shell语法03
笔记来自yxc
函数
bash返回的是exit code,取值为0-255,0表示正常结束。
命令格式:
[function] func_name() { # function关键字可以省略
语句1
语句2
...
}
如果想获取函数的输出结果,可以通过echo输出到stdout中,然后通过$(function_name)来获取stdout中的结果。
不获取 return值和stdout值
func() {
name=keqing
echo "Hello $name"
}
func
获取 return值和stdout值
func() {
name=keqing
echo "Hello $name"
return 123
}
output=$(func)
ret=$?
echo "output = $output"
echo "return = $ret"
exit
exit命令用来退出当前shell进程,并返回一个退出状态;使用$?可以接收这个退出状态。
exit命令可以接受一个整数值作为参数,代表退出状态。如果不指定,默认状态值是 0。
exit退出状态只能是一个介于 0~255 之间的整数,其中只有 0 表示成功,其它值都表示失败。
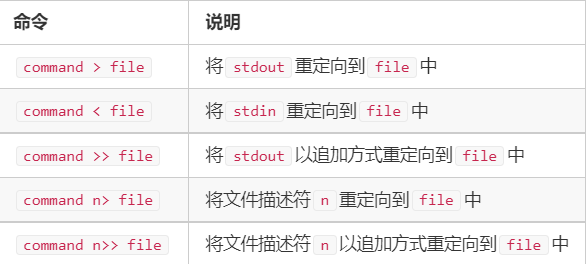
文件重定向
stdin标准输入,从命令行读取数据,文件描述符为0
stdout标准输出,向命令行输出数据,文件描述符为1
stderr标准错误输出,向命令行输出数据,文件描述符为2
echo -e "Hello \c" > output.txt # 将stdout重定向到output.txt中
echo "World" >> output.txt # 将字符串追加到output.txt中
read str < output.txt # 从output.txt中读取字符串
echo $str # 输出结果:Hello World
同时重定向stdin和stdout
从input.txt读取,执行a+b操作并传入到output.txt:
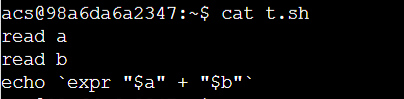
input.txt写入
1
2
./t.sh < input.txt > output.txt
output.txt 显示3
引入外部脚本:
source filename
相当于把文件的内容读取出来
#! /bin/bash
source test1.sh # 或 . test1.sh
echo My name is: $name # 可以使用test1.sh中的变量


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号