Python数据分析-Pyecharts第三方可视化数据分析图表
1. 简介
Pyecharts是一个用于生成Echarts图表的类库。Echarts是百度开源的一个数据可视化JS库。用Echarts生成的图可视化效果非常好,而Pyecharts则是专门为了与Python衔接,方便在Python中直接使用的可视化数据分析图表。使用Pyecharts可以生成独立的网页格式的图表,还可以在flask、django中直接使用,非常方便。
2. Pyecharts图表的组成
Pyecharts不仅具备Matplotlib图表的一些常用功能,而且还提供了独有的、别具特色的功能。主要包括主题风格的设置、提示框、视觉映射、工具箱和区域缩放等。

2.1. 主题风格
theme参数设置值
|
主题 |
说明 |
主题 |
说明 |
|
ThemeType.WHITE |
默认主题 |
ThemeType.ROMA |
罗马假日主题 |
|
ThemeType.LIGHT |
浅色主题 |
ThemeType.ROMANTIC |
浪漫主题 |
|
ThemeType.DARK |
深色主题 |
ThemeType.SHINE |
闪耀主题 |
|
ThemeType.CHALK |
粉笔色 |
ThemeType.VINTAGE |
葡萄酒主题 |
|
ThemeType.ESSOS |
厄索斯大陆 |
ThemeType.WALDEN |
瓦尔登湖 |
|
ThemeType.INFOGRAPHIC |
信息图 |
ThemeType.WESTEROS |
维斯特洛大陆 |
|
ThemeType.MACARONS |
马卡龙主题 |
ThemeType.WONDERLAND |
仙境 |
|
ThemeType.PURPLE_PASSION |
紫色热烈主题 |
— |
— |
2.2. 图表标题

2.3. 图例
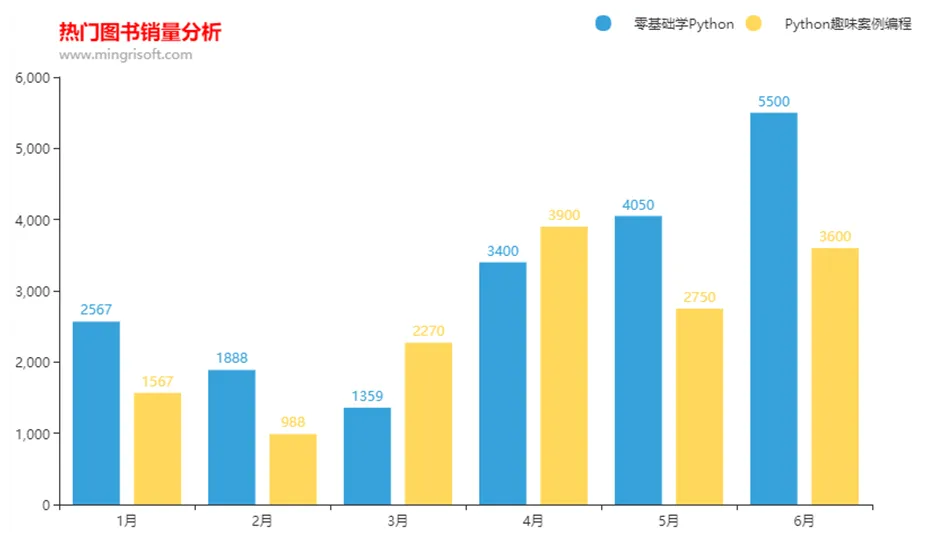
2.4. 提示框

2.5. 视觉映射

2.6. 工具箱

2.7. 区域缩放

3. Pyecharts图表的绘制(课上学习代码)
3.1. 柱状图——Bar模块
绘制柱状图/条形图主要使用Bar模块实现,主要方法介绍如下:
add_xaxis():x轴数据。
add_yaxis():y轴数据。
reversal_axis():翻转x、y轴数据。
add_dataset():原始数据。一般来说,原始数据表达的是二维表。
代码示例:
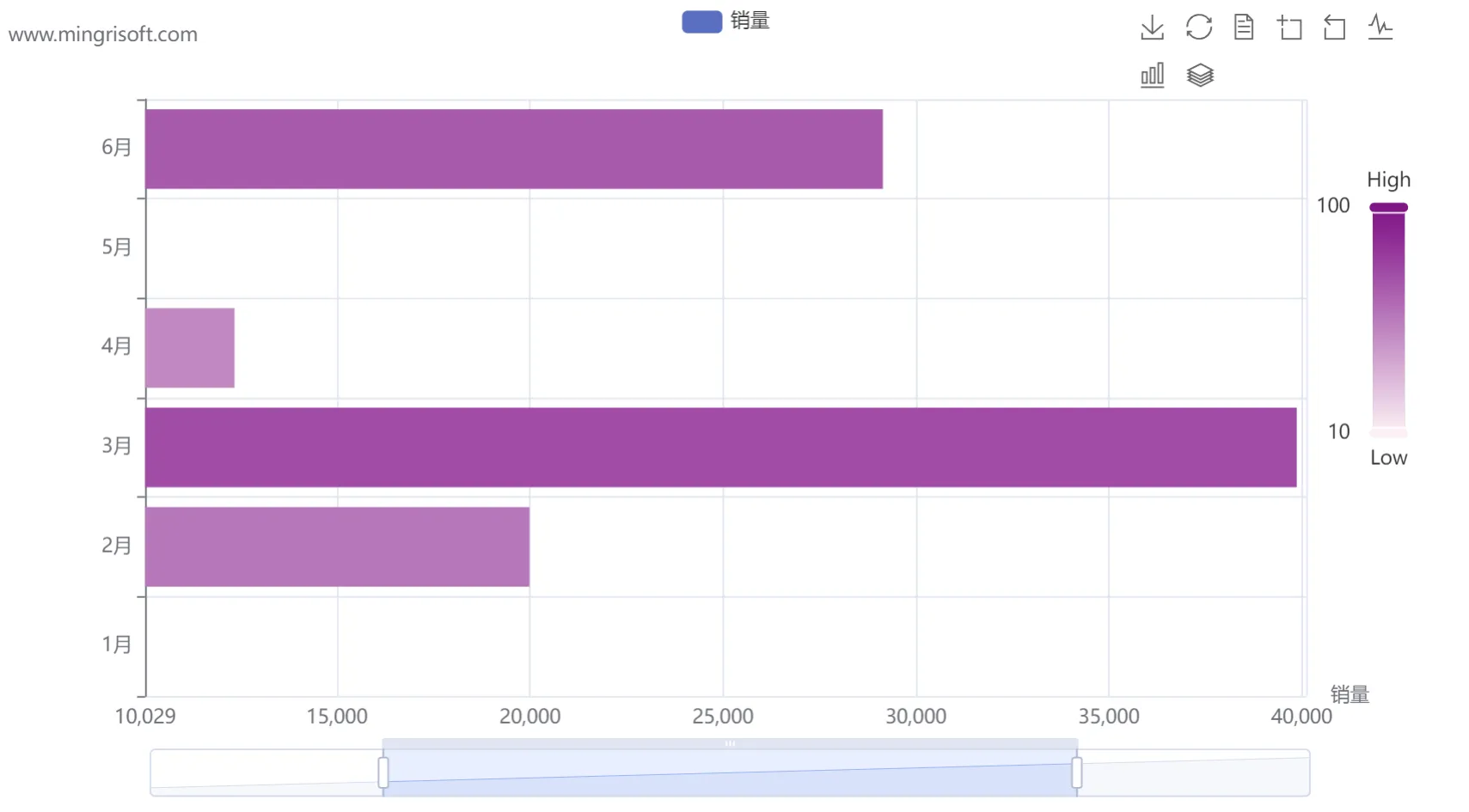
1 from pyecharts import options as opts 2 from pyecharts.charts import Bar 3 4 bar = Bar() 5 # 为柱状图添加数据 6 bar.add_dataset(source=[ 7 ["val", "销量", "月份"], 8 [24, 10009, "1月"], 9 [57, 19988, "2月"], 10 [74, 39870, "3月"], 11 [50, 12345, "4月"], 12 [99, 50145, "5月"], 13 [68, 29146, "6月"] 14 ] 15 ) 16 bar.add_yaxis( 17 series_name="销量", # 系列名称 18 y_axis=[], # 系列数据 19 encode={"x": "销量", "y": "月份"}, # 对x轴y轴数据进行编码 20 label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False) # 不显示标签文本 21 ) 22 bar.set_global_opts( 23 title_opts=opts.TitleOpts("线上图书月销量分析", # 主标题 24 subtitle='www.mingrisoft.com'), # 副标题 25 xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name="销量"), # x轴坐标轴名称 26 yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(type_="category"), # y轴坐标轴类型为“类目” 27 # 视觉映射 28 visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts( 29 orient="vertical", # 竖直放置颜色条 30 pos_right=20, # 离容器右侧的距离 31 pos_top=100, # 离容器顶端的距离 32 min_=10, # 颜色条最小值 33 max_=100, # 颜色条最大值 34 range_text=["High", "Low"], # 颜色条两端的文本 35 dimension=0, # 颜色条映射的维度 36 range_color=["#FFF0F5", "#8B008B"] # 颜色范围 37 ), 38 # 工具箱 39 toolbox_opts=opts.ToolboxOpts(is_show=True, # 显示工具箱 40 pos_left=700), # 工具箱离容器左侧的距离 41 # 区域缩放工具条 42 datazoom_opts=opts.DataZoomOpts() 43 ) 44 bar.render("mycharts.html") # 生成图表
运行结果:
3.2. 折线/面积图——Line模块
代码示例:
1 import pandas as pd 2 from pyecharts.charts import Line 3 from pyecharts import options as opts 4 5 # 导入Excel文件 6 df = pd.read_excel('books.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet2') 7 x = list(df['年份']) 8 y1 = list(df['京东']) 9 y2 = list(df['天猫']) 10 y3 = list(df['自营']) 11 line = Line() # 创建面积图 12 # 为面积图添加x轴和y轴数据 13 line.add_xaxis(xaxis_data=x) 14 line.add_yaxis(series_name="自营", y_axis=y3, areastyle_opts=opts.AreaStyleOpts(opacity=1)) 15 line.add_yaxis(series_name="京东", y_axis=y1, areastyle_opts=opts.AreaStyleOpts(opacity=1)) 16 line.add_yaxis(series_name="天猫", y_axis=y2, areastyle_opts=opts.AreaStyleOpts(opacity=1)) 17 # 渲染图表到HTML文件,存放在程序所在目录下 18 line.render("myline2.html")
运行结果:

3.3. 饼形图——Pie模块
代码示例:
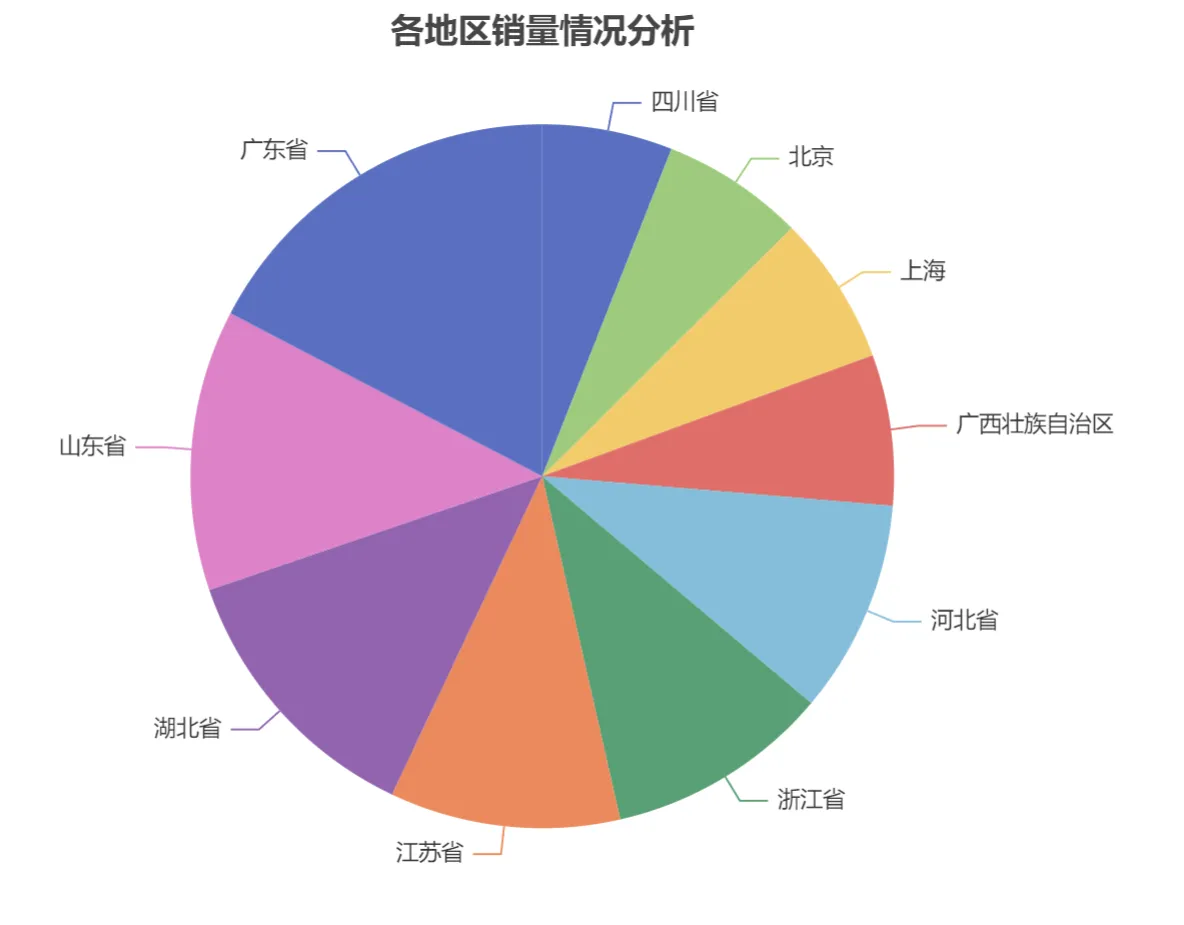
1 import pandas as pd 2 from pyecharts.charts import Pie 3 from pyecharts import options as opts 4 5 # 导入Excel文件 6 df = pd.read_excel('data2.xls') 7 x_data = df['地区'] 8 y_data = df['销量'] 9 # 将数据转换为列表加元组的格式([(key1, value1), (key2, value2)]) 10 data = [list(z) for z in zip(x_data, y_data)] 11 # 数据排序 12 data.sort(key=lambda x: x[1]) 13 14 pie = Pie() # 创建饼形图 15 # 为饼形图添加数据 16 pie.add( 17 series_name="地区", # 序列名称 18 data_pair=data, # 数据 19 ) 20 pie.set_global_opts( 21 # 饼形图标题居中 22 title_opts=opts.TitleOpts( 23 title="各地区销量情况分析", 24 pos_left="center"), 25 # 不显示图例 26 legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(is_show=False), 27 ) 28 pie.set_series_opts( 29 # 序列标签 30 label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(), 31 ) 32 # 渲染图表到HTML文件,存放在程序所在目录下 33 pie.render("mypie1.html")
运行结果:
3.4. 箱形图——Boxplot模块
代码示例:
1 import pandas as pd 2 from pyecharts.charts import Boxplot 3 4 # 导入Excel文件 5 df = pd.read_excel('Tips.xlsx') 6 y_data = [list(df['总消费'])] 7 8 boxplot = Boxplot() # 创建箱形图 9 # 为箱形图添加数据 10 boxplot.add_xaxis([""]) 11 boxplot.add_yaxis('', y_axis=boxplot.prepare_data(y_data)) 12 # 渲染图表到HTML文件,存放在程序所在目录下 13 boxplot.render("myboxplot.html")
运行结果:

3.5. 涟漪特效散点图——EffectScatter模块
代码示例:
1 import pandas as pd 2 from pyecharts.charts import EffectScatter 3 4 # 导入Excel文件 5 df = pd.read_excel('books.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet2') 6 # x轴和y轴数据 7 x = list(df['年份']) 8 y1 = list(df['京东']) 9 y2 = list(df['天猫']) 10 y3 = list(df['自营']) 11 # 绘制涟漪散点图 12 scatter = EffectScatter() 13 scatter.add_xaxis(x) 14 scatter.add_yaxis("", y1) 15 scatter.add_yaxis("", y2) 16 scatter.add_yaxis("", y3) 17 # 渲染图表到HTML文件,存放在程序所在目录下 18 scatter.render("myscatter.html")
运行结果:

3.6. 词云图——WordCloud模块
代码示例:
1 from pyecharts.charts import WordCloud 2 from jieba import analyse 3 4 # 基于TextRank算法从文本中提取关键词 5 textrank = analyse.textrank 6 text = open('111.txt', 'r', encoding='gbk').read() 7 keywords = textrank(text, topK=30) 8 list1 = [] 9 tup1 = () 10 11 # 关键词列表 12 for keyword, weight in textrank(text, topK=30, withWeight=True): 13 print('%s %s' % (keyword, weight)) 14 tup1 = (keyword, weight) # 关键词权重 15 list1.append(tup1) # 添加到列表中 16 # 绘制词云图 17 mywordcloud = WordCloud() 18 mywordcloud.add('', list1, word_size_range=[20, 100]) 19 mywordcloud.render('wordclound.html')
运行结果:

3.7. 热力图——HeatMap模块
代码示例:
1 import pyecharts.options as opts 2 from pyecharts.charts import HeatMap 3 import pandas as pd 4 5 # 导入Excel文件 6 df = pd.read_csv('data.csv', encoding='gb2312') 7 series = df['中奖号码'].str.split(' ', expand=True) # 提取中奖号码 8 # 统计每一位中奖号码出现的次数 9 df1 = df.groupby(series[0]).size() 10 df2 = df.groupby(series[1]).size() 11 df3 = df.groupby(series[2]).size() 12 df4 = df.groupby(series[3]).size() 13 df5 = df.groupby(series[4]).size() 14 df6 = df.groupby(series[5]).size() 15 df7 = df.groupby(series[6]).size() 16 # 横向表合并(行对齐) 17 data = pd.concat([df1, df2, df3, df4, df5, df6, df7], axis=1, sort=True) 18 data = data.fillna(0) # 空值NaN替换为0 19 data = data.round(0).astype(int) # 浮点数转换为整数 20 # 数据转换为HeatMap支持的列表格式 21 value1 = [] 22 for i in range(7): 23 for j in range(33): 24 value1.append([i, j, int(data.iloc[j, i])]) 25 # 绘制热力图 26 x = ['第1位', '第2位', '第3位', '第4位', '第5位', '第6位', '第7位'] 27 heatmap = HeatMap(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width='600px', height='650px')) 28 heatmap.add_xaxis(x) 29 heatmap.add_yaxis("aa", list(data.index), value=value1, # y轴数据 30 # y轴标签 31 label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True, color='white', position="center")) 32 heatmap.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="统计2014~2019年双色球中奖号码出现的次数", pos_left="center"), 33 legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(is_show=False), # 不显示图例 34 xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts( # 坐标轴配置项 35 type_="category", # 类目轴 36 splitarea_opts=opts.SplitAreaOpts( # 分隔区域配置项 37 is_show=True, 38 # 区域填充样式 39 areastyle_opts=opts.AreaStyleOpts(opacity=1) 40 ), 41 ), 42 yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts( # 坐标轴配置项 43 type_="category", # 类目轴 44 splitarea_opts=opts.SplitAreaOpts( # 分隔区域配置项 45 is_show=True, 46 # 区域填充样式 47 areastyle_opts=opts.AreaStyleOpts(opacity=1) 48 ), 49 ), 50 # 视觉映射配置项 51 visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(is_piecewise=True, # 分段显示 52 min_=1, max_=170, # 最小值、最大值 53 orient='horizontal', # 水平方向 54 pos_left="center") # 居中 55 ) 56 heatmap.render("heatmap.html")
运行结果:

3.8. 水球图——Liquid模块
代码示例:
1 from pyecharts.charts import Liquid 2 3 # 绘制水球图 4 liquid = Liquid() 5 liquid.add('', [0.7]) 6 liquid.render("myliquid.html")
运行结果:

3.9. 日历图——Calendar模块
代码示例:
1 import pandas as pd 2 from pyecharts import options as opts 3 from pyecharts.charts import Calendar 4 5 # 导入Excel文件 6 df = pd.read_excel('202001.xls') 7 data = df.stack() # 行列转换 8 # 求最大值和最小值 9 mymax = round(max(data), 2) 10 mymin = round(min(data), 2) 11 # 生成日期 12 index = pd.date_range('20200601', '20200630') 13 # 合并列表 14 data_list = list(zip(index, data)) 15 # 生成日历图 16 calendar = Calendar() 17 calendar.add("", 18 data_list, 19 calendar_opts=opts.CalendarOpts(range_=['2020-06-01', '2020-06-30'])) 20 calendar.set_global_opts( 21 title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="2020年6月加班情况", pos_left='center'), 22 visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts( 23 max_=mymax, 24 min_=mymin + 0.1, 25 orient="horizontal", 26 is_piecewise=True, 27 pos_top="230px", 28 pos_left="70px", 29 ), 30 ) 31 calendar.render("mycalendar.html")
运行结果:

时间:2024年2月24日

 Python数据分析-Pyecharts第三方可视化数据分析图表
Python数据分析-Pyecharts第三方可视化数据分析图表

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号