比赛链接:
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/33190
A.Don't Starve
题意:
地图上有 \(n\) 个点,每个点有食物,从原点出发,每次走的距离要严格小于之前走的距离,离开当前点之后,当前点的食物会刷新,问最多能吃到多少食物。
思路:
首先先跑出各点之间的距离,然后根据边长从大到小排序。
定义 \(f[i]\) 表示以第 \(i\) 个点结束时能吃到的最多的食物数量。
当前的状态是从上次走的状态转移过来的,每次长度相同的边一起更新,采用滚动数组优化空间。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
const int INF = 1e9 + 10;
struct edge{
LL u, v, d;
};
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
LL n;
cin >> n;
vector <LL> x(n + 1), y(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
cin >> x[i] >> y[i];
vector <edge> e;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ){
if (i == j) continue;
e.push_back({i, j, (x[i] - x[j]) * (x[i] - x[j]) + (y[i] - y[j]) * (y[i] - y[j])});
}
sort(e.begin(), e.end(), [](edge a, edge b){
return a.d > b.d;
});
vector <LL> f(n + 1, -INF), g(n + 1);
f[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0, j; i < e.size(); i = j ){
j = i;
while(j < e.size() && e[i].d == e[j].d){
g[e[j].v] = -INF;
j ++ ;
}
for (int k = i; k < j; k ++ )
g[e[k].v] = max(g[e[k].v], f[e[k].u] + 1);
for (int k = i; k < j; k ++ )
f[e[k].v] = max(f[e[k].v], g[e[k].v]);
}
cout << *max_element(f.begin(), f.end()) << "\n";
return 0;
}
B.Watches
题意:
有 \(n\) 块手表,第 \(i\) 块手表的价格为 \(a_i\),如果选择买 \(k\) 个,那么第 \(i\) 块手表的价格会变成 \(a_i + i * k\),现在有 \(m\) 的钱,问最多能买多少表。
思路:
因为手表的价格排序后是单调的,所以考虑二分去做。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
LL n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector <LL> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
cin >> a[i];
auto check = [&](LL x){
vector <LL> b(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
b[i] = a[i] + i * x;
sort(b.begin(), b.end());
LL sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= x; i ++ )
sum += b[i];
return sum <= m;
};
LL L = 0, R = n;
while(L < R){
LL mid = (L + R + 1) >> 1;
if (check(mid)){
L = mid;
}
else{
R = mid - 1;
}
}
cout << L << "\n";
return 0;
}
C.Bit Transmission
题目:
给定一个长为 \(n\) 的二进制字符串,进行 \(3 * n\) 次询问,每次询问位置 \(p\),返回一个值,若为 "YES",说明这位上为 1,否则为 0,询问中最多有一个回答是错误的,问能否根据询问判断二进制字符串是什么。
思路:
先统计每一位上 "YES" 和 "NO" 出现的次数。
如果出现次数相同(包括未出现的,即两个都是 0),那么肯定无法判断。
如果两个的出现次数都大于 1,因为错误最多只有一个,所以也不可能。
如果错误的地方有多个,也不可能。
如果没有错,但是某一位上,只有一个 "YES" 或 "NO",那么这一位有可能是错的,无法判断。
除去上述情况,其他都能准确判断二进制字符串。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
LL n;
cin >> n;
vector cnt(n, vector<LL>(2, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < 3 * n; i ++ ){
LL p;
string s;
cin >> p >> s;
s == "YES" ? cnt[p][0] ++ : cnt[p][1] ++ ;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ){
if (cnt[i][0] == cnt[i][1]){
cout << "-1\n";
return 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ){
if (cnt[i][0] > 1 && cnt[i][1] > 1){
cout << "-1\n";
return 0;
}
}
LL num = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ){
if (cnt[i][0] > 0 && cnt[i][1] > 0){
num ++ ;
}
if (num > 1){
cout << "-1\n";
return 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ){
if (!num && cnt[i][0] + cnt[i][1] == 1){
cout << "-1\n";
return 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ){
cout << (cnt[i][0] > cnt[i][1] ? 1 : 0);
}
return 0;
}
D.Birds in the tree
题意:
给定一棵有 \(n\) 个节点的树,每个节点的权值为 0 或 1,求有多少个联通子图的节点权值相同。
思路:
树形 \(dp\),定义 \(dp[i][0/1]\) 表示以 \(u\) 为根的子树中有多少联通子图的节点权值为 0/1。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
const int P = 1e9 + 7;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
LL n;
string s;
cin >> n >> s;
vector < vector<LL> > g(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i ++ ){
LL u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
vector < array<LL, 2> > dp(n + 1);
LL ans = 0;
function <void(LL, LL)> dfs = [&](LL u, LL fa){
dp[u][0] = dp[u][1] = 1; //自己本身算一个
LL ans1 = 0, ans2 = 0;
for (auto v : g[u]){
if (v == fa) continue;
dfs(v, u);
dp[u][0] = dp[u][0] * (dp[v][0] + 1) % P; //选择子树或不选
dp[u][1] = dp[u][1] * (dp[v][1] + 1) % P;
ans1 = (ans1 + dp[v][0]) % P; //计算子树的总答案
ans2 = (ans2 + dp[v][1]) % P;
}
if (s[u - 1] == '0'){
dp[u][1] -- ; //不可能为 1 了
ans = (ans + dp[u][0]) % P; //加上 0 的
ans = ((ans - ans2 + dp[u][1]) % P + P) % P; //去掉子树为 1 的,加上自己为 1。注意取模后再加 P 之后再取模,不然可能为负
}
else{
dp[u][0] -- ;
ans = (ans + dp[u][1]) % P;
ans = ((ans - ans1 + dp[u][0]) % P + P) % P;
}
};
dfs(1, 0);
cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
}
G.KFC Crazy Thursday
题意:
给定长为 n 的字符串,分别统计其中以 'k','f','c' 结尾的回文串的数量。
思路:
\(manahcer\) + 前缀和/差分
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
const int N = 5e5 + 10;
LL n, p[N << 1], sum[N << 1];
char s[N << 1], ss[N];
void manacher(){
s[0] = '-', s[1] = '#';
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ){
s[2 * i + 2] = ss[i];
s[2 * i + 3] = '#';
}
n = n * 2 + 1;
s[n + 1] = '+';
int mid = 0, r = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++ ){
if (i < r) p[i] = min(p[(mid << 1) - i], r - i * 1LL);
else p[i] = 1;
while(s[i - p[i]] == s[i + p[i]]){
p[i] ++ ;
}
if (i + p[i] > r){
r = i + p[i];
mid = i;
}
}
}
void init(){
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ){
p[i] = 0;
sum[i] = 0;
}
}
void solve(){
init();
manacher();
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++ ){ //做一个差分
sum[i] ++ ;
sum[i + p[i]] -- ;
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++ ){ //前缀和累加
sum[i] += sum[i - 1];
}
vector <LL> ans(3);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ){
if (s[i] == 'k'){
ans[0] += sum[i];
}
else if (s[i] == 'f'){
ans[1] += sum[i];
}
else if (s[i] == 'c'){
ans[2] += sum[i];
}
}
cout << ans[0] << " " << ans[1] << " " << ans[2] << "\n";
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> ss;
solve();
return 0;
}
PAM
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
const int N = 5e5 + 10;
char s[N];
LL n;
struct PAM{
LL tr[N][26], fail[N], len[N], cnt[N], idx, last;
PAM(){
fail[0] = 1, fail[1] = 1;
len[1] = -1;
idx = 1;
}
void insert(char c, LL i){
LL p = get_fail(last, i);
if (!tr[p][c - 'a']){
fail[ ++ idx] = tr[get_fail(fail[p], i)][c - 'a'];
tr[p][c - 'a'] = idx;
len[idx] = len[p] + 2;
cnt[idx] = cnt[fail[idx]] + 1;
}
last = tr[p][c - 'a'];
}
LL get_fail(LL u, LL i){
while(i - len[u] - 1 < 0 || s[i - len[u] - 1] != s[i]){
u = fail[u];
}
return u;
}
}pam;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> s;
vector <LL> ans(3);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ){
pam.insert(s[i], i);
LL t = pam.cnt[pam.last];
if (s[i] == 'k') ans[0] += t;
else if (s[i] == 'f') ans[1] += t;
else if (s[i] == 'c') ans[2] += t;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i ++ )
cout << ans[i] << " \n"[i == 2];
return 0;
}
H.Cutting Papers
题意:
求多边形 \(\lvert x \rvert + \lvert y \rvert + \lvert x + y \rvert <= n\) 和圆 \(x^2 + y^2 = (\frac{n}{2})^2\) 的面积并。
思路:
画个图,容易得出答案。
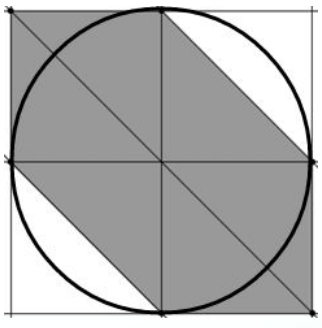
圆的面积为 \(\pi * (\frac{n}{2})^2\)。
多边形的面积为 \(3 * (\frac{n}{2})^2\)。
面积交为 \(\frac{\pi * (\frac{n}{2})^2}{2} + (\frac{n}{2})^2\)。
答案为圆面积 + 多边形面积 - 面积交。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
const double Pi = acos(-1);
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
double n;
cin >> n;
cout << fixed << setprecision(15) << (n / 2) * (n / 2) * (2 + Pi / 2) << "\n";
return 0;
}
K.Headphones
题目:
现在有 \(n\) 对耳机,对方拿了 \(k\) 对耳机,问至少拿多少只耳机,才能凑成比对面多的耳机,不能的话输出 -1。
思路:
首先判断能不能比对面多。若能,在最坏的情况下,自己拿的耳机全是单只的,为了比对方多,所以至少再拿 \(k + 1\) 只。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
LL n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
if (k + 1 <= n - k){
cout << n - k + k + 1 << "\n";
}
else{
cout << "-1\n";
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号