定位方式+偏移:
static:所有不设定定位的元素,定位方式都是static(缺省)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<style type="text/css">
.div1 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
top: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div1"></div>
</body>
</html>
1.不脱离标准流
2.偏移不起作用:top right bottom left
3.消除定位(实战中的应用)
relative:相对定位
1.不脱离标准流
2.偏移起作用:top right bottom left, 起始点从元素本来应该所在的位置的左上点
3.不破坏标准流,把元素移动到需要的地方
4.relative+偏移 vs static+margin的区别?
a. relative只是移动了元素,但是标准流不受影响;
b.margin虽然也满足移动元素,但是会影响标准流
5.relative作为absolute的基准
6.如果同时设定了left和right,只有left有效;如果同时设定了top和bottom,只有top有效(和定义在先或者在后没有关系)。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<style type="text/css">
.div1 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
top: 100px;
}
.div2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
position: relative;
/*如果不设置偏移,只设置position: relative的话,那么和未设置position: relative一样的效果,因为没有脱离标准流*/
left: 100px;
right: 50px;
/*bottom: 50px;*/
/*备注:如果用margin的话,会脱离标准流*/
margin-top: -50px;
margin-left: 100px ;
}
.div3 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #00f;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="div2"></div>
<div class="div3"></div>
</body>
</html>
/*用position: relative;的效果*/
/*用margin的效果*/
![]()
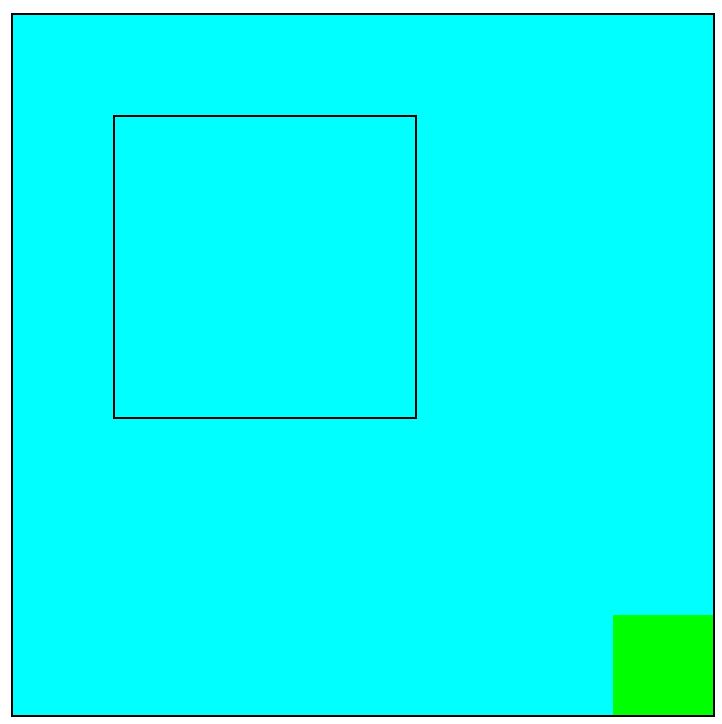
/*同时设定left和right的效果:left: 100px; right: 50px;*/
![]()
absolute: 绝对定位
1.脱离标准流,跟着滚动条一起滚动
2.偏移起作用:top right bottom left
a. 没有任何一层的祖先节点有定位(如relative,absolute,fixed),以浏览器的可视区为起始点
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<style type="text/css">
.div1 {
width: 120px;
height: 120px;
background-color: #f00;
}
.div2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="div2"></div>
</body>
</html>
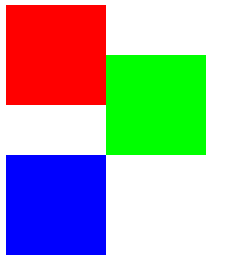
=======运行后的效果,备注:红色的块之所以有空白,那是body对应的margin=========
![]()
![]()
![]()
如果设置body的话,可以比较容易的看出是脱离了body的:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<style type="text/css">
body {
height: 1000px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.div1 {
width: 120px;
height: 120px;
background-color: #f00;
}
.div2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
position: absolute;
/* top: 0;
left: 0; */
bottom: 0;
right: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="div2"></div>
</body>
</html>
![]()
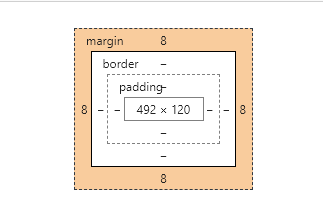
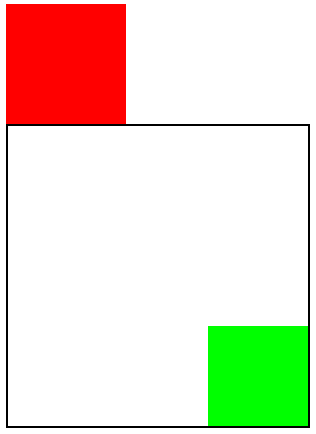
b.父元素有定位(relative,absolute,fixed),以父元素的内角(border和padding的分界线)为起始点;margin对子元素定位有影响,padding, border对子元素定位没有影响
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<style type="text/css">
.div1 {
width: 120px;
height: 120px;
background-color: #f00;
}
.father {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
border: 2px solid #000;
position: relative;
}
.div2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
position: absolute;
bottom: 0;
right: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="father">
<div class="div2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
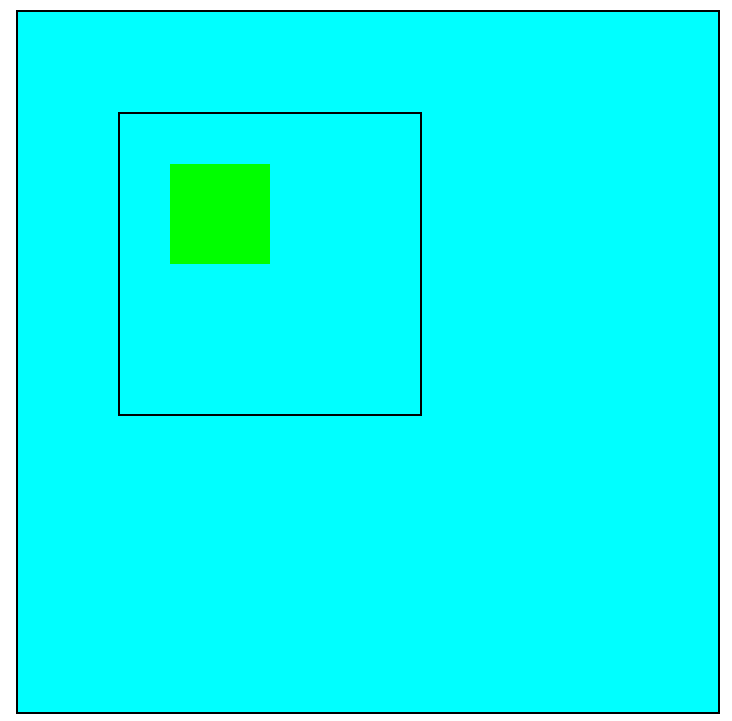
=========运行的结果==========
![]()
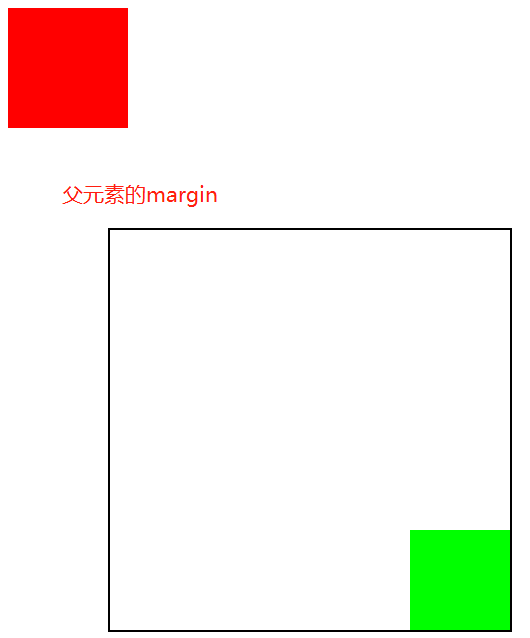
============如果给父元素加margin的话===============
.father {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
border: 2px solid #000;
position: relative;
margin: 100px;
}
![]()
============如果给父元素加padding的话===============
.father {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
border: 2px solid #000;
position: relative;
margin: 100px;
padding: 50px;
}
效果和上图一样,也就是说padding未生效
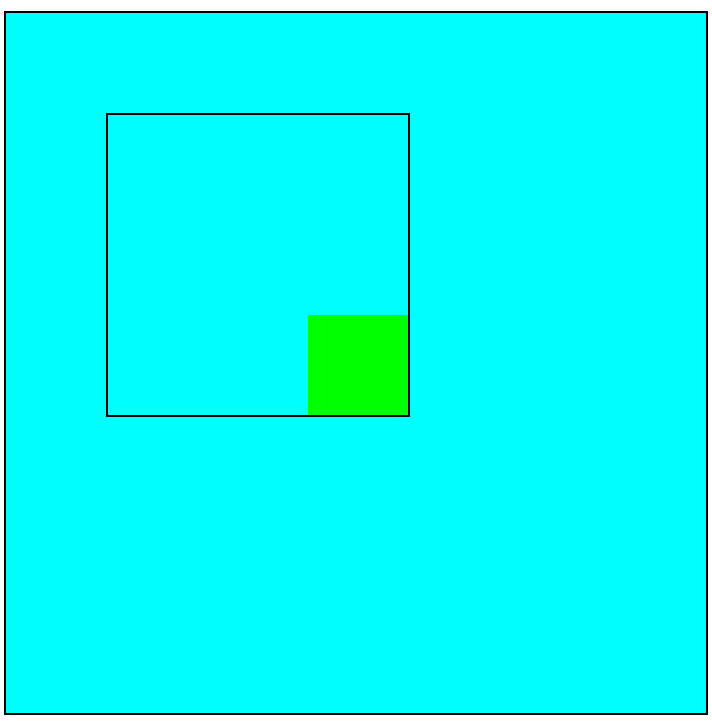
c.如果有一个或者多个祖先元素有定位(relative,absolute,fixed),以最近的祖先元素的内角(border和padding的分界线)为起始点
/*第一种:.father和.grand-father都设置position: relative;则以.father为起始点*/
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<style type="text/css">
.div1 {
width: 120px;
height: 120px;
background-color: #f00;
}
.grand-father {
width: 700px;
height: 700px;
background-color: #0ff;
border: 2px solid #000;
position: relative;
margin: 50px;
}
.father {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 2px solid #000;
position: relative;
margin: 100px;
padding: 50px;
}
.div2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
position: absolute;
bottom: 0;
right: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="grand-father">
<div class="father">
<div class="div2"></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
![]()
/*第二种:.father设置position: relative, .grand-father不设置position: relative;仍然以.father为起始点*/
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<style type="text/css">
.div1 {
width: 120px;
height: 120px;
#f00;
}
.grand-father {
width: 700px;
height: 700px;
background-color: #0ff;
border: 2px solid #000;
/*position: relative;*/
margin: 50px;
}
.father {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 2px solid #000;
position: relative;
margin: 100px;
padding: 50px;
}
.div2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
position: absolute;
bottom: 0;
right: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="grand-father">
<div class="father">
<div class="div2"></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
运行效果和上图一样
/*第三种:.father不设置position: relative, .grand-father设置position: relative;则以.grand-father为起始点*/
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<style type="text/css">
.div1 {
width: 120px;
height: 120px;
#f00;
}
.grand-father {
width: 700px;
height: 700px;
background-color: #0ff;
border: 2px solid #000;
position: relative;
margin: 50px;
}
.father {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 2px solid #000;
/*position: relative;*/
margin: 100px;
padding: 50px;
}
.div2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
position: absolute;
bottom: 0;
right: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="grand-father">
<div class="father">
<div class="div2"></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
![]()
3.设定了position: absolute, 没有设定left,top:
a. 如果没有设定left和top,所有对元素能产生作用的因素全都起作用(就好像没有设定absolute一样的效果):注意,与top: 0; left: 0; 不等价,不设定left和top的情况,left和top被初始化为“应该在“(按标准流去算下位置,但是却脱离标准流)的位置。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<style type="text/css">
.div1 {
width: 120px;
height: 120px;
background-color: #f00;
}
.grand-father {
width: 700px;
height: 700px;
background-color: #0ff;
border: 2px solid #000;
position: relative;
margin: 50px;
}
.father {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 2px solid #000;
position: relative;
margin: 100px;
padding: 50px;
}
.div2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
/*只设定position: absolute;不设定top left或者bottom right*/
position: absolute;
/* top: 0;
left: 0; */
/* bottom: 0;
right: 0; */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="grand-father">
<div class="father">
<div class="div2"></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
========================效果===========================
![]()
b.如果left被设定,top没有:left按照设定,top按照“应该在”的位置
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<style type="text/css">
.div1 {
width: 120px;
height: 120px;
background-color: #f00;
}
.grand-father {
width: 700px;
height: 700px;
background-color: #0ff;
border: 2px solid #000;
position: relative;
margin: 50px;
}
.father {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 2px solid #000;
position: relative;
margin: 100px;
padding: 50px;
}
.div2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
/*设定position: absolute;不设定top,但是设定left*/
position: absolute;
/* top: 0;*/
left: 200px;
/* bottom: 0;
right: 0; */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="grand-father">
<div class="father">
<div class="div2"></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
==========运行效果=========
![]()
c.如果top被设定,left没有:top按照设定,left按照“应该在”的位置
效果和b相似
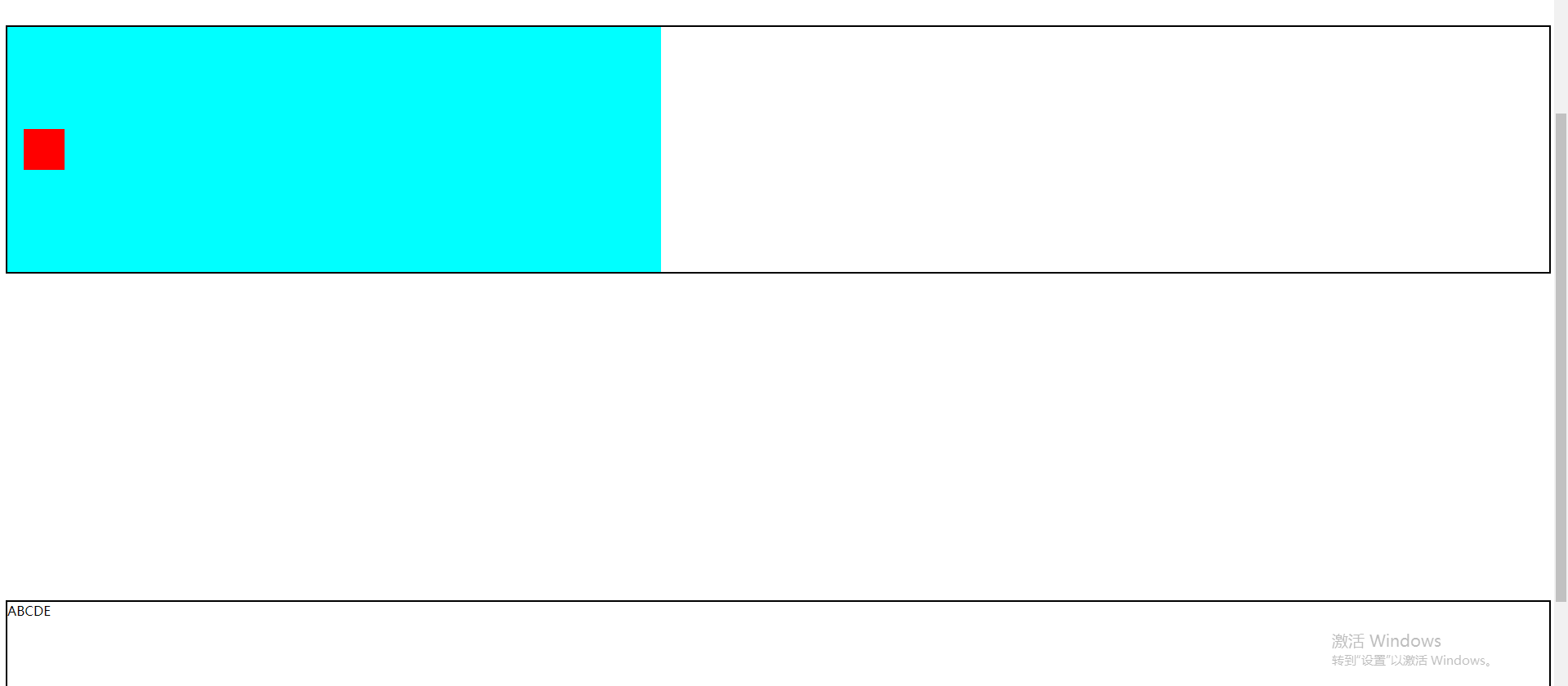
4.relative作为absolute的基准(父r子a)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
.father {
margin-top: 400px;
width: 100%;
height: 300px;
border: 2px solid #000;
/* 2.必须设定father的position */
/* position: absolute; *//*这样设置的话,会影响后面元素的定位*/
position: relative;
}
.button {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: #f00;
/* 1.必须设定button的position为absolute */ /*这样设置的话,可以使button浮在img的上面*/
position: absolute;
top: 125px;
left: 20px;
}
.img {
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
background-color: #0ff;
float: left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="button"></div>
<div class="img"></div>
<div class="img"></div>
</div>
<div class="father">ABCDE</div>
</body>
</html>
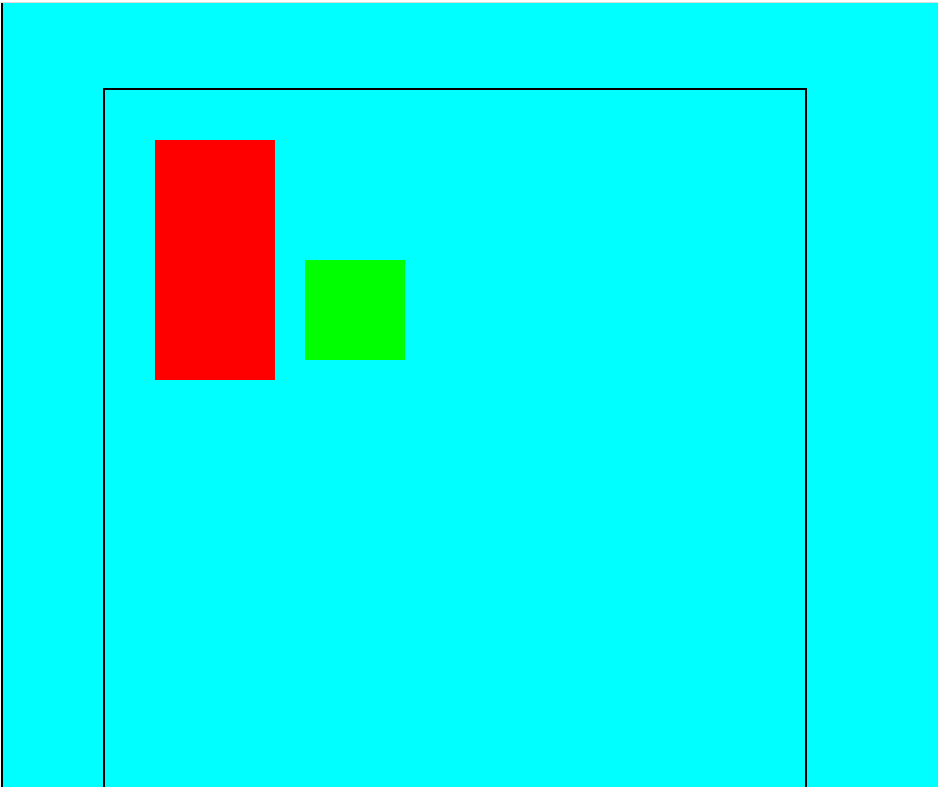
将.father设置成position: absolute;的效果:
![]()
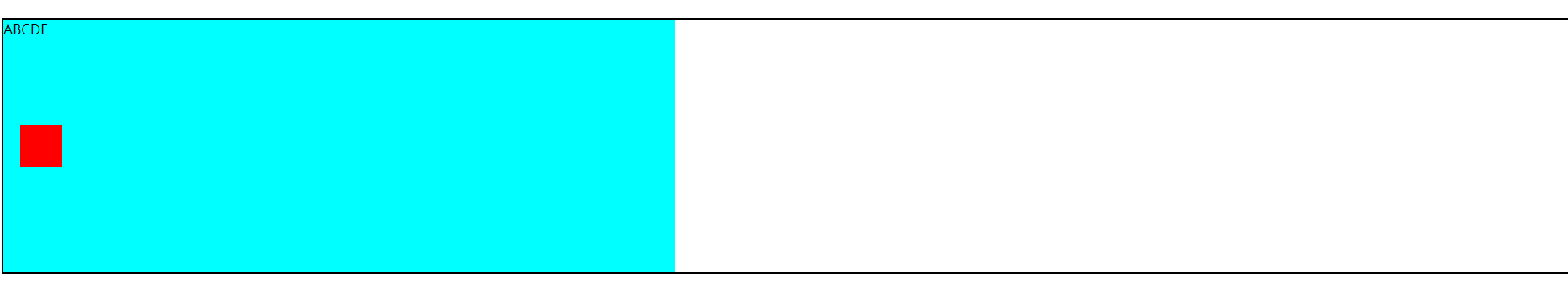
将.father设置成position: relative;的效果(不会影响下面的div的布局):
![]()
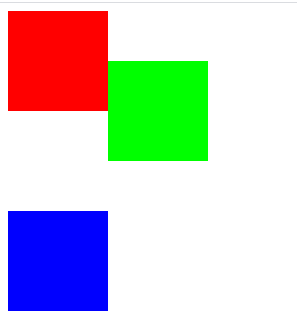





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号