LeetCode 588. Design In-Memory File System
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/design-in-memory-file-system/
题目:
Design a data structure that simulates an in-memory file system.
Implement the FileSystem class:
FileSystem()Initializes the object of the system.List<String> ls(String path)- If
pathis a file path, returns a list that only contains this file's name. - If
pathis a directory path, returns the list of file and directory names in this directory.
- If
void mkdir(String path)Makes a new directory according to the givenpath. The given directory path does not exist. If the middle directories in the path do not exist, you should create them as well.void addContentToFile(String filePath, String content)- If
filePathdoes not exist, creates that file containing givencontent. - If
filePathalready exists, appends the givencontentto original content.
- If
String readContentFromFile(String filePath)Returns the content in the file atfilePath.
Example 1:
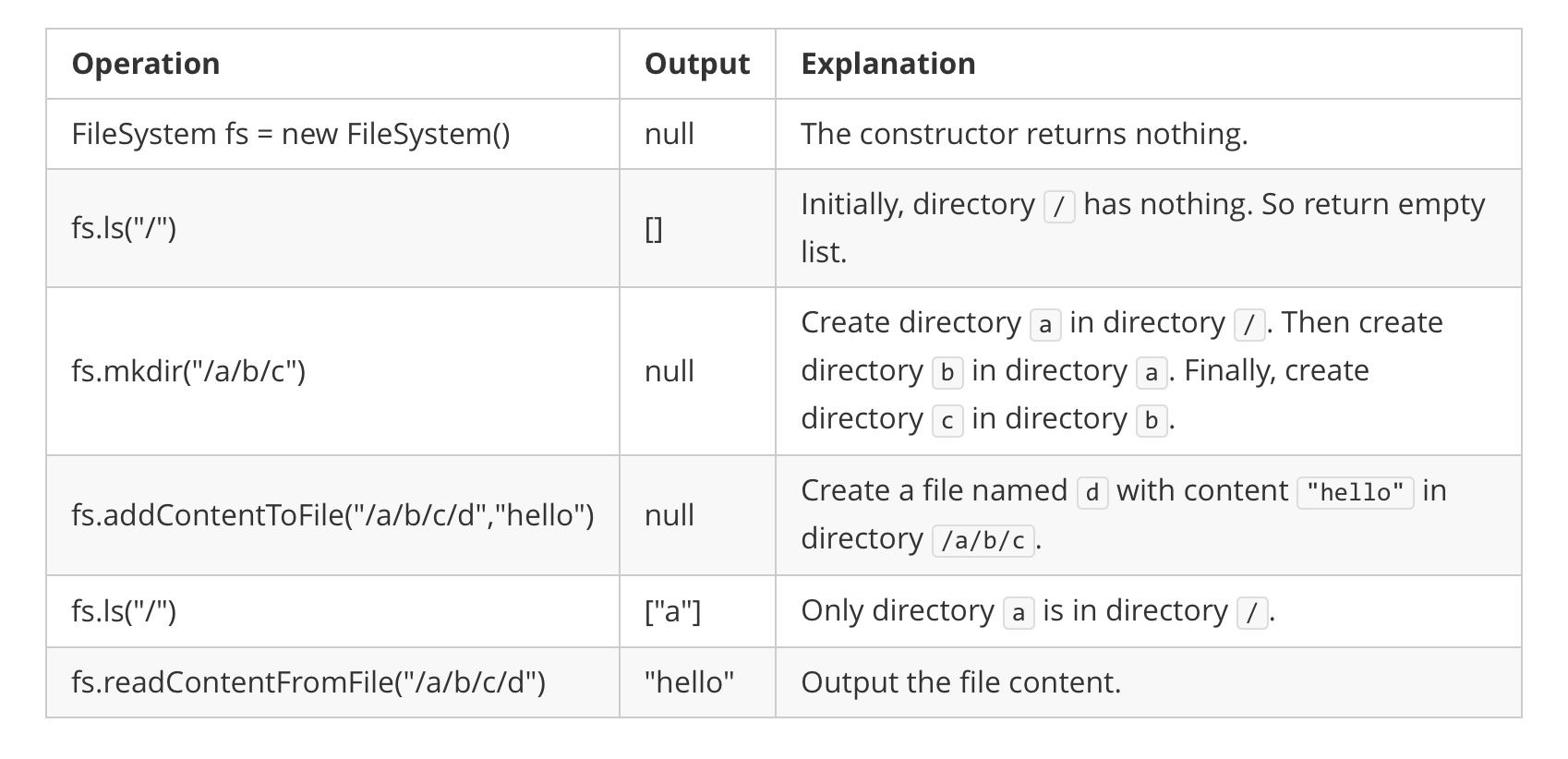
Input
["FileSystem", "ls", "mkdir", "addContentToFile", "ls", "readContentFromFile"]
[[], ["/"], ["/a/b/c"], ["/a/b/c/d", "hello"], ["/"], ["/a/b/c/d"]]
Output
[null, [], null, null, ["a"], "hello"]
Explanation
FileSystem fileSystem = new FileSystem();
fileSystem.ls("/"); // return []
fileSystem.mkdir("/a/b/c");
fileSystem.addContentToFile("/a/b/c/d", "hello");
fileSystem.ls("/"); // return ["a"]
fileSystem.readContentFromFile("/a/b/c/d"); // return "hello"
Constraints:
1 <= path.length, filePath.length <= 100pathandfilePathare absolute paths which begin with'/'and do not end with'/'except that the path is just"/".- You can assume that all directory names and file names only contain lowercase letters, and the same names will not exist in the same directory.
- You can assume that all operations will be passed valid parameters, and users will not attempt to retrieve file content or list a directory or file that does not exist.
1 <= content.length <= 50- At most
300calls will be made tols,mkdir,addContentToFile, andreadContentFromFile.
题解:
It is like Tire.
For each DirNode, it contains a map to children directories DirNode, and a map to children files StringBuilder.
ls has one corner case that when path is "/". since "/".split("/") is empty array. arr[arr.length - 1] will have index out of bound exception.
Time Complexity: ls, O(m + klogk). m = path.length(). k is number of items in the res.
mkdir, O(m).
add, O(m).
readContentFromFile, O(m).
Space: O(n). size of DirNode tree.
AC Java:
1 class FileSystem { 2 DirNode root; 3 4 public FileSystem() { 5 root = new DirNode(); 6 } 7 8 public List<String> ls(String path) { 9 DirNode cur = root; 10 List<String> res = new ArrayList<>(); 11 if(!path.equals("/")){ 12 String [] arr = path.split("/"); 13 for(int i = 1; i < arr.length - 1; i++){ 14 cur.dirs.putIfAbsent(arr[i], new DirNode()); 15 cur = cur.dirs.get(arr[i]); 16 } 17 18 if(cur.files.containsKey(arr[arr.length - 1])){ 19 res.add(arr[arr.length - 1]); 20 return res; 21 } 22 23 cur.dirs.putIfAbsent(arr[arr.length - 1], new DirNode()); 24 cur = cur.dirs.get(arr[arr.length - 1]); 25 } 26 27 res.addAll(cur.dirs.keySet()); 28 res.addAll(cur.files.keySet()); 29 Collections.sort(res); 30 return res; 31 } 32 33 public void mkdir(String path) { 34 DirNode cur = root; 35 String [] arr = path.split("/"); 36 for(int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++){ 37 cur.dirs.putIfAbsent(arr[i], new DirNode()); 38 cur = cur.dirs.get(arr[i]); 39 } 40 } 41 42 public void addContentToFile(String filePath, String content) { 43 DirNode cur = root; 44 String [] arr = filePath.split("/"); 45 for(int i = 1; i < arr.length - 1; i++){ 46 cur.dirs.putIfAbsent(arr[i], new DirNode()); 47 cur = cur.dirs.get(arr[i]); 48 } 49 50 cur.files.putIfAbsent(arr[arr.length - 1], new StringBuilder()); 51 cur.files.get(arr[arr.length - 1]).append(content); 52 } 53 54 public String readContentFromFile(String filePath) { 55 DirNode cur = root; 56 String [] arr = filePath.split("/"); 57 for(int i = 1; i < arr.length - 1; i++){ 58 cur.dirs.putIfAbsent(arr[i], new DirNode()); 59 cur = cur.dirs.get(arr[i]); 60 } 61 62 return cur.files.get(arr[arr.length - 1]).toString(); 63 } 64 } 65 66 class DirNode{ 67 Map<String, DirNode> dirs = new HashMap<>(); 68 Map<String, StringBuilder> files = new HashMap<>(); 69 } 70 71 /** 72 * Your FileSystem object will be instantiated and called as such: 73 * FileSystem obj = new FileSystem(); 74 * List<String> param_1 = obj.ls(path); 75 * obj.mkdir(path); 76 * obj.addContentToFile(filePath,content); 77 * String param_4 = obj.readContentFromFile(filePath); 78 */

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号