467. 环绕字符串中唯一的子字符串
题目:
把字符串 s 看作是“abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz”的无限环绕字符串,所以 s 看起来是这样的:"...zabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzabcd....".
现在我们有了另一个字符串 p 。你需要的是找出 s 中有多少个唯一的 p 的非空子串,尤其是当你的输入是字符串 p ,你需要输出字符串 s 中 p 的不同的非空子串的数目。
注意: p 仅由小写的英文字母组成,p 的大小可能超过 10000。
示例 1:
输入: "a" 输出: 1 解释: 字符串 S 中只有一个"a"子字符。
示例 2:
输入: "cac" 输出: 2 解释: 字符串 S 中的字符串“cac”只有两个子串“a”、“c”。.
示例 3:
输入: "zab" 输出: 6 解释: 在字符串 S 中有六个子串“z”、“a”、“b”、“za”、“ab”、“zab”。.
解答:
首先考虑p的长度是10000级别,那n^2就是一亿级别,肯定不能用两个for循环嵌套。
稍微不那么naive的:
用memo记录每个字母开头的最长连续串长度。
从每个i开始找连续串,如果当前连续串比记录的更长,则更新memo[p[i]-'a']。
class Solution { public: int findSubstringInWraproundString(string p) { vector<int> memo(26,0); int len=p.size(); for(int i=0;i<len;++i){ int j=i+1; while(j<len and (p[j]-p[j-1]+26)%26==1 ){ ++j; } memo[p[i]-'a']=max(memo[p[i]-'a'] , j-i); } return accumulate(memo.begin(), memo.end(), 0); } };

太垃圾了。。
考虑到前一次遍历i-1,p[i-1]='a',然后找到了一个连续串,长度100:abcd...xyzabc...xyzabc...
那么对于i来说,p[i]='b',i到i+98这段就不用找了。所以建立了一个数组dp,dp[i]记录从i开始的最长连续串结尾索引。
class Solution { public: int findSubstringInWraproundString(string p) { vector<int> memo(26,0); int len=p.size(); vector<int> dp(len,0);//dp[i]:从i开始的连续字母串的结尾+1处 for(int i=0;i<len;++i){ int j=i+1; if(i>0 and p[i]-p[i-1]==1){ j=dp[i-1]; } while(j<len and (p[j]-p[j-1]+26)%26==1 ){ ++j; } dp[i]=j; memo[p[i]-'a']=max(memo[p[i]-'a'] , j-i); } return accumulate(memo.begin(), memo.end(), 0); } };
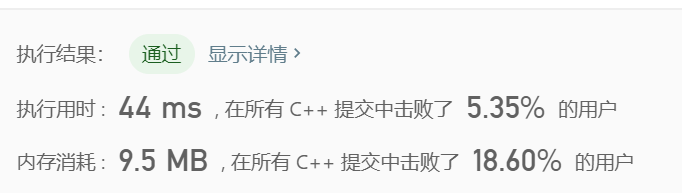
还是好垃圾。。
考虑每次遍历i时,只用到了dp[i-1],所以dp数组可以缩减为一个变量:
class Solution { public: int findSubstringInWraproundString(string p) { vector<int> memo(26,0); int len=p.size(); int last_j=-1; for(int i=0;i<len;++i){ int j=i+1; if(i>0 and p[i]-p[i-1]==1){ j=last_j; } while(j<len and (p[j]-p[j-1]+26)%26==1 ){ ++j; } last_j=j; memo[p[i]-'a']=max(memo[p[i]-'a'] , j-i); } return accumulate(memo.begin(), memo.end(), 0); } };
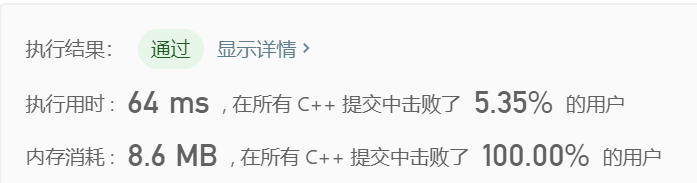
好吧,没什么卵用,看来时间差别不在这,空间倒是少了不少。
看了看评论区,原来应该是记录每个字母(a到z)结束的最长连续串长度。这样只需要从头到尾遍历一次,用一个全局长度k记录当前的连续串长度,并且随着当前遍历到的字符不同去更新相应的dp数组值。
而我一直是记录从每个字母开始的连续串长度。但是二者理论复杂度应该都是O(N)啊,想不通阿。。。
粘贴的评论区代码:
class Solution { public: bool isContinous(char prev, char curr) { if (prev == 'z') return curr == 'a'; return prev + 1 == curr; } int findSubstringInWraproundString(string p) { vector<int> dp(26, 0); int N = p.size(); int k = 0; for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) { if (i > 0 && isContinous(p[i - 1], p[i])) { ++k; } else { k = 1; } dp[p[i] - 'a'] = max(dp[p[i] - 'a'], k); } return accumulate(dp.begin(), dp.end(), 0); } };
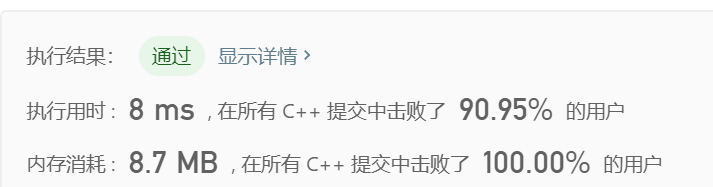
后来发现问题不在于是记录字母开头的最长串还是记录字母结尾的最长串,而是我考察相邻字符用的是求余,这个方法太慢了,改成普通判断AC时间就上去了:
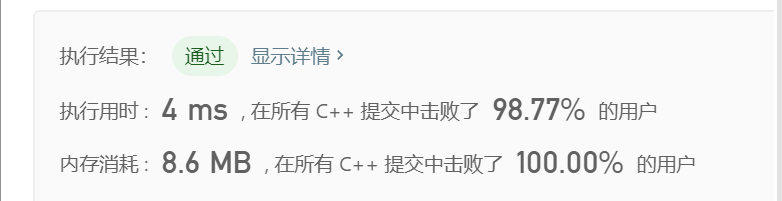
class Solution { public: bool check(char& x,char& y){ return y-x==1 or (y=='a' and x=='z'); } int findSubstringInWraproundString(string p) { vector<int> memo(26,0); int len=p.size(); int last_j=-1; for(int i=0;i<len;++i){ int j=i+1; if(i>0 and check(p[i-1],p[i])){ j=last_j; } while(j<len and check(p[j-1],p[j])){ ++j; } last_j=j; memo[p[i]-'a']=max(memo[p[i]-'a'] , j-i); } return accumulate(memo.begin(), memo.end(), 0); } };


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号