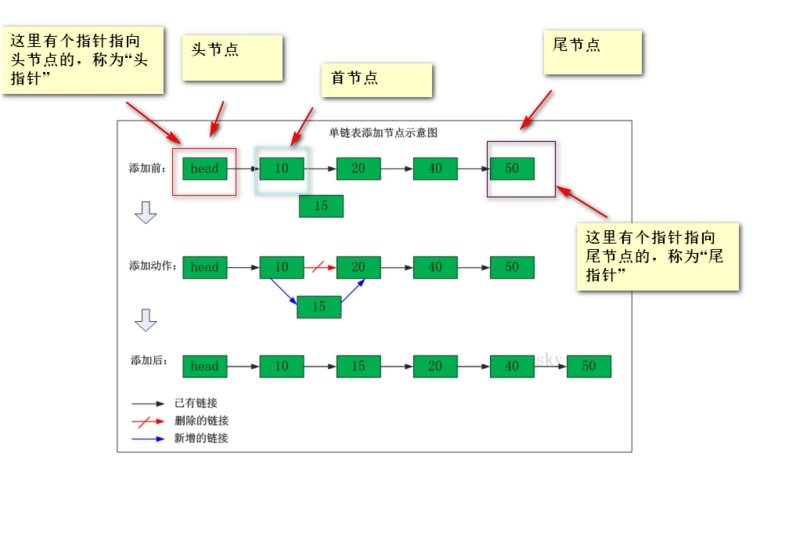
确定一个链表只需要头指针,通过头指针就可以把整个链表都能推导出来。
链表分为好几类:
1)单向链表:一个节点指向下一个节点
2)双向链表:一个节点有两个指针域
3)循环链表:能通过任何一个节点找到其他所有的节点,将两种(双向/单向)链表德尔最后一个节点指向第一个节点从而实现循环。
节点类
public class Node{ //数据域 public Integer data; //指针域 public Node next; public Node(){} public Node(int data){ this.data=data; } public Node(int data,Node next){ this.data=data; this.next=next; } }
定义head节点在成员变量上
private static Node node=new Node();
创建链表(增加节点)
//向链表中添加数据 public static void addData(int value){ //初始化要加入的节点 Node newNode=new Node(value); //临时节点 Node temp=head.next; //找到尾节点 while(temp!=null){ temp=temp.next; } temp.next=newNode; }
遍历链表
从首节点开始,不断往后面找,直到后面的节点没有数据。
public static void traverse(Node head){ //临时节点 Node temp=head.next; while(temp!=null){ if(temp.data!=null){ System.out.print(temp.data+" "); } temp=temp.next; } System.out.println(); }
获取链表的长度
public static int listLength(Node head){ //临时节点 Node temp=head.next; int size=0; while(temp!=null){ size++; temp=temp.next; } return size; }
插入节点
public static void InsertNode(Node head,int index,int value){ //首先需要判断指定位置是否合法 if(index<1||index>listLength(head)+1){ System.out.println("插入位置不合法"); return; } //初始化要插入的节点 Node newNode=new Node(value); //记录当前遍历的位置 int currentPos=0; //临时节点,从头节点开始 Node temp=head; while(temp!=null){ //找到上一节点的位置 if((index-1)==currentPos){ //temp表示的是上一节点 //将原本由上一个节点的指向交由插入的节点来指向 newNode=temp.next; //将上一个节点的指针域指向要插入的节点 temp.next=newNode; return; } currentPos++; temp=temp.next; } }
删除节点
public static void deleteNode(Node head,int index){ //判断删除位置是否合法 if(index<1||index>listLength(head)+1){ System.out.println("删除位置不合法"); return; } //记录遍历的当前位置 int currentPos=0; //临时节点,从头节点开始 Node temp=head; while(temp!=null){ //找到上一个节点的位置 if((index-1)==currentPos){ //temp表示的是上一个节点 //temp.next表示的是要删除的节点 //将删除的节点存储一下 Node node=temp.next; //删除节点的一个节点交由上一个节点来控制 temp.next=node.next; return; } currentPos++; temp=temp.next; } }
对链表进行排序
public static void sort(Node head){ Node currentNode; Node nextNode; for(currentNode=head.next;curentNode.next!=null;currentNode=currentNode.next){ for(nextNode=head.next;nextNode.next!=null;nextNode=nextNode.next){ if(nextNode.data>nextNode.next.data){ int temp=nextNode.data; nextNode.data=nextNode.next.data; nextNode.next.data=temp; } } } }
找到链表中倒数第k个节点
设置两个指针p1、p2,让p2比p1快k个字节,同时向后遍历,当p2为空,则p1为倒数第k个节点
public static Node findKNode(Node head,int k){ if(k<1||k>listLength(head)){ return null; } Node p1=head; Node p2=head; //p2比p1快k个节点 for(int i=0;i<k-1;i++){ p2=p2.next; } //只要p2为null,那么p1就是倒数第k个节点 while(p2.next!=null){ p1=p1.next; p2=p2.next; } return p1; }
查询链表的中间节点
public static Node searchMid(Node head){ Node p1=head; Node p2=head; //一个走一步,一个走两步,直到为null,走一步的到达的就是中间节点 while(p2!=null&&p2.next!=null&&p2.next.next!=null){ p1=p1.next; p2=p2.next.next; } return p1; }
通过递归从头到尾输出单链表
public static void printListReversely(Node head){ if(head!=null){ printListReversely(head.next); if(head.data!=null){ System.out.println(head.data+" "); } } }
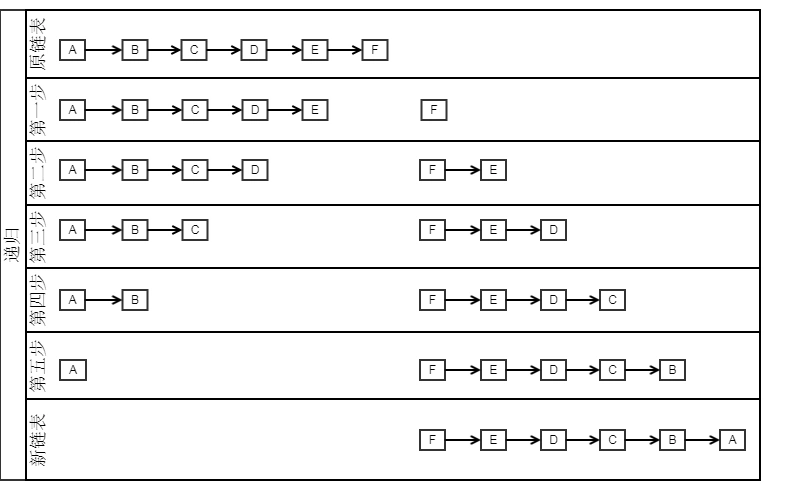
反转链表
public static Node reverseList(Node head){ //反转后节点 Node pre=null; //当前节点 Node cur=head; while(cur!=null){ //记录剩余节点 Node next=cur.next; //设置当前节点的下一节点为反转后节点 cur.next=pre; //设置反转后节点为当前节点 pre=cur; cur=next; } return pre; }



 posted on
posted on

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号