Python数据分析-Series与DataFrame对象
1. 简介
Pandas是Python数据分析重要的库,而Series和DataFrame是Pandas库中两个重要的对象,也是Pandas中两个重要的数据结构。

两者关系:
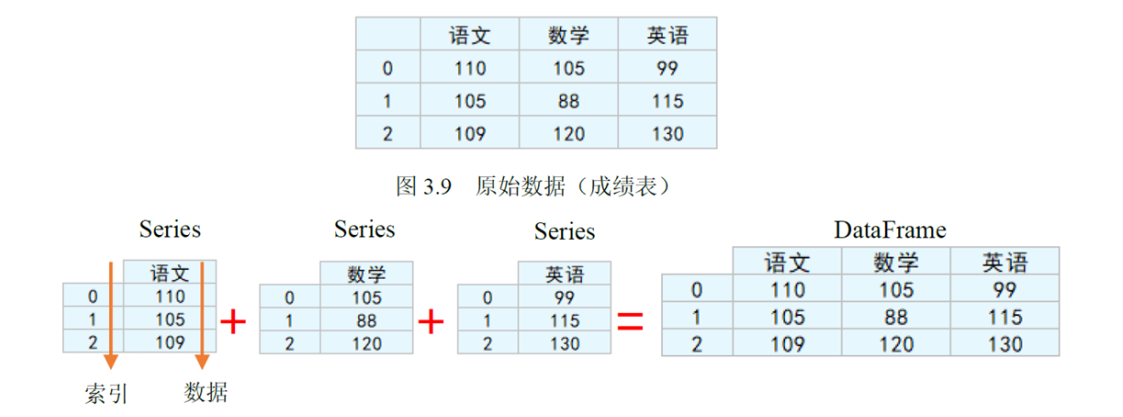
2. Series对象
2.1. 创建Series对象
创建Series对象主要使用Pandas的Series()方法,语法如下:
pandas.Series(data=None, index=None, dtype=None, name=None, copy=None, fastpath=False)
常用:
pandas.Series(data=None, index=None)
参数说明:
- data:array-like, Iterable, dict, or scalar value。
Contains data stored in Series. If data is a dict, argument order is maintained.
- index:array-like or Index (1d)。
Values must be hashable and have the same length as data. Non-unique index values are allowed. Will default to RangeIndex (0, 1, 2, …, n) if not provided. If data is dict-like and index is None, then the keys in the data are used as the index. If the index is not None, the resulting Series is reindexed with the index values.
- dtype:str, numpy.dtype, or ExtensionDtype, optional。
Data type for the output Series. If not specified, this will be inferred from data.
- name:Hashable, default None。
The name to give to the Series.
- copy:bool, default False。
Copy input data. Only affects Series or 1d ndarray input. See examples.
代码示例:
1 ## 从指定了 Index 的字典构造 Series 2 data = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3} 3 s = pd.Series(data=data, index=['a', 'b', 'c']) 4 # 结果 5 >>> s 6 a 1 7 b 2 8 c 3 9 dtype: int64
1 ## 字典的键与 Index 值匹配,因此 Index 值不起作用。 2 data = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3} 3 s = pd.Series(data=data, index=['x', 'y', 'z']) 4 5 # 结果 6 >>> s 7 x NaN 8 y NaN 9 z NaN 10 dtype: float64
3. DataFrame对象
3.1. DataFrame结构

3.2. 创建一个DataFrame对象
创建DataFrame主要使用Pandas的DataFrame()方法,语法如下:
pandas.DataFrame(data=None, index=None, columns=None, dtype=None, copy=None)
参数说明:
- data:ndarray (structured or homogeneous), Iterable, dict, or DataFrame。
Dict can contain Series, arrays, constants, dataclass or list-like objects. If data is a dict, column order follows insertion-order. If a dict contains Series which have an index defined, it is aligned by its index. This alignment also occurs if data is a Series or a DataFrame itself. Alignment is done on Series/DataFrame inputs.
If data is a list of dicts, column order follows insertion-order.
- index:Index or array-like。
Index to use for resulting frame. Will default to RangeIndex if no indexing information part of input data and no index provided.
- columns:Index or array-like。
Column labels to use for resulting frame when data does not have them, defaulting to RangeIndex(0, 1, 2, …, n). If data contains column labels, will perform column selection instead.
- dtype:dtype, default None。
Data type to force. Only a single dtype is allowed. If None, infer.
- copy:bool or None, default None。
Copy data from inputs. For dict data, the default of None behaves like copy=True. For DataFrame or 2d ndarray input, the default of None behaves like copy=False. If data is a dict containing one or more Series (possibly of different dtypes), copy=False will ensure that these inputs are not copied.
代码示例:
1 ## 从字典构造 DataFrame。 2 data = {'col1': [1, 2], 'col2': [3, 4]} 3 df = pd.DataFrame(data=data) 4 5 # 结果 6 >>> df 7 col1 col2 8 0 1 3 9 1 2 4
1 ## 从字典(包括 Series)构造 DataFrame 2 data = {'col1': [0, 1, 2, 3], 'col2': pd.Series([2, 3], index=[2, 3])} 3 df = pd.DataFrame(data=d, index=[0, 1, 2, 3]) 4 # 结果 5 >>>df 6 col1 col2 7 0 0 NaN 8 1 1 NaN 9 2 2 2.0 10 3 3 3.0
4. Pandas与Python数据类型对应表

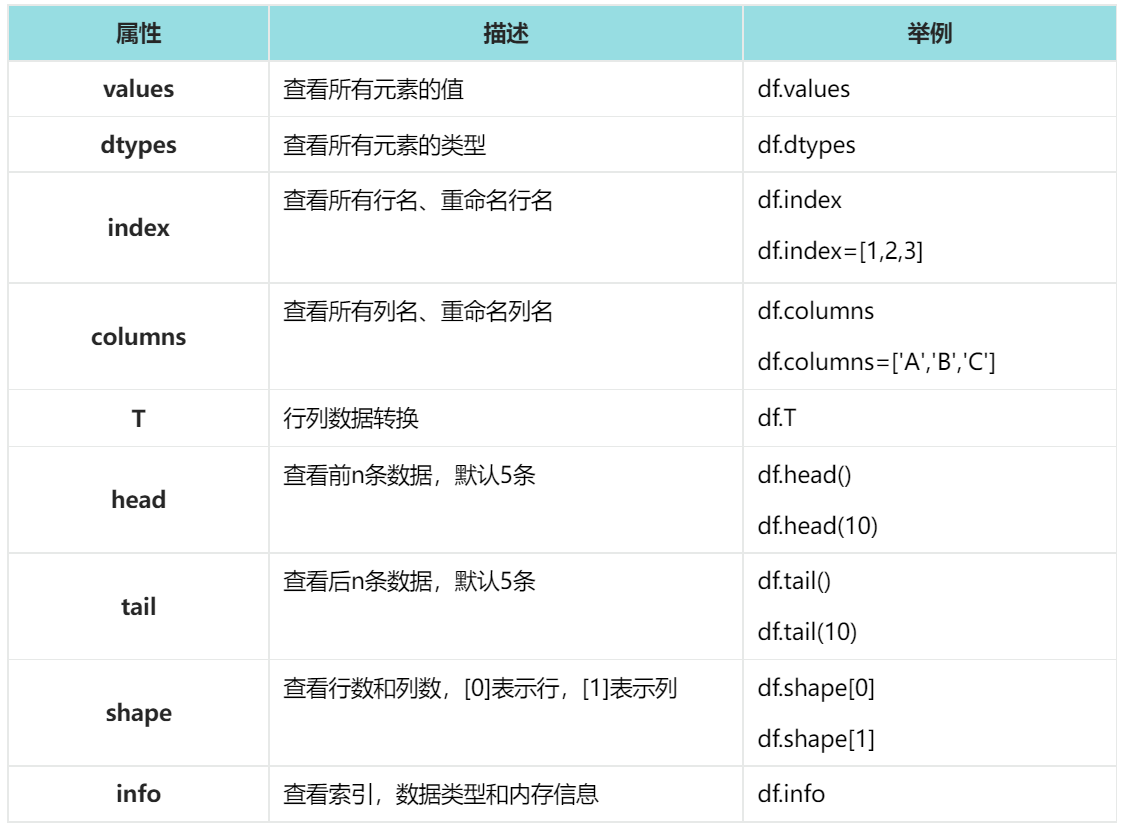
5. DataFrame重要属性
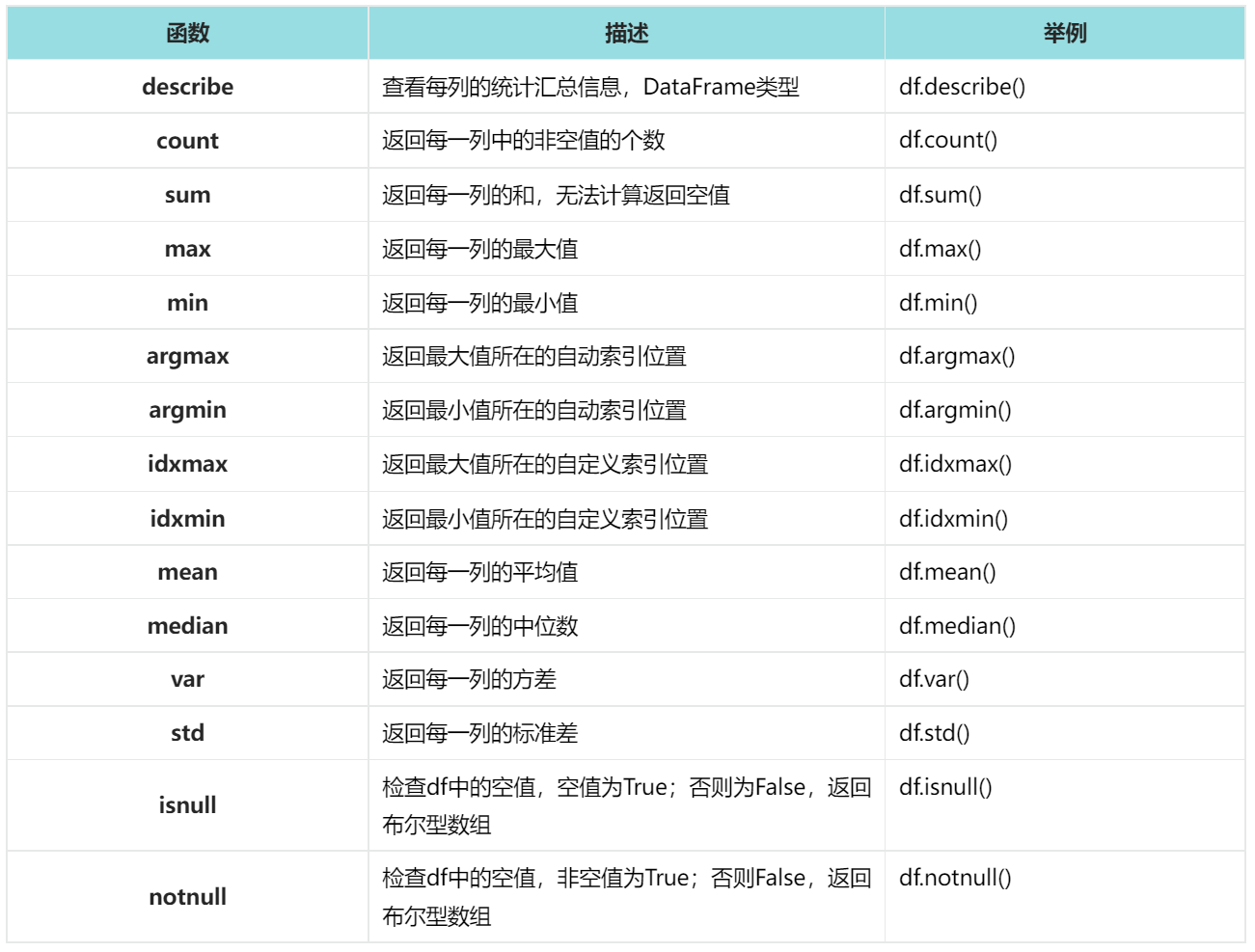
6. DataFrame重要函数
时间:2024年2月1日

 Python数据分析-Pandas库及其应用-Series与DataFrame对象
Python数据分析-Pandas库及其应用-Series与DataFrame对象

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号