20250801 字符串
KMP
AC自动机
我居然会SAM不会AC自动机?
AC(Aho–Corasick)自动机是 以 Trie 的结构为基础,结合 KMP 的思想 建立的自动机,用于解决多模式匹配等任务。
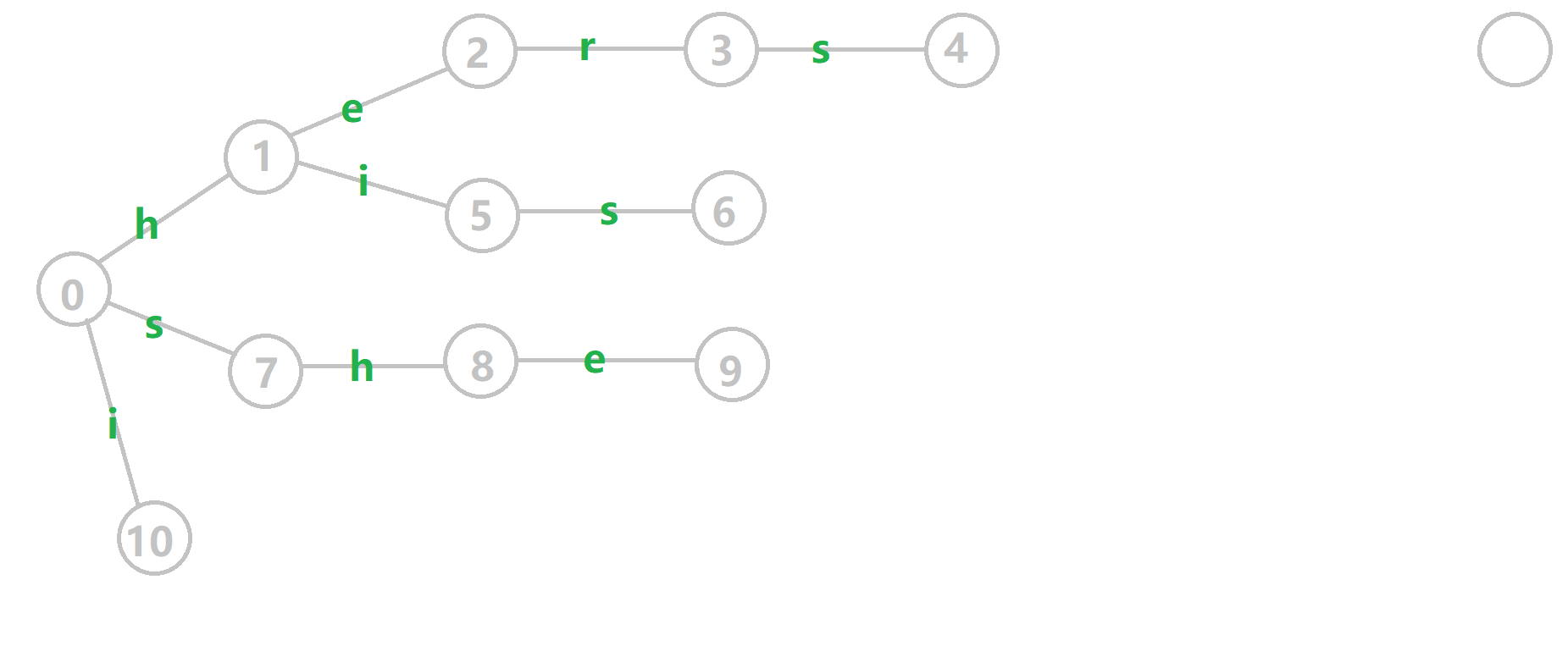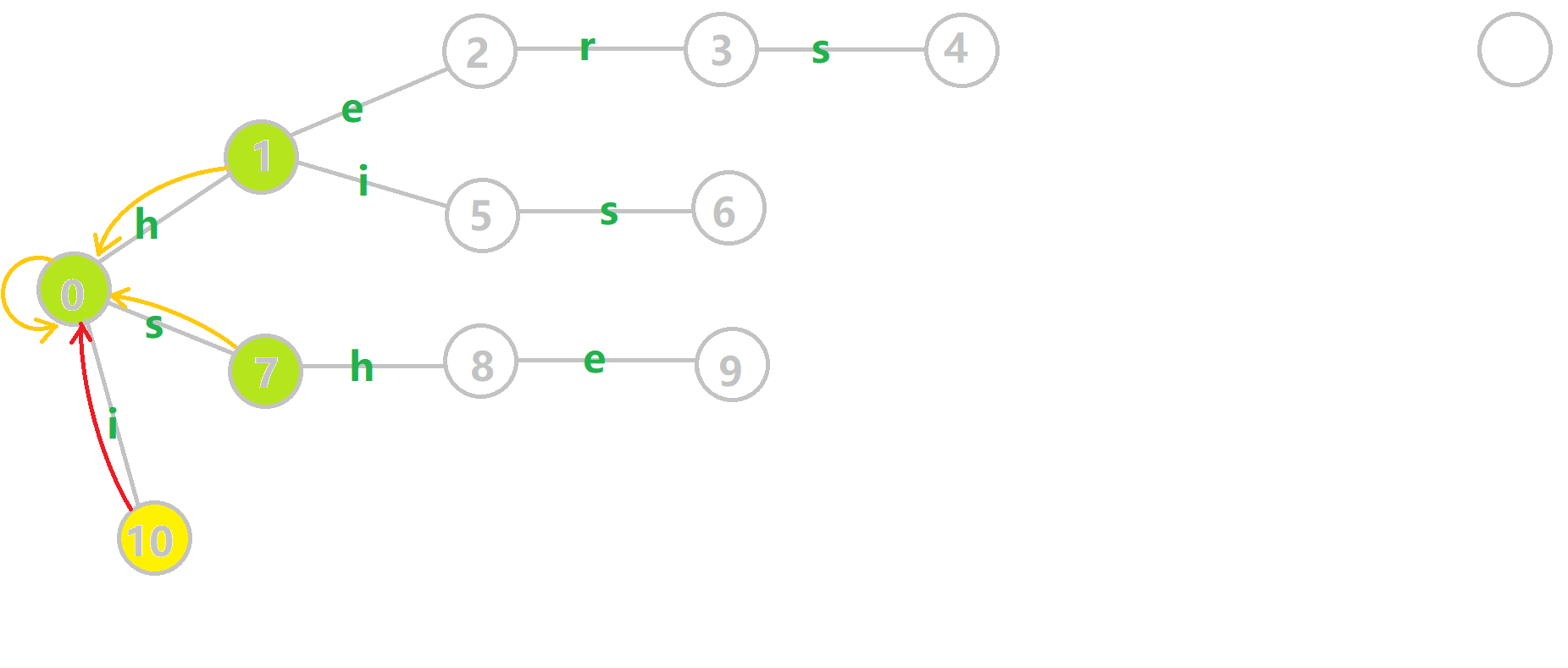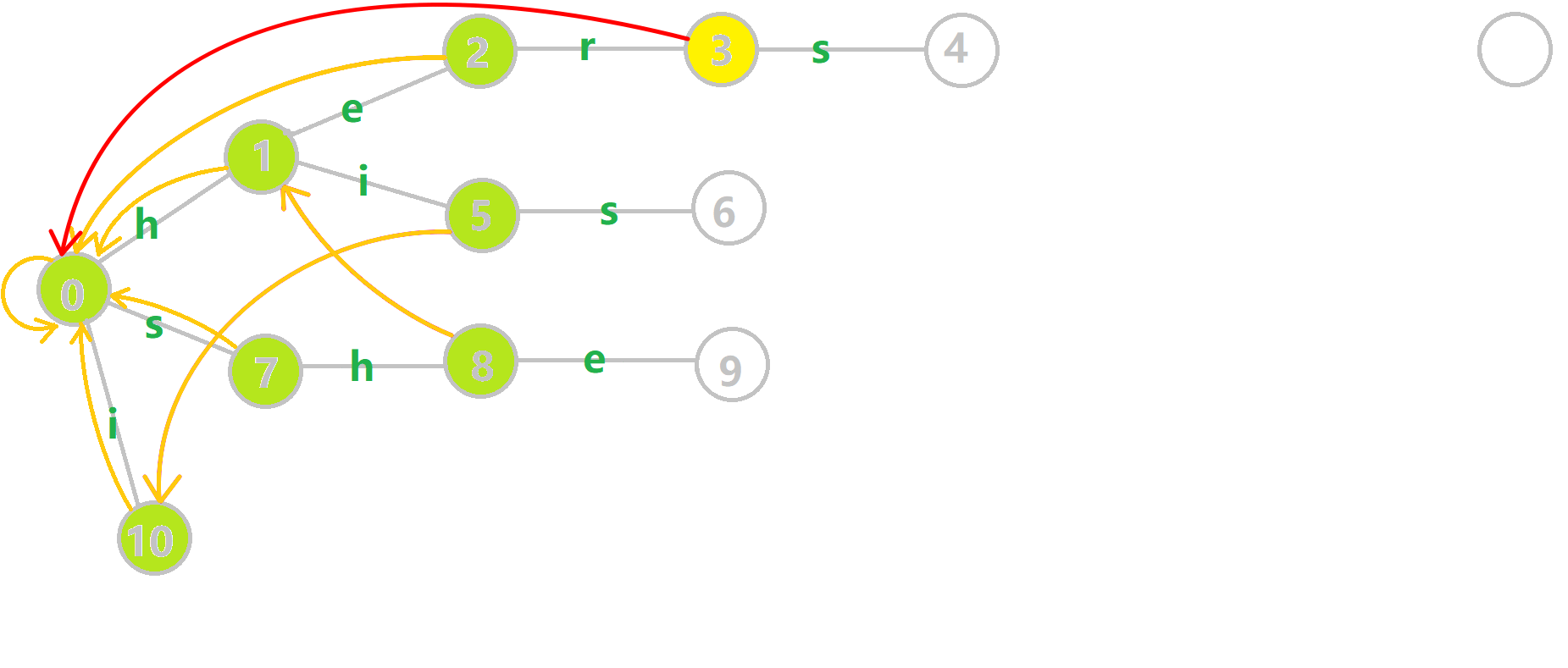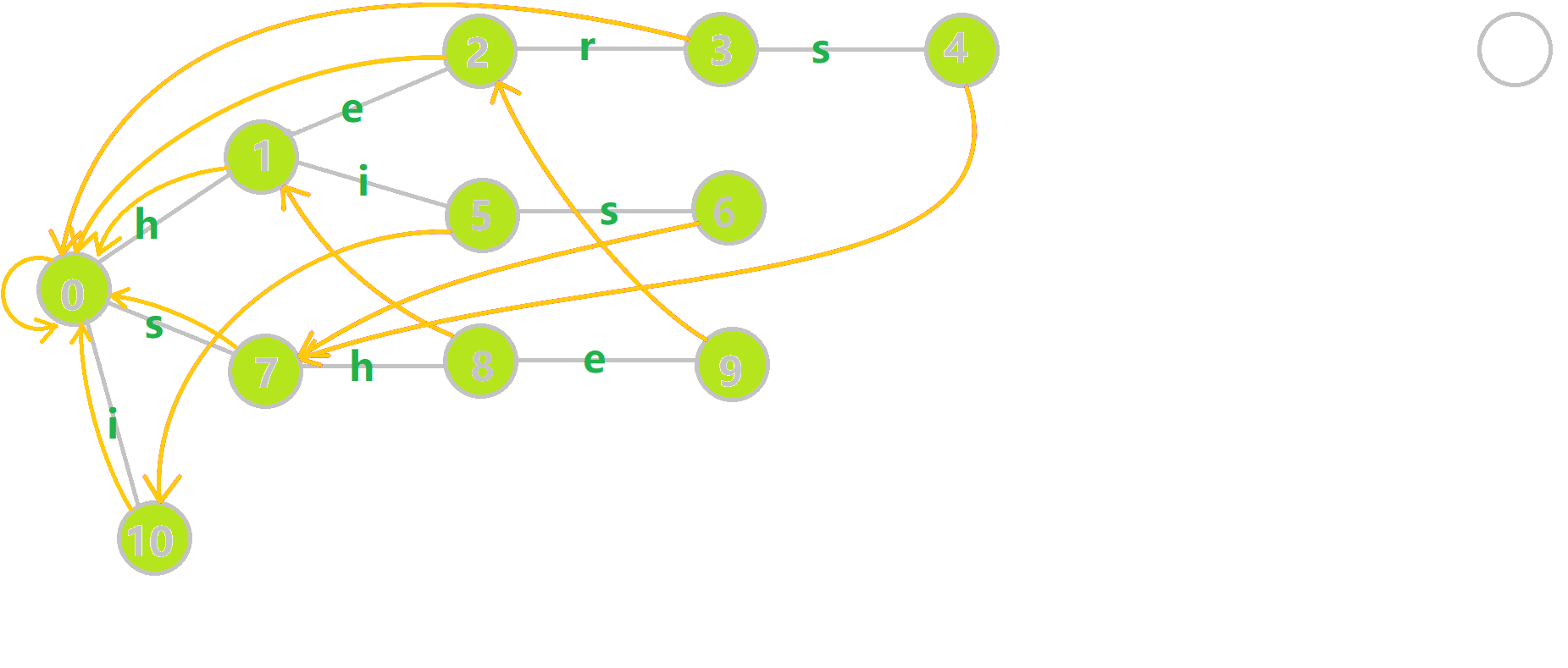
void build() {
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
if (tr[0].son[i]) q.push(tr[0].son[i]);
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (tr[u].son[i]) {
tr[tr[u].son[i]].fail = tr[tr[u].fail].son[i];
q.push(tr[u].son[i]);
} else
tr[u].son[i] = tr[tr[u].fail].son[i];
}
}
}
这是AC自动机
fail指针建出来的树叫fail树
fail树节点s的子树大小表示s被多少其他串包含
例题:
P2414 [NOI2011] 阿狸的打字机
跳fail
显然每个节点有且仅有一个fail指针
所以,这就是一棵树??
把这个fail反过来看
现在的问题是什么?
原来是y的某个节点往上跳能不能到达x
现在反过来:
x往下跳能够到达几个y的节点
那,不就是求子树和???
如果把所有y的节点全部打上一个1的标记
那么,每次就变成了求x末节点的子树和
而一个点的子树在dfs序上一定是连续的一段
这样还是可以拿到70分
你把他在树上,每次动态求子树(本质上还是个扫描线),就可以了。
我们把Trie树dfs遍历一遍
访问到的时候打一个+1
结束的时候打一个−1
每次访问到一个结束节点的时候,
一定是有且仅有这个串的节点被打了标记
这样就可以直接回答这个串的相关询问了
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 200000 + 5;
struct Node {
int vis[26]; // Trie 原始子边
int Vis[26]; // Trie 子边的备份,用于原 Trie DFS
int fail; // fail 指针
int fa; // Trie 父节点(用于处理 B 回退)
int lt; // 对应第几条打印串的末节点(P 操作)
} t[MAX];
int nd[MAX];
int n = 0, tot = 0;
int c[MAX], dfn[MAX], low[MAX], tim = 0;
inline int lowbit(int x) { return x & -x; }
void Modify(int x, int v) {
for (; x <= tim; x += lowbit(x)) c[x] += v;
}
int Query(int x) {
int s = 0;
for (; x > 0; x -= lowbit(x)) s += c[x];
return s;
}
vector<int> e[MAX];
struct QueryItem { int x, y, id, ans; } Qs[MAX];
bool cmpY(const QueryItem &a, const QueryItem &b) { return a.y < b.y; }
int ql[MAX], qr[MAX];
void buildFail() {
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
int to = t[0].vis[i];
if (to) q.push(to);
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
for (int c = 0; c < 26; ++c) {
int v = t[u].vis[c];
if (v) {
t[v].fail = t[t[u].fail].vis[c];
q.push(v);
} else {
t[u].vis[c] = t[t[u].fail].vis[c];
}
}
}
}
void dfsFail(int u) {
dfn[u] = ++tim;
for (int v : e[u]) dfsFail(v);
low[u] = tim;
}
void dfsTrie(int u) {
Modify(dfn[u], +1);
if (t[u].lt) {
int y = t[u].lt;
for (int i = ql[y]; i <= qr[y]; ++i) {
int x = Qs[i].x;
Qs[i].ans = Query(low[ nd[x] ]) - Query(dfn[ nd[x] ] - 1);
}
}
for (int c = 0; c < 26; ++c) {
int v = t[u].Vis[c];
if (v) dfsTrie(v);
}
Modify(dfn[u], -1);
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
string s;
cin >> s;
int now = 0;
for (char ch : s) {
if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') {
int c = ch - 'a';
if (!t[now].vis[c]) {
t[now].vis[c] = ++tot;
t[tot].fa = now;
}
now = t[now].vis[c];
} else if (ch == 'B') {
now = t[now].fa;
} else if (ch == 'P') {
nd[++n] = now;
t[now].lt = n;
}
}
int m;
cin >> m;
for (int i = 0; i <= tot; ++i)
for (int c = 0; c < 26; ++c)
t[i].Vis[c] = t[i].vis[c];
buildFail();
for (int i = 1; i <= tot; ++i) {
e[ t[i].fail ].push_back(i);
}
dfsFail(0);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
cin >> Qs[i].x >> Qs[i].y;
Qs[i].id = i;
}
sort(Qs + 1, Qs + m + 1, cmpY);
for (int i = 1, j; i <= m; i = j) {
int y = Qs[i].y;
ql[y] = i;
j = i;
while (j <= m && Qs[j].y == y) j++;
qr[y] = j - 1;
}
dfsTrie(0);
vector<int> ans(m+1);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
ans[ Qs[i].id ] = Qs[i].ans;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) cout << ans[i] << '\n';
return 0;
}
P4052 [JSOI2007] 文本生成器
AC自动机上DP板子题。
先容斥
f[i][j]表示当前在节点j,且串长为i时的情况
求所有不可读的情况
一个串可读,就是他的fail链一直跳,会跳到单词末尾,
这个可以预处理
定义f[i][j]表示当前在j点且串长为i时不经过单词结尾的路径条数
然后从父亲往儿子转移即可
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int mod = 10007;
int n, m, cnt;
int ch[5005][26], dp[111][5005], fail[5005];
bool war[5005];
string str;
void insert(const string& str, int len) {
int now = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
int p = str[i] - 'A';
if (!ch[now][p]) ch[now][p] = ++cnt;
now = ch[now][p];
}
war[now] = true;
}
void build() {
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
if (ch[0][i]) q.push(ch[0][i]);
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
if (ch[u][i]) {
fail[ch[u][i]] = ch[fail[u]][i];
war[ch[u][i]] |= war[fail[ch[u][i]]];
q.push(ch[u][i]);
} else {
ch[u][i] = ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
}
int qpow(int a, int b) {
int ans = 1;
while (b) {
if (b & 1) ans = ans * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cin >> str;
insert(str, str.size());
}
build();
dp[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j <= cnt; ++j)
for (int k = 0; k < 26; ++k)
if (!war[ch[j][k]])
dp[i + 1][ch[j][k]] = (dp[i + 1][ch[j][k]] + dp[i][j]) % mod;
int ans = qpow(26, m);
for (int i = 0; i <= cnt; ++i)
ans = (ans - dp[m][i] + mod) % mod;
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
P3311 [SDOI2014] 数数
和上一题类似,但是有一个n的限制
DP多加一维代表有没有顶到限制。

答案氏顶到的+没有顶到的
PAM
NOIP不考,总结先咕咕咕
MANACHER
SA
SAM
好像就没啥了
对了,还有
子序列自动机
子序列自动机ch[x][c]表示x下一个c的下标,很简单吧
Machine buildSeq(const string &s) {
int L = s.size();
Machine M;
M.n = L+1;
M.nxt.resize(L+1);
for(int c = 0; c < SIGMA; ++c) M.nxt[L][c] = -1;
for(int i = L-1; i >= 0; --i) {
M.nxt[i] = M.nxt[i+1];
M.nxt[i][s[i]-'a'] = i+1;
}
return M;
}
字符集较大
如果不随人愿,字符集较大(比如字符集大小为 105),那么直接维护 toi,c,时间和空间复杂度都是庞然大物。改为用可持久化线段树去维护,也就是 i 代表的线段树为它的 to 的值。
因为 i 的改变,只会让 las 改变一个位置的值,这就相当于单点修改,所以时间复杂度是 O(nlog∣∑∣) 的。
void plant0(int &o,int l,int r){
dcnt++,o=dcnt;
if(l==r){tre[o].val=n+1;return;}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
plant0(tre[o].lv,l,mid),plant0(tre[o].rv,mid+1,r);
}
void plant(int ori,int &o,int l,int r,int wei,int val){
dcnt++,o=dcnt;
tre[o]=tre[ori];
if(l==r){tre[o].val=val;return;}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(wei<=mid)plant(tre[ori].lv,tre[o].lv,l,mid,wei,val);
if(wei>mid) plant(tre[ori].rv,tre[o].rv,mid+1,r,wei,val);
}
int query(int o,int l,int r,int wei){
if(l==r)return tre[o].val;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(wei<=mid)return query(tre[o].lv,l,mid,wei);
if(wei>mid) return query(tre[o].rv,mid+1,r,wei);
}
void build(){
plant0(rot[n],1,m);
for(int i=n;i>=1;--i)plant(rot[i],rot[i-1],1,m,S[i],i);
}
应用
P5826 【模板】子序列自动机
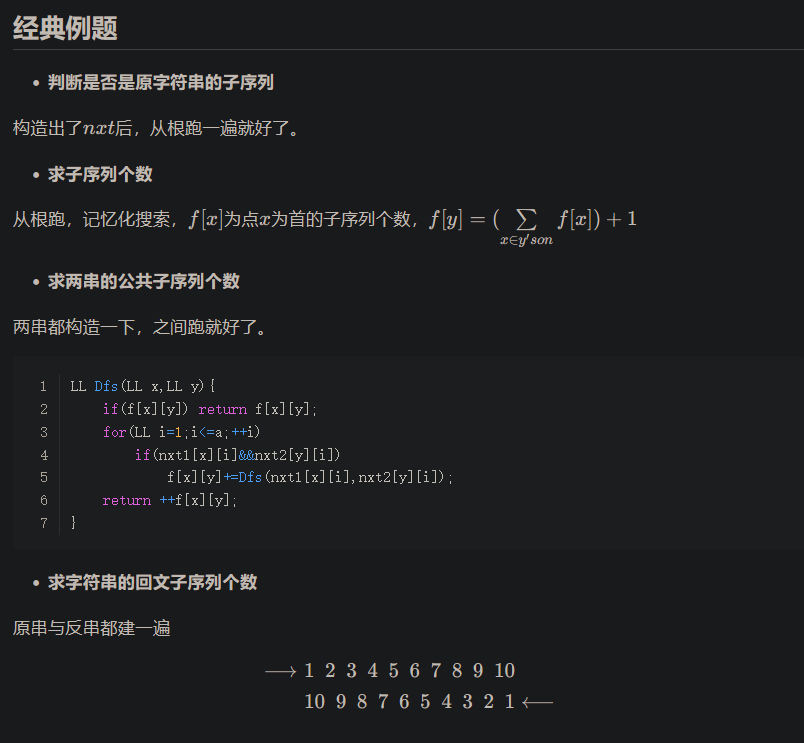
P4112 [HEOI2015] 最短不公共子串
把SAM和子序列自动机都建出来。
然后DFS四遍即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int SIGMA = 26;
struct Machine {
int n;
vector<array<int,SIGMA>> nxt;
};
Machine buildSAM(const string &s) {
int maxn = s.size()*2 + 5;
vector<array<int,SIGMA>> ch(maxn);
vector<int> link(maxn), len(maxn);
int tot = 1, last = 1;
for(auto &row: ch) row.fill(0);
link[1] = 0; len[1] = 0;
for(char cc: s) {
int c = cc - 'a';
int p = last, np = ++tot;
last = np;
len[np] = len[p] + 1;
ch[np].fill(0);
for(; p && !ch[p][c]; p = link[p]) ch[p][c] = np;
if(!p) link[np] = 1;
else {
int q = ch[p][c];
if(len[q] == len[p]+1) link[np] = q;
else {
int nq = ++tot;
len[nq] = len[p]+1;
ch[nq] = ch[q];
link[nq] = link[q];
link[q] = link[np] = nq;
for(; p && ch[p][c] == q; p = link[p]) ch[p][c] = nq;
}
}
}
Machine M;
M.n = tot;
M.nxt.resize(tot);
for(int i = 1; i <= tot; ++i) {
for(int c = 0; c < SIGMA; ++c) {
int v = ch[i][c];
M.nxt[i-1][c] = v ? v-1 : -1;
}
}
return M;
}
Machine buildSeq(const string &s) {
int L = s.size();
Machine M;
M.n = L+1;
M.nxt.resize(L+1);
for(int c = 0; c < SIGMA; ++c) M.nxt[L][c] = -1;
for(int i = L-1; i >= 0; --i) {
M.nxt[i] = M.nxt[i+1];
M.nxt[i][s[i]-'a'] = i+1;
}
return M;
}
int solve(const Machine &A, const Machine &B) {
int nA = A.n, nB = B.n;
vector<char> vis(nA * nB);
queue<pair<int,int>> q;
q.emplace(0,0);
vis[0] = 1;
int d = 0;
while(!q.empty()) {
int sz = q.size();
while(sz--) {
auto [u,v] = q.front(); q.pop();
for(int c = 0; c < SIGMA; ++c) {
int u2 = A.nxt[u][c];
if(u2 < 0) continue;
int v2 = B.nxt[v][c];
if(v2 < 0) return d+1;
int idx = u2 * nB + v2;
if(!vis[idx]) {
vis[idx] = 1;
q.emplace(u2,v2);
}
}
}
++d;
}
return -1;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
string a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
Machine samA = buildSAM(a);
Machine samB = buildSAM(b);
Machine seqA = buildSeq(a);
Machine seqB = buildSeq(b);
cout<<solve(samA,samB)<<"\n";
cout<<solve(samA,seqB)<<"\n";
cout<<solve(seqA,samB)<<"\n";
cout<<solve(seqA,seqB)<<"\n";
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号