第十一次
1、定义一个点类Point, 包含2个成员变量x、y分别表示x和y坐标,2个构造器Point()和Point( intx0,y0),以及一个movePoint (int dx,intdy)方法实现点的位置移动,创建两个Point对象p1、p2, 分别调用movePoint方法后,打印pl和p2的坐标。[必作题]
package zuoye;
public class Point {
int x;
int y;
public Point(){
}
public Point(int x,int y){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
public void movePoint(int x,int y){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
}
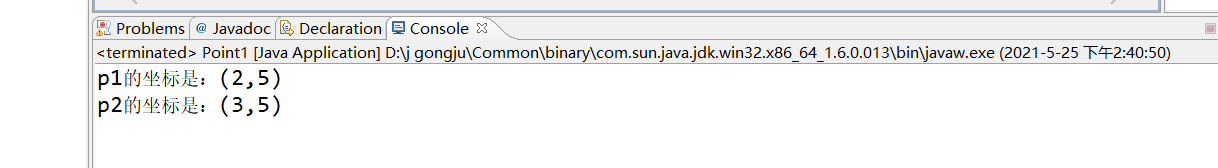
package zuoye;
public class Point1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Point p1=new Point(1,2);
Point p2=new Point(3,4);
p1.movePoint(2,4);
p2.movePoint(3,5);
System.out.println("p1的坐标是:("+p1.x+","+p2.y+")");
System.out.println("p2的坐标是:("+p2.x+","+p2.y+")");
}
}
2、定义一个矩形类Rectangle: (知识点: 对象的创建和使用)[必做题]
2.1 定义三个方法: getArea(求面积、getPer0求周长,showAll0分 别在控制台输出长、宽、面积周长。
2.2 有2个属性:长length、 宽width
2.3 通过构造方法Rectangle(int width, int length),分别给两个属性赋值
2.4 创建-个Rectangle对象, 并输出相关信息
package zuoye;
public class Rectangle {
int length;
int width;
public Rectangle(){
}
public Rectangle(int length,int width){
this.length=length;
this.width=width;
}
public double getArea(){
return(length*width);
}
public double getPer(){
return(length+width)*2;
}
public void showAll(){
System.out.println("长是:"+length);
System.out.println("宽是:"+width);
System.out.println("面积是:"+(length*width));
System.out.println("周长是:"+(length+width)*2);
}
}
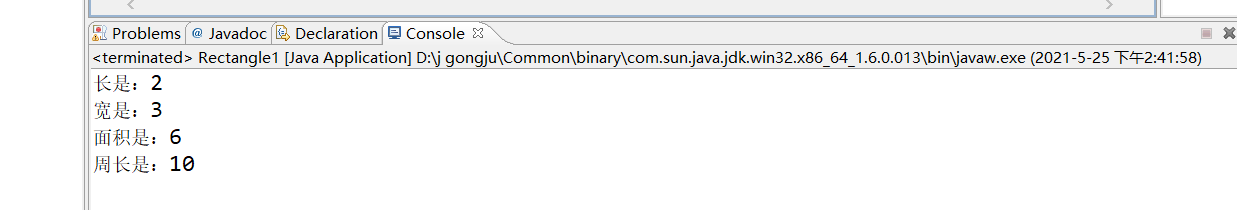
package zuoye;
public class Rectangle1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Rectangle s=new Rectangle(2,3);
s.showAll();
}
}
3、定义一-个笔记本类,该类有颜色(char) 和cpu型号(int) 两个属性。[必做题]
3.1无参和有参的两个构造方法;有参构造方法可以在创建对象的同时为每个属性赋值;
3.2 输出笔记本信息的方法
3.3 然后编写一-个测试类,测试笔记本类的各个方法。
package zuoye;
public class Pc {
char color;
int cpu;
public Pc(){
}
public Pc(char color,int cpu){
this.color=color;
this.cpu=cpu;
}
public void showAll(){
System.out.println("颜色:"+color);
System.out.println("型号:"+cpu);
}
}
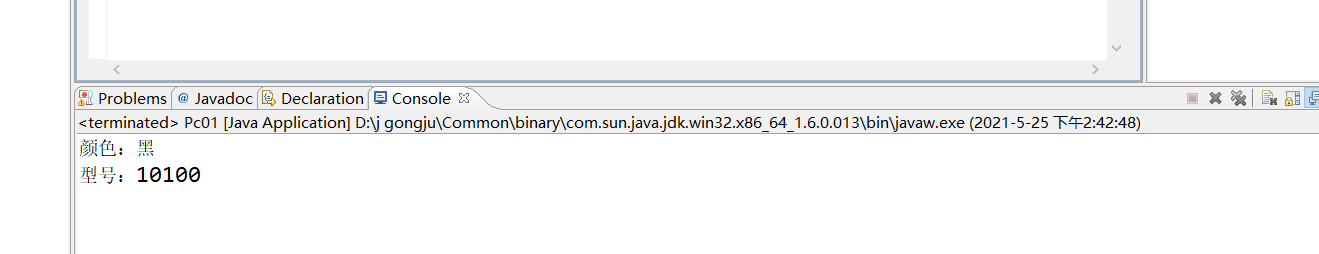
package zuoye;
public class Pc01 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Pc a=new Pc('黑',10100);
a.showAll();
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号