接记忆化搜索了,但由于单次求前缀后缀貌似做不到什么好的方法,复杂度玄学,能过。
实际上可以把记忆化搜索换成 dp,反过来考虑一个 \(|W(x)|\) 更小的有没有可能被一个 \(|W(x)|\) 更大的作为前缀后缀搜索到,然后再用 JCY_ 大佬的方法把这个东西 hash 一下,就可以过了。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5, V = 1e2 + 5;
int n[2], a[2][N], dpl[2][2][N], dpr[2][2][N], cnt[V], buc[N * 2], k, fl;
typedef tuple<int, int, int, int*, int*> tpi;
vector<tpi> rge;
void csort(int p){
auto f = [](tpi p, int x){
if(x == 0) return get<0>(p);
else if(x == 1) return get<1>(p);
return get<2>(p);
};
memset(buc, 0, sizeof(buc));
vector<tpi> ret(rge.size());
for(tpi t : rge) buc[f(t, p)]++;
for(int i = 1; i <= 100; ++i) buc[i] += buc[i - 1];
for(int i = rge.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) ret[--buc[f(rge[i], p)]] = rge[i];
rge = ret;
}
void solve(){
bitset<V> bs[2];
cin >> n[0] >> n[1];
for(int t : {0, 1}){
for(int i = 1; i <= n[t]; ++i)
cin >> a[t][i], bs[t][a[t][i]] = 1;
}
if(bs[0] != bs[1]) return cout << 0 << '\n', void();
k = bs[0].count();
if(k == 1) return cout << 1 << '\n', void();
fl = 0;
memset(dpl, 0, sizeof(dpl));
memset(dpr, 0, sizeof(dpr));
for(int t : {0, 1}){
for(int i = 1; i <= n[t]; ++i){
dpl[fl][t][i] = dpr[fl][t][i] = a[t][i];
}
}
for(int i = 2; i <= k; ++i){
fl ^= 1;
memset(dpl[fl], 0, sizeof(dpl[fl]));
memset(dpr[fl], 0, sizeof(dpr[fl]));
rge.clear();
for(int idx : {0, 1}){
memset(cnt, 0, sizeof(cnt));
int l = 1, w = 0;
for(int r = 1; r <= n[idx]; ++r){
w += !(cnt[a[idx][r]]++);
while(w > i) w -= !(--cnt[a[idx][l]]), ++l;
if(w == i && (r == n[idx] || cnt[a[idx][r + 1]] == 0)){
int tmpl = l;
while(w == i) w -= !(--cnt[a[idx][tmpl]]), ++tmpl;
rge.emplace_back(dpl[fl ^ 1][idx][l], dpr[fl ^ 1][idx][r], a[idx][tmpl - 1], &dpl[fl][idx][l], &dpr[fl][idx][r]);
l = tmpl;
}
}
}
csort(2), csort(1), csort(0);
int tot = 0;
int *x, *y;
tie(ignore, ignore, ignore, x, y) = rge[0];
*x = *y = ++tot;
for(int i = 1; i < rge.size(); ++i){
tie(ignore, ignore, ignore, x, y) = rge[i];
auto eq = [](tpi a, tpi b){
return get<0>(a) == get<0>(b) && get<1>(a) == get<1>(b) && get<2>(a) == get<2>(b);
};
if(!eq(rge[i], rge[i - 1])) ++tot;
*x = *y = tot;
}
}
cout << (dpl[fl][0][1] == dpl[fl][1][1]) << '\n';
}
int main(){
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(0);
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T--) solve();
return 0;
}
P3482 SLO-Elephants
可以把原题看成处理多个环的情况,考虑每个环。发现在环上交换时,必须考虑在一处类似断环为链的操作。那么这个断点可以选择环上最小的,也可以选择全局最小的,各自的代价不同,取较小的加到答案就行。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e6 + 5, inf = 1e9;
int p[N], len, n, a[N], b[N];
bitset<N> vis;
ll w[N], sum, minx, totmin = inf;
void chmin(ll &a, ll b){ a = min(a, b); }
void dfs(int u){
if(vis[u]) return;
vis[u] = 1, ++len, sum += w[u], chmin(minx, w[u]);
dfs(p[u]);
}
int main(){
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(0);
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> w[i], chmin(totmin, w[i]);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
cin >> b[i];
p[a[i]] = b[i];
}
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
if(!vis[i] && p[i] != i){
len = 0, sum = 0, minx = inf;
dfs(i);
// cout << len << ' ' << sum << ' ' << minx << '\n';
ans += min(sum + (len - 2) * minx, sum + minx + (len + 1) * totmin);
}
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
P3483 STR-Fire Brigade
又一个暴力分讨题,类似 DRZ-Trees。分 9 种情况把绝对值去掉,这题不太一样的是最后有一种是三维偏序。本题卡常,注意常数。
一个 cdq 的实现,迄今为止写过最史的东西。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define Tp template<typename T>
#define Ts template<typename T,typename... _T>
char buf[1<<20],*p1=buf,*p2=buf;
#define getchar() (p1==p2&&(p2=buf+fread(p1=buf,1,1<<20,stdin),p1==p2)?EOF:*p1++)
Tp inline void read(T& x){
x=0;char c=getchar();bool f=0;
for(;!isdigit(c);c=getchar())if(c=='-')f=1;
for(;isdigit(c);c=getchar())x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+(c^48);
f&&(x=-x);
}
Ts inline void read(T& x,_T&... y){read(x),read(y...);}
template<typename T>void qw(T x)
{
if(x<0)x=-x,putchar('-');
if(x/10)qw(x/10);
putchar(x%10+48);
}
using ll = long long;
using namespace std;
const ll N = 6e5 + 5;
const ll M = N;
typedef struct Point2 {
ll first, second;
} Pair;
struct Point {
ll x, id, fl, y, v;
};
ll x[N], y[N], n, p, ans[N][3], xp[2][N], yp[2][N], a[N], b[N], c[N], d[N], val[N], typ[N];
bitset<N> fz;
Point rg[2][N];
ll _id[N];
struct BIT{
ll tr[N], siz;
ll lowbit(ll x){return x & (-x);}
void init(ll x){ memset(tr, 0, sizeof(tr)); siz = x; }
void add(ll x, ll k){
for(ll i = x; i <= siz; i += lowbit(i)) tr[i] +=k;
}
ll qry(ll x){
if(x <= 0) return 0;
ll ret = 0;
for(ll i = x; i; i -= lowbit(i)) ret += tr[i];
return ret;
}
ll qry(ll l, ll r){
if(l > r) return 0;
return qry(r) - qry(l - 1);
}
}tr;
ll tmp_arr[M], tmp_cnt;
Pair pair_arr[N];
ll pair_cnt;
void solve1(){
tmp_cnt = 0;
pair_cnt = 0;
for(ll i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = y[i];
pair_arr[pair_cnt].first = x[i];
pair_arr[pair_cnt].second = y[i];
pair_cnt++;
}
for(ll i = 1; i <= p; ++i) tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = c[i] - 1;
sort(pair_arr, pair_arr + pair_cnt, [](const Pair& a, const Pair& b) {
return a.first < b.first;
});
sort(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt);
tmp_cnt = unique(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt) - tmp_arr;
auto f = [](ll i){
ll H = xp[0][i] + yp[0][i] - xp[1][i] - yp[1][i];
if(H < 0) return 0;
else if(H == 0) return 1;
return 2;
};
auto g = [&](ll y){
return lower_bound(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt, y) - tmp_arr + 1;
};
tr.init(tmp_cnt);
ll it = 0;
for(ll j = 1; j <= p; ++j){
ll i = _id[j];
while(it < pair_cnt && pair_arr[it].first < a[i]) {
tr.add(g(pair_arr[it].second), 1);
it++;
}
ans[i][f(i)] += tr.qry(g(c[i] - 1));
}
}
void solve2(){
tmp_cnt = 0;
for(ll i = 1; i <= n; ++i) tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = 2 * y[i];
for(ll i = 1; i <= p; ++i){
if(yp[0][i] <= yp[1][i]){
typ[i] = 0;
val[i] = -xp[0][i] + yp[1][i] + yp[0][i] + xp[1][i];
}
else{
typ[i] = 1;
val[i] = -xp[1][i] + yp[1][i] + yp[0][i] + xp[0][i];
}
tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = val[i];
tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = 2 * c[i];
tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = 2 * d[i];
}
sort(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt);
tmp_cnt = unique(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt) - tmp_arr;
auto g = [&](ll y){
return ll(lower_bound(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt, y) - tmp_arr + 1);
};
tr.init(tmp_cnt);
ll it = 0;
for(ll j = 1; j <= p; ++j){
ll i = _id[j];
while(it < pair_cnt && pair_arr[it].first < a[i]) {
tr.add(g(2 * pair_arr[it].second), 1);
it++;
}
ll l = g(2 * c[i]), r = g(2 * d[i]);
ll tmpvl = g(val[i]);
if(!typ[i]){
ans[i][0] += tr.qry(l, min(tmpvl - 1, r));
ans[i][1] += tr.qry(max(l, tmpvl), min(tmpvl, r));
ans[i][2] += tr.qry(max(l, tmpvl + 1), r);
}
else{
ans[i][0] += tr.qry(max(l, tmpvl + 1), r);
ans[i][1] += tr.qry(max(l, tmpvl), min(tmpvl, r));
ans[i][2] += tr.qry(l, min(tmpvl - 1, r));
}
}
}
void solve3(){
tmp_cnt = 0;
for(ll i = 1; i <= n; ++i) tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = y[i];
for(ll i = 1; i <= p; ++i) tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = d[i] + 1;
sort(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt);
tmp_cnt = unique(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt) - tmp_arr;
auto f = [](ll i){
ll H = xp[0][i] - yp[0][i] - xp[1][i] + yp[1][i];
if(H < 0) return 0;
else if(H == 0) return 1;
return 2;
};
auto g = [&](ll y){
return lower_bound(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt, y) - tmp_arr + 1;
};
tr.init(tmp_cnt);
ll it = 0;
for(ll j = 1; j <= p; ++j){
ll i = _id[j];
while(it < pair_cnt && pair_arr[it].first < a[i]) {
tr.add(g(pair_arr[it].second), 1);
it++;
}
ans[i][f(i)] += tr.qry(g(d[i] + 1), tr.siz);
}
}
void solve4(){
tmp_cnt = 0;
pair_cnt = 0;
for(ll i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = 2 * x[i];
pair_arr[pair_cnt].first = y[i];
pair_arr[pair_cnt].second = 2 * x[i];
pair_cnt++;
}
for(ll i = 1; i <= p; ++i){
val[i] = yp[1][i] - yp[0][i] + xp[1][i] + xp[0][i];
tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = val[i];
tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = 2 * a[i];
tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = 2 * b[i];
}
sort(pair_arr, pair_arr + pair_cnt, [](const Pair& a, const Pair& b) {
return a.first < b.first;
});
sort(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt);
tmp_cnt = unique(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt) - tmp_arr;
auto g = [&](ll x){
return ll(lower_bound(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt, x) - tmp_arr + 1);
};
tr.init(tmp_cnt);
ll it = 0;
for(ll j = 1; j <= p; ++j){
ll i = _id[j];
while(it < pair_cnt && pair_arr[it].first < c[i]) {
tr.add(g(pair_arr[it].second), 1);
it++;
}
ll l = g(2 * a[i]), r = g(2 * b[i]);
ll tmpvl = g(val[i]);
ans[i][0] += tr.qry(l, min(tmpvl - 1, r));
ans[i][1] += tr.qry(max(l, tmpvl), min(r, tmpvl));
ans[i][2] += tr.qry(max(l, tmpvl + 1), r);
}
}
ll tot[2] = {0};
void cdq(ll l, ll r, ll idx){
if(l == r) return;
ll mid = (l + r) >> 1;
cdq(l, mid, idx), cdq(mid + 1, r, idx);
ll i = l;
for(ll j = mid + 1; j <= r; ++j){
ll id = rg[idx][j].id;
ll fl = rg[idx][j].fl;
ll vl = rg[idx][j].v;
if(id == 0) continue;
while(i <= mid && rg[idx][i].y <= rg[idx][j].y){
ll type = rg[idx][i].fl;
ll v = rg[idx][i].v;
i++;
if(type != 0) continue;
tr.add(v, 1);
}
ans[id][0] += tr.qry(vl - 1) * fl;
ans[id][1] += tr.qry(vl, vl) * fl;
ans[id][2] += tr.qry(vl + 1, tr.siz) * fl;
}
for(ll pos = l; pos < i; ++pos){
ll type = rg[idx][pos].fl;
ll v = rg[idx][pos].v;
if(type != 0) continue;
tr.add(v, -1);
}
if(l == 1 && r == tot[idx]) return;
sort(rg[idx] + l, rg[idx] + r + 1, [](Point a, Point b) {
return a.y < b.y;
});
}
ll tmp5_0[M], tmp5_0_cnt;
ll tmp5_1[M], tmp5_1_cnt;
void solve5(){
tmp5_0_cnt = 0;
tmp5_1_cnt = 0;
for(ll i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
tmp5_0[tmp5_0_cnt++] = 2 * (x[i] + y[i]);
tmp5_1[tmp5_1_cnt++] = 2 * (x[i] - y[i]);
}
for(ll i = 1; i <= p; ++i){
if(yp[0][i] <= yp[1][i]) typ[i] = 0, val[i] = xp[0][i] + xp[1][i] + yp[0][i] + yp[1][i];
else typ[i] = 1, val[i] = xp[0][i] + xp[1][i] - yp[0][i] - yp[1][i];
if(typ[i] == 0) tmp5_0[tmp5_0_cnt++] = val[i];
else tmp5_1[tmp5_1_cnt++] = val[i];
}
for(ll t : {0, 1}){
if(t == 0) {
sort(tmp5_0, tmp5_0 + tmp5_0_cnt);
tmp5_0_cnt = unique(tmp5_0, tmp5_0 + tmp5_0_cnt) - tmp5_0;
} else {
sort(tmp5_1, tmp5_1 + tmp5_1_cnt);
tmp5_1_cnt = unique(tmp5_1, tmp5_1 + tmp5_1_cnt) - tmp5_1;
}
}
for(ll i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
ll v = lower_bound(tmp5_0, tmp5_0 + tmp5_0_cnt, 2 * (x[i] + y[i])) - tmp5_0 + 1;
rg[0][++tot[0]] = Point{x[i], 0, 0, y[i], v};
v = lower_bound(tmp5_1, tmp5_1 + tmp5_1_cnt, 2 * (x[i] - y[i])) - tmp5_1 + 1;
rg[1][++tot[1]] = Point{x[i], 0, 0, y[i], v};
}
for(ll i = 1; i <= p; ++i){
ll fl = typ[i];
ll v;
if(fl == 0) {
v = lower_bound(tmp5_0, tmp5_0 + tmp5_0_cnt, val[i]) - tmp5_0 + 1;
} else {
v = lower_bound(tmp5_1, tmp5_1 + tmp5_1_cnt, val[i]) - tmp5_1 + 1;
}
rg[fl][++tot[fl]] = Point{a[i] - 1, i, 1, c[i] - 1, v};
rg[fl][++tot[fl]] = Point{a[i] - 1, i, -1, d[i], v};
rg[fl][++tot[fl]] = Point{b[i], i, -1, c[i] - 1, v};
rg[fl][++tot[fl]] = Point{b[i], i, 1, d[i], v};
}
for(ll t : {0, 1}){
sort(rg[t] + 1, rg[t] + 1 + tot[t], [](Point a, Point b) {
return a.x == b.x ? a.id < b.id : a.x < b.x;
});
tr.init(tot[t]);
cdq(1, tot[t], t);
}
}
void solve6(){
tmp_cnt = 0;
pair_cnt = 0;
for(ll i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = 2 * x[i];
pair_arr[pair_cnt].first = y[i];
pair_arr[pair_cnt].second = 2 * x[i];
pair_cnt++;
}
for(ll i = 1; i <= p; ++i){
val[i] = yp[0][i] - yp[1][i] + xp[1][i] + xp[0][i];
tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = val[i];
tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = 2 * a[i];
tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = 2 * b[i];
}
sort(pair_arr, pair_arr + pair_cnt, [](const Pair& a, const Pair& b) {
return a.first > b.first;
});
sort(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt);
tmp_cnt = unique(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt) - tmp_arr;
auto g = [&](ll x){
return ll(lower_bound(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt, x) - tmp_arr + 1);
};
tr.init(tmp_cnt);
ll it = 0;
for(ll j = 1; j <= p; ++j){
ll i = _id[j];
while(it < pair_cnt && pair_arr[it].first > d[i]) {
tr.add(g(pair_arr[it].second), 1);
it++;
}
ll l = g(2 * a[i]), r = g(2 * b[i]);
ll tmpvl = g(val[i]);
ans[i][0] += tr.qry(l, min(tmpvl - 1, r));
ans[i][1] += tr.qry(max(l, tmpvl), min(r, tmpvl));
ans[i][2] += tr.qry(max(l, tmpvl + 1), r);
}
}
void solve7(){
tmp_cnt = 0;
pair_cnt = 0;
for(ll i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = y[i];
pair_arr[pair_cnt].first = x[i];
pair_arr[pair_cnt].second = y[i];
pair_cnt++;
}
for(ll i = 1; i <= p; ++i) tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = c[i] - 1;
sort(pair_arr, pair_arr + pair_cnt, [](const Pair& a, const Pair& b) {
return a.first > b.first;
});
sort(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt);
tmp_cnt = unique(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt) - tmp_arr;
auto g = [&](ll y){
return lower_bound(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt, y) - tmp_arr + 1;
};
auto f = [](ll i){
ll H = xp[1][i] + yp[0][i] - xp[0][i] - yp[1][i];
if(H < 0) return 0;
else if(H == 0) return 1;
return 2;
};
tr.init(tmp_cnt);
ll it = 0;
for(ll j = 1; j <= p; ++j){
ll i = _id[j];
while(it < pair_cnt && pair_arr[it].first > b[i]) {
tr.add(g(pair_arr[it].second), 1);
it++;
}
ans[i][f(i)] += tr.qry(g(c[i] - 1));
}
}
void solve8(){
tmp_cnt = 0;
for(ll i = 1; i <= n; ++i) tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = 2 * y[i];
for(ll i = 1; i <= p; ++i){
tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = 2 * c[i];
tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = 2 * d[i];
if(yp[0][i] <= yp[1][i]){
typ[i] = 0;
val[i] = yp[0][i] + yp[1][i] - xp[1][i] + xp[0][i];
}
else{
typ[i] = 1;
val[i] = xp[1][i] - xp[0][i] + yp[1][i] + yp[0][i];
}
tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = val[i];
}
sort(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt);
tmp_cnt = unique(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt) - tmp_arr;
auto g = [&](ll y){
return ll(lower_bound(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt, y) - tmp_arr + 1);
};
tr.init(tmp_cnt);
ll it = 0;
for(ll j = 1; j <= p; ++j){
ll i = _id[j];
while(it < pair_cnt && pair_arr[it].first > b[i]) {
tr.add(g(2 * pair_arr[it].second), 1);
it++;
}
ll l = g(2 * c[i]), r = g(2 * d[i]);
ll tmpvl = g(val[i]);
if(!typ[i]){
ans[i][0] += tr.qry(l, min(r, tmpvl - 1));
ans[i][1] += tr.qry(max(l, tmpvl), min(r, tmpvl));
ans[i][2] += tr.qry(max(l, tmpvl + 1), r);
}
else{
ans[i][0] += tr.qry(max(tmpvl + 1, l), r);
ans[i][1] += tr.qry(max(tmpvl, l), min(tmpvl, r));
ans[i][2] += tr.qry(l, min(tmpvl - 1, r));
}
}
}
void solve9(){
tmp_cnt = 0;
for(ll i = 1; i <= n; ++i) tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = y[i];
for(ll i = 1; i <= p; ++i) tmp_arr[tmp_cnt++] = d[i] + 1;
sort(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt);
tmp_cnt = unique(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt) - tmp_arr;
auto g = [&](ll y){
return lower_bound(tmp_arr, tmp_arr + tmp_cnt, y) - tmp_arr + 1;
};
auto f = [](ll i){
ll H = xp[1][i] + yp[1][i] - xp[0][i] - yp[0][i];
if(H < 0) return 0;
else if(H == 0) return 1;
return 2;
};
tr.init(tmp_cnt);
ll it = 0;
for(ll j = 1; j <= p; ++j){
ll i = _id[j];
while(it < pair_cnt && pair_arr[it].first > b[i]) {
tr.add(g(pair_arr[it].second), 1);
it++;
}
ans[i][f(i)] += tr.qry(g(d[i] + 1), tr.siz);
}
}
signed main(){
ll t;
read(t, t, n, p);
for(ll i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
read(x[i], y[i]);
}
for(ll i = 1; i <= p; ++i){
for(ll t : {0, 1})
read(xp[t][i], yp[t][i]);
if(xp[0][i] > xp[1][i]){
fz[i] = 1;
swap(xp[0][i], xp[1][i]);
swap(yp[0][i], yp[1][i]);
}
a[i] = min(xp[0][i], xp[1][i]);
b[i] = max(xp[0][i], xp[1][i]);
c[i] = min(yp[0][i], yp[1][i]);
d[i] = max(yp[0][i], yp[1][i]);
_id[i] = i;
}
sort(_id + 1, _id + 1 + p, [](ll x, ll y){
return a[x] < a[y];
});
solve1();
solve2();
solve3();
sort(_id + 1, _id + 1 + p, [](ll x, ll y){
return c[x] < c[y];
});
solve4();
solve5();
sort(_id + 1, _id + 1 + p, [](ll x, ll y){
return d[x] > d[y];
});
solve6();
sort(_id + 1, _id + 1 + p, [](ll x, ll y){
return b[x] > b[y];
});
solve7();
solve8();
solve9();
for(ll i = 1; i <= p; ++i){
if(fz[i]) qw(ans[i][2]), putchar(' '), qw(ans[i][0]), putchar(' ');
else qw(ans[i][0]), putchar(' '), qw(ans[i][2]), putchar(' ');
qw(ans[i][1]), putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号