Spring——bean的生命周期(Springboot --- 2.6.1)
文章目录
- Spring的生命周期
- 0.1 扫描 bean
- 0.2 BeanDefinition 操作bean的初始信息
- 0.3 beanDefinitionMap 放bean的初始信息的
- 0.4 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 工厂后置处理器
- 0.5 实例化对象
- 1、实例化Bean
- 2、设置对象属性(依赖注入):
- 3、处理Aware接口:接着,Spring会检测该对象是否实现了xxxAware接口,并将相关的xxxAware实例注入给Bean:
- 4、BeanPostProcessor后置处理器
- 5 、前置方法执行完之后执行初始化方法
- 6、 DisposableBean接口(清理阶段)
- 7、 destroy-method:(自定义结算方法了)

Spring的生命周期
0.1 扫描 bean
去扫描XML/注解/JavaConfig
0.2 BeanDefinition 操作bean的初始信息
将信息封装成BeanDefinition 然后把BeanDefinition放到一个beanDefinitionMap中
/*
* Copyright 2002-2020 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.beans.factory.config;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanMetadataElement;
import org.springframework.beans.MutablePropertyValues;
import org.springframework.core.AttributeAccessor;
import org.springframework.core.ResolvableType;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
/**
* A BeanDefinition describes a bean instance, which has property values,
* BeanDefinition描述了一个具有属性值的bean实例,
* constructor argument values, and further information supplied by
* 构造函数参数值,以及由
* concrete implementations.
* 具体实现。
*
* <p>This is just a minimal interface: The main intention is to allow a
* {@link BeanFactoryPostProcessor} to introspect and modify property values
* and other bean metadata.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Rob Harrop
* @since 19.03.2004
* @see ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#getBeanDefinition
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ChildBeanDefinition
*/
public interface BeanDefinition extends AttributeAccessor, BeanMetadataElement {
/**
* Scope identifier for the standard singleton scope: {@value}.
* 作用域的标识符, 用来标准单例的范围
* <p>Note that extended bean factories might support further scopes.
* 注意bean的工厂容器,以后的版本可以支持更多的作用域
* @see #setScope
* @see ConfigurableBeanFactory#SCOPE_SINGLETON
*/
String SCOPE_SINGLETON = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON;
/**
* Scope identifier for the standard prototype scope: {@value}.
* 作用域标识符,原型作用域
* <p>Note that extended bean factories might support further scopes.
* 同上
* @see #setScope
* @see ConfigurableBeanFactory#SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
*/
String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE;
/**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is a major part
* 指示 {@code BeanDefinition} 是应用程序主要部分的角色提示。
* of the application. Typically corresponds to a user-defined bean.
* 通常对应于用户定义的 bean。
*/
int ROLE_APPLICATION = 0;
/**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is a supporting
* part of some larger configuration, typically an outer
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition}.
* {@code SUPPORT} beans are considered important enough to be aware
* of when looking more closely at a particular
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition},
* but not when looking at the overall configuration of an application.
*/
int ROLE_SUPPORT = 1;
/**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is providing an
* entirely background role and has no relevance to the end-user. This hint is
* used when registering beans that are completely part of the internal workings
* of a {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition}.
*/
int ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE = 2;
// Modifiable attributes
/**
* Set the name of the parent definition of this bean definition, if any.
*/
void setParentName(@Nullable String parentName);
/**
* Return the name of the parent definition of this bean definition, if any.
*/
@Nullable
String getParentName();
/**
* Specify the bean class name of this bean definition.
* <p>The class name can be modified during bean factory post-processing,
* typically replacing the original class name with a parsed variant of it.
* @see #setParentName
* @see #setFactoryBeanName
* @see #setFactoryMethodName
*/
void setBeanClassName(@Nullable String beanClassName);
/**
* Return the current bean class name of this bean definition.
* <p>Note that this does not have to be the actual class name used at runtime, in
* case of a child definition overriding/inheriting the class name from its parent.
* Also, this may just be the class that a factory method is called on, or it may
* even be empty in case of a factory bean reference that a method is called on.
* Hence, do <i>not</i> consider this to be the definitive bean type at runtime but
* rather only use it for parsing purposes at the individual bean definition level.
* @see #getParentName()
* @see #getFactoryBeanName()
* @see #getFactoryMethodName()
*/
@Nullable
String getBeanClassName();
/**
* Override the target scope of this bean, specifying a new scope name.
* @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON
* @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
*/
void setScope(@Nullable String scope);
/**
* Return the name of the current target scope for this bean,
* or {@code null} if not known yet.
*/
@Nullable
String getScope();
/**
* Set whether this bean should be lazily initialized.
* <p>If {@code false}, the bean will get instantiated on startup by bean
* factories that perform eager initialization of singletons.
*/
void setLazyInit(boolean lazyInit);
/**
* Return whether this bean should be lazily initialized, i.e. not
* eagerly instantiated on startup. Only applicable to a singleton bean.
*/
boolean isLazyInit();
/**
* Set the names of the beans that this bean depends on being initialized.
* The bean factory will guarantee that these beans get initialized first.
*/
void setDependsOn(@Nullable String... dependsOn);
/**
* Return the bean names that this bean depends on.
*/
@Nullable
String[] getDependsOn();
/**
* Set whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean.
* <p>Note that this flag is designed to only affect type-based autowiring.
* It does not affect explicit references by name, which will get resolved even
* if the specified bean is not marked as an autowire candidate. As a consequence,
* autowiring by name will nevertheless inject a bean if the name matches.
*/
void setAutowireCandidate(boolean autowireCandidate);
/**
* Return whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean.
*/
boolean isAutowireCandidate();
/**
* Set whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate.
* <p>If this value is {@code true} for exactly one bean among multiple
* matching candidates, it will serve as a tie-breaker.
*/
void setPrimary(boolean primary);
/**
* Return whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate.
*/
boolean isPrimary();
/**
* Specify the factory bean to use, if any.
* This the name of the bean to call the specified factory method on.
* @see #setFactoryMethodName
*/
void setFactoryBeanName(@Nullable String factoryBeanName);
/**
* Return the factory bean name, if any.
*/
@Nullable
String getFactoryBeanName();
/**
* Specify a factory method, if any. This method will be invoked with
* constructor arguments, or with no arguments if none are specified.
* The method will be invoked on the specified factory bean, if any,
* or otherwise as a static method on the local bean class.
* @see #setFactoryBeanName
* @see #setBeanClassName
*/
void setFactoryMethodName(@Nullable String factoryMethodName);
/**
* Return a factory method, if any.
*/
@Nullable
String getFactoryMethodName();
/**
* Return the constructor argument values for this bean.
* <p>The returned instance can be modified during bean factory post-processing.
* @return the ConstructorArgumentValues object (never {@code null})
*/
ConstructorArgumentValues getConstructorArgumentValues();
/**
* Return if there are constructor argument values defined for this bean.
* @since 5.0.2
*/
default boolean hasConstructorArgumentValues() {
return !getConstructorArgumentValues().isEmpty();
}
/**
* Return the property values to be applied to a new instance of the bean.
* <p>The returned instance can be modified during bean factory post-processing.
* @return the MutablePropertyValues object (never {@code null})
*/
MutablePropertyValues getPropertyValues();
/**
* Return if there are property values defined for this bean.
* @since 5.0.2
*/
default boolean hasPropertyValues() {
return !getPropertyValues().isEmpty();
}
/**
* Set the name of the initializer method.
* @since 5.1
*/
void setInitMethodName(@Nullable String initMethodName);
/**
* Return the name of the initializer method.
* @since 5.1
*/
@Nullable
String getInitMethodName();
/**
* Set the name of the destroy method.
* @since 5.1
*/
void setDestroyMethodName(@Nullable String destroyMethodName);
/**
* Return the name of the destroy method.
* @since 5.1
*/
@Nullable
String getDestroyMethodName();
/**
* Set the role hint for this {@code BeanDefinition}. The role hint
* provides the frameworks as well as tools an indication of
* the role and importance of a particular {@code BeanDefinition}.
* @since 5.1
* @see #ROLE_APPLICATION
* @see #ROLE_SUPPORT
* @see #ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
*/
void setRole(int role);
/**
* Get the role hint for this {@code BeanDefinition}. The role hint
* provides the frameworks as well as tools an indication of
* the role and importance of a particular {@code BeanDefinition}.
* @see #ROLE_APPLICATION
* @see #ROLE_SUPPORT
* @see #ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
*/
int getRole();
/**
* Set a human-readable description of this bean definition.
* @since 5.1
*/
void setDescription(@Nullable String description);
/**
* Return a human-readable description of this bean definition.
*/
@Nullable
String getDescription();
// Read-only attributes
/**
* Return a resolvable type for this bean definition,
* based on the bean class or other specific metadata.
* <p>This is typically fully resolved on a runtime-merged bean definition
* but not necessarily on a configuration-time definition instance.
* @return the resolvable type (potentially {@link ResolvableType#NONE})
* @since 5.2
* @see ConfigurableBeanFactory#getMergedBeanDefinition
*/
ResolvableType getResolvableType();
/**
* Return whether this a <b>Singleton</b>, with a single, shared instance
* returned on all calls.
* @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON
*/
boolean isSingleton();
/**
* Return whether this a <b>Prototype</b>, with an independent instance
* returned for each call.
* @since 3.0
* @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
*/
boolean isPrototype();
/**
* Return whether this bean is "abstract", that is, not meant to be instantiated.
*/
boolean isAbstract();
/**
* Return a description of the resource that this bean definition
* came from (for the purpose of showing context in case of errors).
*/
@Nullable
String getResourceDescription();
/**
* Return the originating BeanDefinition, or {@code null} if none.
* <p>Allows for retrieving the decorated bean definition, if any.
* <p>Note that this method returns the immediate originator. Iterate through the
* originator chain to find the original BeanDefinition as defined by the user.
*/
@Nullable
BeanDefinition getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
}
这个Map的key应该是beanName,value则是BeanDefinition对象
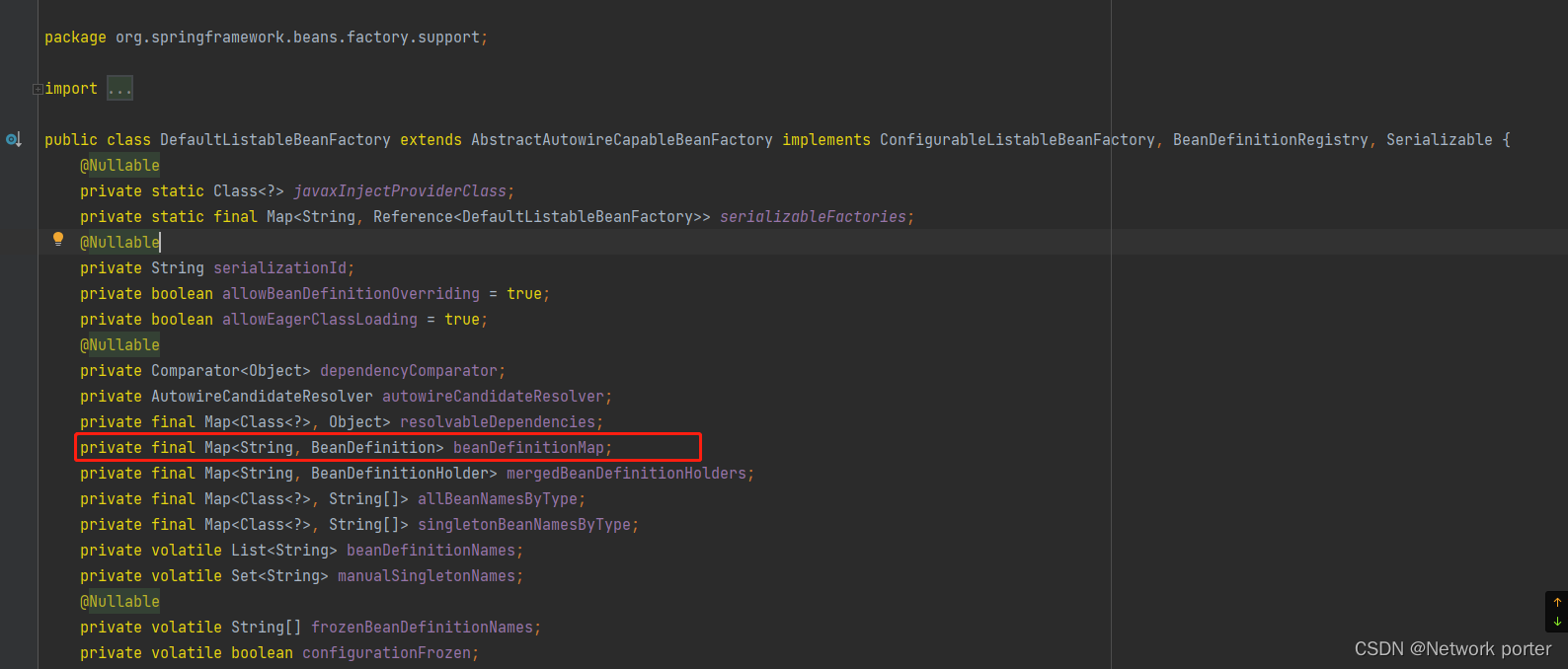
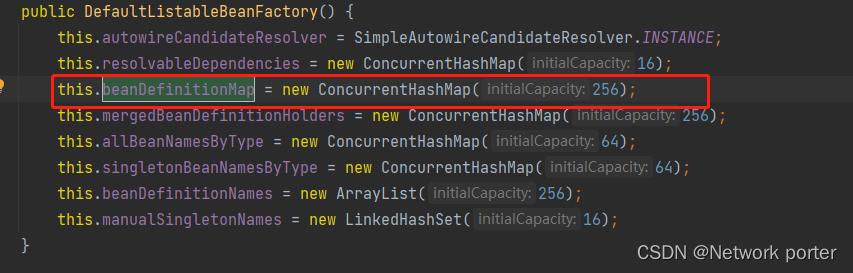
0.3 beanDefinitionMap 放bean的初始信息的
遍历 beanDefinitionMap 加载元数据 注意没有还没实例化
参考文章 作者 全都是泡沫啦:spring boot的BeanDefinitionMap初始化过程
0.4 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 工厂后置处理器
执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor这个Bean工厂后置处理器的逻辑,可以自定义BeanFactoryPostProcessor来对我们定义好的Bean元数据进行获取或者修改
例如占位符信息就是利用BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现类 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 完成的占位符配置
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 继承 》 PlaceholderConfigurerSupport(占位符配置器支持) 继承 》PropertyResourceConfigurer(属性资源配置)实现 》BeanFactoryPostProcessor (bean工厂后置处理器)
这个
0.5 实例化对象
BeanFactoryPostProcessor后置处理器执行完了以后,就到了实例化对象啦
在Spring里边是通过反射来实现的,一般情况下会通过反射选择合适的构造器来把对象实例化
但这里把对象实例化,只是把对象给创建出来,而对象具体的属性是还没注入的
构造器注入, setter 方法注入, 根据注解注入()。
1、实例化Bean
对于BeanFactory容器,当客户向容器请求一个尚未初始化的bean时,或初始化bean的时候需要注入另一个尚未初始化的依赖时,容器就会调用createBean进行实例化。对于ApplicationContext容器,当容器启动结束后,通过获取BeanDefinition对象中的信息,实例化所有的bean。
BeanDefinition 描述了一个 bean 实例,它具有属性值、构造函数参数值以及具体实现提供的更多信息。这只是一个最小的接口:主要目的是允许 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 内省和修改属性值和其他 bean 元数据。自:2004 年 3 月 19 日另见:ConfigurableListableBeanFactory.getBeanDefinition、org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition、org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ChildBeanDefinition
作者:Juergen Hoeller、Rob Harrop
2、设置对象属性(依赖注入):
实例化后的对象被封装在BeanWrapper对象中,紧接着,Spring根据BeanDefinition中的信息 以及 通 过BeanWrapper提供的设置属性的接口完成依赖注入。
package org.springframework.beans;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
/**
* The central interface of Spring's low-level JavaBeans infrastructure.
*
* <p>Typically not used directly but rather implicitly via a
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory} or a
* {@link org.springframework.validation.DataBinder}.
*
* <p>Provides operations to analyze and manipulate standard JavaBeans:
* the ability to get and set property values (individually or in bulk),
* get property descriptors, and query the readability/writability of properties.
*
* <p>This interface supports <b>nested properties</b> enabling the setting
* of properties on subproperties to an unlimited depth.
*
* <p>A BeanWrapper's default for the "extractOldValueForEditor" setting
* is "false", to avoid side effects caused by getter method invocations.
* Turn this to "true" to expose present property values to custom editors.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 13 April 2001
* @see PropertyAccessor
* @see PropertyEditorRegistry
* @see PropertyAccessorFactory#forBeanPropertyAccess
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory
* @see org.springframework.validation.BeanPropertyBindingResult
* @see org.springframework.validation.DataBinder#initBeanPropertyAccess()
*/
public interface BeanWrapper extends ConfigurablePropertyAccessor {
/**
* Specify a limit for array and collection auto-growing.
* <p>Default is unlimited on a plain BeanWrapper.
* @since 4.1
*/
void setAutoGrowCollectionLimit(int autoGrowCollectionLimit);
/**
* Return the limit for array and collection auto-growing.
* @since 4.1
*/
int getAutoGrowCollectionLimit();
/**
* Return the bean instance wrapped by this object.
*/
Object getWrappedInstance();
/**
* Return the type of the wrapped bean instance.
*/
Class<?> getWrappedClass();
/**
* Obtain the PropertyDescriptors for the wrapped object
* (as determined by standard JavaBeans introspection).
* @return the PropertyDescriptors for the wrapped object
*/
PropertyDescriptor[] getPropertyDescriptors();
/**
* Obtain the property descriptor for a specific property
* of the wrapped object.
* @param propertyName the property to obtain the descriptor for
* (may be a nested path, but no indexed/mapped property)
* @return the property descriptor for the specified property
* @throws InvalidPropertyException if there is no such property
*/
PropertyDescriptor getPropertyDescriptor(String propertyName) throws InvalidPropertyException;
}
3、处理Aware接口:接着,Spring会检测该对象是否实现了xxxAware接口,并将相关的xxxAware实例注入给Bean:
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
/**
* A marker superinterface indicating that a bean is eligible to be notified by the
* Spring container of a particular framework object through a callback-style method.
* The actual method signature is determined by individual subinterfaces but should
* typically consist of just one void-returning method that accepts a single argument.
*
* <p>Note that merely implementing {@link Aware} provides no default functionality.
* Rather, processing must be done explicitly, for example in a
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor}.
* Refer to {@link org.springframework.context.support.ApplicationContextAwareProcessor}
* for an example of processing specific {@code *Aware} interface callbacks.
*
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.1
*/
public interface Aware {
}
①BeanNameAware (Bean的id值)
如果这个Bean已经实现了BeanNameAware接口,会调用它实现的setBeanName(String beanId)方法,此处传递的就是Spring配置文件中Bean的id值;
/*
* Copyright 2002-2016 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
/**
* Interface to be implemented by beans that want to be aware of their
* bean name in a bean factory. Note that it is not usually recommended
* that an object depends on its bean name, as this represents a potentially
* brittle dependence on external configuration, as well as a possibly
* unnecessary dependence on a Spring API.
*
* <p>For a list of all bean lifecycle methods, see the
* {@link BeanFactory BeanFactory javadocs}.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 01.11.2003
* @see BeanClassLoaderAware
* @see BeanFactoryAware
* @see InitializingBean
*/
public interface BeanNameAware extends Aware {
/**
* Set the name of the bean in the bean factory that created this bean.
* <p>Invoked after population of normal bean properties but before an
* init callback such as {@link InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet()}
* or a custom init-method.
* @param name the name of the bean in the factory.
* Note that this name is the actual bean name used in the factory, which may
* differ from the originally specified name: in particular for inner bean
* names, the actual bean name might have been made unique through appending
* "#..." suffixes. Use the {@link BeanFactoryUtils#originalBeanName(String)}
* method to extract the original bean name (without suffix), if desired.
*/
void setBeanName(String name);
}
②BeanFactoryAware (传递的是Spring工厂自身)
如果这个Bean已经实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,会调用它实现的setBeanFactory()方法,传递的是Spring工厂自身。
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
/**
* Interface to be implemented by beans that wish to be aware of their
* owning {@link BeanFactory}.
*
* <p>For example, beans can look up collaborating beans via the factory
* (Dependency Lookup). Note that most beans will choose to receive references
* to collaborating beans via corresponding bean properties or constructor
* arguments (Dependency Injection).
*
* <p>For a list of all bean lifecycle methods, see the
* {@link BeanFactory BeanFactory javadocs}.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 11.03.2003
* @see BeanNameAware
* @see BeanClassLoaderAware
* @see InitializingBean
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware
*/
public interface BeanFactoryAware extends Aware {
/**
* Callback that supplies the owning factory to a bean instance.
* <p>Invoked after the population of normal bean properties
* but before an initialization callback such as
* {@link InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet()} or a custom init-method.
* @param beanFactory owning BeanFactory (never {@code null}).
* The bean can immediately call methods on the factory.
* @throws BeansException in case of initialization errors
* @see BeanInitializationException
*/
void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}
③ApplicationContextAware (传入Spring上下文)
如果这个Bean已经实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,会调用setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext)方法,传入Spring上下文;
/**
* Interface to be implemented by any object that wishes to be notified
* of the {@link ApplicationContext} that it runs in.
*
* <p>Implementing this interface makes sense for example when an object
* requires access to a set of collaborating beans. Note that configuration
* via bean references is preferable to implementing this interface just
* for bean lookup purposes.
*
* <p>This interface can also be implemented if an object needs access to file
* resources, i.e. wants to call {@code getResource}, wants to publish
* an application event, or requires access to the MessageSource. However,
* it is preferable to implement the more specific {@link ResourceLoaderAware},
* {@link ApplicationEventPublisherAware} or {@link MessageSourceAware} interface
* in such a specific scenario.
*
* <p>Note that file resource dependencies can also be exposed as bean properties
* of type {@link org.springframework.core.io.Resource}, populated via Strings
* with automatic type conversion by the bean factory. This removes the need
* for implementing any callback interface just for the purpose of accessing
* a specific file resource.
*
* <p>{@link org.springframework.context.support.ApplicationObjectSupport} is a
* convenience base class for application objects, implementing this interface.
*
* <p>For a list of all bean lifecycle methods, see the
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory BeanFactory javadocs}.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Chris Beams
* @see ResourceLoaderAware
* @see ApplicationEventPublisherAware
* @see MessageSourceAware
* @see org.springframework.context.support.ApplicationObjectSupport
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware
*/
public interface ApplicationContextAware extends Aware {
/**
* Set the ApplicationContext that this object runs in.
* Normally this call will be used to initialize the object.
* <p>Invoked after population of normal bean properties but before an init callback such
* as {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet()}
* or a custom init-method. Invoked after {@link ResourceLoaderAware#setResourceLoader},
* {@link ApplicationEventPublisherAware#setApplicationEventPublisher} and
* {@link MessageSourceAware}, if applicable.
* @param applicationContext the ApplicationContext object to be used by this object
* @throws ApplicationContextException in case of context initialization errors
* @throws BeansException if thrown by application context methods
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanInitializationException
*/
void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException;
}
去实现 ApplicationContextAware 接口创建一个工具类,可以去完成这样的业务需求:获取 ApplicationContext 对象进而获取 需要的Spring Bean
4、BeanPostProcessor后置处理器
在Aware 执行完就(如果实现了这个接口才会)会开始调BeanPostProcessor:如果想对Bean进行一些自定义的处理,那么可以让Bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口(Bean 后置处理器)
那将会调用postProcessBeforeInitialization 前置方法,和 postProcessAfterInitialization 后置方法,
通过这两个方法在bean初始化前操作,和初始化后操作
也是对AOP的实现的关键 (AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator)
/*
* Copyright 2002-2019 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.beans.factory.config;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
/**
* Factory hook that allows for custom modification of new bean instances —
* for example, checking for marker interfaces or wrapping beans with proxies.
*
* <p>Typically, post-processors that populate beans via marker interfaces
* or the like will implement {@link #postProcessBeforeInitialization},
* while post-processors that wrap beans with proxies will normally
* implement {@link #postProcessAfterInitialization}.
*
* <h3>Registration</h3>
* <p>An {@code ApplicationContext} can autodetect {@code BeanPostProcessor} beans
* in its bean definitions and apply those post-processors to any beans subsequently
* created. A plain {@code BeanFactory} allows for programmatic registration of
* post-processors, applying them to all beans created through the bean factory.
*
* <h3>Ordering</h3>
* <p>{@code BeanPostProcessor} beans that are autodetected in an
* {@code ApplicationContext} will be ordered according to
* {@link org.springframework.core.PriorityOrdered} and
* {@link org.springframework.core.Ordered} semantics. In contrast,
* {@code BeanPostProcessor} beans that are registered programmatically with a
* {@code BeanFactory} will be applied in the order of registration; any ordering
* semantics expressed through implementing the
* {@code PriorityOrdered} or {@code Ordered} interface will be ignored for
* programmatically registered post-processors. Furthermore, the
* {@link org.springframework.core.annotation.Order @Order} annotation is not
* taken into account for {@code BeanPostProcessor} beans.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Sam Brannen
* @since 10.10.2003
* @see InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
* @see DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor
* @see ConfigurableBeanFactory#addBeanPostProcessor
* @see BeanFactoryPostProcessor
*/
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this {@code BeanPostProcessor} to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* 初始化前的后处理
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
/**
* Apply this {@code BeanPostProcessor} to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The
* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created
* objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks.
* <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,
* in contrast to all other {@code BeanPostProcessor} callbacks.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean
* 初始化后的后处理 由于这个方法是在Bean初始化结束时调用的,可以被应用于内存或缓存技术;
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
5 、前置方法执行完之后执行初始化方法
InitializingBean 与 init-method:如果Bean在Spring配置文件中配置了 init-method
属性,则会自动调用其配置的初始化方法。
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
/**
* Interface to be implemented by beans that need to react once all their properties
* have been set by a {@link BeanFactory}: e.g. to perform custom initialization,
* or merely to check that all mandatory properties have been set.
*
* <p>An alternative to implementing {@code InitializingBean} is specifying a custom
* init method, for example in an XML bean definition. For a list of all bean
* lifecycle methods, see the {@link BeanFactory BeanFactory javadocs}.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @see DisposableBean
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition#getPropertyValues()
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinition#getInitMethodName()
*/
public interface InitializingBean {
/**
* Invoked by the containing {@code BeanFactory} after it has set all bean properties
* and satisfied {@link BeanFactoryAware}, {@code ApplicationContextAware} etc.
* <p>This method allows the bean instance to perform validation of its overall
* configuration and final initialization when all bean properties have been set.
* @throws Exception in the event of misconfiguration (such as failure to set an
* essential property) or if initialization fails for any other reason
*/
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
6、 DisposableBean接口(清理阶段)
当Bean不再需要时,会经过清理阶段,如果Bean实现了DisposableBean这个接口,会调用其实现的destroy()方法;
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
/**
* Interface to be implemented by beans that want to release resources on destruction.
* 想要在销毁时释放资源的 bean 实现的接口。
* A {@link BeanFactory} will invoke the destroy method on individual destruction of a
* scoped bean. An {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext} is supposed
* to dispose all of its singletons on shutdown, driven by the application lifecycle.
* {@link BeanFactory} 将在单独销毁作用域 bean 时调用 destroy 方法。
* {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext} 应该在应用程序生命周期的驱动下在关闭时处理其所有单例。
*
* <p>A Spring-managed bean may also implement Java's {@link AutoCloseable} interface
* for the same purpose. An alternative to implementing an interface is specifying a
* custom destroy method, for example in an XML bean definition. For a list of all
* bean lifecycle methods, see the {@link BeanFactory BeanFactory javadocs}.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 12.08.2003
* @see InitializingBean
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition#getDestroyMethodName()
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory#destroySingletons()
* @see org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#close()
*/
public interface DisposableBean {
/**
* Invoked by the containing {@code BeanFactory} on destruction of a bean.
* @throws Exception in case of shutdown errors. Exceptions will get logged
* but not rethrown to allow other beans to release their resources as well.
*/
void destroy() throws Exception;
}
7、 destroy-method:(自定义结算方法了)
最后,如果这个Bean的Spring配置中配置了destroy-method属性,会自动调用其配置的销毁方法。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号