【力扣】组合总和
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum
给定一个无重复元素的数组 $candidates$ 和一个目标数 $target$ ,找出 $candidates$ 中所有可以使数字和为 $target$ 的组合。
$candidates$ 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
说明:
所有数字(包括 target)都是正整数。
解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
所求解集为:
[
[7],
[2,2,3]
]
示例 2:
输入:candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8,
所求解集为:
[
[2,2,2,2],
[2,3,3],
[3,5]
]
作者:liweiwei1419
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/solution/hui-su-suan-fa-jian-zhi-python-dai-ma-java-dai-m-2/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
思路分析:根据示例 1:输入: candidates = [2, 3, 6, 7],target = 7。
候选数组里有 2,如果找到了组合总和为 7 - 2 = 5 的所有组合,再在之前加上 2 ,就是 7 的所有组合;
同理考虑 3,如果找到了组合总和为 7 - 3 = 4 的所有组合,再在之前加上 3 ,就是 7 的所有组合,依次这样找下去。
这一类问题都需要先画出树形图,然后编码实现
编码通过 深度优先遍历 实现,使用一个列表,在 深度优先遍历 变化的过程中,遍历所有可能的列表并判断当前列表是否符合题目的要求,成为「回溯算法」(个人理解,非形式化定义)。
以下给出的是一种树形图的画法。对于组合来说,还可以根据一个数选和不选画树形图,请参考 官方题解 或者 @elegant-pike 的 评论。
以输入:candidates = [2, 3, 6, 7], target = 7 为例:
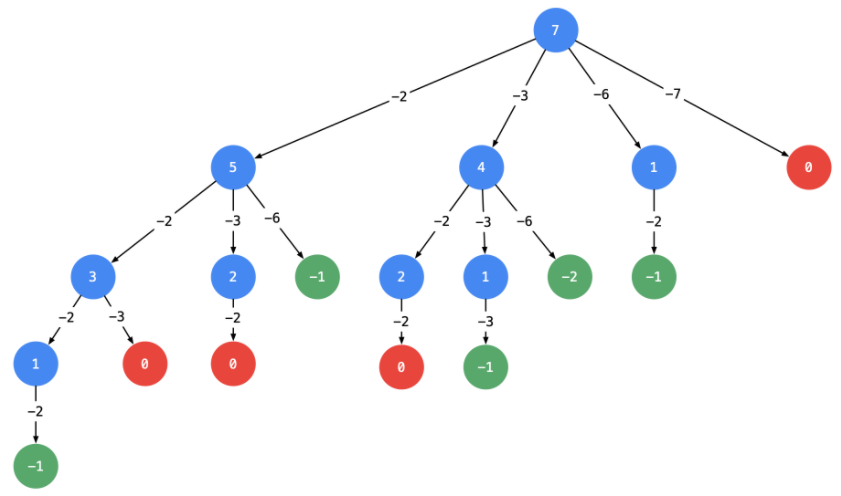
说明:
以 target = 7 为 根结点 ,创建一个分支的时 做减法 ;
每一个箭头表示:从父亲结点的数值减去边上的数值,得到孩子结点的数值。边的值就是题目中给出的 candidate 数组的每个元素的值;
减到 0 或者负数的时候停止,即:结点 0 和负数结点成为叶子结点;
所有从根结点到结点 0 的路径(只能从上往下,没有回路)就是题目要找的一个结果。
这棵树有 4个叶子结点的值 0,对应的路径列表是 [[2, 2, 3], [2, 3, 2], [3, 2, 2], [7]],而示例中给出的输出只有 [[7], [2, 2, 3]]。即:题目中要求每一个符合要 求的解是 不计算顺序 的。下面我们分析为什么会产生重复。
产生重复的原因是:在每一个结点,做减法,展开分支的时候,由于题目中说 每一个元素可以重复使用,我们考虑了 所有的 候选数,因此出现了重复的列表。
一种简单的去重方案是借助哈希表的天然去重的功能,但实际操作一下,就会发现并没有那么容易。
可不可以在搜索的时候就去重呢?答案是可以的。遇到这一类相同元素不计算顺序的问题,我们在搜索的时候就需要 按某种顺序搜索。具体的做法是:每一次搜索的时候设置 下一轮搜索的起点 begin,请看下图。
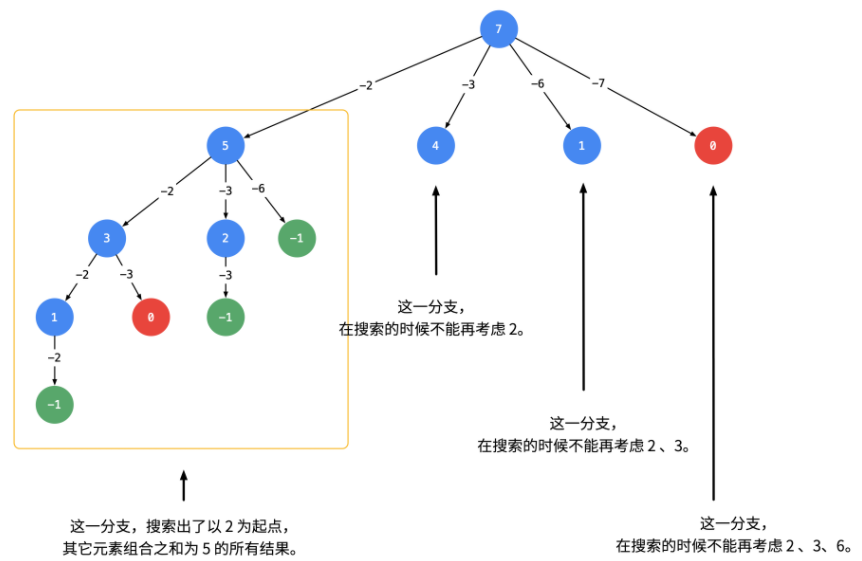
即:从每一层的第 2 个结点开始,都不能再搜索产生同一层结点已经使用过的 candidate 里的元素。
1 from typing import List 2 3 4 class Solution: 5 def combinationSum(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]: 6 7 def dfs(candidates, begin, size, path, res, target): 8 if target < 0: 9 return 10 if target == 0: 11 res.append(path) 12 return 13 14 for index in range(begin, size): 15 dfs(candidates, index, size, path + [candidates[index]], res, target - candidates[index]) 16 17 size = len(candidates) 18 if size == 0: 19 return [] 20 path = [] 21 res = [] 22 dfs(candidates, 0, size, path, res, target) 23 return res 24 25 作者:liweiwei1419 26 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/solution/hui-su-suan-fa-jian-zhi-python-dai-ma-java-dai-m-2/ 27 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
剪枝提速
根据上面画树形图的经验,如果 target 减去一个数得到负数,那么减去一个更大的树依然是负数,同样搜索不到结果。基于这个想法,我们可以对输入数组进行排序,添加相关逻辑达到进一步剪枝的目的;
排序是为了提高搜索速度,对于解决这个问题来说非必要。但是搜索问题一般复杂度较高,能剪枝就尽量剪枝。实际工作中如果遇到两种方案拿捏不准的情况,都试一下。
1 from typing import List 2 3 4 class Solution: 5 def combinationSum(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]: 6 7 def dfs(candidates, begin, size, path, res, target): 8 if target == 0: 9 res.append(path) 10 return 11 12 for index in range(begin, size): 13 residue = target - candidates[index] 14 if residue < 0: 15 break 16 17 dfs(candidates, index, size, path + [candidates[index]], res, residue) 18 19 size = len(candidates) 20 if size == 0: 21 return [] 22 candidates.sort() 23 path = [] 24 res = [] 25 dfs(candidates, 0, size, path, res, target) 26 return res 27 28 作者:liweiwei1419 29 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/solution/hui-su-suan-fa-jian-zhi-python-dai-ma-java-dai-m-2/ 30 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
官方题解
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/solution/zu-he-zong-he-by-leetcode-solution/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
方法一:搜索回溯
思路与算法
对于这类寻找所有可行解的题,我们都可以尝试用「搜索回溯」的方法来解决。
回到本题,我们定义递归函数 $dfs(target, combine, idx)$ 表示当前在 $candidates$ 数组的第 $idx$ 位,还剩 $target$ 要组合,已经组合的列表为 $combine$。递归的终止条件为 $target <= 0$ 或者 $candidates$ 数组被全部用完。那么在当前的函数中,每次我们可以选择跳过不用第 $idx$ 个数,即执行 $dfs(target, combine, idx + 1)$。也可以选择使用第 $idx$个数,即执行 $dfs(target - candidates[idx], combine, idx)$,注意到每个数字可以被无限制重复选取,因此搜索的下标仍为 $idx$。
更形象化地说,如果我们将整个搜索过程用一个树来表达,即如下图呈现,每次的搜索都会延伸出两个分叉,直到递归的终止条件,这样我们就能不重复且不遗漏地找到所有可行解:
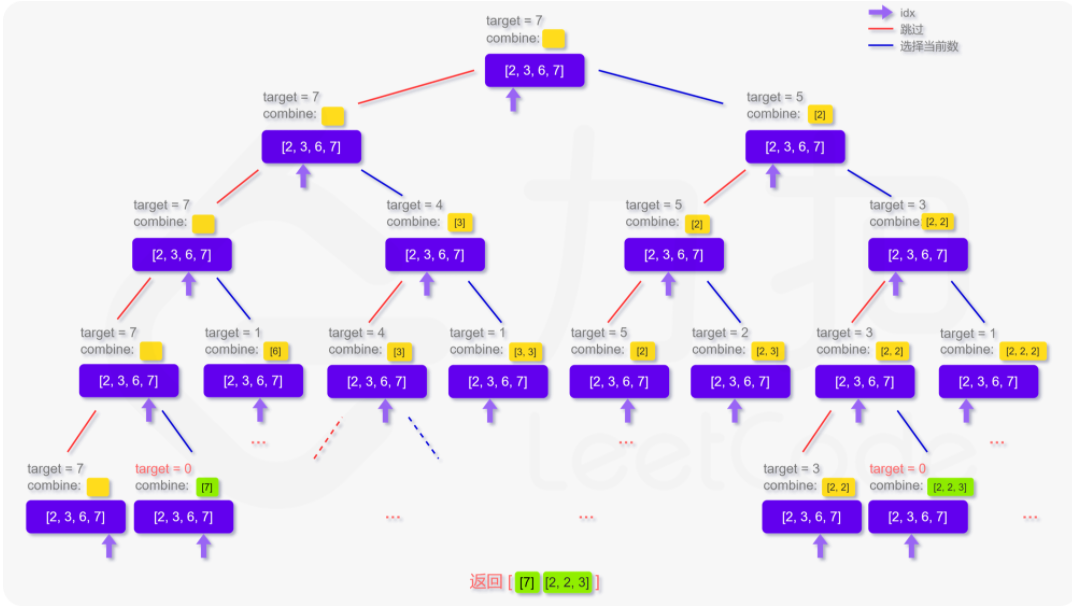
1 class Solution: 2 def combinationSum(self, candidates, target): 3 ans = [] 4 temp = [] 5 def recursion(idx, res): 6 if idx >= len(candidates) or res >= target: 7 if res == target: 8 ans.append(temp[:]) 9 return 10 temp.append(candidates[idx]) 11 recursion(idx, res + candidates[idx]) 12 temp.pop() 13 recursion(idx + 1, res) 14 recursion(0, 0) 15 return ans



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号