构造文件输入流
我们可以构造一个文件输入流,然后再利用read方法读取文件中的一个字节:
1 package com.hw.file0205;
2
3 import java.io.FileInputStream;
4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
5 import java.io.IOException;
6
7 public class TestInputStream {
8 public static void main(String[] args) {
9 FileInputStream input = null; //创建文件输入流,这里先赋值为null
10 try {
11 input = new FileInputStream("F://骚操作//something.txt");
12 int a = input.read(); //读取该文件中的一个字节。
13 System.out.println((char)a);
14 }catch (IOException e) {
15 // TODO Auto-generated catch block
16 e.printStackTrace();
17 }finally{
18 try {
19 if(input != null){
20 input.close(); //要记得关闭!
21 }
22
23 } catch (IOException e) {
24 // TODO Auto-generated catch block
25 e.printStackTrace();
26 }
27 }
28 }
29 }

我的这个文件是这样的:
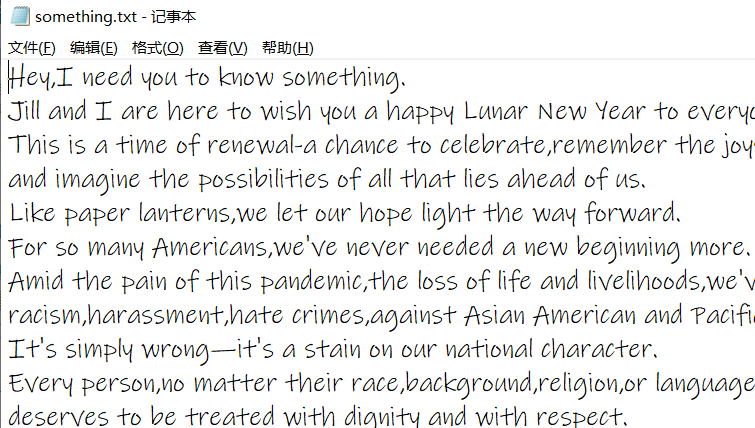
此外,这份代码里面有很多try-catch语句,这是因为有很多异常,建议有异常的话就当场全部都用try-catch解决,不要遇到就抛。
另外,input.close()是必须要用的,因为文件输入流是无论如何都要关闭的,但是如果放在try里面,一旦有什么异常的话,可能就不会执行这句代码了,所以,我们把它放在finally里面,这样一来,就肯定能够关闭输入流了。
可以看到,这里只能读取一个字符,那如果我想要把所有的字符都读取怎么办呢?很简单,用一个循环就搞定了。
1 package com.hw.file0205;
2 import java.io.FileInputStream;
3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
4 import java.io.IOException;
5
6 public class TestInputStream {
7 public static void main(String[] args) {
8 FileInputStream input = null; //创建文件输入流,这里先赋值为null
9 try {
10 input = new FileInputStream("F://骚操作//test.txt");
11
12 int a = -1;
13 while(true)
14 {
15 a = input.read();
16 if(a==-1) break;
17 System.out.print((char)a);
18 }
19 }catch (IOException e) {
20 // TODO Auto-generated catch block
21 e.printStackTrace();
22 }finally{
23 try {
24 if(input != null){
25 input.close(); //要记得关闭!
26 }
27
28 } catch (IOException e) {
29 // TODO Auto-generated catch block
30 e.printStackTrace();
31 }
32 }
33 }
34 }


这样就可以了。
但是要注意啊,如果是中文字符的话就不行了,至少用这种字节流是肯定不行的。因为中文字符占不止一个字节,用这种方法是肯定不行的!
再看:其实我们还可以采取另外一种方法:利用字节数组。
1 package com.hw.file0205;
2 import java.io.FileInputStream;
3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
4 import java.io.IOException;
5
6 public class TestInputStream {
7 public static void main(String[] args) {
8 FileInputStream input = null; //创建文件输入流,这里先赋值为null
9 try {
10 input = new FileInputStream("F://骚操作//test.txt");
11
12 byte[] data = new byte[4];
13 while(true)
14 {
15 int length = input.read(data);
16 if(length==-1) break;
17 for(int i = 0;i < length;i++)
18 {
19 System.out.print((char)data[i]);
20 }
21 }
22 }catch (IOException e) {
23 // TODO Auto-generated catch block
24 e.printStackTrace();
25 }finally{
26 try {
27 if(input != null){
28 input.close(); //要记得关闭!
29 }
30
31 } catch (IOException e) {
32 // TODO Auto-generated catch block
33 e.printStackTrace();
34 }
35 }
36 }
37 }
上面这份代码中,数组的长度是4,那么就会按照四个字节四个字节读取(即按照数组长度来读取)。利用字节数组的话,我们需要知道一个长度length,read方法有一个返回值,就是这个length,表示当前读取的字节数。因为文件中的字节数不一定是4的整数倍,有可能到最后还剩下两个字节或一个字节,这个时候我们就需要这个length来判断了。并且,当读到文件末尾的时候,length等于-1,这个时候应该要把循环break掉。读取字节的for循环条件的设置就是这样,只能读取length范围内的字节。

假如不用for循环,而改成这样:
1 while(true)
2{
3 int length = input.read(data);
4 if(length==-1) break;
5 System.out.print((char)data[0]);
6 System.out.print((char)data[1]);
7 System.out.print((char)data[2]);
8 System.out.print((char)data[3]);
9 System.out.println();
10}

输出结果就是上面这样了。最后一个感叹号是落单的,就直接把上面那一行的给弄下来了。
再或者,还可以用string。构造String的时候是可以传一个数组过去的,然后系统会把数组里面的元素组拼成一个字符串。
1 package com.hw.file0205;
2 import java.io.FileInputStream;
3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
4 import java.io.IOException;
5
6 public class TestInputStream {
7 public static void main(String[] args) {
8 FileInputStream input = null; //创建文件输入流,这里先赋值为null
9 try {
10 input = new FileInputStream("F://骚操作//test.txt");
11
12 byte[] data = new byte[4];
13 while(true)
14 {
15 int length = input.read(data);
16 if(length==-1) break;
17 String str = new String(data,0,length); //同样需要给定起始索引,以及要读取的长度。
18 System.out.print(str);
19 }
20 }catch (IOException e) {
21 // TODO Auto-generated catch block
22 e.printStackTrace();
23 }finally{
24 try {
25 if(input != null){
26 input.close(); //要记得关闭!
27 }
28
29 } catch (IOException e) {
30 // TODO Auto-generated catch block
31 e.printStackTrace();
32 }
33 }
34 }
35 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号